Introduction
Papa John’s International Inc. is an American-based restaurant franchise company specializing in pizza delivery and carryout (“Company overview,” 2017). The enterprise was founded in 1984 by John Schnatter and Bob Ehringer (Smith, 2013). In 2016, Papa John’s International Corporation owned more than 5, 000 brand restaurants and 4, 353 franchised restaurants (“Company overview,” 2017). Furthermore, in three decades of operation, the company has established its outlets in 45 countries (“Company overview,” 2017). It follows that the organization’s management team is capable of transforming cash flows into a substantial growth of the market share. The company’s success is underscored by the fact that in 2016, it increased its net income by 18 percent and revenues by 8.5 percent (Maze, 2016).
The aim of this paper is to analyze the company’s profile and competitive standing. The paper will also provide strategic alternatives for Papa John’s that can help it to strengthen its competitive edge.
Company Mission and Critique
Papa John’s International Inc.’s current mission is to focus on the customers, team members, franchises, and shareholders. Because Papa John’s wants customer satisfaction, the firm uses fresh ingredients to produce high-quality pizza. The corporation ensures teamwork by providing a training program to the employees; hence, they are able to work on a level ground whereby they understand each other. This motive perpetuates the spirit of teamwork. By doing this, Papa John’s has created a superior brand loyalty through true, superior quality products, well-known customer relations, and excellent community service. With such a strong mission in place, Papa John’s is bound to succeed and create a bigger business empire that will outmatch the competitors.
Outside Stakeholder Groups
The two outside stakeholder groups in Papa John’s International Inc. include the shareholders and customers.
Shareholders
Shareholders are the ones who provide equity capital to finance the daily functioning and operation of Papa John’s International Inc. Because the shareholders are responsible for the firm’s financial resources, they present varying interests. Most of them are interested in earning returns from their investment in the company. Others prefer that Papa John’s management should strictly limit risks. The shareholders also have a differing preference for the timing of the returns as some of them are interested in the immediate benefits while others in long-term benefits. This has led to ideological conflicts among the shareholders as they have differing needs for controlling the company.
For Papa John’s to reconcile the conflict, the senior management must put efforts to use the correct approach that will bring out the picture of the relative importance of the shareholders of the company. The company should act towards the satisfaction of the financial interests of the shareholders (Papa John’s, 2016b). Handling the shareholders according to their different levels of interest will bring about harmonious coordination of various parts of the firm, which will underpin its success.
There are two types of shareholders in Papa John’s International Inc. namely institutional investors and mutual fund holders. The institutional investors own approximately 85.8% of the total shares in the organization (Papa John’s, 2016b). The institutional investors hold a percentage float of 117.48 in the company. The mutual fund holders own 50% percent of Papa John’s International Inc. (Papa John’s, 2016a).
Customers
The firm’s customers comprise a major part of the external stakeholders. Therefore, it has an obligation to ensure that the needs of the customers are met and if this does not happen then the company will most likely go out of business (Navarro-García, Arenas-Gaitán, & Rondán-Cataluña, 2014). The customers always demand quality and safe products and the integrity of the service providers. Therefore, management at the firm has a duty to ensure that the designing, production, and selling of high quality and standard pizzas. Papa John’s International Inc. keeps the interests of the customers in mind when making decisions on new flavors. It is important for the company’s management to offer common and quality training to the employees. This strategy will ensure customer satisfaction across various sectors of the company because they will be equipped with the best ways of treating the customers.
External Environment
Success Factors
The most important element that has contributed to the success of Papa John’s is the availability of a ready market for their goods and services. Without a reliable market, no business can thrive. The firm is located in an environment with a large working population that spends surplus income on buying its luxurious services. The availability of a large population with a taste for their goods and services has resulted in an increase in demand and, consequently, Papa John’s will put more effort to intensify its supply (Papa John’s, 2016a). This inclination to a good market position has contributed to the thriving of the business.
