Abstract
Smart Mobile devices have become very popular both in the social and business world. This paper seeks to discuss the effect of these devices among people in the social as well as the business settings. There will be in-depth discussion on the devices’ effects of people’s lives at work, private social life, in government and education.
Introduction
Since the industrial revolution, technology has been characterised by stativity, well apart from a few applications like the wheel, the train, the automobile and the airplane. Given the bulk of the equipment used in the above-mentioned inventions, stativity was not much of a choice.
Telecommunication gadgets like the Morse code and the telephone were grounded as well and their sizes and modes of operation did little to enable much movement. Two centuries later, technology experts are of the opinion that mobility displayed by telecommunication gadgets today is likely to get out of hand and possibly impact negatively on human life. Of particular importance to this discussion are the developments characterising the information and communications technology sector.
The last two decades have experienced some of the most effective ICT inventions in human history. The technology boom of the last decade of the 20th century provided the platform for the development of mobile technology that today has changed the ways of communication (Gallagher 2005, et al, p. 67). Technology nowadays is so mobile that business and individuals who fail to adapt to it risk being left behind, literary. Nothing in the 21st century captures the very spirit technological mobility as the mobile phone does.
The smart phone stands out nowadays as the epitome of synchronisation and mobility of technology. While its benefits cannot be overstated, there is genuine concern that the overall, especially adverse effects of this very technology have been grossly overlooked.
Which therefore begs the question; will the ever-increasing number of smart mobile devices (i-Phones etc) impact on the way we conduct our lives (work and private)? The answer to the above question is to the affirmative. The specifics of the answer will therefore form the main content of this discussion.
This paper will address the particular impacts on both work and private lives of human beings of smart mobile devices. It’s important to note that the impacts that will be discussed will touch on both the negative and positive sides of smart mobile devices. Besides, the above, there will also be a discussion on how smart mobile technology impacts education as well as government.
In this paper, the words; business and work will be used interchangeably but will have similar meaning in the same context. Also, the words; smart phones and smart mobile devices will be used interchangeably.
Before the analysis is carried out however, it’s important to have a brief look on general effects of smart mobile devices, an enhancement of the affirmative answer given above
Smart Mobile Devices Impacts Human life
According to Salt (2011, p. 152), the advent of advanced technologies like the smart mobile services has drastically altered human being’s work, life and relationships. However, Salt (2011, p. 152) singles out the mobile phone, social media such as Facebook and Twitter and smart phones as some of the technologies that are increasingly defining how people work and form relationships in the social arena.
The smart phone technology is undoubtedly influencing the formation of protocols and strange social behaviours that all lead to addiction. Through addiction to smart mobile devices, people are fast becoming slaves to the gadgets which dictate them what to do while defining every sphere of their lives.
As evidenced in the figure below, there are currently close to 500 million smartphone users in the world. That number is set to increase by 32.4% to 1.2 billion people by the year 2015. The growth of the smartphone usage by the above margin is likely to net more people to the addition that currently is being experienced. In turn the effects; both negative and positive will trickle down to the populations.
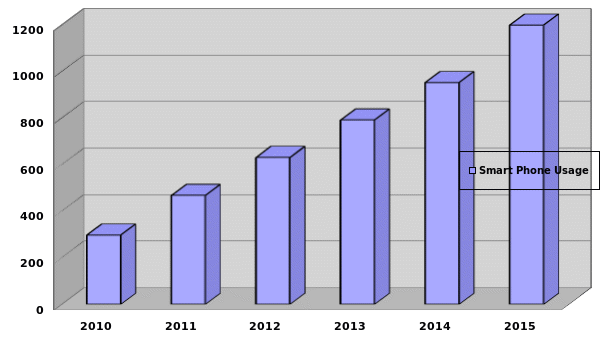
Fig 1.0. Projected growth in Smartphone usage, Source: Gartner and Berg Insight
Impact on work/Business
Business communication is nowadays technology oriented (Stockard 2011, p. 153), letters, memos and reports have been replaced by technologies such as NetMeeting and LiveMeeting. Additionally, business communication is increasingly relying on the telephone especially Smartphones such as Blackberry and i-Phone (Stockard 2011, p. 153). Stockard adds that because phones can nowadays send messages as fast as the PC, business communication has become easier and quicker.
