Executive Summary
Distribution centres and warehouses are those physical facilities that are used to store and ship inventory. Warehouses serve customer directly but are commonly used to store raw materials that are needed to be shipped to the manufacturing firm and finished goods that are shipped to the retailing firms. Value addition in warehousing takes place in terms of consolidation, product mining, service and smooth flow of operations.
The goods that enter the warehouse or rather the inbound goods are safeguarded in the warehouse until the outbound process for these goods is initiated. The warehousing process involves controlling the flow of goods in and out of the warehouse through proper documentation and recording. Certain important activities of warehousing are receiving, storing, packing, marking, and shipping and so on. Receiving the goods is considered a crucial activity of warehousing. The person in charge at the warehouse should be watchful of the goods entering the warehouse. Proper verification of the delivery documentation has to be done prior to the acceptance of the goods.
The proposed site will have a warehouse and a park for leisure. The warehouse the industries in the area. The warehouse is a profitable venture as cost benefit analysis shows a positive net preset value of 946, 449 at cost of capital of 9% and 819,112 when subjecting the cost capital to sensitivity changes.
Introduction
Edinburgh being a growing capital city in Europe, it requires various development projects to keep the growth rate. In the city there is a site at Freer St, Fountainbridge which needs to be used for a project. The project will involve the conversion of the existing land for brewery into warehousing facility and a park. The area has many industries that have inventory that require warehousing facility. The area has good road network and other infrastructures.
The business environment is becoming increasingly challenging. In certain countries like India, firms have to deal with several bottlenecks such as outdated technology, underdeveloped infrastructure, inappropriate payment systems and ineffective scheduling and control systems, which have hampered their progress. The opening up of economies across the world to global competition has increased the level of competition has increased the level of competition that domestic companies have to face. Domestic companies operating in automobiles, steel, electronic and other manufacturing sectors have to overcome the threat to their market share posed by foreign companies.
The need for operations managers to reduce manufacturing costs, optimise productivity and improve product quality in order to stay in the market has become imperative. Many organizations now recognize the importance of automation, optimisation of scheduling and a proper inventory management system, and are incorporating total quality management and total quality in their operations
Every organization invests a considerable amount of capital on materials. Even before we talk about planning and control it is inevitable that the material is stored in a safe place and such place of storing materials is termed as a warehouse. Hence, Warehousing can be defined as the process of storing goods or merchandise safely.
Site Description
The site is situated in Freer St, Fountainbridge and it is a land that was used by a brewery company for their activities. The brewery company was called Scottish and Newcastle. The property is freehold and it is on sale. However before converting the property in to use, £ 50,000 will be used to appraise viability and determine how it will be used. The property will be converted into warehousing with a large parking and a small space outside the building for family gathering. This property will be of good use because it is near to the city as well as there is good infrastructure.
The activities that will take place in the site will depend on demand since the environment has necessary facilities, infrastructure and it is environmental friendly for the construction of warehouse and a resting place for members of the society. The area facing the canal will be a good site for tourist therefore, while constructing warehouse a small park will be set aside to attract various families and tours. Warehouses are always constructed in places where there are enough utilities like electricity, water, sewerage line and good infrastructure. This place is ideal for warehouses and a park.
The area has already been identified various documentation will be need for the site to be made good use of. In the construction will need permit and legal authorization from authorities to allow us to construct a park and warehousing facilities in the area. The building been a freehold but initially been used as a brewery we shall apply for change of ownership and use. An advertisement will be put in local daily regarding change of uses of land to avoid resistance from members of the public whom may be having interest in the propriety such as those people who were employees in the brewery.
The client will be required to pay for all outstanding charges on the property to allow it to be turned into use.
Market Analysis
Edinburgh the being a modern capital city, it is known to be among the largest metropolitan and also the largest urban zone within the bounds of European Union at par. Edinburgh is rated to be among most visited place and city in the globe, and with that, its international airport is also rated to be among most crowded airspace and the busiest airport among other cities in the Europe. With the vast development and continuous ardour for success in business and all other aspects, Edinburgh has been a point of influence for other neighbouring countries and even intercontinental change pilots.
The economic crises experienced in the year 2008 did not spare Edinburgh economy. However it recovered and continued to experience new investments from foreigners with the economic boom experienced in recent years before 2010. The support and attention given by national governments to the various industries, as well as the economic growth in the Great Britain, have favoured the development of the Edinburgh.
