Introduction
Diversity is significant among universities since it enhances multiculturalism and promotes socialization among students. The U.S. is one of the few countries with a diverse student population. The country hosts thousands of students from different parts of the world. While the country is on the frontline of promoting diversity, many Black students are discriminated against for their skin color and socioeconomic status. Consequently, access to quality education by African American students has been hindered. This research focuses on the impact of bullying and racism among African American students in the country. The study is both quantitative and qualitative and will mine data from the existing literature. Moreover, the study involves a sampled student population that will help in understanding the problem. Exploring the impact of bullying and discrimination among Black students is crucial for educational institutions and policymakers.
Problem Background
Problem Investigated
The U.S. is one of the few countries that offer the quality university education needed by students globally. The country is endowed with prestigious universities like Harvard and Stanford. Therefore, universities attract bright students from different parts of the world. Among the students admiring joining American universities are Africans and African Americans. While the country is famous for its quality education, many cases of racism against the Black community have been recorded. Consequently, African and African American students are not an exemption. Recently, the country has recorded increasing rates of racism. Consequently, many Black students find it uncomfortable to study in U.S. colleges. Moreover, the students are exposed to psychological torture that is detrimental to their mental health and social interactions. Therefore, bullying and other forms of racial discrimination among Black students in U.S. universities are detrimental to social development.
Research Significance
Investigating the impact of bullying and discrimination against Black students is significant. The study will involve students in American colleges and universities who will share their experiences of bullying. Therefore, the study will help the audience understand the impact of the act. Moreover, the research will explore existing literature on the social issue and fill the gap in the existing studies. Consequently, this study will help scholars further the study of the overarching thematic area. Upon studying the existing literature and analyzing the results, the research will suggest mechanisms that educational institutions can adopt to overcome bullying and racial discrimination against Black students. This study is important to academia, educational institutions, and policymakers.
Research Questions and Objectives
This research involves an investigation of bullying and racism as social problems. The research will involve students in U.S. institutions of higher learning. While the central issue under investigation is the impact of bullying and discrimination against Black students in the country, the study will aim to answer the following questions.
- What are the impacts of bullying and racism among Black students in U.S. universities?
- What is the significance of cultural diversity among U.S. universities?
- How have the U.S. universities approached bullying and racism against Black students?
- What can the institutions of higher learning do to reduce bullying and racism against Black students?
Based on the above research questions, this study will aim to achieve its objectives. The set research aims and objectives are crucial in answering the research questions. Moreover, the research objectives will allow the research to stick to the study’s central theme. This study will aim to achieve the following objectives.
- Investigate the extent of bullying and racism against Black students in U.S. universities.
- Investigate the impact of bullying and racism against Black students in the U.S.
- Investigate the importance of multiculturalism among U.S. universities.
- Recommend effective mechanisms that U.S. universities, policymakers, and other educational stakeholders can adopt to encumber bullying and racism.
Literature Review
A literature review involves the search and evaluation of existing literature on the thematic area. The review is significant since it provides foundational knowledge on the research topic. Moreover, it is through the literature review that research can identify existing gaps in the thematic area and give recommendations (Bahishti, 2021). This study will adopt a narrative literature review due to limited research time. While bullying and racism encumber social development in a community, the themes have been less explored by the existing literature. However, the existing literature focuses on the specific thematic areas of racism and bullying. Therefore, this literature review will explore cultural diversity, Black students’ lives, discrimination against Black students, and the impact of racism and bullying among U.S. universities. Finally, the researcher will summarise gaps in the reviewed literature that this study aims to fill.
Cultural Diversity In the U.S. Universities
Cultural diversity plays a significant role in social development among universities. According to Mercer (2022), cultural diversity is the existence of a variety of ethnic groups within a society or a social institution. Race, age, gender, and religion, among other social factors, are elements of diverse cultures, as shown in figure 1.0 (Faltas, 2018). American universities recruit students from different cultural backgrounds to enhance a diverse learning institution (Ford, 2021). Diversity is crucial in any society since it promotes peace and makes a society an interesting place to live (Haessly, 2021). Since different cultures have their own beliefs and interests, they can share them with others (Ford, 2021). Consequently, the students appreciate other people’s ways of living and perspectives on life. Promoting cultural diversity within universities helps promote peace and unity among students.
