Introduction
Pay-for-performance (PFP) is an incentive scheme where staff can receive extra, performance-based compensation for their duties when they attain a specific target. The framework is made to motivate employees, and it is one way of aligning with the goals and objectives of a given organization. Due to competitiveness, many firms have been keeping top performers through this initiative, which means having a variable budget to cater to that strategy. This paper explores how PFP can be executed in the United States Air Force.
Brief Background of the Organization and Industry
The US Air Force (USAF) refers to the air service department in the military. The service was created in 1907 as part of the US Signal Corps before being established as a separate branch in 1947 (Clemson, 2022). The roles of the USAF include controlling the air space, integrated global intelligence, commanding and controlling, and rapid global mobility, among others. There are more than 328,820 active personnel, and the headquarters is in The Pentagon, Virginia (Clemson, 2022). President Biden is the commander in chief of the US armed forces and the secretary of defense Frank Kendall III. Major achievements and challenges have occurred during the service discharge of military duties (Clemson, 2022). USAF has been key in innovation and research through its personnel.
The US needs to commence a PFP program in the USAF to combat some of the issues. There is an issue of advanced skills whereby most air force vessels are fourth-generation aircraft, making them vulnerable to air-defense systems. The USAF has held more than 1700 F-35A aircraft, which are useful in defeating their adversaries (“United States Air Force, 2022”). The air force budget has been lower than that of the navy and army for many years, and due to that, the USAF has requested $234 billion in its 2023 budget in what it terms as transformational change (“United States Air Force, 2022”). USAF has built a supercomputer, Condor Cluster, which helps analyze satellite imagery.
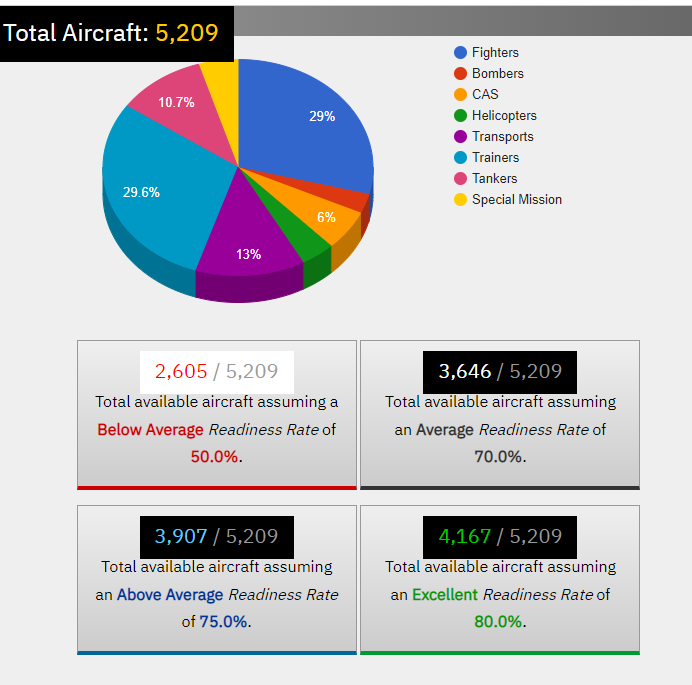
Presidents Ronald Reagan and George Bush served as members of the USAF before rising to be heads of state. During the bumblebee fight, the USAF F-117 fighter used aerodynamics, a notable strategy (“United States Air Force, 2022”). The current active inventory consists of 5209 aircraft, as shown in Figure 1 (“United States Air Force, 2022”). Globally, the US Air Force is ranked first with a force concentration of 1976 units for the attack, 1692 for support, and 2419 for the future (“United States Air Force, 2022”). USAF is one of the advanced service departments that can support military functions at any time required by the commander in chief.
PHP Plans to Consider
There are various types of PHP that an organization can consider in the military. Although it appears not highly feasible to incorporate this incentive scheme in the industry, a careful articulation on the matter would yield significant. This essay recommends using merit pay and bonuses (Dewi et al., 2022). When it comes to merit pay, a person will have their salary increased if they perform in a satisfying way. This category welcomes measures of individual successes and achievements in the military. The criteria would determine the amount of bonus a soldier will get from the initial planning to meet a specific objective (Dewi et al., 2022). There is a need to have transparency while running this initiative so that it does not lead to conflict within the service.
To effectively measure personnel’s merit, the National Security Personnel System (NSPS) is highly recommended. NSPS is a personnel-management tool that will enable USAF employees to have an opportunity for merit-based salary increments (Dewi et al., 2022). For example, soldiers who excel well in the field of research about national intelligence or any interior matter coordinated by the Department of Defense (DoD) will be rewarded by having this consideration. Skilled people are working in the air force who can effectively combat issues such as terrorism, national epidemics, and disasters. Additionally, any soldier who completes a certain mission by USAF will be part of this PHP.
