Neuropathy is a lesion of the nerves of the peripheral system, which stems from the spinal cord and brain. Their task is to ensure the motor activity of the limbs and the transmission of impulses to the periphery from the central nervous system. Neuropathies can be painless with a gradual loss of sensitivity and painful characterized by extreme burning sensations in limbs. Neuropathies are caused by diabetes, HIV infection, hepatitis C, intestinal damage, and exposure to toxins, among which is Agent Orange, a powerful herbicide used by the U.S military forces during the Vietnam War. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathies in patients exposed to Agent Orange comprise prevalent neuropathic pain and gradual loss of functions (Rasekhi et al., 2018).
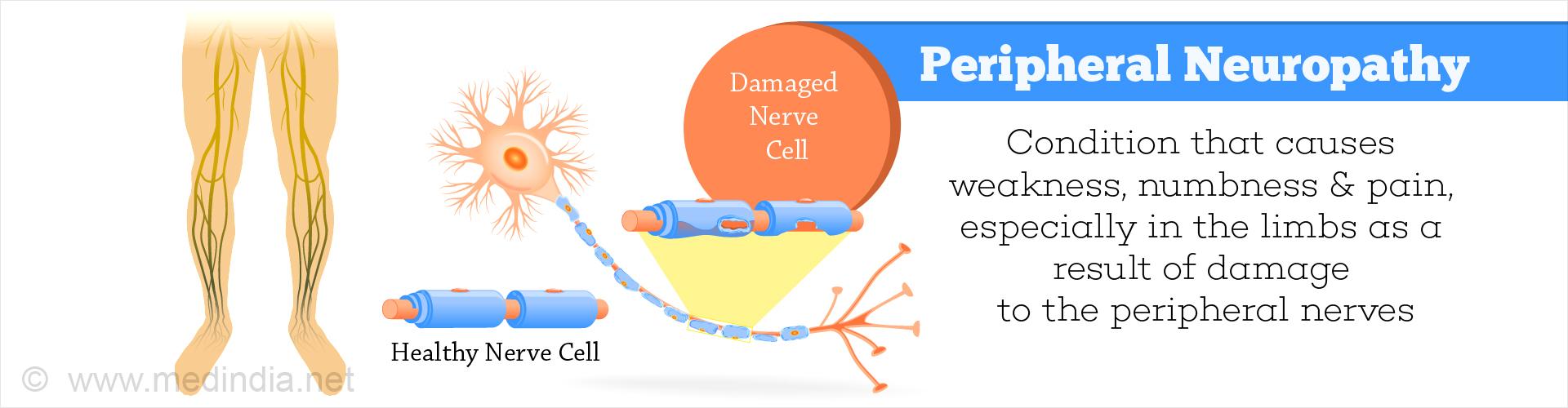
There are no symptoms at the initial stage of the disease caused by Agent Orange in most cases. A slight tingling of the skin, tickling, and a feeling of crawling goosebumps are not perceived by patients as an alarming signal. As the disease progresses, there are such sensations as if gloves or socks are worn, indicating a complete loss of sensitivity. Neuropathy spreads to sensory nerves, gradually deepening into the motor and autonomous ends (Stellman, J. M., & Stellman, S. D, 2018). The feeling of crawling goosebumps turns into the painful sensation that deepens as the disease progresses and more and more nerves are involved. Later the pain is accompanied by fiction loss, numb limbs, and muscle weakness (Picture 2). Risk factors of neuropathies include diabetics of any type, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barre syndrome (Staff, 2020). Moreover, the course of the disease is affected by long-term use of antibiotics, anticonvulsants, chemotherapy drugs, impaired metabolism and diseases of the endocrine system, poisoning with arsenic, lead, acetone, mercury, and other toxins, as well as vitamin B deficiency.
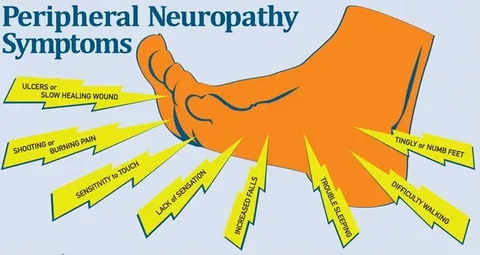
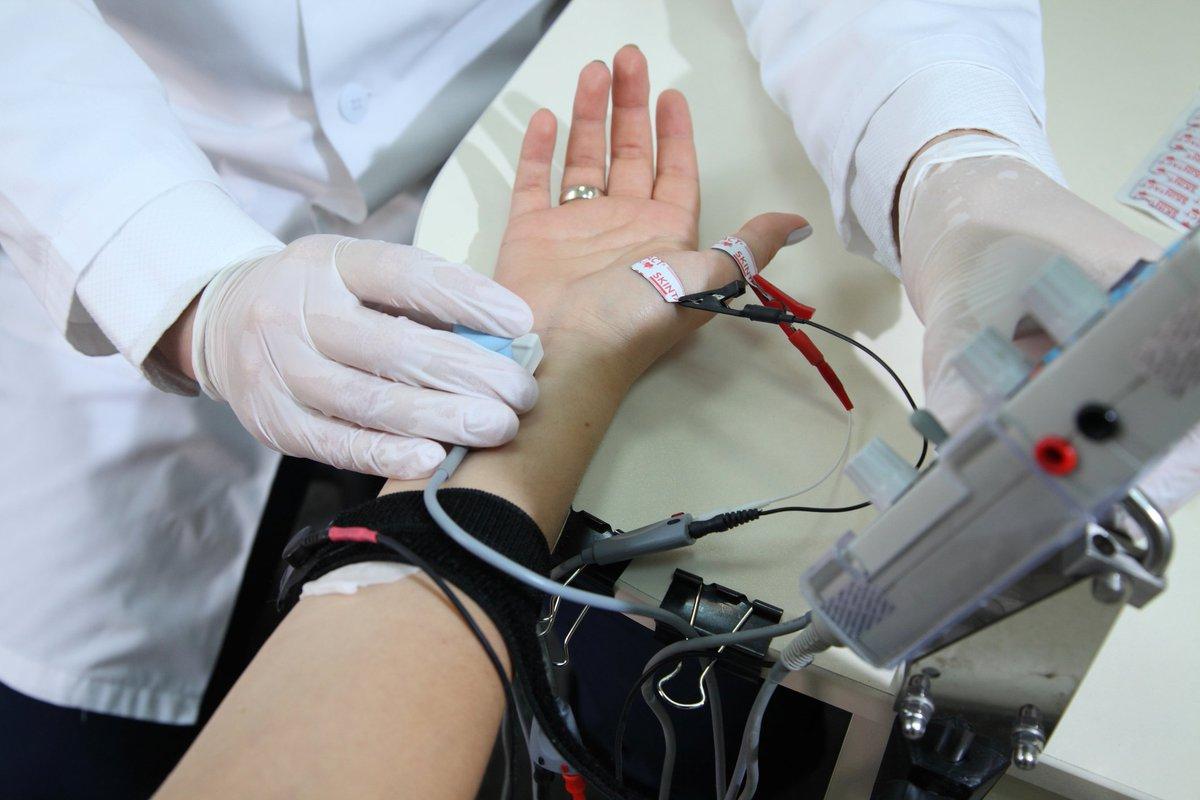
When detecting peripheral neuropathy, one cannot do without electroneuromyography (ENMG). ENMG shows how nerve signals are transmitted at rest and during contraction, so this diagnostic method determines whether the muscle itself or the nerves that are connected to it are damaged (Mathis et al., 2021). A needle is inserted into the muscle, then the electrical activity is measured (Picture 3). If the response pulse is low during muscle stimulation, then the diagnosis is confirmed. In addition to the examination, laboratory tests can help identify the root cause – a blood test, cerebrospinal fluid is examined, blood sugar levels are determined, and hormonal background is measured.
