Introduction
Risk management involves identifying and assessing the risk factors with intention to minimize their impact in the organization. There are risks that can be controlled and those that cannot. The role of a manager will be to develop a strategic plan for the risks both internal and external risks.
Barclays bank is a world leading financial service provider that has its branches in 50 countries worldwide and employs about 147,500 people. The bank deals inn variety of financial products and service ranging from corporate banking to mortgage services. Barclays bank is listed on the London stock exchange as a public company that complies with the UK combined code on corporate governance (Gorrod, 2004).
Barclays bank has a clear risk management strategy whose objective include
- Identifying the bank significant risks
- Ensure business growth is supported by conclusive risk management structure
- Establishing strong and independent review on risk management policies
- Enable management and executive group control and coordinating of risk responsibility in the bank
- Communicating risk management policies within the bank
The bank group risk management policies have remained unchanged since 2009 when it was last reviewed. The responsibility of risk management in Barclays bank group is mandated to all levels of management within the group starting from the top management and executive committee to each unit managers and risk managers. Barclays bank has a risk oversight committee that is responsible for reviewing and formulating the risk strategy in the organization (Barclays Bank, 2010).
In management of risk, the bank employs several models and approaches in dealing with uncertainty. This models range in their application. They can be used in decisions concerning credit determination, pricing, and portfolio management, risk assessment regulatory capital calculation. This types of strategy covers credit, market, and operational risk (Hallenbeck, 1986).
The bank uses the following models in analyzing risks factors in their operating environment. These models of estimation include probability of default (PD), exposure at default (EAD) and loss given default (LGD).To minimize the risks factors, the bank developed a group model risk policy (GMRP) that is reviewed annually and is managed by the independent group risk function.
The group risk policy minimizes the potential for risk by setting minimum standards for implementation and model development process. The model also sets governance policies concerned with risk management (Horne & Wachowicz, 2008).
Barclays Bank Risk Governance Model
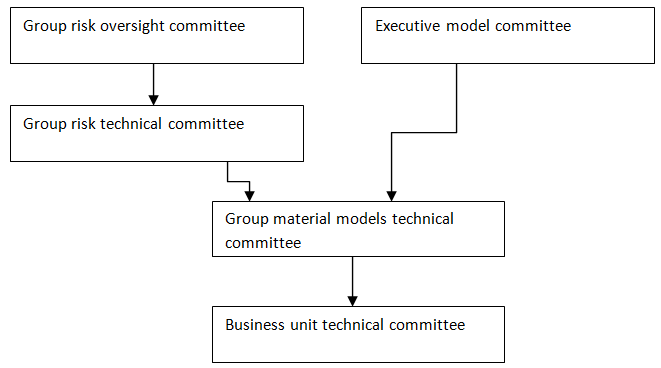
Source: self generated
Current Risk Management Process
Risk management aims to identify and assess risk factors in the environment in which the firm operates. Examining of internal and external environment is an important step in risk management. In the Barclays bank, risk management process is represented by the figure below
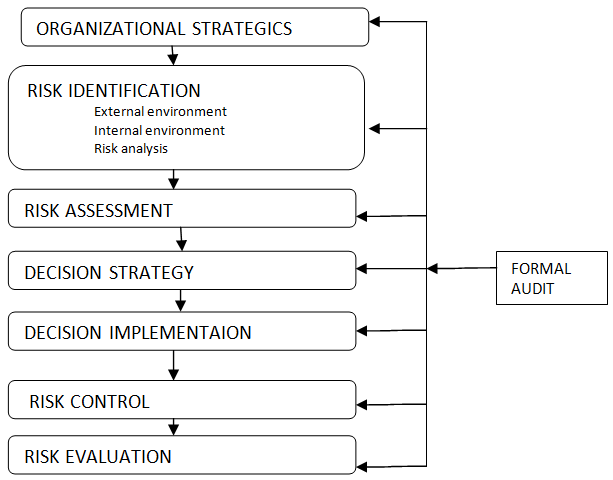
Risk identify
Barclays bank contracts a private consultant in identification of the risk factors that affects the bank. The private consultant is responsible for assessing financial and social risks. He/she would write a conclusive report to the bank’s risk management team. Risk factors the bank encounters will majorly include-credit risk, market risk, political uncertainty, traded market, capital and technological liabilities, operation risks and liquidity risk.