To date back its statistics population, migration was growing in figures as seen by the in national Statistics in 2009 wherein they have labelled the number of settlers according to race which means migrants were at that time potentially growing to becoming the core populace of the city. They are of mixed race and Edinburgh has been known as the most race-diverse city there is.
In relation to the diverse populace of Edinburgh, it has been more open to embrace other cultures, beliefs and even style in some other aspects of its growth. With its vast race diversity and openness to culture and change, it has been inflicted with other customs, people and practices in one way or another. The thing is that it is up to the Edinburgh if they will continue to cohabitate with the diversity that their city has or continue to accept change without compromising other native beliefs, culture, and all other else.
The commercial buildings in Edinburgh generate about 25 million tons of carbon dioxide of each year. The survey also stated that if the businesses continue to go as they are currently going then this number could double by the end of 2010. When we take a look at the water consumption, we can see that the commercial building of Edinburgh alone consume more than 20 giga-liters of water per annum. Another amazing figure is that of the waste material that is produce per annum in the country, which is estimated to be 110,000 tons per year being dropped off at landfills across the country.
With this said it is obvious that pressures are likely to build and due to such pressures businesses are being driven to show their commitment to the environment and to adopt sustainable business practices. This movement is being followed across the globe and most corporations are moving towards building corporate sustainability. A recent study has shown that those organizations that have a certain thing of going green have shares with values approximately 5% higher as compared to the competition (Nymer, 2000).
The major buildings present in Edinburgh generate approximately 110,000 tons of water per annum, out of which 5,000 tons alone relates to Edinburgh. There are many projects that are being proposed to the commercial property industry, each carrying its own challenges. Some of the proposals include recycling of paper, glass, cardboard, plastic, food and aluminium. A survey suggests that when a large commercial building is considered, it only needs to send off 25% of its waste materials to the landfill. What about the remaining 75%? This remaining percentage can be easily recycled by the implementation of recycling programs. Though setting up the plants of the recycling plants in the existing buildings might be a challenge there are many benefits attached to it. There is one benefit of rebates that is included by the installation of such plants.
Justification of the project
The economic development in Edinburgh is credited back to history when development policies were socialist inspired. Though the town is economic, growing rate was of a snail’s pace a few years ago, Edinburgh has been able to find its way to gradually opening up new markets. Her income per capital is increasing and this trend will continue. Now, Edinburgh has achieved a ‘free market’ economy and considered being among the fastest growing cities in Europe. Edinburgh economy is a collective responsibility of its business community.
Different sectors in Edinburgh have contributed to the growth and sustaining of the economic growth and development. The main sectors being direct foreign investments, the finance sector, manufacturing industry and the working force from the huge population. The growing economy has placed the living standards high. The major setback in the economic growth has been economic crisis of 2008. For the Edinburgh to achieve its dreams, it had to attract new investors.
It introduced favorable macroeconomic performances and development reforms. The Edinburgh governance also checked on other uneconomic dimensions in order to achieve a favorable social development. For the city to progress in its economic reforms, it gave priorities to some of her public sector reforms. They include; infrastructure, eliminating labor regulation, reforms in lagging states and, HIV/AIDS.
Outskirts are the main source of raw materials, food and products Edinburgh population. It is the nation’s largest economic sector and contributes significantly in the economic development of Edinburgh. In an effort to increase its economic growth and development, Edinburgh requires warehouses. The foreign capital has since then played an important role in the economic development of Edinburgh. To attract more foreign investors, the Indian government has been pushing for economic reforms and securing of legislation. Just like in other developing nations, direct foreign investment has been the key to economic development and has been the source to external finances.
All the above contributions have made Edinburgh merge as one of the fastest growing cities. This is credited to a number of things such as her population demography. The population has a fall in the birth and death rate leading to the lowest number of median ages than any other economies. Such a trend means that the working age population will increase while the non-working population will reduce. This lowers the dependent population as compared to the working age. Edinburgh’s banking system has developed to be among the leading in the Europe. The system allows most people to be able to save a large amount of their income. The result is a rise in the country’s rate of savings and an increase in the number of citizens working and contributing to economic growth.
