Introduction
Leaders are often forced to find a procedure to search for and understand true administrative techniques such as implementation of models for enhanced management. The personnel are made of diverse age groups, and therefore there is need to find different and unique styles of developing the way people interact through building rapport and communicating.
There have been evident increases on the number of interests in leadership styles and theories since the twentieth century. Leadership theories of the early styles mainly focus on the qualities that are distinguished between the subordinates and their leaders.
The subsequent theories changed focus to identification of variables required to cater for various situational demands and the diverse levels of skills. Diverse leadership theories emerged but there are common classifications of various groupings.
Theories of Leadership
Great Man Theory
Acts on assumption that leaders exist intrinsically means the leadership is thus an aspect of birth and not formation. According to this theory, leaders exist as heroic figures, and mythically they are bale to meet demand due to ability to respond in accordance with the human needs/demands.
The term is a clear indication that the theory emerged when leadership qualities were primarily based on single gender; “male” and was particularly based on military form of leadership (Daft and Marcic, 2008, 182).
Trait Theories
The theories are also based on inheritance of various leadership traits/qualities. The theories are often base on specific leadership qualities and behaviors attributable to certain people. According to Dodds (2008, 1), the trait theories were conflicting since there was lack of explanation to cases of people who possessed these leadership traits but were not leaders.
Situational and Contingency theories
These theories forms an analysis of environmental variables that assist to determine leadership style that is best suited for a given situation. The theories therefore indicate that there is no particular leadership style that best suites all situations (Miller, 2008, 1).
Success depends on numerous situational variables, for instance style of leadership, qualities of followers and other aspects of the circumstance. Situational variables may therefore determine the leaders’ decisions.
Behavioural Theories
According to Mathis et al, these theories emphasize that leaders are made and not born (2008, 29). The ability to lead therefore depends on the leader’s actions as opposed to the environmental influences of other personal traits. Any one has the ability to gain skills of becoming an effective leader through guidance, active teaching, surveillance or presentation.
Participative Theories
The leader in this case considers the input or efforts of other involved persons. The leaders support involvement and participation of staff in decision-making procedures and other relevant fields. The leader is however in control of inputs from other group members.
Management Theories
“These are transactional presumptions that focus mainly on supervision and organization of group performances (Mathis et al, 2008, 29)”. The theories have deeper focus upon rewarding mechanisms for successful employees and punishment of failures.
Relationship Theories
They are transformational mechanisms that strengthen the links between managers and other personnel (subordinates). The leaders who use this form of model encourage members by inspiring them to achieve better results and emphasize the importance of having highly motivated employees.
The members are thus assisted to understand the importance of better and higher quality tasks, need for better group performance and ability to engage a fulfilling participation in accordance with personal abilities. According to Pride et al, “Leaders with this style often have high ethical and moral standards (2009, 71).”
Current Leadership Development Plans
The current leadership development plan is based on a model that assists in defining and responding to the queries of why leadership development is important. The model therefore lacks various development features but it is a management plan that improves performance through enhancement of underlying leadership elements.
The leadership style is both an individual or group administrative capability. Current model is therefore an oriented model that expresses organization performance in-terms of skills and knowledge that enhance performance.
The tasks for organization personnel are arranged in a manageable framework, to form a clear understanding of who does best and in what area. In accordance with Clark (2008, 1), “individual attributes, competency and outcome” are the main aspects that determines effectiveness of a leader.
Existing leadership Development Plan

Individual Attributes
Common Cognitive Ability – My common cognitive abilities mainly involves educational intelligence as opposed to exposure, involvement or experiences.
Specific Cognitive Ability – I have gained intellectual capabilities cumulatively through continual career growth. The cognitive ability therefore forms the concepts acquired mainly through experiences and it depends on my mental capabilities.
Motivation- I have the motivation and will to act in accordance with influences such as the overall performance requirement for the firm.
Personality – My personality involves personal leadership traits/characteristic that assist in overcoming complex organizational demands for instance charismatic leadership style.
Personal Competency
Skills for solving Problems – the model enable me to strengthen my creative ability to solve simple as well as complex organizational challenges
Judgement Skills – I also have the ability to identify and understand social problems such as work-related conflicts, which requires an understanding of the personnel and how their social system works. I am thus in a position of smoothing the employees progress by coordinating them to work as a group or team.
Knowledge – the model has assisted me to cumulatively acquire information for managing complexity involved in organizing learning and data mining.
