Communication process – it is the series of step by step actions we take between two entities to exchange messages successfully. There is the sender who initiates the message sending, there is also the message which is the intended information to be sent, it also involves encoding of the message which is transforming the thoughts in a form that can be sent, such as words (Rice and Atkin 15). There is also a channel of communication which is the means by which the message will be sent. The final recipient of the message is known as the receiver (Turow 100). The receiver has to decode the message to get an understanding of the intended message. The receiver and sender must have a similar field of experience which is the same knowledge and understanding of the message for the process to be effective.
Persuasion Matrix is a model that tries to explain how mass media communication helps in persuading people. This model considers that persuasion is due to successfully transiting several steps before persuasion. It has two sets of variables, namely input and output. The independent variable is the one that can be controlled during communication. On the other hand, dependent variable is the phases that the receiver will go through while being persuaded. The matrix is important as it serves as a very great visual tool to indicate how message components target persuasion phases. This matrix is important in IMC process as it deals with how we can persuade our target customers or clients to influence their behavior and attitudes towards what we need to convince them to buy.
The Elaboration Likelihood Model (EML) model was proposed by Petty and Caciapo (1986) and views persuasion as a method in which the rate of success of influence mainly is dependent on the way the recipient of the message will make sense from the message sent to them (John, Singh, and Woo 88).
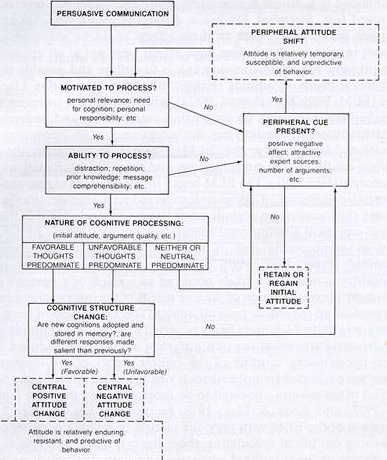
This model has two routes of persuasion. First is the central route that consists of consideration of the argument cases in the message sent. The second route is the peripheral route which happens if the listener or recipient decides whether they agree with the message depending on any other cues apart from the strength of the ideas presented in the message.
Culture should be taken into consideration when asking an individual to perform a certain action as different cultures have different beliefs. Some may consider action being asked to carry out as a taboo within their culture, and yet the same action is not a taboo in a different culture. Marketers must consider how to make a particular message to a specific culture and ensure they are most-effective (Petty and Cacioppo 78). For example you cannot convince a Muslim to buy a meal that contains pork as it’s a taboo in their culture. Another case is in Ireland where they consume on average 155 litres of beer each per year compared with only 29 litres by the Italians and only 41 litres by the French.
Various appeals can be used in advertisement to persuade customers to purchase products, they include: Musical Appeal where music can be used to capture the attention of people easily as it is linked to emotions and memories of people (Solomon, Hughes, Chitty, Marshall, and Stuart 300). Sexual Appeal where nudity and any other sexual approaches have been used to make advertisements. Humor Appeals help to easily grab attention and retain it at the same time and is also easily remembered (Tyagi 120). Fear Appeals are used commonly because they always work. It lightens the tone and also makes it more memorable. Rational Appeals which mainly involve emphasizing on details, the importance of the product and facts of the products to help persuade customers and they are also usually low cost.
Works Cited
John, Morris, Allan Singh, and Coon Woo. Elaboration Likelihood Model:A Missing Intrinsic Emotional Implication. N.p., 2009. Print.
Petty, Richard E, and John T. Cacioppo. Attitudes and Persuasion-Classic and Contemporary Approaches. London: Oxford, 1981. Print.
Rice, Ronald E, and Charles K. Atkin. Public Communication Campaigns. New York: Sage Publications, 2012. Print.
Solomon, Michael, Andrew Hughes, Bill Chitty, Greg Marshall, and Elnora Stuart. Marketing: Real People, Real Choices. New York: Pearson Higher Education AU, 2013. Print.
Turow, Joseph. Media Today: Mass Communication in a Converging World. N.p., 2013. Print.
Tyagi, C. L. Advertising Management. New York: Atlantic Publishers & Dist, 2004. Print.