The bank utilizes the risk assessment matrix (R.A.M). This tool is used for acquiring information to prioritize assets and identify mitigation requirement. This model enables the organization to develop policies that will ensure better response in case of a risk. Risk assessment matrix consists of six steps (Moteff, 2005).
- Identify business process and function in an organization
- Rank these functions and processes in order of their vulnerability to risk factors
- Identify threats of risk to these business functions and processes
- Determine the specific risk to each process and function.
- Put up appropriate resources and plans s in place to deal with the risk factors.
Risk Response
The bank categorizes risks into either environmental or social risks. To reduce the effects of the risks on the bank operations, the bank management conducts employee training to create risk awareness (Gorrod, 2004). Responses to the risks affecting the bank could take various forms such as:
- Transference- involves the change of the impacts of the risks to other of the bank such as insurance companies.
- Risk Mitigation- these include the activities of the bank that help reduce the impacts of the risk to the bank. The activities may include taking preventative actions and project monitoring.
- Avoidance- Involves activities that will prevent the risk from occurring. This may involve changing the kind of project or process that is vulnerable to risk.
- Acceptance- this happens whenever the bank accepts the impacts of the risk factor. This is possible if the bank realizes that it has run out of options to mitigate the risks.
- Deferment: this is the transfer of the risk factor form the present period to a later period.
Training program for employees with direct contact to customer is one of the risk management policies the bank employs. For technical risks, technical oriented solutions to the potential risk is developed and employed by the banks strategic organ to mitigate the risk (Hallenbeck, 1986).Risk mitigation will include risk identification of critical sectors in the organization and control strategies incorporated to these points.
These control strategies will form part of organizational guidelines, which should be included in standard practice in the organization (Porteous & Pradip, 2005).
Risk Monitoring and Control
Risk management committees are responsible for monitoring and evaluating the risk policy adopted by the bank. Review of risk management strategy is continuously reviewed to determine its effectiveness in dealing with potential risks (Alexander & Sheedy, 2005). Review of the risk evaluation is also important to identify the trigger event that lead to the occurrence of this risk.
This will help the organization in future to control risk factors effectively. Risk status report is an important tool in risk management and should be delivered to risk management team regularly. Risk management should be a continuous process of assessment in the life cycle of a project (Standards Association of Australia, 1999).
Risk Management Issues
Risk management as a strategy suffers from number of problems variety from resource allocation to the risk model to be used (Rescher, 1983). Some of these problems include
- Resource scheduling:-This involves allocation of resource from financial to human power to deal with the risk
- Nature of risk:-Barclays bank has been unable to in developing a clear strategic risk policy on natural disasters or even acts of terrorism
- Management of risk:-Managing of risk in an organization requires component personnel who can analysis and accurately predict an occurrence of risk. If these managers are not competent enough then the organization will be in a constant threat from risks in the operating environment
- Tool and techniques for risk management:-It is often difficult to ascertain the right tool to manage risks. Different tools will vary in their accuracy in risk prediction.
List of References
Alexander, C. & Sheedy, E. (2005) The professional risk managers’ handbook: A comprehensive guide to current theory and best practices. PRMIA Publications, New York.
Barclays Bank, (2010) Case studies. Web.
Barclays Bank, (2010) Social and environmental risk governance. Web.
Barclays Bank, (2010) Social and environmental risk management in lending. Web.
Gorrod, M. (2004) Risk management systems: Technology trend finance and capital markets, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Hallenbeck, W. (1986) Quantitative risk assessment for environmental and occupational health, Lewis Publishers, London.
Horne, J. & Wachowicz, J. (2008) Fundamentals of financial management: tools of financial analysis, 13 Edn, Pearson international edition, Boston.
Kim, H. (2005) Project Manager’s Spotlight on Risk Management. Jossey-Bass.
Moteff, J. (2005) Risk Management and Critical Infrastructure Protection: Assessing, Integrating, and Managing Threats, Vulnerabilities and Consequences. Washington DC: Congressional Research Service.
Porteous, B. & Pradip, T. (2005) Economic Capital and Financial Risk Management for Financial Services Firms and Conglomerates. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Rescher, N. (1983) A Philosophical Introduction to the Theory of Risk Evaluation and Measurement. New York: University Press of America.
Standards Association of Australia, (1999) Risk management. North Sydney: Standards Association of Australia.