Introduction
Outsourcing can be traced from earlier years of the Roman Empire when collection of taxes started (Duffy 30). With the dynamics and changing times, firms are exposed to different business environments both nationally and internationally. The business environment greatly impacts on its profitability, operational costs, production cost and internal structuring.
With improvement of faster internet, ubiquity has been reinforced thus shrinking of business distance (UNCTAD 3). This has consequently allowed for outsourcing of various crucial operations like labour.
While labour constitutes one of the integral parts for success or failure, it also significantly constitutes part of the recurrent expenditure for firms that should be minimized while ensuring maximum output. In the event of fulfilling this, a company is able to enjoy increased profitability. This paper examines the economics of outsourcing.
The Theory of Outsourcing
According to UNCTAD, business outsourcing entails relinquishing certain services that were usually performed in house to third parties either off shore or onshore (5). The growth of outsourcing can be traced back from the location of Mexican export assembly plants next to US so as to offer cheap labour.
But in recent years, the growth has been phenomenal due to high speed low cost internet making a number of corporate functions to be mobile. Large companies from US and Europe- mainly UK are the main users accounting for 60% & 30 % respectively with US & UK having the bulk share at 70% while India being the main recipient.
The business outsourcing is expected to grow in bounds and leaps as by 2002 it was estimated to worth US $ 32 TO 35 Billion which was just a mere 1 % of the market for business functions that could be performed remotely at US $ 3 trillion. Figure 1 below represents the overall outsourcing decision.
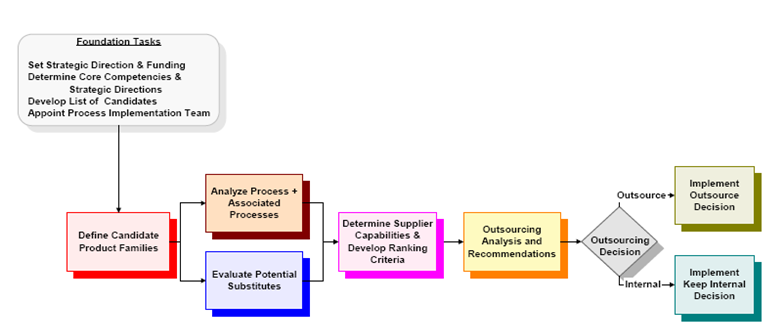
Figure1: Overall outsourcing decision. Source: Phelps & Fleischer (12).
According to Keränen, Kaushik, & Sharan, figures regarding outsourcing are fairly similar in Finland, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and Denmark (33). The graph below represents outsourcing R&D services among Finnish SME’s.
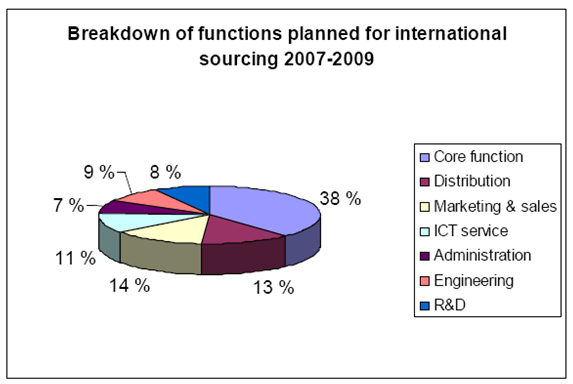
Source: Keränen, Kaushik, & Sharan (13).
Lastly the phenomenal growth of outsourcing will continue as indicated with trends like unexpected sources and sophistication of the process (UNCTAD 25). The business process outsourcing trend has been supported by many management theories and methodologies as an approach to reducing costs, improving quality and speed time to market.
Duffy notes that the 3 key drivers of outsourcing is lower process cost, reduce risk and increase process quality and flexibility with most respondents at 87% saying quality is the main drive (9).
The services that can be outsourced includes; customer interaction centres, data entry and conversion services, finance and accounting services, translation services, press and digital pre media services, geographic information systems, human resource services, distance learning services, marketing, advertising services and legal services (UNCTAD 5).
Articles Summary
Agency theory approach to outsourcing
This theoretical concept forms the centrality of business delegation by exploring relationship factors such as governance, mechanism, strategic intent and conditions of the outsourcing arrangements. It identifies the need for principal (client) to apportion some work to the other party which is an agent or vendor through contract in three dimensions. The first dimension is the economic relationship whereby each has different goals.
The second is the competitive relationship whereby each has a difference in risk preferences. Lastly is the relationship of partnering whereby each party is uncertain in the process (Duffy 30). Hence, in a nutshell agency theory considers contractual relationship in a perspective of behaviour – based or outcome-based.
