Scope Statement
The city of Madrid uses landfills as part of its waste management efforts. After landfills fill up, they require rehabilitation. This project relates to the construction of a sustainable green park in Madrid as part of a land reclamation program on a decommissioned landfill. The city council of Madrid is in charge of the preliminary processes including land stabilization, and certification of the land as fit for public use.
It is also in charge of rehabilitating access roads to the site. Greenscape International Plc (GI) has won the tender to construct a sustainable green park on the site. This tender includes organic development, construction of a maintenance office, and provision of renewable lighting.
The scope of the project includes laying turf, planting trees, and landscaping. It also includes the design and installation of park equipment and buildings, provision of water and sanitation facilities at the maintenance workshop, installation of the solar powered street lighting, and a mini waste collection and recycling facility. The city council of Madrid designed the park, and invited bids for its delivery.
Pre Planning
Project Selection Criteria
For the City Council of Madrid, this project is part of larger land reclamation program, which exists to rehabilitate landfills that are out of use. Its role in selecting this project was the development of the projects objectives and its design for fulfilment by a third party. The city council needed a project that would give the city an opportunity to make good use of the land left behind by one of the recently decommissioned landfills. The council chose to include a sustainable green park as one of the projects in its land rehabilitation program.
On the other hand, GI chose this project because it met three key conditions, which the company uses to determine projects to pursue. The first condition is that the project is in an urban area. GI seeks to develop sustainable green spaces in urban areas because of the unabated development of manmade structures that turn cities into concrete jungles. Secondly, the project had the support and participation of the city council of Madrid.
The participation of local authorities is a critical success factor for the development of green spaces. All projects that GI engages in must fulfil this condition. The third condition is that the project must make business sense. GI calculates a favourable return on the project and sends its bid based on this price. The Madrid project met this condition.
Estimation of Project Times and Costs
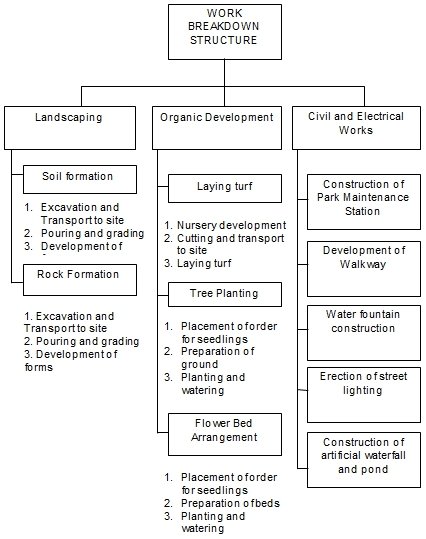
The project will have three major phases covering a total of nine weeks. The first one is landscaping. This will involve soil excavated from fresh landfills to the new site in order to create the required topography. It will also include the development of rock formations. The plan includes various natural and artificial rock faces designed to increase the aesthetic appeal of the park. The second phase of the project will be organic development.
This includes laying turf, planting of trees and planting of flowers in the park. The turf for the project will come from GI labs while the trees and flowers will come from local nurseries so that they blend well with the vegetation in Madrid. The third phase of the project will comprise civil and electrical works.
These will include construction of a maintenance station at the park, construction of walkways, building of water fountains and erection of solar powered streetlights. The maintenance station will provide an office space for the park manager and employees along with the security office. It will also have paper collection points and a mini-organic matter digester for compost development from the parks waste.
Table 1: Estimated project time and cost
Risk Identification, Analysis and Mitigation
The following table shows the analysis of the risks expected in this project, their severity and the mitigating measures identified to manage the risk.
Table 2: Risk analysis
The Project Team, Organization and Culture
The project team for this project will comprise the implementation team from GI, local employees, GI top management for project oversight, and representatives from the Madrid City Council. Details of the team will be the subject matter of another section of this report.
The Budgeting Strategy
GI specializes in international green space development. This gives the company the capacity to determine costs reasonably accurately on matters like the cost of turf, cost of senior staff, and the risks associated with international projects. GI developed the budgets for this project based on its experience in similar projects, and using estimates from suppliers in Madrid for the items it will procure from there.
It is important to account for differences in the cost of hiring staff in different countries. For instance, costs of hiring staff in South America is less than the cost of hiring similar staff in North America because of the market forces. This makes the overall costs of projects in some countries to be less than the cost in other countries.
There is a significant impact to international projects from the economic performance of the countries. Economic issues such as inflation, currency exchange rates, price controls, minimum wage laws, and fiscal policies all affect the financing of international projects. The costs included in the budget of the project reflect the considerations given to these forces.
Project Plan
The Work Breakdown Structure
The work breakdown structure for this project is in Table 3 below. The details relating to the construction of the maintenance office at the part are not included because it is in the hands of a subcontractor. However, the work break down structure shows the elements included in that phase of the project to enable the Civil Engineer from GI to measure accurately the progress of the project.