In addition, the availability of affordable raw material for the production of Pizza and other products has also promoted the company’s activities. The unavailability of raw materials can paralyze their daily activities (Köseoglu, Ross, & Okumus, 2016). This situation can lead to an ultimate end of production, which can result in the loss of customers and eventual closure.
Besides, the availability of improved better roads and affordable, accessible, and fast methods of propulsion have had a significant impact on the success of the business. Good roads enable fast transportation of perishable goods to Papa John’s International Inc. (Köseoglu et al., 2016). The vehicles are also cheap in terms of transportation costs due to favorable federal laws that have lowered the taxation on fuel products. As a result, the company is able to work efficiently and smoothly. Lastly, the existence of favorable federal laws governing the worker’s compensation, minimum wages, and payroll taxes has boosted the business significantly (Köseoglu et al., 2016). Since most of the workers in Papa John’s industry are middle earners, the company pays them at standard affordable rates and still makes enough profit to maintain the daily running of its operations.
Strengths of Papa John’s Competitive Forces
The competing industries greatly challenge their development. Some of the competitors are well-established with a larger pool of financial sources and other essential resources that John’s International Inc. lacks. Some of the competitors have also been in existence for a longer period of time than this firm (Köseoglu et al., 2016). Therefore, they have a higher level of penetration to the market and a stronger, more established ways of advertisement in the market.
Within the QSR pizza category, Papa John’s competitors such as Caesars and Domino’s dominate the national chains (Syed, 2016). When one or more of Papa John’s competitors change their pricing or even other marketing strategies, they impose a lot of damage to Papa John’s sales and earnings. Indeed, the firm faces an active competition even in the most attractive commercial real estate cities. The supermarkets continue to increase their supply of fresh and frozen pizza to the customers, further imposing a big threat to then Papa John’s International Inc.
Industry Factors Driving Change to the External Environment
One of the major industry factors driving change to the external environment in regard to Papa John’s International Inc.’s activities is the continuous expansion and building of more restaurants in the newly identified real estate cites. This state has affected the external environment as more land is cleared to create room for construction. Wastes from Papa John’s industry such as used polythene bags and wrapping materials render the external environment dirty when carelessly disposed of.
The US Market and Market Position of Papa John’s International Inc.
Papa John’s International Inc. functions under five primary divisions in the US namely the North America commissaries, domestic restaurants of the company, North America franchising, international operations, and all other business entities. The headquarters of Papa John’s International Inc. is located in Louisville in Kentucky.
Comparison of Business Strategies
The firm’s competitors in the international market have a beta of 0.6. This value indicates that their average stock price 33% less volatile than S&P. On the other hand, Papa John’s International Inc. has a beta of 0.5, indicating that its average international stock price is 50% less volatile than the S&P 500 (Papa John’s, 2016a). This shows that the company’s products are better as compared to those of its rivals.
Future Factors
At the outset, there is a high demand for restaurant goods based on price, consumer income, and advertising. If this position poses a high risk to Papa John’s International Inc. then the firm should ensure that all the featured companies keep their foods and labor costs under checks and control in addition to creating new products to keep customers coming into the restaurant (Papa John’s, 2016a). This approach will enable Papa John’s to remain relevant and profitable.
The United States and Global Markets
The top markets inside the US are the North America commissaries and North America franchising. The markets outside the US are international operations in Asia, China, and Africa. The strategic goal in the global market is to expand its pizza business by establishing branches in other countries. Papa John’s International Inc.’s global competitive strategies include providing fresh and comparatively cheaper food products to customers. This objective will entail the creation of superior brand loyalty through authentic, superior quality products, legendary customer relations, and exceptional community services (Papa John’s, 2016a). However, other businesses similar to Papa John’s are already in the market with outstanding brands that will possibly pose stiff competition to its business.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
To begin with, Papa John’s uses high-quality ingredients that are fresh in pizza production. Most of its competitors use frozen pizza. Thus, the firm meets the customers’ expectations as compared to its competitors (Hoover’s, 2014; Papa John’s, 2016a; Zikmund, Babin, Carr, & Griffin, 2013). To ensure a constant quality of its products, the firm uses its resources in the dough production facilities and commissaries for monitoring. In addition, the company offers efficient and strong employee training thereby it produces high-quality workers who know how to handle customers in an ethical manner (Barrows, Vieira, & DiPietro, 2016). Its competitive advantage squarely relies on the ability of the store managers to properly train employees, which has created a good customer experience. Furthermore, the organization has a powerful marketing strategy that enables it to reach out to customers at the local and regional level. It also has an efficient restaurant layout that is employee-friendly. Customers can see through the entire store and watch the pizzas being made (Barrows et al., 2016). The layout also provides the employees with a clear view of the restaurant’s front in a way that enables them to serve the customers better.
