Introduction
Historically, manufacturing management concept was coined by Adam Smith in eighteenth century in his contribution to specialization of labor in manufacturing. Adam Smith indicated that industrial jobs can be broken into smaller jobs and laborers were recommended to specialize in areas that they deem perfect, skilled and efficient (Anon, 1998).
Accordingly, Fredrick Taylor coined the scientific management theory and implemented Adam Smith’s recommendation to manufacturing set up. In this respect, organizations in the service and manufacturing industries have a production or an operation department. The departments are significant in that they provide the services or the goods that translates to organizations’ revenues.
Production or operations management is the process through which inputs resources are combined and transformed in production synergies of the organization, to provide value added outputs in a planned and controlled criteria, utilizing organizations’ policies and procedures (Anon, 1998). Essentially, production is that part of organization concerned with bringing inputs together and transforming them into a range of quality output product. Production entails a set of interconnected activities to create a product.
Production management refers to activities of manufacturing of goods while operations management involves activities in the delivery of services. Applying the scientific management theory, managers in the contemporary industries have adopted to techniques and procedures, concentrating on increased quality and economic efficiency in manufacturing products. According to Llopis & José (nd), research shows that laborers in organizations are focused in waste reduction and realizing high level of efficiency and quality.
The paper focuses on the production management in a case study of IDT Australia limited. Importantly, the case study provides a detailed analysis of quality management in organizations. In addition, a recommendation or suggested strategies to improve current situation is also provided.
Research objectives
The objectives of the study include:
- To establish quality management process and the vital quality management activities in organizations
- To elaborate the concept of standards, assurance and control to organization quality management
- To explain organizations quality measurement and limitations in total quality management
- To bring forth suggestion on the improvement of the current situation in quality management in IDT Australia limited
IDT Australia limited
Institute of drug technology Australia Ltd (IDT) operates in a highly monitored and specialized field of manufacturing pharmaceutical drugs and substances. Based in Melbourne, Australia, IDT is Australian pharmaceutical contract manufacturing organization for over 25 years of experience in production for local and international markets.
The company possesses international recognized pharmaceutical producing facilities. According to company profile, the company is primarily committed to supply of drugs and provision of research and development and other technical services. The company commits its resources in four activities that include; new drug development and scale up, clinical research services, API manufacture and pharmacy services.
According to the AusBiotech (2009), the company’s “state of art” facilities are developed and designed to conform to the international regulations and standards GLP/GMP requirements.
The company’s 15 manufacturing suites have been purposely constructed as contained suites, enabling the production of highly potent and cytotoxic drug in a human health conducive environment (AusBiotech, 2009). IDT has employed approximately over 100 employees where around 65 staffs are engaged in manufacturing and the other 35 staffs employed at the clinical facility.
The company does not face stiff competitions since it has a distinct competitive advantage. Among its competitive advantage include; confidentiality in drug development and manufacture, access to the most prominent clinical facility nationally and overseas, access to large database of clinical trials volunteers and experience of over 25 years in drugs manufacture and research contract (AusBiotech, 2009).
Production management
Anon (nd) defines production as “the step by step conversion of one form of materials into another form through chemical or mechanical process to create or enhance utility of the products to the user”. Ideally, production can be seen as a function in organizations that convert inputs into outputs that are of high quality level (Bagad, 2008). Similarly, production is a process of adding value to inputs. The figure below shows an example of production process adopted by most of manufacturing industries including IDT Company.
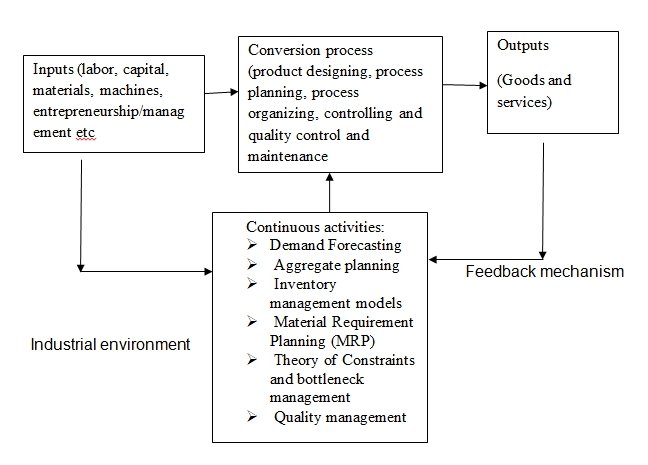
Figure one: production process diagram, source (anon, nd)
As the above diagram indicates, manufacturing is a system that comprises transforming inputs into outputs through a certain process and management of the system to produce high quality products economically and efficiently. The continuous monitoring of the production process is one of the most important function of management (Hakes 1991). Ideally, management team concentrates on Demand Forecasting, Aggregate planning, Inventory management, material Requirement Planning (MRP), Constraints and bottleneck managemen,t and Quality management.