Proposal for Development Site
Due lack of warehousing services in the area a warehouse will be constructed and act as distribution centre. Distribution centres and warehouses are those physical facilities that are used to store and ship inventory. Warehouses serve customer directly but are commonly used to store raw materials that are needed to be shipped to the manufacturing firm and finished goods that are shipped to the retailing firms. Value addition in warehousing takes place in terms of consolidation, product mining, service and smooth flow of operations. The goods that enter the warehouse or rather the inbound goods are safeguarded in the warehouse until the outbound process for these goods is initiated.
The warehousing process involves controlling the flow of goods in and out of the warehouse through proper documentation and recording. Certain important activities of warehousing are receiving, storing, packing, marking, and shipping and so on. Receiving the goods is considered a crucial activity of warehousing. The person in charge at the warehouse should be watchful of the goods entering the warehouse. Proper verification of the delivery documentation has to be done prior to the acceptance of the goods
Firms use thousands of varieties of materials that vary in prices, usage and lead-time. It is neither desirable nor possible to exercise the same degree of control over all the materials. So, it is necessary that firms pay more attention to those items whose usage value or consumption value is high and less attention to those items whose usage value is low. The ABC classification system is used to alter the expenses associated with controlling the materials according to their usage value. This kind of classification was not possible in the traditional warehousing mechanism.
The role of warehouse in a supply chain is to store goods safely and at the same time aids in transportation or shipping of the goods to various destinations. The warehouse has many functions such as storage, packaging, transportation, enabling constant supply of inventory to companies and other services that are related to stock management. Transportation consolidation – the following figure clearly depicts how this takes place in warehousing.
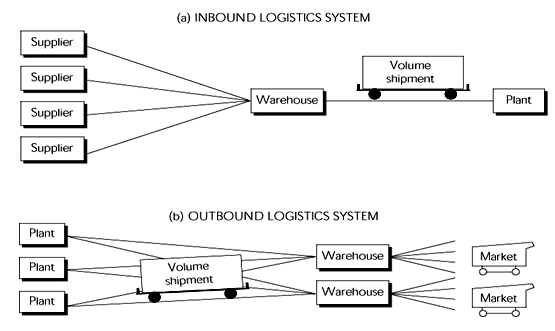
The purpose of warehousing- The main purpose of warehousing is to store or hold raw materials or finished goods until that particular raw material or good is used or despatched for its respective destination. It is a physical system that comprises a set area or space, tools and labourers to handle the stored goods.
Basic Warehousing operations- As mentioned earlier, a warehouse holds either raw material or finished goods. This function of warehousing of holding goods in storage provides economies in purchasing and production. Some seasonal goods are also held in warehouses to facilitate a smooth flow when demand arises.
Another function of warehousing is stock mixing, which involves sorting out bigger shipments into smaller ones and vice versa. This process helps firms reduce the total transportation costs of delivering finished goods to the customers. Stock mixing also facilitates release of several components at a time for the smooth flow of the production process.
Trans-loading, another function of warehousing uses the warehouse as a station for transferring goods from one place to another. This function of warehousing is also called as cross docking. On one side of the warehouse the shipments are delivered and on the other side, these are split according to the destinations to which they have to be sent. This process reduces storage and multiple handling costs. Yet another function of warehousing is protecting the production process from contingencies, such as employee strikes by locating the warehouses away from the production plants.
The warehouse will consolidate all the requests and ensures that they get into the service order request system that has been built on a SAP platform. Variety of automated tools is used to ensure that all the indents are funnelled without errors into the service order request system. There is a limited human intervention that comes in here and the service order request system is fully automated. Once a service order request comes in each of the items on the indent is checked for the following condition:
If the item is shipped – will it reach in time to the outlet?
If the item shipped reaches the outlet as scheduled will there will be enough shelf life as per the standards prescribed?
Considerations are applied to the following conditions:
- What if there is a transit delay?
- How will the outlet’s business get affected if the perishables reach late?

After applying all the considerations the items are then packed – they come in pre-packed containers – they are only consolidated. For some items cold chain needs to be essentially maintained. Adequate care is taken to ensure that such items get into only refrigerated vans and are not flown in open condition.
Adequate care has to be taken to ensure that there are no wastages and spillages in transit and adequate cold chains are maintained.
Once the service order request system identifies and satisfies that all material indented is readily available in total adherence to the standards prescribed, adequate instructions are generated to the Automated Retrieval System (ARS). The retrieval system works on a number of electrically operated palette movers and stackers, which pick up appropriate stocks from the racks identified. The stacking and storing in the shelves is done based on whether it is a food item or a non food item. Care is taken to ensure the foods that need refrigeration are kept in the specific sections of the warehouse that are refrigerated. Retrieval and storage are very automatic and need minimal human intervention.