Professional Dexterity – I have the skills for enforcing delivery of the right output
Viable Outcomes
My current Leadership plan therefore involves analysis of the degree to which I am in a position to enforce personal duties for success in accordance with the standard analysis criteria.
Current Personal Leadership-Development Model
The model has five attributes namely modelling teams, mentoring personnel, coaching team, training staff and procedures for getting feedback from personnel, as indicated below.
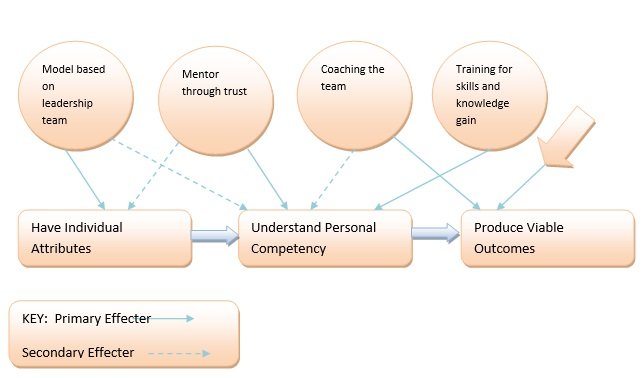
Modelling involves leadership through observing others and imitating good aspects of their social form of learning. It is a more effective style when people are within a common environment with others. Mentoring involves the informal style of encouraging personnel through knowledge interpretation besides providing psychological and social support.
Thirdly, teaching enable those involved to gain new skills and knowledge in support of leadership. It is a slightly different from developmental training that involves provision of knowledge to improve present job-related performances in the aim of enhancing new technological developments. Lastly, feedback enables the personnel to respond by placing personal opinions and take part in decision-making or organizational changes.
Interface of Various Parts of the Model
The modelling of teams’ performances based on leadership strategies and procedures has direct influence on the personal attributes and indirectly affects my procedure of finding and understanding my personal competencies. Leadership of the team therefore mainly depends on mentoring the employees through improvement of their trust.
Subordinates therefore remain encouraged due to my personal critical and accurate knowledge interpretation especially the social and psychological support. The personal trust of employees has direct impact on individual’s understanding of personal competence, but indirectly influences the individual attributes.
I also need to coach the team into production of feasible outcomes. Through the coaching process subordinates are able to understand my personal leadership competency and relate to the anticipated outcome. Training program also converge the teams to a common work environment.
The personnel gain some unique performance and leadership skills and are thus able to support leadership. The procedures for getting feedback from personnel through collection of personal opinions’ questioners support productivity and ability to understand my personal competency.
Lastly the collection of feedback is directly connected to decision-making process since I am able to assign various organizational changes as per the requirements. The whole model therefore enables me to promote interaction of different departmental groupings, different personnel competencies in the knowledge structure.
The interrelation also assists personnel to share tasks by subdividing into various categories depending on leadership skills, competence and professional abilities. Thus is the reason my leadership skills are mainly focused on competency.
The current leadership model focuses of competencies of various personnel. The tasks in the firm are identifiable from the departmental groupings, duties, and project frameworks over and above personnel competency in the knowledge structure.
The interrelation of skills assists personnel to move through a certain career path. Management through competency levels is thus sub-divided into various categories depending on leadership skills, competence and professional abilities.
The competences groupings form the leadership pyramid comprises of various basic leadership requirements as indicated by the illustration below
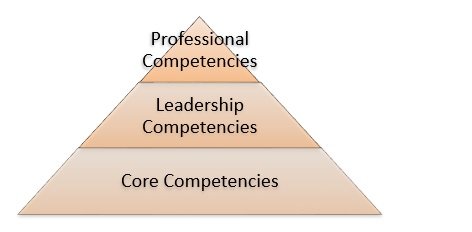
The part of the pyramid shows the core competencies, which entails personal abilities such as the skills for leading others, and the requirement levels of performance. The competencies provide the basis for other forms.
Existing Core Competencies
- Communication skills – My current basic communication skills involves proper, proficient and professional style of presenting instructions or guidance verbally and in written form. I am also able to present my planned activities in a manner that promotes employees participation and voluntary involvement such as sharing of ideas and offering suggestions. Communication also entails active listening to participants, mainly stakeholders, employees and clients concerns. The personal leadership style also focuses on ability to negotiate for the best market offers through skilfully using special wining approaches such as ability to maintain healthy business relationship with potential competitors.
