Abstract
Entrepreneurship is one of the most important aspects of economic development. It has also become a part of the culture, especially in western countries. Since the industrial revolution, many people have been opening their private businesses. This movement inspired people in developing countries to do the same, if not better. Countries like the UAE have developed rapidly for the past 40 years due to tothe growth of entrepreneurship. This paper analyzes different aspects of this phenomenon, using primary and secondary sources.
Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is a complex term that implies various concepts. Entrepreneurial activities depend on many factors, like the political environment and socioeconomic situation. Therefore, entrepreneurs apply different strategies to implement new ideas. The main goal of this paper is to analyze the phenomenon of entrepreneurship, highlighting its major aspects.
Definition
Entrepreneurship is a comprehensive concept that is frequently related to private businesses. However, there is a certain difference between a businessman and an entrepreneur. Although a person might be, both entrepreneurship implies a specific attitude. The idea of entrepreneurship is much deeper than just a business venture because it includes an innovative way of thinking and willingness to take risks, trying to find new solutions to existing problems.
The major attribute of this concept is a passion as it drives a person through difficulties and failures (Drucker, 2014). Therefore, this inner energy allows overcoming different challenges and gives additional strengths to achieve goals. Other important characteristics of entrepreneurs are confidence and self-motivation. They know how to evaluate limitations and keep trying in spite of them. Sometimes, it requires breaking traditional rules and disrupting the status quo.
Hence, entrepreneurs might undertake some ventures of which others are afraid. They can handle failures and might use this experience to design more effective strategies. The main goal of an entrepreneur is to implement their ideas, creating new products that might not be much demanded first but become highly necessary over time.
Famous Entrepreneurs

There are many famous entrepreneurs throughout history and in the modern world. Walt Elias Disney was a very popular American filmmaker and animator. He began drawing pictures when he was a kid and lived on a farm. Later, Disney worked for an advertisement company, but he wanted to establish his own animation studio (Mannheim, 2016). Eventually, he was able to achieve this goal. Moreover, Disney developed his company into the most famous theme park in the world.
Another well-known entrepreneur is Steve Jobs.

He had to leave college because his family could not continue paying for his education. However, it let him found the Apple Computer Company with a talented engineer Steve Wozniak. His innovative vision initiated a digital revolution. Subsequently, Apple drastically changed the information technology industry.
The next famous entrepreneur is Andrew Carnegie. He began to work when he was a child, as Carnegie endured serious deprivation.

