Executive Summary
The study entails a critical country risk analysis on Qatar. The purpose of the study is to determine the degree of risk that Exin Global might encounter by entering the Qatari market. The study focuses on different categories of risk. The core categories include the firm-specific risk or the micro risk, country-specific risk and global specific risks. The firm-specific risk identifies the political risks that the firm might encounter in the host country.
The likelihood of encountering goal conflict by entering into the target market is minimal because of the support given to foreign investments. The Qatari government promotes foreign investment through the foreign investment law. Moreover, the company’s success in the new market will also arise from the strong cultural and institutional frameworks.
For example, the legal framework in Qatar promotes investment by enacting intellectual property laws hence protecting innovation. An efficient banking and financial system further characterize the country and it promotes currency convertibility. The high rate of globalization, an increase in environmental concern such as climate change, and cyber crime might affect the firm’s operational efficiency both in the local and foreign markets.
Introduction
Domestic and international market expansion is one of the most effective ways through which companies can achieve profit and wealth maximization. Exin Global is a multinational corporation established in the UAE’s consumer goods industry. The company specializes in the manufacture of household care products. The company’s Chief Executive Officer is interested in the company’s growth through international market expansion.
The CEO is specifically interested in the firm’s expansion into Qatar as one of the emerging economies. However, some of the firm’s directors are concerned with the business risk exposure that might arise from venturing into some countries.
This aspect underscores the importance of understanding the country risk before the firm’s actual market entry. As a member of the company’s Business Development Committee, I have been tasked with the role of providing a broad country risk analysis for the most viable country that the firm should consider entering.
PESTLE analysis of Qatar
Political and legal environment
Qatar has adopted a monarchical system of government. Moreover, the Qatar government identifies investment and international trade as one of the fundamental components in promoting a country’s economic growth. Subsequently, the country is characterized by minimal bureaucracies that hinder foreign investment.
The Qatar government through the Ministry of Economy and Commerce has simplified the procedures required for foreign investors to establish a business in Qatar. However, foreign businesses are required to apply for a license from the relevant government departments depending on their intended business activity. Qatar has established strong political relations with foreign countries in the Middle East and North Africa region.
Economic environment
Qatar has depicted remarkable economic growth over the past decades. The country’s Gross Domestic Product has increased substantially as illustrated by graph 1 below. The growth in GDP is a strong indicator of the country’s positive economic performance. Thus, the consumers’ purchasing power has grown substantially due to growth in the per capita income.
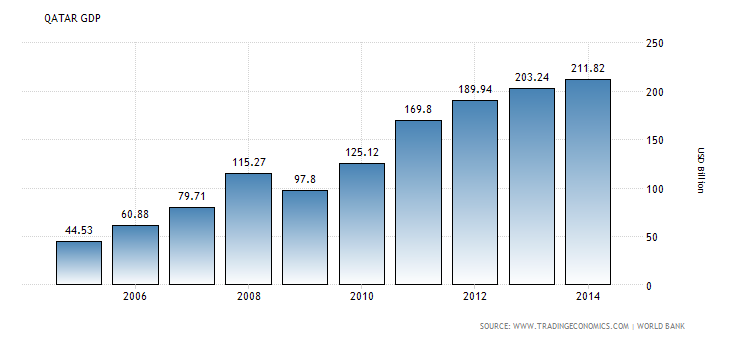
Graph 1: GDP in Qatar (“Trading Economics” par. 3)
Social Environment
The country’s social structure has changed substantially. The country’s society does not have cases of discrimination against foreign companies. For example, the country’s population has increased from 0.97 million in 2006 to 2.27 in 2014. The increase in the population indicates a potential growth in demand for consumer goods. Thus, the company might be able to generate the intended level of sales revenue.