- Teamwork – the existing core competency also Involves enhancement of interpersonal relationships through team participation and enforcing growth of members’ responsibility to achieve set goals. The administrative skills also involve allocation of responsibilities to individuals as well as teams, negotiation and organization of resources in accordance with the tasks and for maximal efficiency aiming at achieving beyond the set goals through influencing group activities.
- Creativity – Problems solving skills works well due to the personal creativity skills of identifying challenges, collecting the relevant information about the challenges and enforcing the brainstorming techniques to come up with appropriate choices. Eventually creativity requires selection of the best course of action through logical analysis of available alternatives.
- Interpersonal Skills – interoperability is a major aspect of current model since the clientele respect, trust and distinction emerges from leadership skills. The current model focuses of treating personnel and clients with dignity they deserve in order to consolidate and cater for individuals’ feelings, desires and needs. Current leadership model thus supports personal abilities/traits by supporting the cultural and social contributions.
- Managing Relationships with Clients – The feedback collected from customers is considered keenly since it encourages collective decision-making procedures and encourages contribution.
- Self-Goals – The personal goals often include the personal deliverables, budgets, time schedules that encourage self-motivation as opposed to passive acceptance of imposed organizational culture. Self-direction enables the team to achieve goals within the set deadlines.
- Flexibility – As the leader, the ambition to accomplish the required and anticipated change that meet organizational needs is desire to adjust the existing norms and make tough but accurate decisions especially to overcome challenges.
- Establishment of Work Relations – work-based relationships requires association between workmates through social networks and building of relationships that are important and constructive at the work base.
- Professionalism – Current I take actions by being the example to the rest. Professional leadership therefore requires one who is able to have a quick and instant link to the current professional developments. My current leader style is also active in supporting community-based developments through active community participation.
- Financial – The leadership program provides keenness on resources management and is able to establish processes that have positive impact at the outcome.
- Business Shrewdness – My current leadership provides insight over key developmental activities especially over the key areas that may affect the firm. The acumen provides improvement on area concern with major system improvement.
Although the current leadership model has the important aspects that form majority of the core competencies, the aspired leadership consist of stronger professional and leadership competencies for guiding or training personnel predominantly the subordinates.
Current Vs Aspired Leadership Competencies
Leadership competencies are skills that are relevant for driving the firm into new and competitive levels particularly through embracing new technological advancements. These basic skills separate bosses or people concern with general management from those skilled and highly motivated leaders. Leadership competencies are thus the basis for other leadership qualities. Common competencies include:
- Leadership Capabilities – My current leadership style has the required attributes that can be mimicked by the team members since they trust my abilities and have high work morale to achieving goals.
- Processing of Company’s Vision – As a leader I have measures of increasing productivity through analysis of areas that requires more support. Visioning also involves “setting of goals, visions and having good organizational guidance principles (Mathis et al, 2008, 25).”
Besides following procedural guidance as indicated in organizational learning, I am capable of implements personal observations to sway the subordinates into better procedures of attaining goals. Visioning also calls for leadership measures to ensure commitment of the team through setting team objectives and convincing those involved to buy to the process.
Currently my aspiration is to have a model that enforce changes and encourages subordinates to embrace these changes, in the aim of preventing service or products deterioration. - Creating a Successful Team – Current leadership model focuses keenly on individual presentation thus establishment of strong group works and work spirits for cooperation and achievement of the set goals. However, my proposed leadership model must focus on the phases of storming ideas for better performance.
- Quick and Accurate Assessment – Situations requires the leader who is in a position to take control as per the situational demand and enhances time management.
- Conflict Management – I am in a position to resolve conflicts timely by solving the problems without offending those involved. “Expertise advice and support by leaders with respect to management of people requires establishment of a win-win situation (Mathis et al, 2008, 25).” One of the major concerns in conflicts management involves evaluation of procedures to establish alternative cause of actions during dispute resolution.
- Project Management – The current leadership model is able to enhance timely procedural measures especially during project-management, for instance ability to ensure that tasks are comprehensively done on time. The organizational goals are easily changed or influenced by external factors, and therefore the leader must be in a position to establish and react to such influences. The leader must also have alternative plans for specific goals. Current management plan will focus on identification and evaluation of current and future projects.
- Employee Involvement Strategy – This involves “development of need for ownership as a measure of bringing employees nearer to the decision-making and planning procedures (Mathis et al, 2008, 25)”. The employees’ success depends on the set objectives and implementation procedures. Empowerment is therefore a vital aspect of accomplishing various aspects in an effective and timely manner.
