Executive Summary
This is a design project for Sharjah Higher Colleges of Technology, UAE. The construction of the stadium is ordered by the government, and the estimated time of completion is August 2018. The following project covers the scope management plan, work breakdown structure, project constraints, time management issues, resource and cost requirements, human resource management, and risk management.
Scope Management Plan
Sharjah Higher Colleges of Technology have long since required a stadium to practice sports and conduct sports competitions of various kinds between faculties and other colleges. Sport promotes healthy living, teamwork, physical prowess, and contributes to the prosperity and well-being of the nation. Simultaneously, sporting competitions have high entertainment value, especially in the UAE, where many sports are spectated and practiced. Simultaneously, Sharjah Higher Colleges of Technology does not have a stadium of their own to practice sports. Our group is tasked with providing a project outline for the construction of the stadium and a plan for its completion. The deadline for the project is at the end of August 2018.
As any stadium requires to be dedicated to a specific sport, this one will be dedicated to soccer. Soccer is considered to be the most popular sport in the UAE and Sharjah specifically. The sport became popularized in the country after 1971 and the establishment of the United Arab Emirates Football Association (“Sports”). Ever since the sport’s popularity grew, and now it is played on both professional, semi-professional, and amateur levels. Thus, dedicating the stadium to soccer is the best choice.
Quantifiable objectives for this project include providing a Work Breakdown Structure, outlining project constraints, activity lists with dependencies, network plans, time plans, resource plans, cost management assignments, human resource management, and responsibility assignments, as well as a risk management plan. The report will be delivered in digital and paper versions and would include MS project charts and a Powerpoint presentation.
The deliverables for this project include finding the correct location for the stadium to be built on, the preparation of the field (which consists of the installation of all game-related equipment and markings around the specific areas), the construction of the spectator places (which includes their design, construction, and safety inspection). The project is expected to end with a grand opening of the stadium.
Work Breakdown Structure
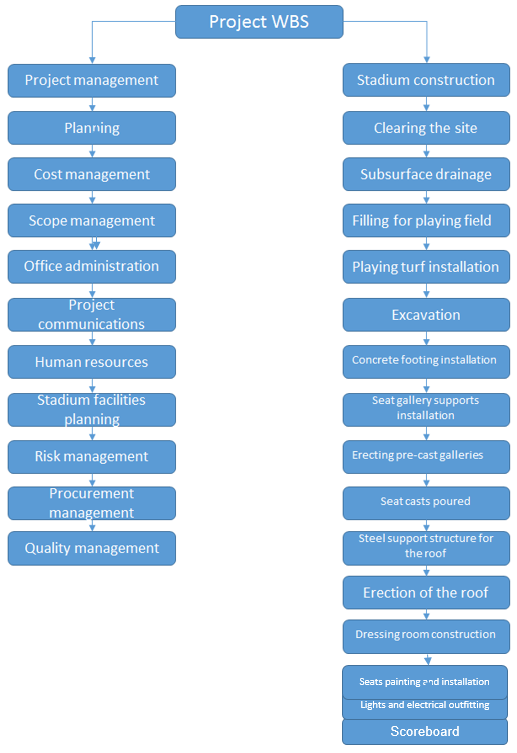
Project management branch.
Total: 1,190,000 USD.
Stadium construction branch.
Total: 4,050,000 USD.
Project Constraints
The premise of the case study states only one constraint for the project, which is time – the stadium is expected to be fully operational by the end of August 2018. However, it is safe to assume that the project will have a finite budget is another constraint. Lastly, the presence and price for organized construction labor, the availability of materials and construction equipment, as well as the availability of land and the location of the stadium, would impose additional constraints that would need to be planned around.
In this scenario, however, time constraints impose resource constraints. Had time not been limited, it would have been possible to accomplish the task and construct the stadium employing a minimum amount of workers over a more extended period of time (“Constraints”). In order to overcome the time constraints, it will be required to employ more construction workers and hasten the working process. That way, the stadium would be completed by the deadline.