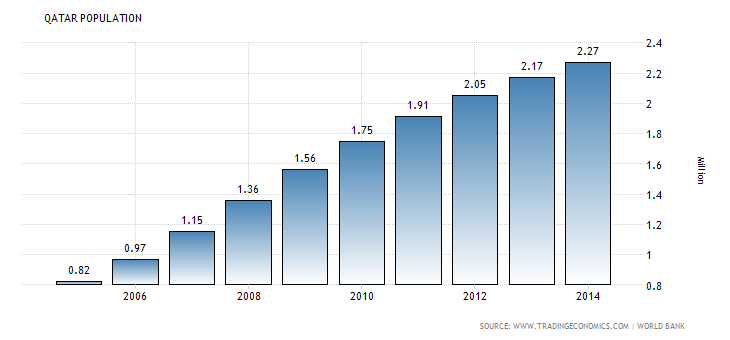
Graph 2: Population growth in Qatar (“Trading Economics” par.5)
Technological environment
Qatar is characterized by strong infrastructural development such as transport and communication networks. The developments have remarkably improved the level of efficiency of conducting business in the country.
Environment
The Qatar government has implemented a strict legislation aimed at curtailing carbon emission. The motive of such legislation is to limit climate change. Therefore, the government is pressuring manufacturing companies to implement effective strategies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Failure to comply with the law might result in a fine.
Country risk analysis
Krummel affirms that country risk is comprised of four main environments that include the political, debt manageability, anthropological and the economic risk (27). Subsequently, understanding the country risk analysis is essential determining the probability of multinational enterprises succeeding or failing in the in the international market.
Thus, conducting country risk analysis is vital in evaluating a multinational enterprise capacity to generate cash flow. Therefore, country risk analysis is essential to improving the MNCs capacity in making long-term financial or investment decisions. Country risk varies across different countries. Subsequently, evaluating country risk enables MNCs to determine the most feasible foreign market to enter (Madura 439).
Political risk
The political risk in Qatar can be defined as moderate. First, the government is focused on promoting international trade. Subsequently, the Qatar government has ensured ease of currency convertibility by eliminating foreign exchange controls or restrictions. Therefore, foreign investors in Qatar can easily remit their profits to the parent country without any restrictions. Additionally, foreign investors operating in Qatar are not restricted to convert local currency into foreign currency.
Therefore, Exin Global operations in Qatar will not be hindered by external currency inconvertibility. Rochon and Rossi assert that external currency inconvertibility occurs if foreign residents are limited from converting local currency into foreign currency (125).
The ease of currency convertibility in the country is further increased by the country’s banking system. Qatar is characterized by an elaborate banking system and regulatory system. Qatar is currently in the process of implementing the Basel Standards to establish a strong banking system.
Financial risk factor
One of the essential indicators of a country’s financial risk entails the interest rate. The rate of interest influences the cost of sourcing debt finance from commercial banks. The Qatar government has managed to maintain the rate of interest rate below 10%. In 2014, the World Bank estimated the lending interest rate to be 4.96%, which is substantially low. The graph below illustrates the trend in the country’s rate of interest from 2006 to 2014.
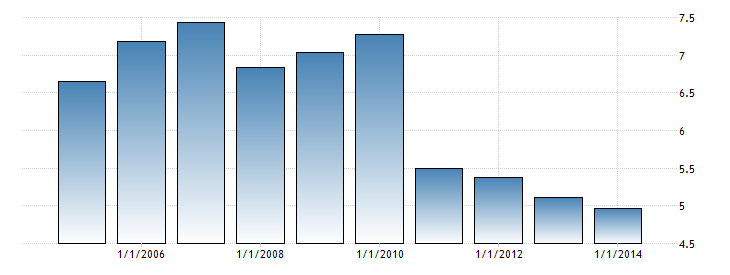
Graph 3: Interest rate in Qatar (“Trading Economics” par. 2)
The low rate of interest indicates that the country is likely to experience significant economic growth due to the ease with which businesses access financial credit. Moreover, the country is characterized by a moderate rate of inflation as illustrated by graph 3. The average rate of inflation in Qatar between 2005 and 2015 is estimated to be 3.48%.