For a long time the business world has relied on the PC for conducting business. The PC still maintains its rightful place in the day-to-day running of organizations and conduction of business. However, the advent of the smart phone is increasingly diminishing the importance of the PC in business transactions.
This is because the smart mobile gadgets like smart phones and tablets have what the PC doesn’t; mobility and portability. The above features coupled with the presence of integrated PC features in smartphone makes them attractive and addictive to business people. The addiction and effect of these devices on work lives can be capture through a Ring Central online survey that was carried out in the year 2010.
Increased reliance on Smart mobile devices for conducting business
In the survey, respondents ranked the smartphone and intimate life both at 40% as the two most important things that they can’t do without in their lives. Additionally, the majority of respondents totaling 79% cited the smart phone as the main business tool for conducting business easily beating the home and office phones (Trade 2010).
This is in contrast a few years ago when laptops were the main gadgets through which business was conducted remotely. The smartphone however easily beats the laptop as the primary preference in conducting remote business especially because it enable people access the physical tools that were only found in the office.
Some business people (34%) admitted to using the smartphone for business more than the computer (Trade 2010).
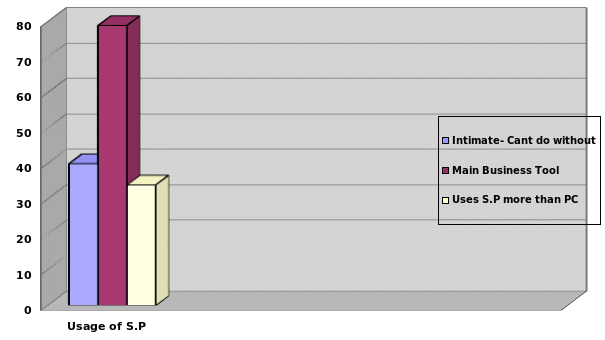
Levels of addiction of the smartphones, Source: Ringcentral Online survey
People are now increasingly addicted to productivity
Many business people and those that are in both formal and informal employment admitted that they are addicted to the smart mobile devices for the sole purpose of improving productivity in their respective work areas. Again, the ability to conduct business from any location came top among the reasons the respondents gave.
To that effect, 40% of respondents ranked smart phones as being significant as intimate relations. Hypothetically, therefore these people cannot easily choose between their social lives and the gadgets they are holding (Trade 2010). This therefore shows a worrying trend where people may rank non-living requirements like gadgets ahead of social and personal development.
In a nutshell, business people as well as those that are working in the formal sector have demonstrated an unmatched passion for smart mobile devices. The fact that it has changed their way of life as shown above underscores the critical role these devices play and the depth of their effect.
Of more importance however is the dynamism that these gadgets have brought to the business world. They have reduced overreliance on the PC and the business phone as the main tools of conducting business. Mobility and speed have now become the norm thanks to these devices.
Impact on Private Life
Many academics and political critics have conceded that the smart mobile devices like the BlackBerry can result into negative impact on the balance between work life and family life (Sweeny 2009, p. 190).
Addiction to mobile smart devices has not only affected business/ or work relationships of the users. There is sufficient reason to believe that the addiction has extended to the private or social lives of many people that use them.
Increasingly, people have found themselves in the awkward position where they need to split their time between their social lives and business. This effect will be captured through a presentation of different social scenarios that are aimed at showing the skewed devotion and commitment to family and relationships due to the use of mart mobile devices. In all the scenarios, the use of the gadgets is a deviation from the norm as we know it.
Less family time
Nowadays, many people are devoting more time to business than to family. It’s not uncommon for people to conduct business while on a weekend or holiday alone or with family. Smart mobile devices come in handy in when one needs to check on the developments in the business world.
During this time, people split their time between being with family and communication various business issues. People with the smart gadgets find it difficult to keep to themselves without referring to their devices in social functions such as funerals and weddings and children’s outings. Subtly, and without realizing, these actions indicate lack of attention on the family and other social relationships which takes its toll in the long-run (Powell, p. 181).
Less privacy
According to Furnell et al (2011, p. 50), the use of smart phones by people with no or little technical knowledge exposes them to the risk of being attacked through the use of their gadgets as security or attack vectors. In fact, most people who use these devices have little or no technical knowledge on measures that mitigate these risks.
Many of the smart mobile devices have been fitted with advanced microchips which make it easier for surveillance of the holder. The log installed in the smart devices can record all the places the holder has been to and sometimes the activities they have been up to.