Another constraint imposed on the project lies in materials and financial resources (“Constraints”). As we assume the number of resources spent on this project by the government is finite, it is paramount to optimize the number of construction workers at hand, their working schedules, as well as the supply and resource schedules. That would allow saving both time and money, as with adequate planning and intense working schedules that lack or have minimized downtimes, it is possible to complete the project with fewer expenditures on resources, transportation, warehousing, and labor.
External constraints on the project could potentially include the lack of a qualified workforce and materials to accomplish this project (“Constraints”). However, the possibility of these constraints to become relevant is unlikely, as Sharjah is the third largest and third most populous city in the UAE, with a large market of construction services.
Time Management
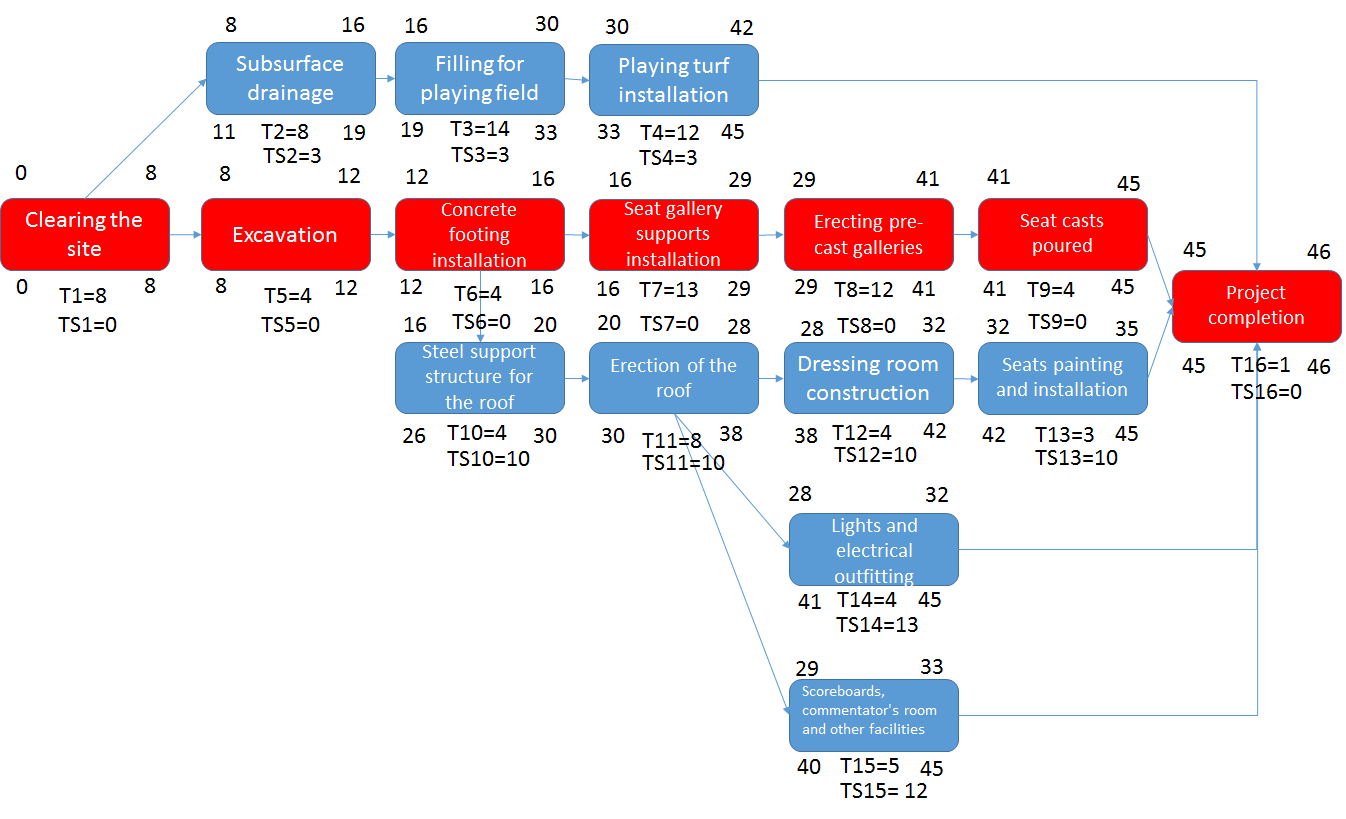
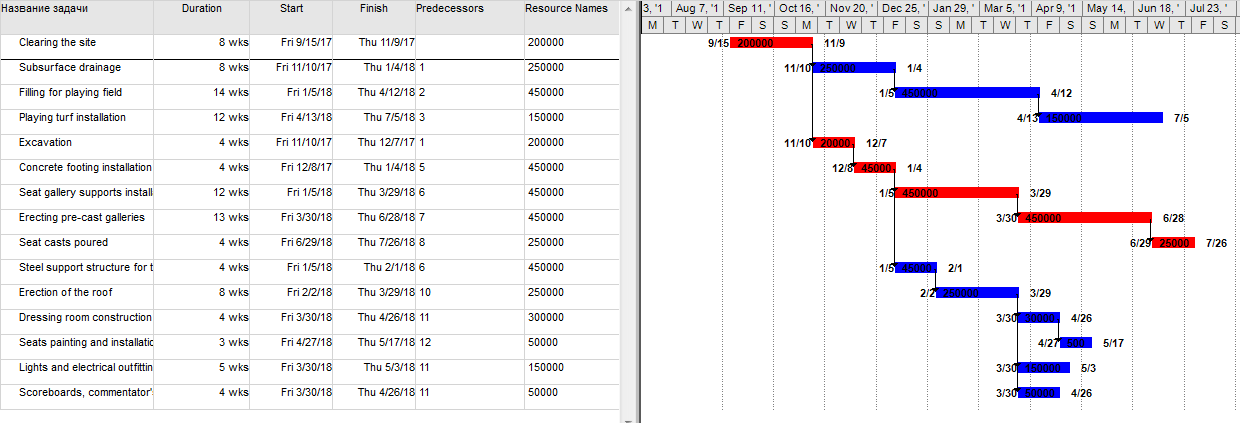
Resource Requirements
The resources required for stadium construction vary in their nature and could be classified into different subgroups. These groups are (“Resources”):
- Construction materials – these include concrete, cement, sand, brick, steel armature, waterproofing materials, steel beams, electrical equipment, paint, and other materials required for the construction of the stadium and the spectator stands.
