Introduction
Objective
The research seeks to establish the impacts of group variables, performance variables, and independent variables on the performance and profitability of Mitsui Sumitomo and Asahi insurance companies.
Overview of the companies under study
Mitsuisumitomo insurance company is involved in domestic non life insurance. Moreover, it participates in global life insurance, risk cover, and finance generating activities or businesses.
It has over time countered hindrances to growth with anticipation of becoming one of the leading companies in non life insurance industry. It has endeavored to commit itself in offering one of the highest quality services with the main target of establishing a sure breakthrough to growth as an insurance company meeting anticipated global standards.
Asahi mutual life insurance company is also another player in the insurance industry in Japan. It currently stands as one of the largest life insurance companies in Japan.
It has extended its services to countries like China to sell it life insurance policies. In addition, it offers group operations to China. This has greatly increased demand of it services in China. However, the company involves in, performance appraisal to meet global standards.
Conceptual model
The profitability and performance of insurance company is determined by the following factors, (Embley 134):
Operation factors
- claim settlement with minimal disputes
- companies infrastructure such as buildings, road
- information dissemination through agents and brokers
- customer satisfaction
Organizational factors
- staff qualifications
- adaptability to market trends
- involvement in community projects
- rates of return on investments
Others
- government policies
- legality of the practices
- competition
- sampling variability
Conceptual model on the effects of staff qualification on claim settlement in insurance companies.
- Literature review
Independent variable is a characteristic which is manipulated by a researcher in case of an experiment or case study in order to identify its effects in another variable mostly dependent variable(Embley 134).
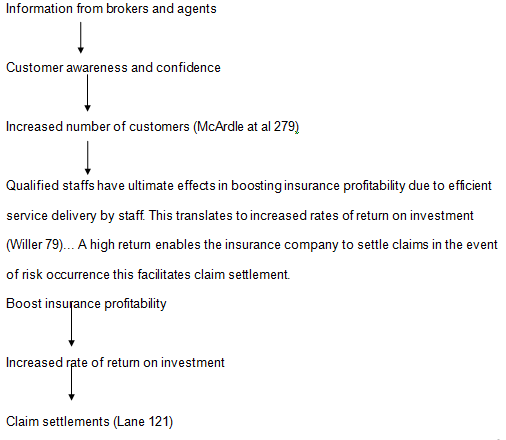
A dependent variable or orientation variable is the characteristic which the researcher studies to record the effects of the independent variable on the conceptual model; (McArdle at al 279) staff qualification is the independent variable since the researcher seeks to establish the effects of staff qualification on time, service evaluation, and amount of settlement to be made in case of a claim by the insured.
Therefore claim settlement is dependent on staff qualification or competence level (Willer 79).
Figure 1
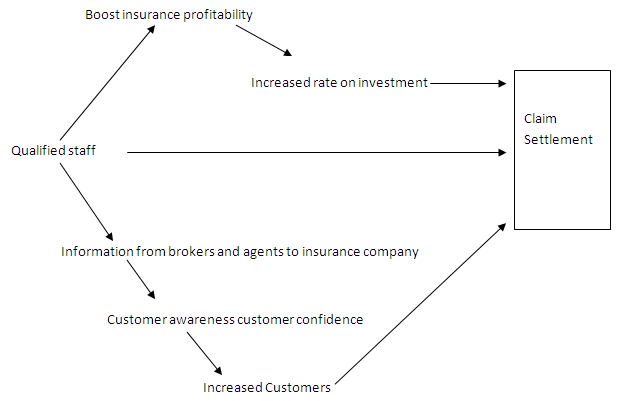
Qualified staff is the independent variable; the researcher manipulates staff competences to find out the impacts on the dependent variables. Qualified staff enables the brokers and agents to get relevant and factual information regarding the company. Therefore, they are able to influence the potential customers to the companies (Willer 79).
Moreover, the information disseminated by brokers and agents is thoroughly scrutinized. Availability of adequate information regarding a company to customers boosts the customers awareness this in turn increases customer confidence. The customers are able to sell companies policies to other potential customers. This results to the increased number of the customer to the company.
Regression analyses
The above questionnaire was issued to the respondents who are either customers or potential customers to the two insurance companies. That is Asahi and Mutsui insurance companies. There were twenty respondents on the study.3.2 data collected (Chatterjee and Hadi 8).