Later, he had a very successful career in the Pennsylvania Railroad Company. However, Carnegie set up his own businesses, and one of the most profitable was the Carnegie Steel Mill. Although he became a billionaire, Carnegie did much charity work. He donated billions of dollars to various libraries and educational institutions throughout the United States.
Economy and Entrepreneurship
Economic development directly depends on entrepreneurship. Various studies reveal that it improves economic performance, creating new jobs, and reducing the level of poverty. Although entrepreneurship is recognized as a key factor in economic growth, it might have a negative effect as well. These two aspects are strongly interdependent. For example, governmental policies can both cultivate or hinder entrepreneurial initiatives.
The capitalist economy requires competition and innovations, and successful entrepreneurs create an environment that stimulates the development of different industries. New businesses galvanize markets as they offer unique products and services. They attract new customers, and it motivates other companies to think outside of the box. It is found that there is a rapid growth of entrepreneurial activities in African-American communities (see fig. 1).
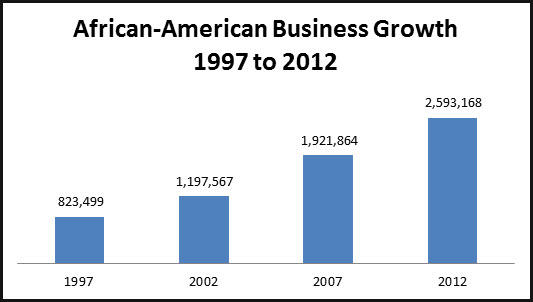
However, according to Gines (2015), African-Americans makeup 13 percent of the population but own only 9 percent of businesses. Also, in spite of the fact that the development of technologies might disrupt regular manufacturing positions, it offers various new opportunities for a career like maintenance services. Another important factor is that small business are very flexible. Therefore, such companies are much more adjustable to fast-changing market conditions than greater organizations. Small ventures can complete short-term projects, whereas it takes much longer to get work done for large companies.
Evolution of Entrepreneurship
The idea of entrepreneurship has evolved over time, and it has correlated with the development of capitalism. Adam Smith’s theory offers three essential aspects of an effective market. These are competition, adequate information, and the absence of externalities. Unregulated capitalism might result in a large gap between the poor and the rich. Such inequality is a fundamentally political issue, and it leads to the idea of more equitably distributed goods and services.
Entrepreneurs have improved this situation, though indirectly, throughout history. The earliest merchants were typical enterprisers. For example, Marco Polo, who established trading expeditions across Asia, became a very successful entrepreneur. However, later enterprisers applied other strategies. Eli Whitney invented the machine that separated cotton fibers, and it was the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. Another example is Martha Harper, who used an innovative strategy that is known today as franchising. Entrepreneurs have changed global business traditions and developed national economies, fostering prosperity in deprived areas (Toma, Grigore, &Marinescu, 2014).
Therefore, entrepreneurship was always a popular activity. However, the increasing involvement of governments has a crucial impact on entrepreneurial methods. Nowadays, enterprises are focused on the development of living systems like national health care, broadcasting industry, education system, and others. They offer new, more effective methods and approaches in these fields, affecting a greater audience.
Government Programs
Nowadays, governments widely support entrepreneurship through various programs, making it a more popular business concept. Such programs focus on several aspects. First, they improve cooperation between researchers and businesses. Governments work with research institutes and private companies in order to establish a close partnership. Second, governmental programs aimed at eliminating regulatory barriers for entrepreneurs. It includes incorporating digital technologies that facilitate licensing processes. Also, such programs offer information technology tools for enterprisers. Online government services have become more effective and responsive. Third, they create solid networks that assist in the development of business.
Therefore, these programs help to attract new entrepreneurs. Similar policies are successfully applied in the United Arab Emirates. For example, the time for obtaining building permits has become much shorter due to the new online service for applicants. Also, they reduced the number of documents required for export. In addition, their programs reduced the minimum capital for limited liability companies. These reforms resulted in 23,000 young entrepreneurs and 160,000 new employees (“Entrepreneurship and innovation,” n.d.). Therefore, the UAE government fosters entrepreneurial initiatives across the country.
Entrepreneurship in Non-Capitalist Countries
Entrepreneurship develops similarly in other societies. Governmental programs that support innovations are designed in many countries throughout the world. They are aimed at the same goals: facilitating new businesses and developing existing ones. However, entrepreneurship in non-capitalist countries has several distinct characteristics. For example, socialist entrepreneurs are limited in ways to achieve their goals.
However, they promote moral principles like honesty and reliability through their enterprises. Also, socialist businessmen are focused mostly on the interests of their employees. However, it does not mean that these characteristics negatively affect entrepreneurship. Norway and Sweden are partly socialist countries, but they have one of the highest start-up rates in the world. However, entrepreneurs in poor countries often need support. For example, Hydroponics Kenya, a non-governmental organization (NGO), helps local farmers to cope with climate change (Rasagam, n.d.). This organization established several hydroponics systems in Rwanda, Uganda, and Kenya.
Another example is farmers in Jamaica, who do not have direct access to markets. The NGO Agro Central offered an online system that assisted farmers in distributing their products. Another case took place in Bangladesh, where Muhammad Yunus implemented his microcredit concept (“Q&A with Muhammad Yunus,” n.d.). He established a credit system that provided small loans with low-interest rates. This system helped poor women start their own sewing shops.
Conclusion
In conclusion, entrepreneurship embraces various ideas and approaches. Entrepreneurs have a specific vision and way of thinking. They break conventional norms and invent new approaches. Such risky individuals change the course of history and speed up the development of society. There are various examples of successful enterprises that had a significant impact on the entire world. However, political and economic environments might hinder the growth of entrepreneurship.
Therefore, it is necessary to champion business ventures that cannot develop due to serious difficulties. There are different ways to support such companies. Governments design special programs that facilitate business processes. Also, NGOs might play a crucial role in promoting the interests of entrepreneurs. Therefore, entrepreneurship is one of the most important aspects that both depend on and influence international communities.
References
Drucker, P. (2014). Innovation and entrepreneurship. New York, NY: Routledge.
Entrepreneurship and innovation (n.d.). Web.
Gines, D. (2015). Economic empowerment through entrepreneurship. Web.
Mannheim, S. (2016). Walt Disney and the quest for community. New York, NY: Routledge.
Q&A with Muhammad Yunus (n.d.). Web.
Rasagam, G. (n.d.). Why we should champion entrepreneurs in developing countries. Web.
Toma, S. G., Grigore, A. M., & Marinescu, P. (2014).Economic development and entrepreneurship. Procedia Economics and Finance, 8, 436-443.