Weakness
Papa John’s is still considered new in the market and it is not as large as the competitors who have a double amount of stores (Weinzimmer & Nystrom, 2015). In addition, it has limited menu items as compared to the competitors who have a wide range of items in their menus. It is also difficult for the customers to switch loyalty as many of those competitors already have their favorite customers.
Opportunities
The company has an opportunity to add more items on its menu to allow customers to choose their favorite food from a wide range. For instance, they can add sandwiches to salads to the menu which will satisfy the needs of some customers (Weinzimmer & Nystrom, 2015). Since Papa John’s is still treated as a new company, it can establish strong brand recognition to attract customers. Furthermore, it can open more stores to seize a larger market size. In addition, the company can use the power of the internet especially social media to market its pizza products (He, Wang, & Zha, 2014). This strategy will increase its popularity in the market. The restaurant should also leverage new technologies, thereby streamlining its cost structure.
Threats
Papa John’s competitors offer a wide variety in their menu while Papa John’s offers a selected few services (Weinzimmer & Nystrom, 2015). Competitors’ brands are better positioned in comparison with Papa John’s brands, which poses a threat of reducing the company’s customer base through aggressive marketing tactics.
However, the company’s tangible goods have a higher competitive value because they use fresh ingredients in the manufacture as compared to the competitors. As much as the competitors are able to reach many customers due to their large market range, Papa John’s has the advantage of establishing a stronger brand which will attract more customers.
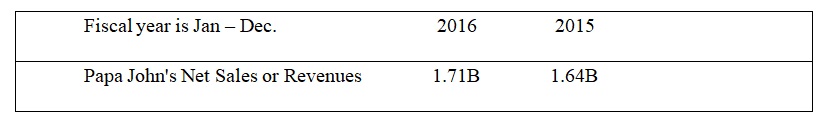
Revenue and Net Profit Comparison
Table 1 shows a comparison of 2015 vs 2016 revenue and net profit of the company.
Current Strategy
At the back of today’s competitive business environments, firms ought to design, develop, and implement sound strategies that align with their long-term objectives. It is impossible for an organization to grow without a clear roadmap to steer it towards the desired growth level. The path to success is contained in its business strategy that outlines the steps for achieving long-term goals (Clegg, Kornberger, & Pitsis, 2015). Papa John’s current strategy is based on menu offerings that are of the highest quality, a coherent operating system, provision of training to their employees, an elaborate marketing strategy, constructive use of technology, and an elaborate franchise system.
The company’s business strategy is achievable because of its components that are mentioned above. According to Clegg et al. (2015), a practicable corporate plan must be founded on the principals of customer satisfaction, growing the organization’s market share, innovation, and efficient utilization of physical resources. Papa John’s current strategy incorporates these principals; therefore, it can be attained. However, the leadership of the organization and its decision-making process determines whether the company achieves its strategy or not. It is, therefore, imperative that the company puts necessary measures in place to ensure that the key drivers of their strategy, as outlined in their strategic elements, are put to practice to achieve its strategy.