The country experiences fluctuations in the rate of inflation. In June 2008, the country’s rate of inflation reached its highest point at 16.59%. However, Qatar has managed to lower the rate of inflation significantly. By the end of October 2015, the rate of inflation in Qatar was estimated to be 1.7%, which is considerably low.
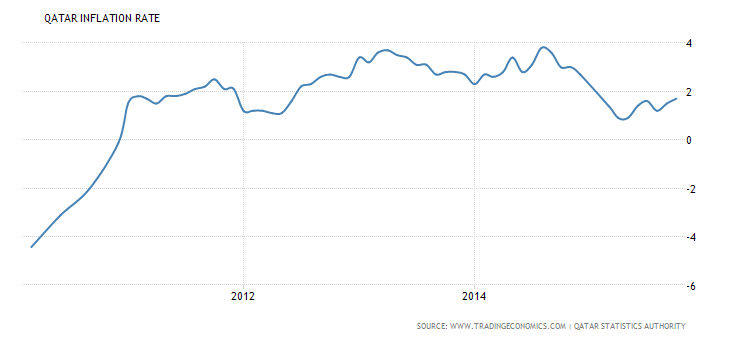
Graph 4: Rate of inflation in Qatar (“Trading Economics” par. 6)
The rate of inflation has a significant effect on the operation of Multinational Corporation. Sharan posits that if a “multinational company exports its products to countries characterized by high inflation rather than setting up a manufacturing unit in there, the exports are more likely to have a high competitive edge” (214). The low rate of inflation in Qatar is a strong indicator of the enabling economic environment in the country. Subsequently, Exin Global is likely to gain a high competitive edge by establishing a manufacturing unit in the country.
In addition to the low cost of manufacturing, Exin Global is likely to benefit from the resulting low consumer price index because of the low rate inflation. The Qatar economy has been characterized by a marginal change in the consumer price index as illustrated by graph 5 below.
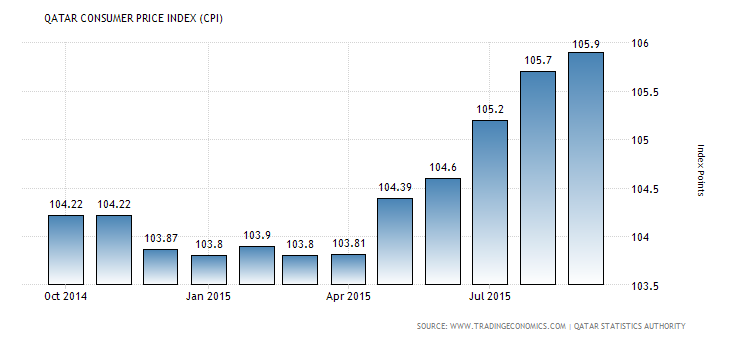
Graph 5: Consumer Price Index (“Trading Economics” par.5)
The marginal change in the CPI indicates that the cost of living in Qatar has not increased significantly. Hence, the firm will benefit from the high consumer purchasing power. Consumers in Qatar will be in a position to afford Exin Global products. Therefore, the demand for consumer goods is likely to be stimulated.
Similar to other countries in the Gulf region, Qatar has adopted a fixed exchange regime. The rationale behind the adoption of the fixed exchange regime is to ensure the stability of the country’s currency. Currently, the fixed rate of exchange is pegged at QAR 3.64=USD 1.
The Qatar government expects the exchange rate to remain stable until the end of 2016 (“Trading Economics” par.8). By establishing business operations in Qatar, Exin Global is likely to achieve the desired sales growth in sales. The growth in sales will arise from the stable exchange rate.
Assessment of risk factors
Macro-assessment of country risk
Macro-political risk
According to Madura, macro assessment of country risk entails consideration of the diverse variables that are likely to affect country risk (253). Undertaking a macro-assessment of country risk will give Exin Global a broad understanding of the general factors that are likely to affect the company’s operation in the host country.