Black Students the U.S. Universities
U.S. universities promote multiracial education and recruit students from different parts of the world. The universities have adopted ethical codes that promote social diversity and help African and African American students. Although Black students are given equal opportunities as White students, their enrollment population is lower. For instance, according to the 2019 data by PNPI, out of 16.6 million undergraduates enrolled in the fall of 2019, only 2.1 million were Black students. Surprisingly, the number of Black student enrolment has declined in the past decades (Miller, 2020). However, the statistics show that about 72% of Black students are likely to receive students (PNPI, 2022). Although the Black student population in U.S. universities is declining, there has been no research on the cause of the rapid drop. Unlike White students, Black students’ enrollment rates are still low among U.S. universities.
Racial Bullying in the U.S. Universities
Black students in U.S. universities face difficulties, including bullying and racial discrimination. Racial discrimination is any form of prejudice against an individual based on their skin color, race, or ethnic origin (Webb et al., 2022). Meanwhile, bullying is aggressive behavior among students that involves a real or perceived power imbalance (Ahmed et al., 2022). Therefore, racial discrimination and bullying do not bear similar meanings. However, racism based on socioeconomic status presents a power imbalance that leads to bullying (Webb et al., 2022). Black students are more vulnerable than White students and are often victims of racism and bullying.
Racism and bullying are common among U.S. universities due to weak institutional structures and poor ethical mechanisms. According to Feder (2020), seven factors contribute to racism and subsequent bullying in U.S. universities: categories, factions, segregation, hierarchy, media, power, and passivism. While categories organize students into distinct groups, factions trigger intergroup competition (Feder, 2020). Meanwhile, segregation hardens racist perceptions among students. Hierarchy emboldens students to feel and behave in a racist manner (Sharma, 2022). While power is significant in legislating racism, the media underrepresents the Black community in the U.S. Passivism which encourages overlooking and denying racism encourages students and educational stakeholders to do the same (Feder, 2020). Therefore, racial discrimination and bullying among U.S. universities is a multifaceted issue that ought to be addressed by relevant authorities.
Impacts of Racist Bullying Among Black Students
Racist bullying among Black students in U.S. universities is detrimental to the victim’s mental health and socialization. Racism exposes Black students to psychological torture that affects their everyday educational activities (Showunmi & Tomlin, 2022). The racially bullied students concentrate less in class since they live in constant fear of aggressive attacks (Madfis et al., 2021). Moreover, low self-esteem is evident among racially bullied students. Consequently, the victims perform poorly in class and indulge in substance abuse (Madfis et al., 2021). Moreover, the bullied victims have become aggressive toward their oppressors leading to criminal activities. Furthermore, racist bullying creates class and ethnic wars among students (Showunmi & Tomlin, 2022). The universities are, therefore, presented as disunited, leading to poor performance. Racial bullying among Black students in U.S. universities encumbers institutional and personal growth among individual schoolers.
Gaps in the Existing Literature
The existing literature extensively explores racism in the American culture but fails to give insights into the possible ways of eliminating the problem. The literature discusses the impacts of racism and how it has grown among Americans. However, there is less research conducted on racial bullying at U.S. universities. Moreover, the literature inadequately explores the negative impact of racial bullying in universities. Although the reviewed works significantly account for historical injustices among African Americans, they insufficiently provide data on the importance of cultural diversity. Furthermore, the existing literature generalizes racism and fails to focus on it at the university level. This study will explore the impacts of racial bullying at the university level. Moreover, the researcher will also recommend possible measures against the issue. Therefore, the study will fill the gaps in the existing literature.
Methodology
This study involved qualitative and quantitative methodologies. The participants involved were university students in U.S. universities. The study involved a total of one hundred and fifty participants, who were categorized as either Black or White. The participants were subjected to questions that were consistent with the research objectives. The researcher used random sampling when selecting the participants to avoid any form of bias. Although the participants came from different U.S. universities, it was impossible to involve all the universities given the time limitation and study scope. Therefore, the participating students came from six U.S. universities.
The collection of the research data was ethical since the participants were allowed to fill in the data with their consent. Data collection was done through the distribution of questionnaires that had uniform questions on the impact of bullying and participants’ discriminative experiences. The questionnaires were developed through the use of Google Forms, which was convenient. The online survey was significant since it allowed the researcher to collect data without the need to physically meet the participants. Moreover, the inbuilt Google Forms features helped in analyzing the collected data. Microsoft Excel helped in data analysis and presentation. The collected qualitative and quantitative data were analyzed for interpretation.