Long-Term Objectives
The company has a long-term objective of building global brand loyalty that will be the strongest in the pizza industry. The enduring success of any organization is anchored on its ability to set achievable longstanding strategic objectives that guide its operations and growth (Hill, Jones, & Schilling, 2014). The company’s long-term objectives are achievable because they are based on delivering value to the customer. It is outlined in the company’s objectives that it aims to build a strong brand by putting into practice the major building blocks of their business strategy. This underpinning shows that the company knows its long-term goals and has a clear plan to achieve them. Lasting objectives are also meant to improve an organization’s position in a competitive environment. The position can only be improved if the objective is studied properly to ensure that it is all-encompassing, measurable, and viable. The objective of improving the brand will be determined by the number of increased sales the company manages in the near future.
Organization Chart Structure
The business strategy and long-term objective cannot be achieved without a competent team to facilitate its operations. The company has a functional organizational structure with divisional leaders that are responsible for various departments. The nature of the chart determines the success of the company because it puts in place human resources that will ensure the timely and effective execution of its business strategy (Goetsch and Davis, 2014). A good organizational structure promotes specialization, ensures efficient control of resources, facilitates easy communication, and improves the performance of employees (Goetsch and Davis, 2014). It enables it to perform these functions efficiently and timely. The company’s organizational structure has divisional heads whose functions are aligned with the elements of their business strategy. For example, the senior vice president for marketing has functions that are aligned with the strategic component of elaborate promotion of the company’s products. This kind of chart that aligns the functions of its leaders to the business strategy ensures that the company always stays on track to accomplish its goals and objectives.
Summary of the Top Current Risks
Every organization faces certain business risks that need to be overcome for them to be successful. Papa John’s Pizza comes across various threats since it operates in an environment that does exercise full control. Currently, the firm’s major risks include a dip in profits as a result of increased competition. The pizza industry is mature and experiences fast growth. Many players continue to enter the industry, and the established companies are also expanding their franchises (Navarro-García et al., 2014). This scenario presents a major risk that can lead to plummeting prices thereby decreasing the firm’s profit margins.
Another risk for the company is the changing customer taste. Consumer needs are always dynamic, and their preferences can change as a result of a new ingredient introduced a competitor or new technology introduced into the industry. There could also be concerns about the quality of foods and other health risks such as break out of communicable diseases. One of Papa John’s Pizza’s main strategies is the use of franchises and food outlets to conduct its businesses (Hoover’s, 2014). It does not have close control over the franchises and outlets and, thus, the hygiene conditions in them can potentially affect the reputation of the company’s brand and result in reduced sales.
Alteration in the laws concerning privacy is also another main threat to the business. The company relies on direct communication strategies such as emails, texts, and mailings to market its food services. The laws regulating these communication platforms are subject to federal, state, local, and international legislation (He et al., 2014; Hoover’s, 2014; Zikmund et al., 2013). Any changes can adversely affect the company’s marketing plans.
Besides, the company uses different ingredients drawn from different markets to make its pizzas. Increases in the prices of ingredients and other items would increase the production costs and lower the company’s profit margins.
A possible occurrence of natural calamities can negatively affect its operations. For instance, catastrophes such as hurricanes could occur and affect the company’s operations. Such disasters can destroy their outlets or interfere with the transport system thereby hindering delivery services. These risks present various threat levels to the operations of the organization (Barrows et al., 2016). However, most of them are manageable risks that can be averted or managed if the company puts necessary measures in place to deal with them.
Competition Analysis
Domestically, Papa John’s Pizza’s main competitors include Pizza Hut, Domino’s Pizza, and Little Caesars Pizza. Pizza Hut is a well-established company with food chain outlets in more than 95 countries over the world (Morris, 2016; Syed, 2016). This company is a major threat to Papa John’s Pizza because of its better financial resources, global reach, and a number of sales that it commands domestically (Weinzimmer & Nystrom, 2015). Domino’s Pizza is another strong competitor. The strengths of the company stem from its use of technology to offer services to the customers. It recently launched a zero-click order system where customers can order pizza without clicking. The GPS system that allows it to track customers so that their orders are not put into the oven until they are close to the stores also gives it a competitive edge (Morris, 2016; Papa John’s, 2016b). Caesars Pizza also presents a major threat to Papa John’s International Inc. mainly because of its low prices.