Quality management
The term quality is frequently used in production processes. Departments of trade and industry define this term as “delighting the customers by fully meeting their want, needs and expectations” (Anon 1998, p.12). Radziwill (2005), argues that quality is an indicator of high and improved performances, whether in relation to the individual performance, teams, products or the whole company. Quality can also refer to free from deficiencies or abnormality of products, or leading to total satisfaction to the expectation of the end user.
Organizations evaluate or measure quality through their performances, costs, prices, supply time, consistency, accessibility, and upkeep of customer relationship. Thus, organizations must first recognize customers’ expectations and need to deliver quality to the market. Market research becomes significant process of establishing products features and the customers’ expectations.
Quality management entails the process of planning. Organizing, staffing, directing and controlling quality system s in organizations to meet products requirements and customers’ expectations.
Radziwill (2005) defines quality management as to involve developing and applying quality management and control systems in production, operations or delivering substantial satisfaction to the customer. In other words, quality management system can be viewed as tailored tender of principles into a collection of standards, policies, procedures, tools and methodology implemented to achieve quality goals of all industrial participants (Radziwill, 2005).
Markets acts as interface between customers and organizations and grounds of evaluating quality of products offered by different organizations. Market environments are ever dynamic and organizations must be vigilant in supplying and maintaining quality on their products. Competitions in the market have changed directions and quality provision is now a competitive strategy.
Macro-economic factors are still changing and enforced through rules, requirements and procedures. International standards of organizations have brought forth another approach to enforce quality in organizations. In this regards, organizations qualifying to promote and maintain quality are recognized as ISO quality certified.
Moreover, there exists interconnectedness between all participants in a production process to ensure total quality control. Various interfaces exist in the process such as customer-organization interface and supplier-organization interface (Hakes, 1991). Thus, cooperation of all is vital to enhance a total control system. Therefore supply chain management becomes a significant approach to managing total quality.
Customers and suppliers in quality management
Basically, organizations must understand who their customers are, what are their needs and expectations and how the organization can find out these. Again, the firm must know how to evaluate the ability to meet these wants and expectations, is the organization capable to meet these?, can the company continue to meet these needs and expectations in long run?, and how the organization can control and evaluate the performance in meeting customers’ needs and expectations (Hill et al., 2001).
Similarly, organizations are customers of a certain suppliers. Therefore, for organization to improve the supply chain and achieve quality management objectives there is a need to understand it’s internal and external suppliers. Organizations must know who their external and internal suppliers are, and what are the organizations needs and expectations from suppliers, and how to effectively communicate these needs.
In additions, organizations must evaluate whether potential suppliers are capable of achieving their needs and expectations and strategize on the effective approach to communicate any change in expectations. As noted by Bagad (2008), the realistic perfect situation is an open partnership relationship between all parties where share and benefit concept exist. This means that as the organization is aware of the customers’ benefits they must conversely appreciate the expectations of their suppliers.
Quality planning
Managers frequently argue with their counterparts on how essential quality management is vital as competitive edge, yet relatively a very small percentage know how to implement it in their organizations (Bagad, 2008).
By committing organization to quality management, staffs must also understand systems necessary to upgrade the production process. In his research on quality management in organization, Anon (nd) indicated that quality is synonymous of integrity, standardization in production process and the customer trustworthiness towards company’s products.
To achieve organization goals, mission and realize vision, planning is the first function of management and unto which all other functions depend on. In this regard, as Bagad (2008) suggests, without adequate planning for quality management, control and assurance becomes problematic to organizations. Proper total quality planning provide avenue to quality control and assurance translating to objectives accomplishment.
Quality control
A proper quality management system enhances firms to accomplish objectives targeted and sustain the strategy. As Bagad (2008) states, it is imperative for organization leaders and managers are responsible in monitoring the quality journey. Once the quality management strategy is implemented, it needs performance evaluation to control the policy.
Through monitoring and controlling, the desired level of performance is realized and also sustainable in long run. Quality Control should be established in all levels of organization’s management. Ideal control is undertaken by quality control team via activities of performance evaluation and monitoring (Bagad, 2008).