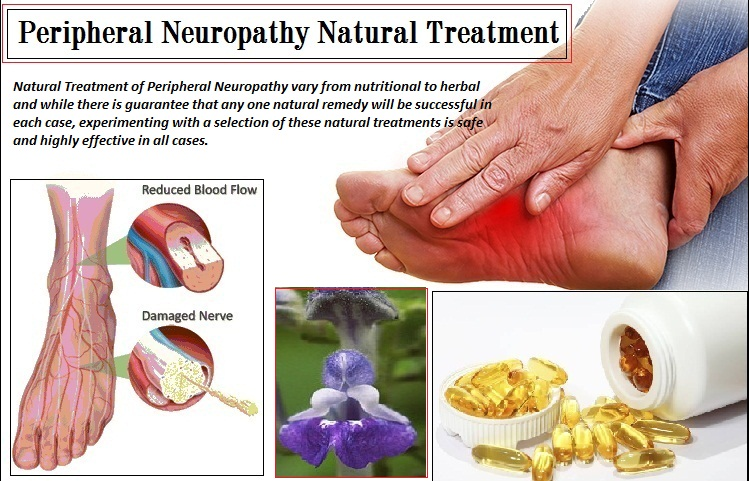
Treatment of peripheral neuropathy is based on taking medications. The doctor prescribes painkillers, anti-inflammatory, sedatives, and drugs that enhance blood supply. A course of vitamin B injections is attributed, which normalizes nerve conduction and stimulates the synthesis of new nerve fibers. Together with B vitamins, vitamins C and E are useful. It is prescribed to take antioxidants that destroy free radicals, as well as anticholins that restore muscle sensitivity.
Peripheral neuropathy is not completely cured, but the symptoms can be controlled. Usually, after a course of treatment, improvements are noticeable after a few months. During recovery, you cannot do without physiotherapy. Such FTL sessions as electrophoresis, mud applications, shock wave therapy, and magnetotherapy accelerate blood circulation, and maintain muscle tone (Staff, 2020). IRT has a beneficial effect on peripheral nerves. Acupuncture involves inserting needles into specific points to stimulate nerve impulses. Thus, pain is reduced, and sensitivity is stabilized. Pathology often develops in people with a low-activity lifestyle, so when working sedentary, one should get up every hour, warm up, and walk. Current research shows that spinal cord stimulation gives the best results for alleviating pain in Agent Orange-induced neuropathies (Rasekhi et al., 2018). Moreover, studies highlight the importance of maintaining a normal weight and the exclusion of the use of alcohol and nicotine. Natural substances in peripheral neuropathy treatment also help alleviate pain and improve sensitivity (Picture 3).
References
Mathis, S., Soulages, A., Vallat, J. M., & Le Masson, G. (2021). Epidemics and outbreaks of peripheral nervous system disorders: II. Toxic and nutritional causes. Journal of Neurology, 268(3), 892-902.
Rasekhi, R., Babb, D., & Price, C. (2018). Neuromodulatory burst therapy for Agent Orange–induced peripheral neuropathy: A case report. A&A Practice, 10(7), 165-167.
Staff, N. P. (2020). Peripheral Neuropathies Due to Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies, Toxins, and Medications. CONTINUUM: Lifelong Learning in Neurology, 26(5), 1280-1298. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000908
Stellman, J. M., & Stellman, S. D. (2018). Agent Orange during the Vietnam War: the lingering issue of its civilian and military health impact. American Journal of Public Health, 108(6), 726-728.