Internationally, the company operates in Asia, Europe, Latin America, the Caribbean, North Africa, and the Middle East (Papa John’s International Inc., 2017). Some of its domestic competitors also double as its international competitors. In Asia, for example, its biggest opponent is Pizza Hut, which has over 1500 pizza outlets in China alone (Morris, 2016). Other Asian competitors include Domino’s Pizza and California Pizza Kitchen. The biggest European rivals include Domino’s Pizza, Pizza Express, and Pizza Hut. Other players in Latin America and the Caribbean include Pizza Hut, Domino’s, and Little Caesars Pizza (Papa John’s, 2016b). In North Africa and the Middle East, the main rivals are Pizza Hut, Sbarro Pizza, and Domino’s Pizza.
It is clear from the above analysis that the biggest global competitors to Papa John’s International Inc. are Pizza Hut and Domino’s Pizza. These companies were founded earlier than Papa John’s and their strength in the market is manifested in the number of outlets they have in the world (Papa John’s, 2016b; Köseoglu et al., 2016). They also have financial resources that are superior to Papa John’s. In its long-term objectives, the firm aspires to build the strongest pizza brand in the world. If that is to be achieved, it must put into practice strong competitive strategies to ensure that it matches and surpasses the competitiveness of its rivals. Its exemplary customer service strategies and unique ingredients used in its pizzas are a good start. It must also implement extensive and unique global marketing campaigns to outstrip those of the competitors.
Financial Analysis
The company’s latest annual report shows that its total revenues amounted to $1, 598, 149 in 2014, and $1, 637, 375 in 2015 (Papa John’s, 2016a). Pizza Hut’s revenues reached $1, 214, 235 in the last year (Yum, 2016). It follows that the company outperformed its main competitor whose revenues diminished in comparison with the previous year. Revenues of Domino’s, on the other hand, reached $2, 216, 523 in 2016, which represents a substantial improvement when compared to financial performance in 2015—$1, 93, 827 (Domino’s, 2016). It follows that although Papa John’s is lagging behind Domino’s to a considerable degree in terms of the share of its revenues, the company has managed to show stronger financial performance than Pizza Hut in 2015.
Strategic Alternatives
The analysis of the competitive environment in which Papa John’s operates suggests that the company should opt for an alternative business-level strategy to improve its standing in the market. The superiority of cash flows of Domino’s Pizza and Pizza Express prevents the company from competing on the basis of low-cost margins. It has to do with the fact that this strategy necessitates large sales volumes. Therefore, the following actionable strategic alternatives connected to the SWOT analysis are available for the organization: diversification, technology investment, and positioning.
Diversification
The key company’s weakness is its limited product range in comparison with its immediate competitors. Therefore, Papa John’s can gain a competitive edge by introducing new menu items. The strategy is also derived from the restaurant’s strengths—the use of fresh ingredients and a highly trained workforce.
Technology Investment
Technology investment is a strategy that rests on an opportunity identified in the SWOT analysis. By leveraging new technologies, the company can both achieve higher cost savings and boost its sales. For example, the restaurant can invest in energy-efficient ovens and ‘visible promise time’ displays (Taylor, 2016).
New Positioning
The choice of positioning as a strategic alternative for Papa John’s is dictated by one of its threats—a weak brand positioning. Even though the company tries to find a distinctive place for its products in the target audience’s mind, its current attempts are lacking inefficiency. Taking into consideration the fact that Domino’s sales are disproportionately rising, the company has to review its marketing strategy, thereby improving its positioning.
Implementation Plan
New positioning has been chosen as a strategic alternative for Papa John’s. Currently, the company projects an image of a healthy pizza restaurant, which does not strike a chord with its target customers. Therefore, the company is recommended to pivot towards an emphasis on family values.
Strategic Goal and Objectives
The strategic goal of taking the new positioning approach to redefining Papa John’s niche, thereby expanding its current sphere of influence on the market. The implementation of this alternative will allow the company to achieve the following objectives: increase its customer base, grow its market share, and enhance its corporate identity.
