Description
- Childhood development is a crucial concept allowing educators to develop efficient teaching strategies and contribute to a faster knowledge acquisition by learners;
- A profound understanding of the student’s current developmental stage is imperative for meeting their needs successfully and creating a favorable academic environment;
- Piaget’s theory can be deemed as one of the most popular iterations of the phenomenon of childhood development; it provides a deep insight into the nature of cognitive functions and the way in which they are acquired.

Definition
- Schema: a key element of Piaget’s theory and the primary building block of the mental model that will allow for the further acquisition of the relevant knowledge and skills, as well as the interpretation of the reality;
- Assimilation: the process of identifying unique experiences and processing them carefully so that they could be stored in the child’s memory for the further usage in a similar scenario;
- Accommodation: the stage of analyzing the newly acquired data so that it could become the foundation for and an integral part of a new schema that will serve as the tool for the child’s interactions with the environment and people around them (Siegler 131).

Background
- Jean Piaget: born in Switzerland, excited about the idea of exploring the specifics of brain functioning and cognitive functions thereof;
- Known for the active promotion of Constructivist principles as the foundation for his interpretation of childhood development;
- Introduced the idea of viewing childhood development from the perspective of both biological and social standpoints;
- Assimilation and accommodation became the cornerstones of Piaget’s developmental theory;
- Equilibration process was introduced into the set of key terms as the concept describing the ability to navigate among the range of available schemata.

Historical Information
- Mother (Rebecca Jackson): encouraged Piaget’s enthusiasm about learning and promoted his further academic development extensively;
- Father (Arthur Piaget): inspired Piaget to be enthusiastic and passionate about the opportunities of learning.

Theory Description
General Principles
- Piaget’s theoretical framework serves as the tool for developing a better understanding of how children acquire knowledge and skills;
- The theory is aimed at describing the key stages passed by a child during the process of cognizing the world around them;
- Schema is viewed as the primary building block that allows connecting the key concepts within the theory;
- The theoretical framework designed by Piaget can be used efficiently in a diverse classroom setting;
- Thus, the needs of learners can be identified and met successfully.

Schemata
- A combination of schemas is known as schemata;
- Schemata contribute to the development of the child’s social skills and the further development of independence in the learning process;
- Different types of schemata exist (e.g., self-schemata, people schemata, event schemata, etc.) to describe the vast variety of social interactions (Kolb 207);
- Stimuli are crucial for launching the process of developing a schema as the means of interpreting the signals retrieved from the contact with the environment;
- The stimuli affect the child’s five primary senses, therefore, allowing the student to engage in the active process of cognizing the world around them.

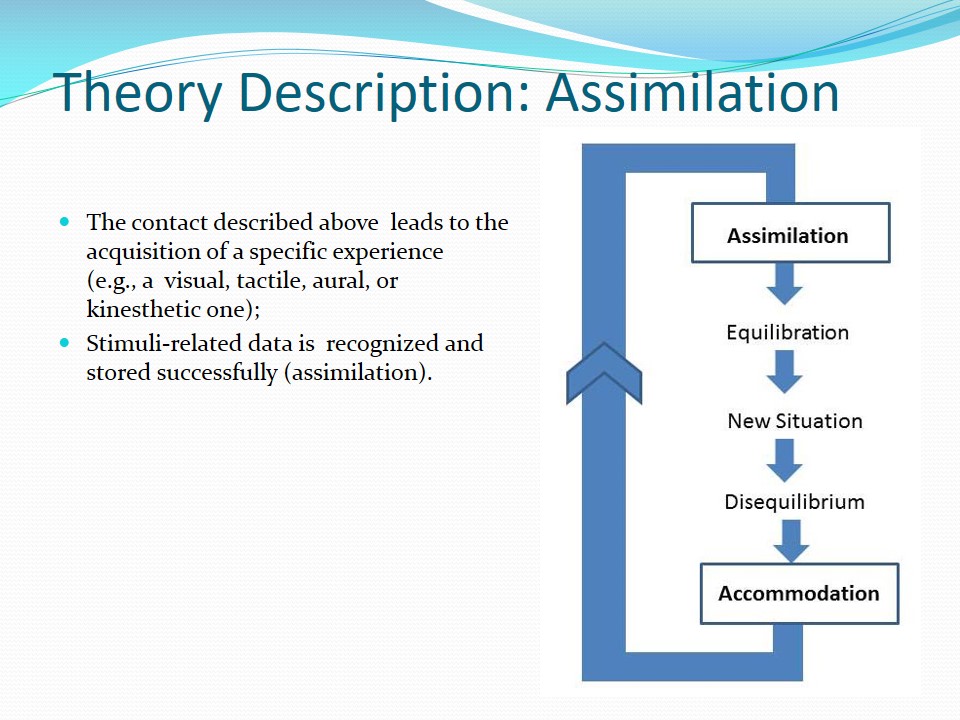
Assimilation
- The contact described above leads to the acquisition of a specific experience (e.g., a visual, tactile, aural, or kinesthetic one);
- Stimuli-related data is recognized and stored successfully (assimilation).
Adaptation
- The developed assimilation is recognized and incorporated into the range of strategies used by a child to interact with the world (accommodation);
- A particular behavioral pattern is produced so that similar instances of contacting with the stimuli in question could lead to the desired outcomes in the future;
- A child learns the lesson and is ready to acquire new skills and knowledge that will support the newly acquired information and serve as the foundation for building the further knowledge.

Discussion
Weaknesses
- The concepts of accommodation and assimilation are rarely viewed apart from each other;
- Instead, they are conflated into a single concept that serves as the means of embracing the continuity of the process;
- The combination of assimilation and accommodation is termed as the process of adaptation;
- Adaptation is viewed as central to the cognitive development in Piaget’s theory;
- Adaptation serves to produce new schemata so that a child could develop the skills necessary for communicating and addressing various social issues.

Strengths
- The strengths of Piaget’s framework include the opportunity for developing a uniform approach that can, later on, be customized to meet the needs of diverse learners;
- The framework also sets the prerequisites for designing a coherent teaching strategy allowing learners to engage in the active process of learning;
- The approach provides a range of opportunities for motivating students and inspiring them to become active learners, as well as engage in the lifelong learning process independently.

Current Thinking
- The weaknesses of Piaget’s framework include the lack of emphasis on the importance of a student’s intellect;
- There is a glaring absence of the theory that explains the development of people in their adolescence;
- The theory cannot be used to meet the needs of students with disabilities (Kolb 203).

Conclusion
- Nevertheless, the framework can be shaped so that innovative approaches toward teaching could be introduced into the curriculum;
- The theory also provides deep insight into the nature of learning;
- The framework promotes active meta-cognition, which is essential for learners in the contemporary environment of multiculturalism and diversity (Liben 107).

Works Cited
“Jean Piaget.” Biographgy. 2016. Web.
Kolb, David A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. FT Press, 2014.
Liben, Lynn S. Piaget and the Foundations of Knowledge. Psychology Press, 2014.
Siegler, Robert S. “Continuity and Change in the Field of Cognitive Development and in the Perspectives of One Cognitive Developmentalist.” Child Development Perspectives, vol. 10, no. 2, 2016, pp. 128-133.