Additionally, it’s easy for the parent companies and other interested parties to monitor the devices remotely illegally or otherwise. No matter the circumstances under which the surveillance takes place, the privacy of the holders of these devices is compromised. It’s no secret that surveillance information from these devices has led to the collapse of many social relations of the holders.
Social Networking
One of the biggest impacts of smart mobile devices is social networking. Butler (2010, p. 100), quoting Comscore, says that over 30% of smartphone users access social networking sites like facebook and twitter using their phones. It’s now possible for people from different locations to communicate and participate in social events without necessarily meeting physically. The social networking impact can be positive or negative depending on the function it plays.
Impact on Government/ Administration
Andersen et al (2011, p. 278) does not entirely see the effects of smart mobile devices as being negative. According to them, mobile communication especially through smart devices positively influences mobile business which in turn reinforces social media. Mobile business and social media therefore reinforce each other in a form of co evolution that has positive consequences (Andersen et al 2011, p. 278).
Through the use of these devices, both commerce and government have been forced to adopt technological changes for better communication and business procedures in the technologically mobile world (Rhomobile 2011, p. 23). On the same note, there is a feeling among many scholars that these gadgets have played and will continue to play a crucial role in social media growth and evolution.
As such they come in hand in the implementation of changes in government and in society especially through participation of citizens in e-democracy. A good example is role smart devices have played in the political crises of North Africa and the Middle East.
Impact on Education
Education is one of the fields that have evolved with time. There is a marked difference between ancient and modern universities. Though there has been considerable adaptation of technology in education, the advent of smart mobile devices is likely to have a major impact on education. Smartphones aide students in accessing online textbooks while connecting them with databases and libraries online when doing research (Wright & Webb 2011, p. 203).
According to Huang & Ling (2011, p. 557), education has also benefited from ubiquitous learning enabled by smart phones that help in individualized learning. Some android smart phones have an embedded system that helps in the creation of an assisted learning that is less bulky and mobile. The system can also improve the improve distraction behavior in students. Additionally, the application helps in the interaction between peers and teachers. The above application has not yet been adopted by the main stream companies. However it offers a glimpse of the impact that smart mobile devices are likely to have on education.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, smart mobile devices offer advanced computing and connectivity abilities compared to normal mobile services. Their impacts are manifested through effects in productivity and communication in the work place, private life, in government and in education. The effects of these devices are both positive and negative.
Their addictive nature and ability to cause distraction is by far the biggest negative effect these devices have on human life. Both private and work lives of the holders gets altered positively or negatively. Social life of the users especially the family is likely to be negatively affected because people extend conduction of business out of the office.
On the brighter side however, smart mobile devices have enhanced the way business is done and productivity has increased in the work place. Also, it has enhanced networking among professionals and people of different classes. Education has also been impacted positively through easy access to research materials in online libraries. Applications such as Google Reader on the Android phone are an example.
The impacts discussed above have so far been as a result of the existing level of technology. As the thesis statement asserts, technology is ever increasing and new products with mobile and smart features are being developed. The way we conduct our lives is sure set to change with these new products.
References
Andersen, K. et al. (2011) Electronic Government and the Information Systems Perspective: Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Butler, M. (2010) Enterprise Social Networking and Collaboration. East Yorkshire: Martin Butler Research Ltd.
Furnell, S. et al. (2011) Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business. New York: Springer Verlag.
Gallagher, P. et al. (2005) Managing the challenges of WTO participation: 45 case studies. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ling, S. & Huang, X. (2011) Advances in Computer Science, Environment, Ecoinformatics, and Education. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Powell, G. (2011) Women and Men in Management. London: Sage Publications.
Rhomobile. (2011) Top Trends in Smartphones: and How Rhomobile helps you write apps for them. San Jose, CA.
Sweeny, A. (2009) BlackBerry planet: the story of Research in Motion and the little device that took the world by storm. Ontario: John Willey & Sons.
Stockard, O. (2011) The Write Approach. Bingley: Emerald Publishing Group.
Salt, B. (2011) The Big Tilt: What Happens When the Boomers Bust and the Xers and Ys Inherit the earth. Victoria: Hardie Grant Books.
Trade, J (2010) Smartphones Changing the Way Business Professionals Work and Live. Web. Web.
Wright, K. & Webb, L (2011) Computer-Mediated Communication in Personal Relationships. NY: Peter Lang Publishing Inc.