Behaviour based contract offers the agent a more authority over the client/ contractor since the agent irrespective of outcome does not bear the risk of the venture. Under this approach the contractor can not evaluate the performance of the agent. While on the other hand, outcome based outsourcing allows the client a free hand over the agent.
Social capital theory approach to outsourcing
Outsourcing relationship, can give forth to realization of social capital in the form of the actual and potential resources. Social capital can be seen as being characterized by two aspects, this namely being; social capital constituting an aspect of the social structure of the deal and secondly social capital facilitating the actions of individual within the structure.
The concept of social capital is significantly concerned with relationships which provide an avenue for trust and co-operation but it has been applied in terms of its role in economic performance through combination and exchange.
The contribution of this approach is the recognition that social capital resides in relationships and relationships are modelled through exchange thus allowing for the creation of social structure throughout the outsourcing period.
Analysis
Outsourcing Reasons
The business environment dynamics and increased global competition has forced companies to be cost effective, by relinquishing peripheral and non core operations leading to specialization.
This allows firms to concentrate on delivering smart product or services which are core to their operations thus an ensured sustained quality.
Apart from the above, the other reasons that might act as an attraction to contract outsourcing include; access to new technological skills brought by the agency, reduced head count as the firm will only employ core staff, enhanced capability of to develop new products as the firm will now be directing it resource to innovation.
The next cluster of reasons can include; reduction in capital costs, reduction in transaction costs, enhanced capability for change that is internally driven, investment in technology especially information and communication technology and lastly the enhancement of firms’ position in value addition as most of the above considerations are path towards value addition (Kakabadse & Kakabadse 20).
Outsourcing Arrangements
The arrangement of outsourcing can be vast ranging from short term contracts for convenience and flexibility or full ownership and merger (Kakabadse & Kakabadse 22). At the same time we can have partial ownership, joint development, retainers, single contracts, multiple vendor contracts, joint ventures, individual, joint venture spin-offs and consortia and shared service consortia.
Currently, there has been emergence of partnership or alliance arrangements which is viewed to provide closer level of interaction between client and provider as an alternative to the more popular project based contracts which are usually shorter, single contracts with preferred suppliers, even though both arrangements have got shared risks.
The assumption that can be built is that no single vendor can poses beyond reproach capabilities in all areas of business and hence a call for selective outsourcing with multiple vendors (Kakabadse & Kakabadse 2).
New Business Supply Chain Models in Relation to Outsourcing
The new models include; fourth party logistics provider, joint service company and finally virtual network consortia. This if well analysed is connected to different outsourcing arrangements. Fourth party logistics provider is a business model that desires to integrate and assemble the resources, capabilities and technologies of its own and other firms to design, build and run comprehensive supply chain solutions.
It aims at transforming of client business through management of variety of services and delivery of complex solutions on behalf of the clients. The one notable about this marketing concept is the ability to provide multi client synergy. The other model is joint service company which is mostly suitable for two or more companies working in strategic partnership and are in need of large transformation while working with minor partners.
It is a separate co-owned, co-managed service company built on innovative culture. The last model is the virtual network consortia that propose to deliver a unique value for a particular service (Alpha Research Consortium).
Conclusion
It is clear from the above indications that business outsourcing and even particular legal outsourcing is the way to. The benefits accrued from outsourcing are much heavier than the anticipated constraints.
Outsourcing allows for; innovation, concentration to core functions and specialization thus ability to produce quality product and services.
Australia as a country and firms operating within it should embrace and adopt the culture as a means of reducing operational and production costs in order to be effective in price leadership that can be translated to clients. It should also be adopted as a means of improving quality through tapping of specialized services and talents all over the world since none can be a master and jack of all trades.
Works Cited
Alpha Research Consortium. “Characteristics, strategies and trends for 3PL/4PL in Australia.” Alpha Research Consortium. Alpha Research Consortium. Web.
Duffy, Maureen Nevin. “Outsourcing a 401(K) plan”. Journal of Accountancy 191.5 (2001): 30–35.Print.
Kakabadse, Andrew, & Kakabadse Nada. Smart sourcing: international best practice. New York: Palgrave, 2002. Print.
Keränen, Seppo, Kaushik, Ashok, and Sharan Dharmesh. “Opportunity mapping: engineering and R&D services for finish manufacturing companies.” FinPro (2009): 5-61. Print.
Phelps, Thomas, & Fleischer Mitchell. Strategic outsourcing decision guidebook. Michigan: Altarum Institute Publication, 2002. Print.
UNCTAD. Business process off shore outsourcing: untapped opportunities for SMEs. Geneva: UN, 2005. Print.