Introduction
The Scandinavian Airlines is also known as SAS. The company was initially referred to as Scandinavian Airlines System and it is the main carrier in three countries, Denmark, Sweden and Norway.
Headquartered in Sigtuna, Sweden, SAS operates in at least thirty countries, with an outstanding international performance and record (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007). Its number of aircrafts is approximated to be 198, which operate to 176 destinations in the world.
The company is also among the oldest carriers, having been established in 1940s as a group of three national airlines, which included DNL from Norway, DDL of 1918 from Denmark and ABA founded in Sweden in 1924 (Bhardwaj, 2010).
This report gives an analysis of the Scandinavian Airlines with regard to a wide range of business aspects. Of great significance in this report will be the major focus on SAS marketing strategies that have propelled the company to its current business niche in a competitive flying business.
What is its secret? To answer this question, the report synthesizes the company’s major product lines and its market segmentation in meeting the needs of customers.
Since customer satisfaction and segmentation are essential business principles, the report further explores the design, management and promotion of its products in order to realize the intended purpose throughout its operations as a flag carrier in the above mentioned three countries.
In other segments, the report will give details on how SAS manages its public image and the management approach in winning the confidence and loyalty of its customers beyond what it can offer. The concluding section of the report will cover several recommendations that are necessary for SAS to remain a major carrier in over thirty countries around the world.
SAS history
As mentioned above, the Scandinavian Airlines company began in 1946 in Denmark before it merged with several companies from other countries through business partnerships, with the merger between SAS and ABA in 1951 culminating into its birth (Bhardwaj, 2010).
Based on a wide range of factors, the three entities under SAS umbrella owned shares as follows: both SAS Norge and SAS Danmark owned 28.6% while SAS Sverige was the majority share holder with 42.8% (Air Review, n.d.).
Throughout its operations and history, SAS has attained significant reputation, outshining its competitors by far. For instance, the carrier became the first to fly on a trans-polar route in the year 1951.
The rout was between Copenhagen and Los Angeles, with four major stops in Greenland, Søndre Strømfjord, Canada and Winnipeg (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
Notably, the route became famous as it was highly preferred by Hollywood personalities flying to Europe. Besides this boost by celebrities, the route further advertised the airline in Europe and other major cities around the world.
By late 1950s, the tans-polar route enjoyed massive popularity among tourists from the United States, an achievement that highly contributed to the success story of the company.
This idea broadened as the company introduced other similar routes to Japan and Alaska even though it experienced license resistance from the former USSR (Air Review, n.d.).
Another achievement for the company was realized in 1957 when it launched “round the world flying service through the North Pole.” Due to its determination and fast expansion, the Scandinavian Airlines joined jet aircraft service in 1957 and acquired Boeing 747, the first of its kind in the year 1971.
As a result of these fascinating advancements, the company continued to dominate and control local markets in the three main countries of origin (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
In order to expand its global influence and coverage, SAS considered the formation of a worldwide alliance when it purchased 18.4% of TAC, Texas Air Corporation. Nevertheless, SAS later sold the stake, but continued to acquire others from different countries.
These included 20% of British Midland, Air Greenland and 95% of a Spanish leading airline, Spanair in 2009. The Star Alliance was formed in 1997 when SAS joined forces with United Airlines, Air Canada, Thai Airways International and Lufthansa (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
However, its 2001 strategy with three other companies, Swissair, Austrian and KLM turned out to be unsuccessful, leading to the dismissal of the company’s CEO as he was believed to have contributed to the financial turnaround of the company (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012).
In order to regain its dwindling status and public image, SAS implemented a new ownership structure which saw Sweden own 21.4% while Norway and Denmark had an equal share holding of 14.3% each.
Unlike in the previous structure, the public was allowed to control 50% of the company’s shares through the stock market (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007). Even though SAS was divided into four different companies in 2004, the two reunited in 2009 to retain a single entity (Ujaraq, 2010).
Scandinavian Airlines Routes
As mentioned before, SAS has its headquarters in Sweden, though the company has a well established market in Europe. According to recent findings, approximately 85% of the company’s non-international flights heavily contribute to its turnover.
Out of these flights, close to 41% were realized with flights headed to Europe while domestic flights added to a total of 30.1% (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
On the other hand, Intra-Scandinavian flights contributed 14.3%. An example of this route is Stockholm-Copenhagen. Lastly, international flights like Stockholm-New York constitute an average of 14.6% of the revenue realized from passengers.