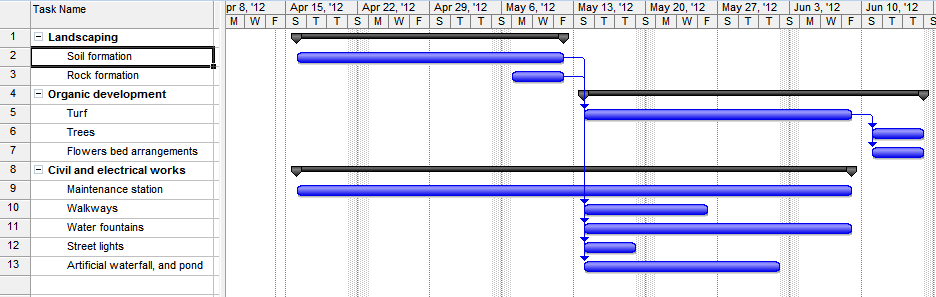
Gantt Chart
Two phases of the project will begin concurrently. The landscaping phase and the civil and electrical construction phases will begin simultaneously. In fact, the first half of the project duration will go to soil formation, rock formation and the first half of the construction of the maintenance station. The rest of the activities depend on the time it takes to finish the landscaping. This means that it is impossible to start on the rest of the tasks except the construction of the maintenance station until after the completion of the soil formation.
The tasks in the civil and electrical works phase can take place concurrently after the completion of the landscaping phase. There is a lot of slack time for most of the tasks under the civil and electrical works phase. The critical path does not run through any of the activities in this phase. If there are any difficulties in the organic development phase, it is possible to reassign resource from this section of the project.
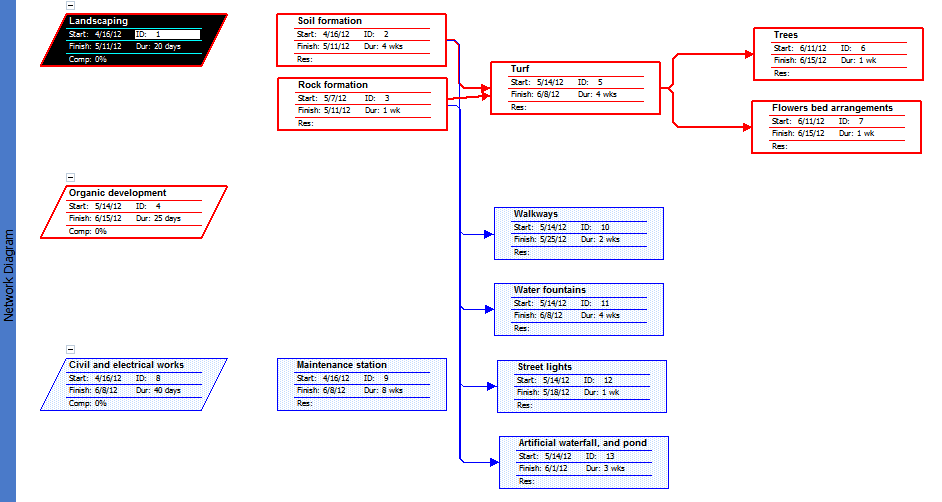
Critical Path
The critical path for this project lies along the landscaping and the organic development phases. Any delays along the critical path will lead to the loss of time. Some of the most critical risks to the project also lay along this line. The highest risk is poor weather, because all the activities on the critical path depend on the weather conditions.
It is impossible to excavate and perform soil formation activities under heavy rain or snow. The same applies for lying of the turf, and the planting of trees and the flowerbeds. Therefore, the timely implementation of this project depends on the weather conditions.
Resource and Recruitment Strategy
GI will use its internal resources for the management and supervision functions. The design team at GI will have the task of supervising the overall implementation of the project to ensure that it keeps within scope. However, the project will be under the control of one of GI International Project Managers. GI will lease most of the Equipment that to use in the project such as trucks, earthmovers, forklifts, and hand held implements.
GI will have a functional Human Resource Officer at the project site. The officer will coordinate hiring and remuneration of local semi skilled staff on casual basis. In addition, GI will station a full time procurement officer who will handle all deliveries and placement of orders to the prequalified suppliers for this project.
The project team will include a Sustainable Development Specialist from GI to oversee the development of the sustainable energy and sustainable environment components of the project. GI will also send its lead electrical engineer to ensure that the installation of the electrical systems such as the solar street lighting and the electricity supply for the maintenance workshop follows the laid down plans.