Once the items are retrieved as per the indent they are sent to the packing bay. The items are packed as per the stringent quality norms of the company and are lined up for transit. Shipment for each client is done by different vendors as per the preference of the client.
The entire incoming stock, storage, retrieval, packing, shipment is tracked using Active RFID technology and is fully automated. The warehouse will have numerous fixed RFID readers across the length, breadth and even on the shelving of the warehouse. This method allows for continuous monitoring of the material and its constant tracking, which is again totally automated. Shipping slips are generated and stuck on the material automatically. The entire warehouse is so fully automated that almost 10,000 items that are stocked for almost 60 days for all the clients is manned by just four people( Ernst, 1998).
The Warehouse and Green Revolution
There are many tools that are used for rating today, one of which is mentioned below but there are certain problems within these tools; they have inherent flaws. Because of these flaws the application of these tools on any project or building is rather problematic. One of the factors, for example, is the weather; there are very limited weather centres around. Now because of this limitation there are chances the temperature requirements of a particular building structure might not be accurate for rating purposes. Apart from this, there might even be a consideration of a weather spike in certain seasons; this will also have an effect on the ratings of the particular building (Emett, 2005).
Green Warehouse
This concept is basically related to the process of building buildings by the implementation of a complete life-cycle model. The problem here is that when we take a look at this, we can see that there are many steps which have to be skipped; the reason being that the buildings are already constructed and operational (Cicchetti 2009). We can see that new technologies are being developed constantly so that there are more efficient buildings being constructed and renovated but the thing is that the best building being built is that which is new.
Green Warehouse designing-Green building is an entire step by step process and for the commercial property industry it is a good step only if the buildings being constructed are new (Cicchetti 2009). If the buildings are old, then redesigning is going to be the biggest headache. In order to redesign for the purpose of become environmentally friendly there are constraints of redesigning itself, along with the materials that must be used, which will be discussed later.
Materials for redesigning- There is a significant impact on the usage of materials in this regard as well; the reason for this is that in order to go green, the materials that should be used in order to change the structure of the property should also be green; materials which are easily renewable as well as recycled. Apart from this there is also the concern of the transportation of the materials. Now for this the suggestion by most environmentalists is that the materials that need to be manufactured should be done in or near the premises (Orsato 2009). This is practically very difficult because of the fact of occupancy. If the changes are being implemented with the tenants being present, then this is highly unlikely because there will be a disturbance cause for them and hence they might even leave the property, which the owners do not want.
Development Appraisal
Appraisal
Before the property developed various activities will take place. Some of the activities that will take place in the area are clearing the ground then construction will follow which will take a period of not less than three years. Like a normal construction building budgeting and cost allocation for the construction will be done and this will involve various professionals who could have been selected by the management.
The project will require a financier building surveyors, engineers that are mechanical, electrical, structural and hydraulic engineers, fire protection services, architecture, internally designers, quantity surveyors, a purchasing consultant, an administrator and many other staff members who will make the construction possible. From the list provided above it can be noted that they are professional who will be hired as consultant. The financing activity of the building will be done by a bank after been consulted by the client. Other category of members will only work as contractors or subcontractors. The administrator will seat with steering committee to come up with the budget that will be used in construction. The same group will allocate funds various activities of the project (Dinsmore, 2005).
Various activities will drive the client to construct warehousing complex and a park. Some of the drivers that motivated the client include profit from the investment in the land and the future economic value of the area. Most investment will be made based on economic benefit that will accrue from a project. The project is said to have over 30 years live with a good return. The cost of the project is highlighted below plus their construction.
Growth options and project evaluation
The objective of any business is to maximize shareholder wealth and in this regard the Net Present Value is the best method to use. The Net Present Value method is simple and straightforward method but when it comes to practical application of this method there may be some problems encountered. Therefore the following things should be kept in mind while using the Net Present Value method.
Relevant costs: past costs are not relevant to this analysis as only futures costs and cash inflows to the project. with the incorporation of other relevant cost and factors such as the improvement in the time delivery, product condition quality, and service reliability, the decision towards the construction of the warehouse could be reversed making the shift an advantageous decision for the company.