Quality assurance and standards
pqcassist, (nd) indicated that, companies committed to inspiring confidence to customers and staffs, break barriers between organization departments and achieve business goals must have quality assurance and standards systems.
According to Bagad (2008), standards are requirements, frameworks or procedures that must be adhered by the individual, government, firms, and industries and are usually enforced to achieve specific targets. Policies in organizations enforce standards for either operating business activities or implementing certain managerial plans.
Standards can only change under a formal framework and passed by key stakeholders of framework. As argued by Radziwill (2005), organization quality systems are focused to attain conformity, reduce variation, eliminate non adding value activities, waste reduction, minimize/prevent workers error and increase integrity thereby improving productivity and customer satisfaction. All organization objectives are attainable by implementing a dynamic, up to standards and assured quality management system (Bagad, 2008).
International organization for standardization is the reputed standard body for quality assurance to partners in all industries across the world. Another is the fair trade partnership agreement. Quality management system certified to ISO 9001 or 9000 refers to organization benefits in achieving consistency business processes and ambitious measurement/evaluation, and cost leaders or performance perfection. IDT Australia is among over one million companies certified for ISO 9001 and 9000 certification across the globe.
For quality assurance the company must be ISO 9001: 2008 certified. The certification is the world’s leading quality management system for assurance and standards.
This certification refers to company assurance in quality standards in areas such as customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, and continuous improvement in quality systems (pqcassist, nd). In addition, the company either small or large must poses realistic approach to decision making, improve in process method, system approach to management and shared beneficial supplier relation must exist (pqcassist, nd).
Current situation in the company
Emphasize on innovation has increased in Australia for the past and recent years. Understanding the quality management concept on managers and employees is much emphasized under industrial research and development. IDT Australia managers are well conversant with the quality management in production and all other areas. The company has employed over 25 PHD doctors and researchers to facilitate the creation and development of effective quality management in assurances and control.
As an international competitive organization, adherence to different quality management standards and policies is pivotal to its success. The company measures its total quality management by a basis on analyzing customer requirement, defining its processes that bring out products and services to the customers and provisions implemented in retaining a quality control system.
IDT organization structure and its functional units are accorded quality control manual and assurance department is instituted in all key quality adherence units. Quality assurance unit in the company concentrates primarily on the customer handling, proper books keeping, products quality and handling and the safety of organization physical and non-physical assets. Current total quality management system implemented by the organization is comprehensive process of stakeholders’ satisfaction.
Stakeholders include the customers, shareholders, suppliers, the government, and the employees. The quality control starts with implementing supply chain effective to meeting both the needs of customers and the suppliers. The company manuals indicate total quality management process comprises of quality assurance to the manufacturing activities and the customer service delivery at the clinic unit.
Basically, IDT Australia limited assurance and control systems ensures that the process prevent problems or issues that may arise, detecting them in advance, identifying accurately their causes, providing remedies immediately, prevent future occurrence and enhance quality progress.
As the objective of the company total quality is providing products of high quality that provide value and meets customers expectation, its system is derived from ISO 9001 certification and framework supplemented by the customer specification requirement (Hill et al., 2001). Currently, the company upholds its ability to provide continuous improvement in quality and increase individual goal accomplishment.
The quality manuals state that, “Quality management system shall promote guidance for the continued efforts including customer satisfaction, quality and reliability of products, process and all attached services” (MarketPublishers, 2011).
Data analysis
The above literature review on production and quality management systems, and the current IDT Australia limited situation has left very many questions unanswered relating to the company’s quality management. The literature brings unclear contribution of quality issues in the organization achievement.
Fundamentally, it is important to understand the various factors that influence the quality of firm’s products and the satisfaction of the customers. The influence of either internal or external factors and the unanswered question persuade the study to carry out more research and conduct a data analysis. Specific objectives of the study are;
- To establish quality management process
- To elaborate the concept of standards, assurance and control
- To evaluate organizations quality measurement and limitations
- To assess and provide suggestion on the improvement.
In general, the concept quality is a multidimensional term which can be measured and evaluated by many factors and indicators that are associated with customer satisfaction and the supply chain quality. In this study, the analysis on the quality management in IDT Australia limited focuses on customer needs fulfillment and satisfaction. Investigating the impact and the quality level of IDT limited by applying customer response is more acceptable than taking the whole supply chain fulfillment.