Importantly, Scandinavian Airlines is the leading share holder in the market with almost 90% of the shares. The company further possesses 80%, 89% and 97% in Sweden, Denmark and Norwegian markets respectively.
Having its management leadership unit in Scandinavian, it deals with high profile competitors like Malmö Aviation and Flynordic (Jens, 2005). Its routes have remained vital in marketing the company’s outstanding performance as a way of winning new customers.
Scandinavian Airlines routes are also important in catering for different market segments. For instance, SAS international serves eleven destinations including New York, Chicago, Bangkok, Dubai and Beijing among others (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012).
The fleet has ten Airbus, seven A340-300s and four A330-300s. SAS Danmark is responsible for all European traffic via, from and to the country. It also augments development of Copenhagen as SAS’s main hub. Additionally, it facilitates the sale of the Group’s airlines and its business partners in the entire Danish market.
It serves up to 23 countries, with 50 destinations and operates with a fleet of 52 aircrafts (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007). On the other hand, SAS Norge caters for customers flying via, from and to Norway.
The airline was founded in 2004. SAS Norge is ranked as the leading air travel operator in domestic routes in the country. Lastly, Swedish travel air market is dominated by SAS Sverige, which coordinates all sales activities among partners in the country besides being responsible for the traffic from, to and via the country (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012).
The adoption of the four airlines was to augment SAS’ ability to cater for different market segments. In other words, the needs of customers are addressed independent of what happens in another country.
This also promotes its service delivery, wins the loyalty of customers, gives the company a positive public image and manages its business products (SAS, 2012).
SAS vision, values and business concept
In promoting its products and winning the confidence of customers, the activities of the Scandinavian Airlines are driven by defined values and vision. This ensures that the company remains focused in pursuing its course and maintains a stable competitive advantage.
The company’s business concept is to serve the entire Europe with air travel and a major hub in North Europe (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007). From a 2006 Annual Report, SAS has a vision of becoming the preferred choice for air travel. On the other hand, SAS’ values are summarized by four ideas as described below:
The company believes that its customers are the most important assets that have to be highly valued in ensuring its success in air travel. As a result, the company lays immense emphasis upon its customers and employees.
Through this consideration, the company strives to respect the environmental and social responsibilities of stakeholders (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012). This is to say that, customers and employees are viewed to be part of the global SAS business family. Secondly, the air carrier maintains a reliable status throughout its operations.
As a result, the company has won the confidence and loyalty of its customers by proving that it is the safest, consistent and trustworthy airline in Europe. This reliability has led to the company being ranked highest in terms of punctuality of its flights (Star Alliance, 2012).
Last year, Scandinavian Airlines was voted as most punctual air Travel Company throughout the year, and position one in July and August of the same year. Similarly, the company was ranked as the most punctual in Europe in 2009 and third place worldwide.
SAS’ third idea is implemented through value addition and creation. In its daily activities, the company has remained determined to pursue a professional methodology through innovative ideas.
In essence, the company develops innovative strategies so that new advancements are merged with existing ones with the aim of maintaining and improving the value of the company’s products and services (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
Additionally, the company observes high levels of openness especially to stakeholders, employees and customers. This is principally achieved through high level of honesty and transparency especially in the overall management.
Scandinavian Airlines Strategies
In promoting its products, winning customer loyalty and catering for the needs of its customers, SAS has several strategies that are considered to be essential drivers. Among these are flight safety, excellent services and punctuality (Jones, 2012).
Notably, the company is interested in offering high quality services to its customers. As a result, the management believes that promoting the safety of customers has significance impact in advancing such a course (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
It therefore invests heavily in maintenance of aircrafts and giving attention to areas that may pose security threats and accidents. The company is also sensitive to effective service delivery.
As a result, the number of employees is determined by the size of the airport and necessary adjustments are frequently made to attain this target. It has a wider scope of becoming the most punctual airline in Europe and around the world (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012).
In appreciating technology, the company has improved its booking services by introducing e-tickets where customers can reserve flight seats at the comfort of their office or at home as long they are connected on the web.
High-class lounges are also used in winning customers. Among other adverts done by the company to market its products, it uses flyer cards to give relevant information to customers, including status of flights, charges, offers and destinations among other particulars (SAS, 2012).