Tactical/Operation Plans
Market research. The repositioning should start with market research, which will involve personal and telephone interviews, electronic media surveys, and observational studies among others.
Competitor positioning analysis. Papa John’s has to investigate competitor’s positioning and messaging strategy.
Development of a positioning statement. A positioning statement reflecting brand vision and mission should be developed.
Development of a marketing campaign. Repositioning requires a comprehensive marketing campaign that should involve social media.
Advertising. To reposition its brand, the company has to dedicate a substantial portion of its resources to advertising. Figure 1 shows the advertising spending of Papa John’s for a period of three years.
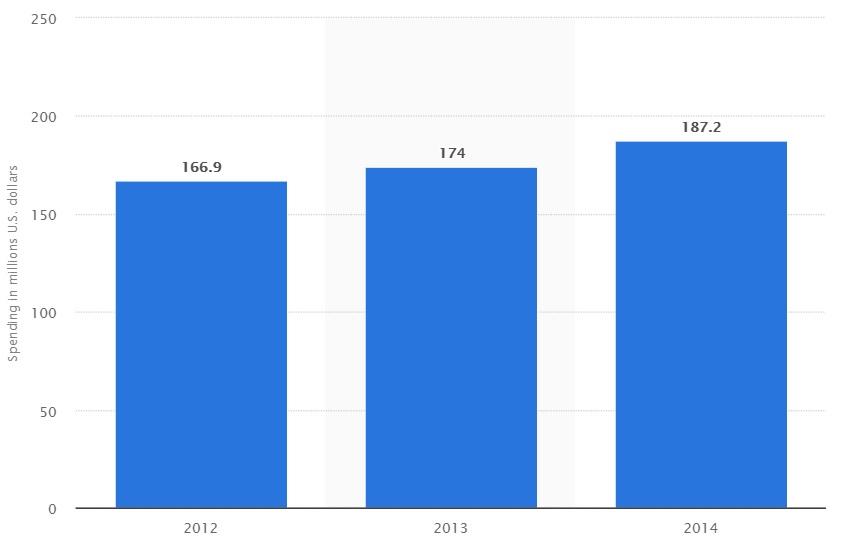
The figure suggests that although the company gradually increased its advertising spending in the period from 2012 to 2014, the growth was only marginal. When compared to the advertising budgets of its competitors, it is clear that the company has to review its ratio of advertising expenses to revenues. For example, the total advertising spending of Domino’s amounted to $246,7M in 2014 and $318.2M in 2016 (Retail Index, n.d.). Therefore, the company is recommended to increase its annual net advertising spending to 2.5 percent of its total revenues.
Other steps that should be taken by the company in the process of repositioning its brand are assignment of a brand focus group, analysis of sales history, analysis of the current brand positioning, SWOT analysis, identification of marketing opportunities, assessment of the brand equity, development of a targeted customer profile, value alignment, test of brand positioning, and implementation of a marketing campaign.
Table 2 illustrates the implementation of the strategic alternative on a timescale.
Table 2. Implementation of the repositioning strategy.
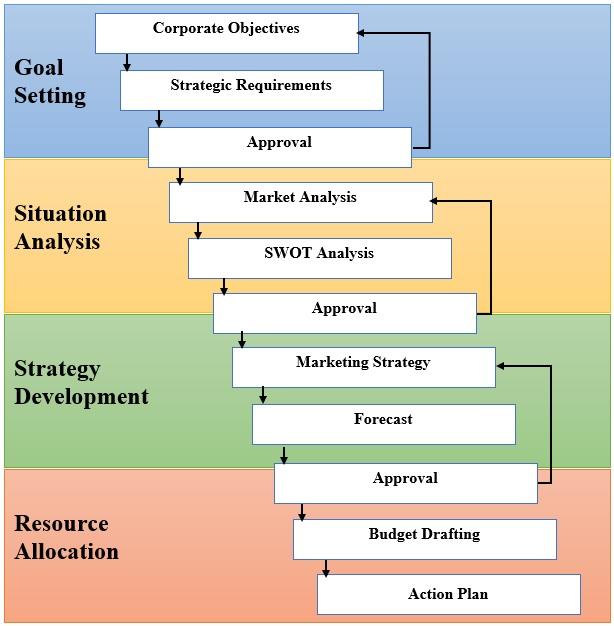
The improvement presupposes the development and implementation of a comprehensive marketing campaign that will help to reposition Papa John’s brand. Figure 2 presents a flowchart of the marketing campaign planning process.