The degree of political risk in a country influences the performance and ease with which multinational corporations conduct business operations in the foreign market. Qatar is located in a region characterized by a significant level of instability and social unrest. One of the notable sources of social unrest relates to the recent Arab Spring that led to the emergence of new political regimes. Moreover, the rate of terrorism in the region is substantially high.
The prevalence of these issues in the region might adversely affect investor confidence. Despite the cases of terrorism and social unrest in the MENA region, Qatar is characterized by minimal political unrest (“AMB Country Risk Report” 3). Therefore, the level of investor confidence in Qatar has not been affected adversely. Due to the minimal cases of social unrests in Qatar, Exin Global is likely to operate smoothly in the host country. Moreover, the likelihood of encountering loss due to social unrest is significantly low.
Despite Qatar’s ranking amongst the peaceful countries in the MENA region, the sustainability of the peaceful conditions in the country remains to be a balancing act. The country has enacted foreign policies aimed at supporting the Muslim Brotherhood in the MENA region, specifically in Egypt (Hawser par. 5).
The country’s foreign policy position might lead to the emergence of distrust amongst countries in the GCC and MENA regions. This aspect might affect the ability of the subsidiary firm established by Exin Global in Qatar capacity to export its products to the neighboring countries.
Macro-financial risk
Qatar’s economy is largely dependent on revenue generated from oil production. Qatar is the global leader concerning the production and exportation of liquefied natural gas. Over 90% of the country’s budget is funded using revenue generated from the exportation of oil (Parasie par.4).
In spite of past positive economic performance, Qatar’s economy might be affected by fluctuation in global oil prices. A recent evaluation of the country’s economic performance by the International Monetary Fund [IMF] indicates that Qatar might experience budget deficit due to the low oil prices currently being experienced n the oil producing countries.
Parasie asserts that the oil generating economies are characterized by booms and bursts (par. 5). The occurrence of a budget deficit might make the Qatari government consider increasing corporate and income taxes to cater for the budget deficit. Increasing the tax rate might adversely affect influence the company’s capacity to generate sales revenue due to a reduction in the consumers’ purchasing power.
Micro-assessment
The political risk affecting the fast moving consumer goods industry in Qatar is relatively low because of the support offered by the government. The Qatar government has established free economic zones such as the Doha Industrial Estate. The rationale of the Doha Industrial Estate is to promote the establishment of medium and light scale industries.
Furthermore, the Qatar government offers investors in the free economic zones a tax holiday depending on the nature of their manufacturing activities. Therefore, Exin Global might benefit from establishing a manufacturing unit within the designated free economic zones. For example, the tax holiday will culminate to a reduction in the cost of operations. Subsequently, the firm will be able to establish operations in Qatar.
Techniques for assessing country risk
To assess the country risk, it is imperative for the company’s management team to undertake an extensive country risk assessment. First, Exin Global management team should conduct a comprehensive reconnaissance on the new market. The firm can achieve this goal by sending the Business Development Committee members to Qatar to assess the attractiveness of the market.
During the inspection visits, the Committee should interview government officials, consumers, and industry executives on the uncertainties that are likely to be encountered in the target country. The firm might conduct a quantitative analysis by evaluating the historical data.
This move will play a critical role in determining how the firm is sensitive to risk the risk factors. Moreover, the Business Development Committee should further consider integrating the Delphi technique. Under this technique, the organization should seek the independent opinion of industry analysts or experts regarding the country risk. The Delphi technique is critical to understanding the perceived country risk (Madura 450).
Alternatively, the business might consider developing a checklist to be used in rating the risk factors. Based on rating, Qatar can be defined to be relatively stable as illustrated in Table 2 below. The table shows that the overall assessment of the country’s risk is stable as indicated by a comparison between the previous and current rating.
Measuring country risk
Before making the decision on the most appropriate foreign country to enter, the company’s management may consider comparing country risk rating. Based on this approach, the company’s management team will be able to make a decision on the most attractive country to enter. In this case, a comparison of the risk rating between Qatar and Kuwait shows that Qatar is the most attractive market. The overall assessment of Qatar has remained stable with a rating of B while that of Kuwait has declined from a rating of B to C.