In this regard, to identify and analyses customer related issues and complaints in the study, freely and accessible information or data is utilized. As Radziwill (2005) supports, Critical Incident Technic (CIT) is the appropriate methodology employed to categorize and systematically analyze customer related issues and complaints from the standpoint of IDT Corporation. The following table provides categories of quality delivered by the company and the associated group of benefit.
Table 1: quality categories and the benefit group
Source: MarketPublishers (2011).
The analysis done identifies that there are certain reasons that make companies become ISO certified. These factors include the relationship with customers, and include internal factors and the external factors. Among all the factors, internal factors are the most preferred.
In addition, the relationship with customers may neither be influenced by the quality control, nor quality system be influenced by customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction and requirement fulfilling may be influenced by the internal marketing strategies. Furthermore, quality management literatures show that external factors and internal factors lead to companies’ certification.
From the table the analysis concludes that, it is imperative for the organization to provide continuous quality improvement criteria where controls and assurance can be benchmarked with their competitors in the global arena. As presented in the literatures, the issue of identifying, assessing quality based on customers’ satisfactions is not adequate. In this respect the research require full primary data collection consideration.
Recommendation
Generally, the adoption and application of ISO 9001 and 9000 in health services and drugs, and the utilization of customer specification is justified by the organization quality management manuals, issues may arise in quality control and assurance.
This way organization is driven by many factors in seeking for certification from either ISO, trade fair or from the government. In certain circumstances, internal factors are largely depended on when seeking certification. Internal factors include the level of employees performance, level of company performance financially and quality of the management.
As argued by Llopis and José (nd), successful implementation of quality management system to organization may reveal benefit of low cost and also differentiation. Therefore, adapting to ISO 9000 is much fair in terms of environmental factors. Essentially, internal factors contribute positively to internal organization improvement, while external factors contribute into good relationship with the external environments.
Llopis and José (nd) indicate external benefits as increasing market share, improved customer satisfaction, attracting new customers and retaining the relationship with customers and suppliers. Internal factors positively lead to increased staffs motivation and productivity, true and fair books of accounts presentation, efficiency achievement and lowering production costs. The motive of organizations is to make profits and increase shareholders wealth.
Based on this, companies that are certified due to internal factors makes higher profits that those certified due to external factors. Therefore, IDT Australia limited should be more focused on internal factors rather than external factors. Essentially, the reason why firms seek certification depends on the amount of internal managers’ dedication to the internal factors. Therefore, internal factors are vital and most recognized influences of certification and quality management systems.
Conclusions
All organizations consist of departments, customers, suppliers, and customer supplier system. Supply chains are exhibited by the suppliers, departments and customers’ interfaces. The objectives of a supply chain monitoring are achieving just in time delivery and meet customers’ expectations through quality products.
Poorly established supply chain translates to poor quality and customer dissatisfaction. Therefore, to achieve total quality throughout the company operations, every participant in the supply quality chain must be focused and trained on customer- supplier relationship. Fundamentally, quality management system can be implemented through a supply chain system.
In this perspectives, internal factors, external factors and the customer relationship with the organization is taken into consideration. The fact that IDT Australia limited has been certified for a long period of time and it has experience of over 25 years does not have an impact of the profits. The firm size qualification quality management is far much influenced by its internal functioning and other internal factors that accelerate quality control and quality assurance to internal and external observers.
List of References
Anon (1998). Production and operations management: An international journal of the Production and Operations Management Society, Volume 7. Production and Operations Management Society, University of California.
Anon. Introduction to production and operations management. Web.
Aus Biotech (2009). IDT Australia Limited Contract cGMP manufacturer of high-potency and cytotoxic active pharmaceutical ingredients and finished solid dosage forms. Web.
Bagad, V.S. (2008). Total Quality Management. Vienna, Austria, Technical Publications.
Hakes, C. (1991). Total quality management: the key to business improvement: A Pera International executive briefing. Canada, Springer.
Hill, N., Self, B., & Roche, G. (2001). Customer satisfaction measurement for ISO 9000:2000. Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann.
Llopis, J. and José, T. J. The Importance of Internal Aspects in Quality Improvement. Department of Business Management, University of Alicante. Web.
Market Publishers (2011). IDT Australia Limited Fundamental Company Report Including Financial, SWOT, Competitors and Industry Analysis. London, Business Analytic Center (BAC).
Pqcassist. Standards Australia – Quality Management Systems: Industry News. Web.
Radziwill, N. M. (2005). Quality Management in Astronomical Software and Data Systems. National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 520 Edgemont Rd., Charlottesville V. A. Web.