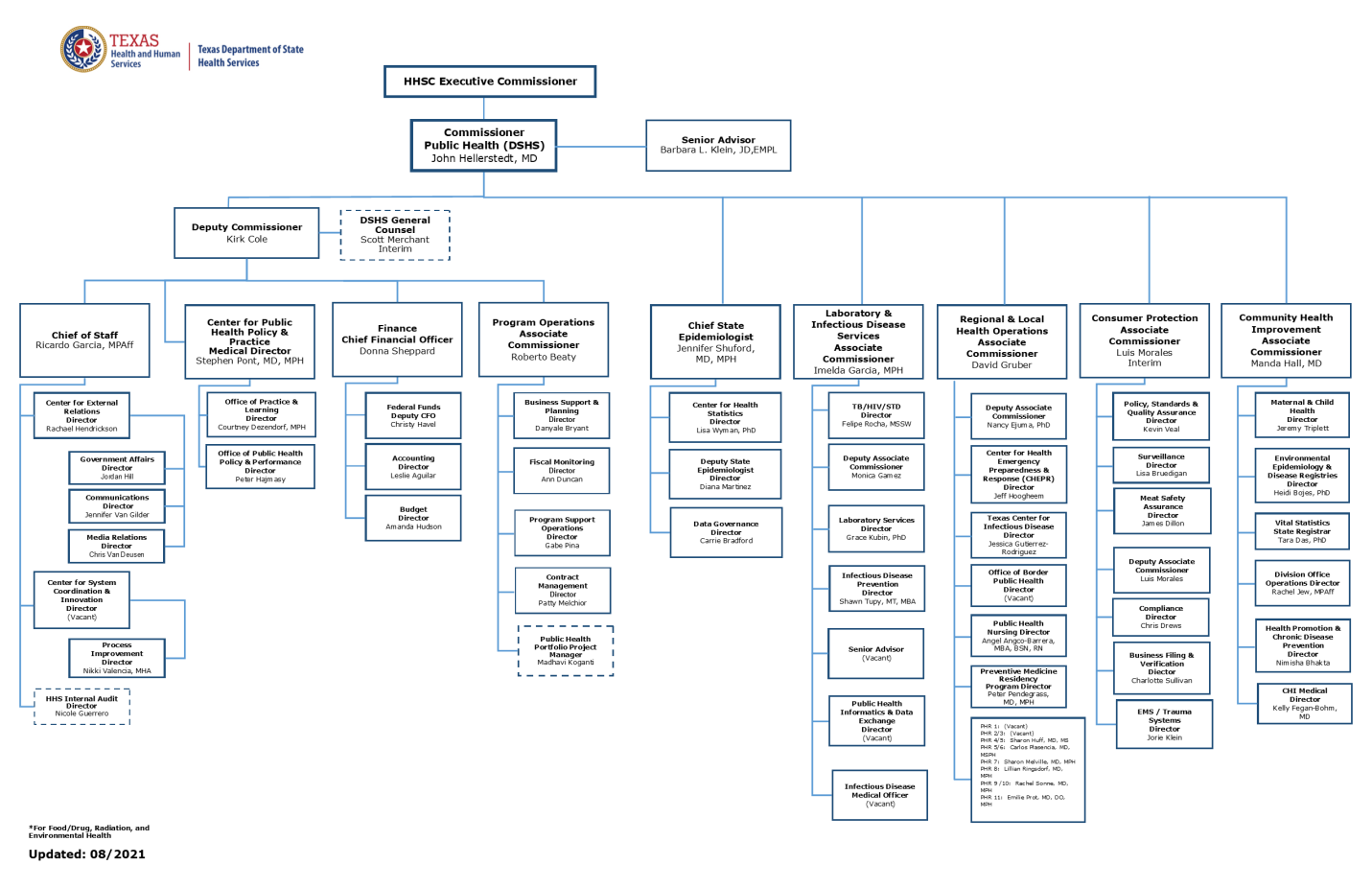
Texas health department is organized in hierarchical departments where the seniors are at the top, and the juniors follow. Each section is assigned different functions to ensure they are meant. The Commissioner of Public Health (DSHS) is the senior-most head, and the other department members follow, and they have to adhere to the rule of the high-ranking (Buxbaum et al., 2020). The figure below shows the general structure of the Texas department of health.
Services offered
The Department of Social and Health Services (DSHS) in Texas is in charge of prevention of diseases, EMS (Emergency Medical Services), health practitioner certification, and infant mortality credentials. DSHS also provides two unique programs for parents of children with disabilities or additional medical needs. Furthermore, it aids in the avoidance of the prevalence of chronic diseases, as well as laboratory analysis. The department also assists in designing and implementing facilities on subjects from asbestos to mobile food vendors to youth camps.
Functions and resources
The department operates state-run medical centers such as clinics, community hospitals, and healthcare institutions. The Texas DSHS has also been reorganized to emphasize public wellness to inhibit and formulate health extortions. Their role is to promote and guard the health of the public and the wellbeing of the environment in which people live, gain knowledge, operate, praise, and play games. There are few resources ready to aid in funding the state ministry of health. In Texas, the agency takes a higher portion of a person’s earnings than any other state. Because of the administration’s increased taxes, the nation ranks inadequately in medical services.
Values and mission
To improve Texans’ health, personal security, and wellbeing by focusing on essential public health operations and improving the quality of work of public resources. The agency’s goal is to inspire with a scientific and data-driven perception. The organization also intends to provide other practitioners to make a service plan that will achieve the client’s needs and work in community engagement, systems, and collaborations by establishing and allocating resources.
Comparing and contrasting
Texas compare with states like Kenya in terms of resources. Kenya faces the same challenge of inadequate funds in its health department. Texas also contrasts in its organizational structure since, despite Kenya having the senior-most head, the juniors do not have to adhere to the instruction given by the high ranking. There is always the freedom of expressing one’s ideas. The services offered also contrast with other countries since other countries, for example, Uganda, focus on health treatment, unlike Texas, which provides treatment and certification.
Reference
Buxbaum, J., Chernew, M., Fendrick, A., & Cutler, D. (2020). Contributions of public health, pharmaceuticals, and other medical care to us life expectancy changes, 1990-2015.Health Affairs, 39(9), 1546-1556. Web.