Table 2: Comparison of country risk (“Economic Intelligence Unit” par.8)
The rating scores range between 1 and 100, where a score of 100=most risky. Similarly, a rating of E represents the riskiest factor.
Incorporating country risk in capital budgeting
The company should further consider integrating country risk in its capital budgeting process. The rationale of integrating country risk in the capital budgeting process is to assess the likelihood of generating and sustaining positive returns in the long-term. To achieve this goal, the company may consider determining the adjusted cash flow and discount rate.
The adjustment of estimated cash flow will enable the company to assess how its cash flows will be affected by the country risk in Qatar. Alternatively, integrating the country risk is also essential in the company’s effort to determine the most appropriate discount rate that the firm should consider in determining project cash flows.
Importance of country risk analysis to Exin Global
The process of undertaking country risk analysis will play a critical role in the company’s effort to evaluate the capacity to generate sales revenue by entering in Qatar. Understanding the country’s labor market risk will enable the firm to determine the ease of sourcing and developing a strong human capital from the host country.
Moreover, country risk analysis will aid in the determination of the ease of undertaking sales and manufacturing activities in Qatar. The attainment of this goal arises from the determination of different issues such as the degree of corruption, bureaucracy, the host government attitude to foreign investors and blockage of fund transfers.
Minimizing country risk
Exin Global should consider minimizing country risk by complying with the laws and regulations specified by the host government. Alternatively, the company should consider sourcing human capital from the host country. The company may consider customizing its products to meet the local market needs. This move will aid in ensuring that it products gain a high level of market acceptability.
Effect of risk on the firm’s profitability
The degree of country risk has a significant effect on the profitability of MNCs. An economy characterized by a high country risk due to cases of security and political unrest means that country might not undertake sales and manufacturing activities without disruptions. Subsequently, the level of profitability might be reduced substantially. Moreover, political unrest might lead to loss of the company’s property hence stalling manufacturing activities.
Actions taken by the government to protect the industry
The Qatar government promotes foreign investment in the consumer goods industry through the enactment of the Foreign Capital Investment Law. According to the law, foreign companies operating in Qatar are not subject to expropriation.
Additionally, the Qatar government does not restrict foreign companies from transferring equity ownership to either local or foreign investors. In addition to the above issues, the Qatar government protects foreign investors by enacting the intellectual property rights. Thus, investors can undertake product invention and innovation in the country.
Conclusion
International market expansion presents one of the most effective strategies that profit-oriented companies can adopt to achieve profit and wealth maximization. However, successful cross-border market expansion depends on how effective business executives understand the host country risk.
Country risk analysis is critical in determining the degree of exposure that a multinational enterprise can encounter in the domestic and host country. It provides multinational corporations with a multidimensional view of the international business environment.
Suggestions
To enter the Qatar market, Exin Global should adopt different techniques in evaluating country risk. One of the most effective techniques entails cross-country rating to identify the most attractive market. Alternatively, the company should further undertake a continuous assessment of the country risk. The continuous assessment will provide the firm with insight on how the country risks changes. Subsequently, it will be possible for the firm to undertake the necessary adjustments to its risk management processes.
Works Cited
AMB Country Risk Report: Qatar. 2015. PDF file. 2015. Web.
Economic Intelligence Unit: Risk briefing; Qatar 2015. Web.
Hawser, Anita. Report; Qatar faces geopolitical risk, 2012. Web.
Krummel, Jacob. International banking business, Berlin: Drucker & Humbolt, 2007. Print.
Madura, Jeff. International financial management, Mason: Cengage, 2009. Print.
Parasie, Nicolas. Qatar risks budget deficit in 2016 due to low oil prices, IMF says, 2015. Web.
Trading Economics: Qatar 2015. Web.
Rochon, Louis, and Sergio Rossi. The encyclopedia of central banking, Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2015. Print.
Sharan, Vyuptakesh. International business; concepts, environment and strategy, Delhi: Pearson, 2006. Print.