This engineer will be on site as needed. GI will station a civil engineer on site throughout the life of the project. The main work that will go into this project is in the field of civil engineering. The role of this engineer will be to ensure all the work done at the site, such as construction of the ponds, the waterfalls and the construction of the maintenance workshop and the laying of the walkways follow strict engineering standards
The actual construction work of these civil engineering elements of the project will not be under GI. GI chose to subcontract these works because it does not have the experience in construction of buildings. However, it is up to GHI to ensure that the building lives up to the design specifications that the City Council of Madrid laid down.
Recruitment strategy for team members
GI will fill the following positions from its staff
Project Manager/ Sustainable Development manager
- Overall manager of the Greenpark development project
- Chief Financial Officer for the project
- Critical Path management
- Liaison person to GI head office, and all project stakeholders.
Civil Engineer
- Supervision of the Civil Engineering works, done by GI and by the sub-contractors
- Development of related reports.
Electrical Engineer
- Overseeing the installation of power supply equipment by the contractor, and by GI
- Development of related reports.
Finance and Procurement Officer
- Management of the project procurement plan
- Ensuring the keeping of the necessary project financial records
- Tracking expenses
- Preparing salaries for local staff.
Human Resource Officer
- Coordination of the appointment of local staff with due regard to Spanish laws
- Handling staffing requirement for the project
- Quality assurance function.
GI will hire locals for the following positions
Two Foremen
- Supervising the assigned work teams
- Issuing daily progress reports to project manager.
Casual laborers (Turf laying 10, Tree and Flower planting 5)
- As assigned by foremen.
The Project Control Strategy
Before the commencement of the active phase of the project, the project manager will ensure that all the required aspects are in place. This includes environmental assessment reports from the Madrid City Council. The project manager will confirm the availability of the staff from GI and take care of all issues relating to their travel and stay in Madrid.
GI uses a project reporting system that requires project teams to confer regularly, at least weekly and for all project managers to participate in an international conference call with the senior management at the GI Headquarters. As such, the project manager retains control over all local issues and executes them within the wider policy framework of GI.
The Project manager, together with the project team, is in charge of ensuring the delivery of the project within time and budget.
The Internationalization Strategy (How do you approach management of cross-functional teams located in different geographies)
The key aspects of GI’s Internationalization strategy are
Use of local personnel to ensure the project team has local understanding
In all GI projects, there are always locals incorporated in the project team to ensure that the project team has a local understanding of the society the project is taking place. This also helps to endear GI to the local clients because of the benefits the locals get as employees of the project. having locals always gives the project team a good understanding of the local culture which is very important in the successful implementation of international projects.
Standard format of reporting on progress to GI Headquarters
GI uses standardized project management processes to manage projects. This makes it easy for any of GI’s international Project Managers to head any of its international projects.
Centralized project proposal development spearheaded by International project managers
Usually, project managers identify potential projects and develop proposal for them. The manager that proposes a project normally heads the team that implements the project. GI retains a number of professionals in its staff such as engineers and economists to help with the specific project tasks requiring their input. These professionals usually are not part of particular projects, but fly into project locations for the duration of need of their services, and then move on to the next project. Consequently, the professionals have developed a lot of understanding of international systems.
Technology
The final strategy that GI uses to overcome international barriers is technology. By use of real time communication, a project in a foreign country does not feel any different to GI compared to one a few miles off the headquarters. This strategy ensures that GI keeps track of all its project teams and their progress no matter their location.
Project approach and methodology
Value driven project management
As an organization, GI believes in the beauty of natural environments. The decision to develop green spaces commercially came from the desire to see more green spaces than concrete in urban spaces. It gives the residents of urban areas a chance to commune with nature. GI also believes in the equality of all people. Hence, it is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on any grounds. The result is that GI has a lot of goodwill from past clients and stakeholders, and locals who had the chance to participate in GI’s projects.
Environmental impact
GI does not engage in projects that do not have a clear net benefit to the environment. Of the environmental cost of undertaking, a project exceeds the benefits that accrue from a project, GI does not engage in that project. On the other hand, GI, guided by its goal of undertaking sustainable projects, always leaves the environment a better place by the construction of green spaces in urban centres across many continents
Ethics and Sustainability
GI believes in ethical business practices. It shuns any suggestions of corruption, bribery, or illicit gain from its business operations. GI does not undertake any project that has questionable financing, or seeks to cover up some environmental harm in a way does not result in a net benefit to the environment and the community.
Reference List
Flannes, S. & Levin, G., 2005. Essential People Skills for Project Managers. Vienna, VA: Management Concepts.
Froeb, L. & McCann, B.T., 2009. Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.
KPMG, 2003. Internal Audit’s Role in Modern Corporate Governance. Hong Kong: KPMG KPMG.
Schartmann, B., 2007. The Role of Internal Auditing in Corporate Governance inEurope: Current Status, Necessary Improvements, Future Tasks. Berlin: Verlag.