The above data represent the study results of company one (Mutsui life insurance)
Summation = 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10 =Ʃ55
Number of observations = 10
Mean Ʃ55/10 =5.5
PF1 =F1(X1, X2, X3, X4, X5) (Cameron and Trivedi l 239).
r=Ʃ(x1-5.5) +(x2-5.5) +……..+(x5-5.5)/√Ʃ(x1-5.5)2 +………. (x5-5.5)2
Ʃ =(x1-5.5) +x2-5.5) +(x3-5.5) +(x4-5.5) +x5-5.5)
=-23-9.5+23+3-14
=20.5
( x1-5.5)2+(x2-5.5)2+(x3-5.5)2+(x4-5.5)2+(x5-5.5)2(Yan and Su 267).
=90.25+529+ 529+9+196
=√1353.25
=36.79
R =20.5/36.79
=0.5572
This is a positive relationship between the variables. The goodness of fit on the observed (O) results and expected (E) results are good. Since (O-E) 2 is low (Cameron and Trivedi 239). The statistical results obtained give a positive relationship between variables hence it is significant in giving the performance and their relationship (.Babbie 56).
The below data represents the responses from the questionnaire in regards to company two (Asahi)
PF2=F2(X1, X2, X3, X4, X5) (Cameron and Trivedi 239).
Summation = 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10 =Ʃ55
Number of observations = 10
Mean Ʃ55/10 =5.5
r=Ʃ(x1-5.5) +(x2-5.5) +……..+(x5-5.5)/√Ʃ(x1-5.5)2 +………. (x5-5.5)2
Ʃ =(x1-5.5 ) +(x2-5.5)+(x3-5.5) +(x4-5.5)+(x5-5.5)
=2+17-39+10+8
=-2
√( x1-5.5)2+(x2-5.5)2+(x3-5.5)2+(x4-5.5)2+(x5-5.5)2
=4+289+1521+64+100
=√1978
=44.4747
r=-2/44.4747
=-0.618
The additive, linear model shows a linear connection between variables. The goodness of fit for the company is poor since the observed (O) results are higher the expected(E) results(O-E) (Yan and Su 267).however, the regression analyses of the statistics above gives the relationship between the variables under study. The analysis gives an impression of the negative relationship between the values.
Linear additive model of the entire sector (Yan and Su 267).
0.5572-0.618
=-0.0608/2
=-0.0304
From the values obtained r ranges from -1 to +1 signifying that r is greater than 0.99 the correlation is considered linear and when r is less than 0.99 the connection has an error (Yan and Su 267).
The additive, linear model essentially takes a simple connection between independent and dependent variables.it therefore gives quick facial impression of the data analysis (Yan and Su 267).
Regression analysis is a tool that measures the relationship between variables. Incase r=0 it means that there is no correlation among variables in question when r=positive value imply a positive relationship and r=negative imply a (-ve) correlation, an increase in one variable leads to decrease in another set of variables.
Regression analysis aid statisticians to identify whether two variables are related or not (Yan and Su 267). These variables are:
- Correlation which describes merely the presences or absence of relation
- Correlation which shows the degree of magnitude of relationship between two measures
Conclusion and recommendations
In a nutshell, all variables including dependent, independent, quantitive or qualitative variables impact on individual performance and profitability. A regression analysis gives the relationship between variables and enables companies to analyze the effects of independent on dependent variables. Companies should always perform regression analysis to improve and assess its continuity in the market.
Works Cited
Babbie, Earl R. The Basics of Social Research. Belmont, CA: Thomson/Wadsworth, 2008. Print.
Cameron, Adrian C, and P K. Trivedi. Regression Analysis of Count Data. 2nd edn. Econometric Society Monograph No.53, Cambridge University Press, 1998. Print.
Chatterjee, Samprit, and Ali S. Hadi. Regression Analysis by Example. Hoboken: Wiley, 2012. Web.
Embley, David W. Handbook of Conceptual Modeling: Theory, Practice, and Research Challenges. Berlin: Springer, 2011. Print.
Lane, Jan-Erik. The Public Sector: Concepts, Models and Approaches. London [u.a.: SAGE, 2000. Print.
McArdle, William D, Frank I. Katch, and Victor L. Katch. Essentials of Exercise Physiology.Baltimore, Mar: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006. Print.
Willer, Mirna. Unimarc Manual: Authorities Format. München: Saur, 2009. Prin
Yan, Xin, and Xiaogang Su. Linear Regression Analysis: Theory and Computing. Singapore: World Scientific Pub. Co, 2009. Web..