Findings and Analysis
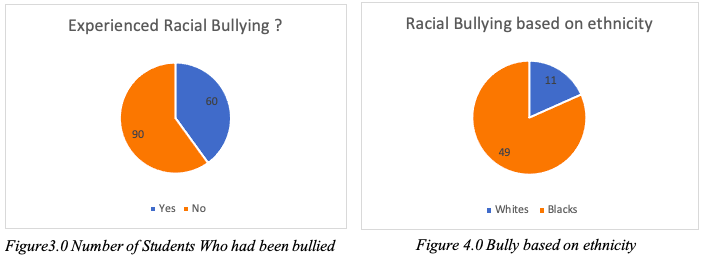
Out of the 150 participants, 80 were Blacks while 70 were Whites. Participants of ages 15 to 25 were 70%, while those aged 26 to 35 were 30%. Therefore, none of the research participants was age 36 and above. All the participants consented to give their responses to the questions asked. Consequently, the data collected was reliable and unbiased since none of the participants was forced to give information. Out of the 150 participants 60 of them had experienced racial bullying while 90 had not as shown in figure 3.0. 82% of the respondents who stated that they had been bullied were Black students, and the remaining 18% were Whites, as shown in figure 4.0.
The participants were asked about the entity to blame for the increased racial bullying on their campuses. 60% of the participants blamed the school management for racial bullying in their institutions. Meanwhile, 35% blamed the student leadership for the issue, and the remaining 5% blamed other stakeholders. When asked about the impact of racial bullying, 90% of the students who had experienced racial bullying agreed that they had low self-esteem and mental health problems. The researcher proposed a list of mechanisms that can be adopted to reduce racial bullying in universities. The responses are summarized in table 1.0 below.
Table 1.0. Mechanism to reduce racial bullying.
Discussion of the Findings
Racial bullying is common in U.S. universities and is facilitated by poor management structure. The university management contributes to racial bullying through the formulation of insensitive ethical codes (McGee et al., 2021). For instance, developing policies that do not favor Black students encourages racial acts from White students. Moreover, the university management has failed to take action against racist actions (McGee et al., 2021). Although the university management is to be blamed for the problem, student leadership has also contributed to racial bullying (Webb et al., 2022). Student leadership is actively involved in the development of institutional structures such as clubs and societies. However, the leadership has failed to address discriminative actions among the societies and clubs. Racial bullying in U.S. universities is significantly contributed by the management and student leadership bodies.
Black students are more vulnerable to racial bullying than Whites. According to a study, the majority of Black students have experienced bullying compared to White students. Black students are discriminated against for their skin color due to their minority status. Moreover, Black students come from poorer families than Whites. Consequently, many of them are bullied based on their race and socioeconomic status. Racially bullied Black students experience mental health problems and low self-esteem (Showunmi & Tomlin, 2022). Although racial bullying is common, it can be reduced by engaging all educational stakeholders. The universities management and student leadership can work together to counter the menace. Moreover, the social campaign against the vices can significantly help reduce racism and bullying in universities.
Although the integration of cultural diversity can help reduce racial bullying, the mechanism is ineffective. Many universities have integrated courses that encourage multiculturalism, but racism is still common in such institutions. Therefore, racial bullying can be encumbered by allowing the students to interact with each other and learn more about different cultures (Feder, 2020). Meanwhile, since mental health problems are the major impacts of racial bullying, the students can be engaged through social activities that promote healthy mental states. Therefore, racial bullying affects Black students in U.S. universities. The students are mentally tortured and exposed to unfriendly learning environments.
Conclusion
Implications of the Results
The study results a show that racial bullying is detrimental to student lives in U.S. universities. According to the results, Black students are the most affected population by racial segregation. Meanwhile, the Whites students are least affected by racial bullying. White students are more likely to discriminate against Black students of their race and socioeconomic status. The results imply that serious actions need to be taken against the racist students who frustrate the lives of other students on the campuses. Additionally, the results imply that the majority of university management has put less effort into curbing bullying among students. The universities can adopt mechanisms that would unify all the stakeholders to fight against racial bullying. Therefore, racial discrimination is one of the major social problems faced by U.S. universities.