Scandinavian Airlines further benefits from its Star Alliance Membership since 1997. The alliance has seen the number of customers increase tremendously, thus allowing it to realize increased overall turnover.
The company has also marketed its services by partnering with other companies especially form Baltic countries (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012). It is worth noting that about fifty destinations in the region are operated by different airliners that are SAS’ partners.
In addressing the needs of customers, the greatest strategy of Scandinavian Airlines is increasing its competitive advantage within the market. It aims at providing services at any time regardless of the location of the customer.
As mentioned earlier, e-booking has become one of the quickest ways of improving the company’s efficacy in service delivery. It is quicker, easily processed and cuts down distribution costs that were experienced during massive manual booking (Scandinavian Airlines, 2012).
In dealing with customer problems online, SAS has partnered with several electronic travel agencies to provide solutions to customers. This has played a major role in promoting the services of the company, where almost 400 travel agencies operate. Through the use of SAS Direct service, customers receive service support concerning any issue ranging from booking to flight status (Kotler, Bowen & Makens, 2009).
Besides e-booking, Scandinavian Airlines uses the internet as a marketing and information tool. Its website is one of the most interactive in air travel in Europe (Ujaraq, 2010).
Literally, the website is a virtual SAS office, having all the information needed by customers. The website details the company’s products including routes, available flights, booking solutions, company profile, current and upcoming offers, annual reports, contact and feedback links among others (Helterlin & Ramalho, 2007).
This plays a major role in promoting SAS products, catering for customers’ needs from different regions and maintaining good public image.
As a distribution channel, it is projected that the website will become a cost-effective marketing tool for future growth. The table below shows e-ticket, self-service and Internet check-in in percentage (Jones, 2012).
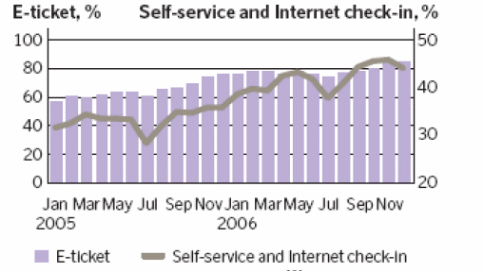
Retrieved from:Case studies: SAS Airline & Ryanair. Umea University. Web.
Additionally, SAS meets the needs of different customers in the market by offering various price options depending on the class and aircraft model. For instance, the company launched a low-cost carrier called Snowflake in 2003 and targets customers who cannot afford high-class flights (Nigam, 2010).
Recommendation and conclusion
From this report, it is doubtless that SAS Airlines is quite strategic in maintaining its competitiveness within European Air Travel. Through effective service delivery and relevant products, the company has won customer loyalty, met the needs of customers from different countries and promoted good public image.
Through approaches like entertainment, accessibility to lounges, offers, e-booking, meals, honest management and discounts, the company has maintained its high profile in the industry.
With its current status, the company has an uphill task to maintain the standards of its services, having in mind that it faces stiff competition from other international carriers.
Continuous training of its employees is paramount coupled with people-oriented management (Kotler, Bowen & Makens, 2009). Lastly, technological advancements have to be improved to catch-up with the ever-changing world.
References
Air Review. SAS Scandinavian Airlines Review and Opinions. Air Review. Web.
Bhardwaj, A. (2010). Scandinavian Airlines: The Green Engine Decision. Slide share. Web.
Helterlin, G., & Ramalho, N. (2007). Case studies: SAS Airline & Ryanair. Umea University. Web.
Jens, F. (2005). Scandinavian Revival. Aviation Week & Space Technology, 162 (3), 411-411.
Jones, P. (2012). Market Segmentation. Global Spec. Web.
Kotler, P., Bowen, J., & Makens, J. (2009). Marketing for hospitality and tourism. London: Pearson.
Nigam, S. (2010). SAS Scandinavian Airlines conquers niche airline marketing by first same sex wedding on a plane. Simpliflying. Web.
SAS. (2012). Customer Success. SAS Institute Inc. Web.
Scandinavian Airlines. (2012). Scandinavian Airlines. SAS. Web.
Star Alliance. (2012). Scandinavian Airlines. Star Alliance. Web.
Ujaraq, P. (2010). Scandinavian Airlines repositioning strategies. Århus School of Business. Web.