The other element of PHP that the USAF should employ is bonuses. This means adding an extra amount on top of what a person gets as salary, which means the base pay will remain the same, but the added amount will bring the difference. This PFP plan is more leaned toward an individual than the entire USAF section since it measures personal performance (Cohen, 2022). The bonus should be a tangible amount that leads to an employee’s high performance. Hence, USAF must make a cost-benefit decision on the one-time costs. The advantage of this PFP is that it leads to self-motivation since accomplishing a goal is a frequent objective every organization has (Boril et al., 2017). These bonuses will be awarded to senior personnel and persons serving in the junior ranks within the section military.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the Plan
USAF should be guided by professional conduct when leveraging on PFPs mentioned above. The management will check various aspects to measure the effectiveness of merit pay and bonuses. First, there will be the determination of new concepts from research that are meant to boost the operations. That may include how technology will be advanced to combat safety issues in jet fighters and other equipment (Boril et al., 2017). There should be a weighing of the extent to which air services have been raised to meet world standards through the application of modern digital tools in managing military aircraft or preventing cyber-attacks through air services manipulation.
The second measure is the rate of airmen turnover. There have been concerns about people who leave the air force, especially those in technical operations. When bonuses and merit pay are properly introduced, these people are expected to remain in service, and thus, USAF will measure effectiveness through military turnovers (Dewi et al., 2022). Lastly, efficacy can be measured by checking if the plans and objectives have been met on time. That includes missions in and out of the country, and the support base on standby to assist in case backup is needed.
Employees Perspectives
Advantages
Having PFP in place leads to motivation whereby members of the USAF will be determined to accomplish various goals. This means airmen will be focused on a particular goal since they know there is a reward. The other advantage is that it reduces friction within the service since NSPS will use specific criteria to obtain results meaning that any loophole realized will be based on personal and not group liability (Dewi et al., 2022). Additionally, the proposed PHPs can ignite innovative minds meaning that members of the USAF will have boosted skills and knowledge relevant to their official duties.
Disadvantages
Employees may find challenges fitting into the new framework because it strains a person to work on personal levels to show improvement. It is a human error to have bias, ignorance, and assumptions. Hence, some members may fill PHP put in place to benefit a few with high military profiles (Dewi et al., 2022). Additionally, the introduction of PHP would mean members of the USAF will be frequently assessed, triggering work-based pressure that may affect performance.
Employer’s Perspectives
Advantages
Introducing PHPs will guarantee high performance toward accomplishing targets set by USAF. That is possible because everyone will work to improve to get a bonus or salary rise. Hence, productivity in military knowledge and operations will be assured. The other advantage is that USAF will benefit from a wide array of research and innovation (Dewi et al., 2022). The reason is that employees with technical roles will work towards establishing up-to-date standards that will keep the section of the US armed forces on a high note.
Disadvantages
USAF will experience high costs while trying to implement PHP. The reason is that various technology is required, and installation is expensive. Furthermore, PHP will call for additional costs in paying bonuses and salary increments to the personnel. The other disadvantage is that the government may be vulnerable to cybercrime if recommended NSPS fails while online (Dewi et al., 2022). Malicious people may obtain sensitive data from the military section and use it to sabotage key operations.
Conclusion and Recommendation
It is possible to have an effective PHP in US Air Force despite the underlying issues that may raise concerns. If a careful articulation of the matter is done through resource planning, realistic goals, and adherence to modern fighting standards, the dispatch of duties will be enhanced due to increased morale and advanced technical parameters put in place. It is recommended that USAF applies merit pay and bonuses at particular time frames to test the feasibility of the two. That should be accompanied by the ability to combat cybercrime, change resistance, and workforce dynamics that may be affected by incentive schemes (Cohen, 2022). If implemented gradually, USAF will foster a transformed air military operation.
References
Boril, J., Smrz, V., & Mach, O. (2017). Development of experimental methods for testing human performance in future military pilot’s preparation framework. 2017 International Conference on Military Technologies (ICMT), 2(5), 21–31. Web.
Clemson. (2022). Air Force History. Air Force history. Web.
Cohen, R. (2022). Hundreds of airmen opt to leave Air Force amid sky-high retention. Air Force Times. Web.
Dewi, N. W., Sulastra, I. M., & Putrayasa, I. M. (2022). Effectiveness of pay for Performance Incentive System on projects performance. Media Bisnis, 14(2), 159–166. Web.
United States Air Force. The world directory of modern military aircraft. (2022). Web.