Cash Flows: Atrill (2004) states that “In Net Present Value analysis, it is cash flows rather than profit flows that are used because it is the former that gives a business command over resources”. This discounted cash flow method only uses real cash flows rather than profits which are subjected to arbitrary set accounting policies. All non-cash items should be added back to the profit and loss account and therefore in this case the depreciation has been added back.
Working capital: Atrill (2004) states that “Any addition to working capital will be treated as a cash outflow and any release of working capital will be treated as a cash inflow in the period in which it occurs”. In this appraisal, working capital is being infused to the tune of £0.55 million every year and as such this addition of working capital has been taken as cash outflow.
Interest payments: interest payment are not considered when calculating cash flows as its rate is used in the weighted average cost of capital used to evaluate the present value of the project. The finance cost is considered in the discount rate and as such all interest payments deducted have been added back to the net profit.
The discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis presented so far treats a project’s expected cash flows as given at the outset. This approach presupposes a static approach to investment decision making: it assumes that all operating decisions are set in advance. In reality, however, the opportunity to make decision contingent on information to become available in the future is an essential feature of many investment decisions.
The warehouse has a cost of capital of 10%. The Net Present Value analysis method evaluates a company’s projects by using the cost of capital. The return on capital should be greater than the cost of capital for any investment to be meaningful. When the cost of capital is used, all interest payments are not deducted in determining the cash flows for the investment project because the cost of financing is taken care of in the cost of capital. As such the interest payments deducted to arrive at the net profit in this assignment have been added back to determine the cash flow.
Consider the decision of whether to construct a warehouse. The cost of doing so is expected to be 4,889,075. Assuming expected revenue to be higher. Clearly, the expected cash inflow is far higher that necessary to recoup the 4,889,075 investment in warehouse, much less to pay the 10% yield required on such a risky investment. Growth options are of great importance to multinational firms. Similarly, the investment that many Western firms are now considering in Eastern Europe can also be thought of as growth options.
Some view investments there as a way to gain entry into a potentially large market. Others see Eastern Europe as am underdeveloped area with educated and skilled workers but low wages, and they view such investments as a low-cost backdoor to Western Europe markets. In either case, companies that invest there are buying an option that will pay off in the event that Eastern European markets boom or those Eastern European workers turn out to the much more productive with the right technology and incentives than they were under communism. Other investments are undertaken, in part, to gain knowledge that can later be capitalized on elsewhere.
The problem of undervaluing investment projects using the standard DCF analysis is particularly acute for strategic investments. Many strategically important investments, such as investments in R&D, factory automation, a brand name, or a distribution network, provide growth opportunities because they are often only the first link in a chain of subsequent investment decisions.
Valuing investments that embody discretionary follow-up projects requires an expanded net present value rule that considers the attendant options. More specifically, the value of an option to undertake a follow-up project equals the expected project NPV using the conventional discounted cash-flow analysis plus the value of the discretion associated with undertaking the project.
Appraising Risk of the Project
Any project has a risk of not generating revenue as expected due uncertainty. The deviation of revenues from expectation is called risk. The outcome of such events may have a positive impact or a negative impact on the business environment. In business, the term risk management was introduced to study risks and the probability of occurrence of positive and negative outcomes of risks and to suggest remedial measures to avoid the negative outcomes of risk taking.
The business environment plays an important role. Business environment comprises of numerous factors which have to be taken into account by the warehouse. The warehouse should be able to adapt to the requirements of these external factors, it would be able to retain its position as the market leader along with a favourable income statement. The most influential factor which has changed the position of the industry is the costs of entrance. There have been so much technological advances in the past decade that it is easier for new companies to enter the market. Moreover, the market favours new companies to come up with warehousing services that are available to the customers at a lower price. It is mainly due to the new entrants that the warehousing industry players are facing difficulty in selling the services.
Similarly; private and public investors alike are interested in determining which town offer the best prospects for sound investments. We are interested in whether sensible economic policies are likely to be pursued because countries adopting such policies will generally have good business environments in which enterprise can flourish. However, because political considerations often lead countries to pursue economic policies that are detrimental to business and to their own economic in health, the focus of a country risk analysis cannot be exclusively economic in nature. By necessity, it must also study the political factors that give rise to particular economic policies.
Simply put, no one can intelligently assess a country’s risk profile without comprehending its economic and political policies and how those policies are likely to affect the country’s prospects for economic growth. Similarly, attempts to forecast exchange rates, inflation rates, or interest rate are helped immensely by a deeper understanding of how those economic parameters are affected by national policies (Stevens, 2002).