- Subordinates’ Training program – Every opportunity presents a learning process and therefore future administration plans requires leaders who are more involved in coaching and mentoring programs as a measure for promoting performance feedback and enhancing career growth for teams as well as individuals. Chances for enhanced success depend on disseminated form of governance. According to Booyens, “the future performance feedback is an integral part of our day-to-day activities (2008, 23).”
Professional Competencies
The training or learning procedures for leaders provide knowledge and skills required for controlling the system processes. The professional competencies are the binding aspects that enable all the other competencies to work as a system unit.
The technical aspects and skills are essential features of professional competencies. As a competent leader I must therefore have general understanding of systems and various processes they control. Technical expertise is thus not a main requirement of the leader since different personnel have specialty such as unique skills and knowledge depending on their area of operations. Some of the professional competency requirements involve:
- Employees’ learning – Includes implementation of facilities to enhance understanding and assist them appreciate the different experiences in their professional fields. The informal learning in organizations also facilitates sense of direction for the personnel particularly when relating with counterparts from different departments.
- Designing of Instructions – “Instructional Design (ISD) Model assists to conduct firm assessment and performance analysis of needs to enhance maximum growth and development of instructional materials for flesh designs (Booyens, 2008, 24). The leader is tasked with the program of enforcing the learning package through evaluating summative and formative ways of enforcing the entire process.
- Rapid Design – Implementation of new techniques requires use of prototypes that assist in delivery of knowledge of new work-related packages
- Consultation – The leader must determine stakeholders’ requests particularly ability to negotiate for solutions and fulfilment of various business requirements
- Instructions – professionalism requires leader’s ability to prepare instructions, demonstrate presentations, clarify enquiries, facilitate transfer of skills, and provide knowledge as well as proper responses to feedbacks.
Summary of my Personal Approach towards Leadership
Good communication skills – I implement my professional style proficiency through presentation, guidance sharing of ideas and offering suggestions. I am an active listener and have ability to skilfully negotiate for the best market offers.
On team work projects, I am able to support and promote employees’ participation. My excellent interpersonal relationships and team participation enforces individual members’ responsibility to achieve the set goals.
I take actions by being an example to the subordinates but as a good administrator, I am capable of allocating responsibilities to individuals as well as teams, negotiation and organize resources in accordance with assigned tasks. This is my simple approach towards maximizing efficiency and aim at achieving beyond set goals through influence of group activities.
My personal creativity skills include ability to identify challenges, collect relevant information about the challenges and enforce brainstorming techniques to come up with appropriate choices. I am thus able to select the best course of action through logical analysis of available alternatives.
I adjust existing norms and make tough but accurate decisions especially to overcome leadership related challenges. Beside the personal leadership traits, I engage diverse knowledge and skills required for controlling the system processes.
Conclusion
The proposed leadership development plan focuses on the participative, management and relational theories. There is a wide gap between the espoused and current leadership model since there is more emphasis on the behavioural theory that emphasizes on learning leadership skills and knowledge.
This leaves out the main aspects of participative and management theories. Focusing on ability to react in accordance with the environmental influences disconnects from need to encourage participation. The inputs by others members are very critical in development. There is a clear indication that my current leadership model often fail to support others’ point-of-views through encouraging participation.
The current leadership style also fails to safeguard organization of group performances, with a deeper focus on rewards for success. One major setback that my new model will address involves relationship theories, where formation of a link between managers and other personnel (subordinates) will be crucial. One of the key issues on the model will focus on competencies and establishment of measurs to maintain relationship to inspire members to achieve better results.
Reference List
Booyens, S. W. (2008). Introduction to Health Service Management. Juta and Company Ltd. South Africa.
Clark, D. R. (2008). Leadership style. Journal of Social Psychology, 116, pp. 221-228. Web.
Daft, R. L. and Marcic, D. (2008) Understanding Management. Kentucky, KY: Cengage Learning.
Dodds, B. (2008). Pandemic Planning and Business Continuity. Web.
Mathis, R, L., Jackson, J. H. and Elliott, T. L. (2007). Human Resource Management. Thomson Southwestern Publishers.
Miller, C. (2008, May 30). Cultural Diversity is an Opportunity. Web.
Pride, W. M., Hughes, J. M. & Kappor, J. R. (2009). Business. Kentucky: KY Cengage Learning Publishers.