What Is Still Needed To Be Learned
Although this study has explored racial bullying among university students, understanding its societal impact is crucial. Racism has its roots in the wider societal population, and it affects victims’ relatives. Bullied students experience mental health problems that can trigger drug abuse. Moreover, low self-esteem among bullied students can affect their routine interactions in their societies. Furthermore, poor quality education caused by racial bullying can lead to increased crimes in society. Consequently, the members of society may face challenges as a result of racial bullying at the university level. Therefore, it is important to learn that racial bullying is detrimental to the entire society and should be stopped at all costs.
Study Limitations
This study was limited to resources, time, and sample population. The study’s thematic area required sufficient data to help in answering the research questions and meeting the set objectives. However, this study was limited to time, leading to a collection of insufficient data on the topic. Moreover, the online data collection method limited the researcher from interacting with respondents. Therefore, insufficient funding limited the study to an online data collection method that is more disadvantageous than conducting interviews and observation. Furthermore, the study involved only 150 participants, who are insignificant to millions of students in U.S. universities. The number of universities involved was unreliable since there are many universities in the U.S. Therefore, the study limitations led to unreliable data that interfered with the accuracy of the results.
Recommendations to Institutions
Racial discrimination and bullying are detrimental to the institutional image and its students. Therefore, the universities can adopt several mechanisms that would help reduce the menace. Firstly, the universities should develop a strict ethical code on racial bullying and any other form of discrimination. The developed code should be introduced to the entire university stakeholders, who should strictly practice it. Secondly, the institutions should involve all the stakeholders including community members in developing mechanisms that promote multiculturalism and reject racial bullying. For instance, the universities can involve their neighboring community in celebrating cultural events that encourage learning about other people’s ways of life. Finally, the universities should introduce a rule that sets the minimum number of Black students that must be enrolled to enhance ethnic balance among students.
Recommendations for Future Studies
This study was limited to time, sample population, and time. Future studies on the thematic area should allocate sufficient time for data collection. Moreover, future studies should have enough resources that would allow the application of other methods of data collection that would improve data accuracy and reliability. This study involves a broad population sample that requires sufficient time for data collection. Future studies should involve enough population that is evenly distributed across the universities in the U.S. Broad sample population would improve the dependency on the collected data and overall research accuracy. Therefore, future studies on the overarching research topic should involve a broad sample population, enough resources, and sufficient time.
References
Ahmed, G. K., Metwaly, N. A., Elbeh, K., Galal, M. S., & Shaaban, I. (2022). Risk factors of school bullying and its relationship with psychiatric comorbidities: a literature review. The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery, 58(1), 1-11.
Bahishti, A. A. (2021). The Importance of Review Articles & its Prospects in Scholarly Literature. Extensive Reviews, 1(1), 1-6.
Faltas, I. (2018). Cultural Diversity in the Community and the Workplace – PA TIMES Online.
Feder, S. (2020). Seven factors contributing to American racism.
Ford, D. Y. (2021). Recruiting & retaining culturally different students in gifted education. Routledge.
Haessly, J. (2021) Weaving a Culture of Peace. In: Standish K., Devere H., Suazo A., Rafferty R. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Positive Peace. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Madfis, E., Hirschfield, P., & Addington, L. A. (2021). School securitization and its alternatives: The social, political, and contextual drivers of school safety policy and practice.School Psychology Review, 50(2-3), 191-205.
McGee, E. O., Botchway, P. K., Naphan-Kingery, D. E., Brockman, A. J., Houston, S., & White, D. T. (2021). Racism camouflaged as impostorism and the impact on black STEM doctoral students.Race Ethnicity and Education, 1-21.
Mercer, J. R. (2022). Labeling the mentally retarded: Clinical and social system perspectives on mental retardation. University of California Press.
Miller, B. (2020). It’s Time to Worry About College Enrollment Declines Among Black Students.
PNPI. (2022). Black Students in Higher Education – PNPI.
Sharma, M. (2022). Endemic Racism in Trump’s America: A Racialized Female Faculty Member’s Experience. Studying Teacher Education, 18(1), 5-22.
Showunmi, V., & Tomlin, C. (2022). Understanding and Managing Sophisticated and Everyday Racism: Implications for Education and Work. Rowman & Littlefield.
Webb, E. K., Etter, J. A., & Kwasa, J. A. (2022). Addressing racial and phenotypic bias in human neuroscience methods.Nature Neuroscience, 25(4), 410-414.