Success Metrics
The successful implementation of the repositioning strategy requires several success criteria. Table 3 shows success metrics for the strategy.
Table 3. Repositioning strategy success metrics.
Conclusion
The paper has evaluated profile, products, services, profitability, and competitive standing of the international restaurant franchise— Papa John’s International Inc. The fundamental analysis has helped to understand the fundamental qualitative aspects of the organization. Upon assessing the business model of the organization, it has been argued that the company’s competitive advantage is derived from its superior product and the ability to leverage its considerable resource pool. The level of the organization’s penetration into the market has substantially increased during the recent years, which serves as evidence of the effectiveness of its management team. Based on the analysis of tangible and intangible characteristics of Papa John’s International Inc., new positioning has been recommended as a strategic alternative for the company. By repositioning, the restaurant chain will be able to strengthen its market standing and revitalize its brand, which is extremely important in the business environment characterized by a high level of competition.
References
Barrows, C., Vieira, E., & DiPietro, R. (2016). Increasing the effectiveness of benchmarking in the restaurant industry. International Journal of Process Management and Benchmarking, 6(1), 79-111.
Clegg, S. R., Kornberger, M., & Pitsis, T. (2015). Managing and organizations: An introduction to theory and practice. New York, NY: Sage.
Company overview of Papa John’s International, Inc. (2017). Web.
Domino’s. (2016). Annual report 2016. Web.
Goetsch, D. L., & Davis, S. B. (2014). Quality management for organizational excellence. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Maze, J. (2016). Papa John’s takes more market share. Web.
He, W., Wang, F., & Zha, S. (2014). Enhancing social media competitiveness of small businesses: Insights from small pizzerias. New Review of Hypermedia and Multimedia, 20(3), 225-250.
Hill, C. W., Jones, G. R., & Schilling, M. A. (2014). Strategic management theory: An integrated approach. Boston, Massachusetts: Cengage Learning.
Hoover’s. (2014). Papa John’s International, Inc. Web.
Köseoglu, M., Ross, G., & Okumus, F. (2016). Competitive intelligence practices in hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 53(1), 161-172.
Morris, C. (2016).American pizza chains slicing up a $45 billion pie. Web.
Navarro-García, A., Arenas-Gaitán, J., & Rondán-Cataluña, F. J. (2014). External environment and the moderating role of export market orientation. Journal of Business Research, 67(5), 740-745.
Papa John’s. (2016a). Form 10-K. Web.
Papa John’s. (2016b). Papa John’s announces third quarter 2016 results. Web.
Papa John’s (2017). Papa John’s Pizza. Web.
Retail Index. (n.d.). Domino’s Pizza. Web.
Smith, A. F. (2013). Food and drink in American history: A “Full Course” encyclopedia (Vols. 1-3). Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO.
Statista. (n.d.). Papa John’s international advertising spending in the United States from 2012 to 2014 (in million U.S. dollars). Web.
Syed, I. (2016).SWOT analysis and operation management decisions of Domino’s pizza. Web.
Taylor, K. (2016). Pizza Hut wants to be like Uber.Business Insider. Web.
Weinzimmer, L. G., & Nystrom, P. C. (2015). The search for opportunities by small business owners. Journal of Small Business Strategy, 7(3), 1-14.
Yum. (2016). Yum brands 2016 annual report. Web.
Zikmund, W. G., Babin, B. J., Carr, J. C., & Griffin, M. (2013). Business research methods. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.