Country risk assessments may be used in investment analyses to screen out countries that are excessively risky or to monitor countries in which the firm is currently doing business to determine whether new policies are called for.
Although expropriation is the most obvious and extreme form of political risk, there are other significant political risks, including currency or trade controls, changes in tax or labour laws, regulatory restrictions, and requirements for additional local production. The common denominator of such risks is not hard to identify: government intervention into the workings of the economy that affects, for good or ill, the value of the firm. Although the consequences usually are adverse, changes in the political environment can provide opportunities as well.
Despite the near-universal recognition among multinational corporations, political scientists, and economists of existence of political risk, no unanimity has yet been reached about what constitutes that risk and how to measure it. The two basic approaches to viewing political risk are from a country-specific and a firm-specific perspective. The firs perspective depends on country risk analysis, whereas the second depends on a more micro approach.
A number of commercial and academic political risk forecasting models are available today. These models normally supply country risk indices that attempt to quantify the level of political risk in each nation. Most of these indices rely on some measures of the stability of the local political regime.
Political stability
Measures of political stability may include the frequency of change s of government, the level of violence in the country, the number of armed insurrections, conflicts with other states, and so on. The basic function of these stability indicators is to determine how long the current regime will be in power and whether that regime also will be willing and able to enforce its foreign investment guarantees. Most companies believe tat greater political stability means a safer investment environment.
Economic factors
Other frequently used indicators of political risk include economic factors, such as inflation, balance-of-payments deficits or surpluses, and the growth rate of per capital GDP. The intention behind these measures is to determine whether the economy is in good shape or requires a quick fix, such as expropriation to increase government revenues or currency inconvertibility to improve the balance of payments. In general, the better a country’s economic outlook, the less likely it is to face political and social turmoil that will inevitably harm foreign companies.
Subjective factors
More subjective measures of political risk are based on a general perception of the country’s attitude toward private enterprise: whether private enterprise is considered a necessary evil to be eliminated as soon as possible or whether it is actively welcomed. The attitude toward multinationals is particularly relevant and may differ from the feeling regarding local private ownership.
An index that tries to incorporate all these economic, social, and political factors into an overall measure of the business climate, including the political environment, is the Profit opportunity Recommendation (POR) rating. The scores of countries listed on the POR scale are based on an aggregation of the subjective assessments of a panel of experts.
Political risk and uncertain property rights: – Models such as POR are useful insofar as they provide an indication of the general level of political risk in a country. Form an economic standpoint, political risk refers to uncertainty over property rights. If the government can expropriate either legal little to property or the stream of income it generates, them political risk exists. Political risk also exists if property owners may be constrained in the way they use their property. This definition political risk encompasses government actions ranging from outright expropriation to a change in the tax that alters the government’s share of corporate income to laws that change the rights of private companies to compete against state-owned companies. Each action affects corporate cash flows and hence the value of the firm (Morgan, 2003).
A useful indicator of the degree of political risk is the seriousness of capital flight. Most countries discourage capital flight because they view it as one way of exporting their resources. By its nature, capital flight is difficult too measure accurately because it is not directly observed in most cases. Nevertheless, one can usually infer the capital outflows; using balance-of-payments figures-particularly the entry labelled “errors and omissions.” These estimates indicate that capital flight represents an enormous outflow of funds from developing countries (David, 2006).
Capital flight occurs for several reasons, most of which have to do with inappropriate economic policies. These reasons include government regulations, controls, and taxes that lower the return on domestic investments. In countries where inflation is high and domestic inflation hedging is difficult or impossible, investors may hedge by shifting their savings to foreign currencies deemed less likely to depreciate. They may also make the shift when domestic interest rates are artificially held down by their governments or when they expect a devaluation of an overvalued currency.
Perhaps the most powerful motive for capital flight is political risk. In unstable political regime, wealth is not secure from government seizure, especially when changes in regime occur. Savings may be shifted overseas to protect them.
Common sense dictates that if a nation’s own citizens do not trust the government, then investment there is unsafe. After all, residents presumably have a better fell for conditions and government intentions than do outsiders. Thus, when analysing investment or lending opportunities, multinational firms and international banks must bear in mind the apparent unwillingness of the nation’s citizens to invest and lend in their own country.
What are needed to halt capital flight are tough-minded economic policies- the kinds of policies that make investors want to put their money to work instead of taking it out.
We now examine in more detail some of the economic and political factors that contribute to the general level of risk in the country as a whole- termed country risk. The primary focus here is on how well the country is doing economically. As noted earlier, the better a nation’s economic performance, the lower the likelihood that its government will take actions that adversely affect the value of companies operating there.
Resource base
The resource base of a country consists of its natural, human, and financial resources. Other things being equal, a nation with substantial natural resources, such as oil or copper, is a better economic risk than is one without those resources. However, typically, all is not equal. The reason has to do with the quality of human resources and the degree to which the resources are allowed to be put to their most efficient use (Emett, 2005).
A nation with highly skilled and productive workers, a large pool of scientists and engineers, and ample management talent will have many of the essential ingredient s needed to pursue a course of steady growth and development. Three additional factors are necessary:
- a stable political system than encourages hard work and risk taking by allowing entrepreneurs to reap the rears from their activities,
- a flexible labour market that permits workers to be allocated to those jobs in which they will be the most productive, and
- a free-market that ensures that the price people respond to correctly signal the relative desirability of engaging in different activities.
In this way, the nation’s human and natural resources will be put on their most efficient uses. The evidence by now is overwhelming that free markets bring wealth and that endless state meddling brings waste. The reason is simple: unlike a government – controlled economy, free markets do not tolerate and perpetuate mistakes (Cleland, 2006).
Conclusion and Recommendation
The building will help solve the warehousing and resting area of the people. The warehouse will have a speciality warehousing solution offered to a number of clients – clients that use perishables in their supply chain to clients whose products would mean difference between life and death to a number of people across the world. This warehouse handling and management will is totally automated. Store and retrieval are fully automated. Lot of foresight has gone into the planning and development of this software. The software tightly integrates not only into the production modules, but also integrates very tightly into the accounting modules used at client locations to ensure that correct bills and invoices are raised appropriately for every shipment that is made from the warehouse.
The advantages and benefits of a warehouse in the area by far outweigh the disadvantages associated with it at all levels of consideration. Though they are merely ways that businesses have devised to increase their capacity for profit, they have helped in the spread of ideas, technology and resources through economies for the benefit of all. The only problem or challenge that warehouse have not covered fully at present and that appears as a thorn in the flesh is the issue of environmental pollution and degradation but this is being rectified to ensure that it maintain their influence on the improvement of human life and life conditions throughout the area. Warehouses are therefore beneficial for all nations and economies as they will effectively lead to their advancement and improvement in terms of society, culture, trade, commerce, finance and the general economy.
The warehouse is so much automated that it tightly integrates into the shipment integration request systems of many logistics service providers. Logistics service providers are chosen by the principal companies and they set the standards for conditions on transit. And warehouse play very minimal role here, other than helping principal companies frame regulations and monitor the shipment end on behalf of the client.
It will offer speciality holding facilities including cold chains that need to be maintained at different temperatures, maintaining cold chain till the time the material leaves the doors of the ware house and enters into refrigerated vans. Cold chains and their maintenance become critical as the warehouse also caters to food and perishable items as well as health care products like insulin. Insulin has special requirements that it needs to be maintained between 4 degrees and 1 degree centigrade at all times or it starts crystallization. Once crystallized the insulin becomes useless for any kind of consumption (Lock, 2007).
References
Cicchetti, C. 2009. Going Green and Getting Regulation Right: A Primer on Energy Efficiency. New York: Public Utilies Reports.
Cleland, D. 2006. Global project management handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
David, C. 2006. Global project management handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Dinsmore, P. 2005. The right projects done right. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Emett, S. 2005. Excellence in Warehouse Management. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons.
Ernst, R. 1998. Global Operations & Logistics. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
John. P. 2007. “Role of warehousing. Business Logistics Management. Web.
Lock, D. 2007. Project management. London: Gower Publishing.
Morgen, W. 2003. Fifty key figures in management. New York: Routledge.
Nymer, R. 2000 International architecture. New York: Addison-Wesley.
Orsato, R. 2009. Sustainability Strategies: When Does it Pay to be Green?. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Atrill, P. 2004. Investment appraisal and Net Present Value analysis. Diploma in Financial Management. Web.
Stevens, M. 2002. Project Management Pathways, Association for Project Management. New York: APM Publishing Limited.
Young-Hoon, K. 2005. A brief history of Project Management/ In: The story of managing projects. London: Greenwood Publishing Group.