- Construction mechanisms – these include all kinds of construction machinery used for lifting, digging, and transportation of construction materials. The examples of construction mechanisms required for this project include excavators, cranes, hauling trucks, graders, concrete mixers, and ground compactors.
- Handheld tools and equipment – these include brushes, shovels, hammers, masonry trowels, wheelbarrows, vibrators, chisels, saws, line levels, drills, ladders, measuring boxes, putty knives, and other equipment used by workers during construction.
- Stadium field-related materials and equipment – as the stadium’s surface will be covered with grass; these materials include grass seeds, soul fertilizers, sprinklers, gardening tools, etc. Other materials and equipment are related to the sport and have plastic seats, marking materials, soccer gates, nets, flags, banners, and other related items.
Cost Management
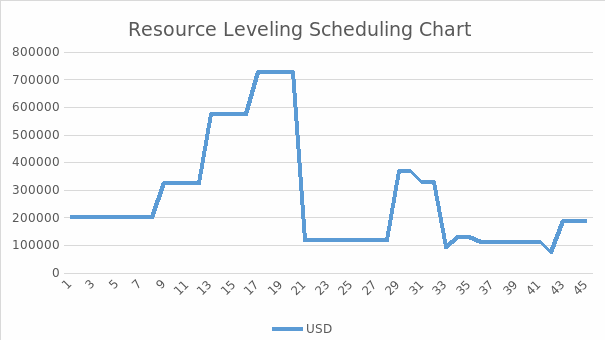
According to the WBS, the total expenditures for the construction part of the project is estimated at 4,050,000 USD. The following chart was created using the Gantt chart and resource requirements for each process to evaluate financial demands for each week. As it is possible to see in the diagram, the highest demand for financial resources happens between 17-20 weeks, peaking at 728600 USD per week.
Human Resource Management
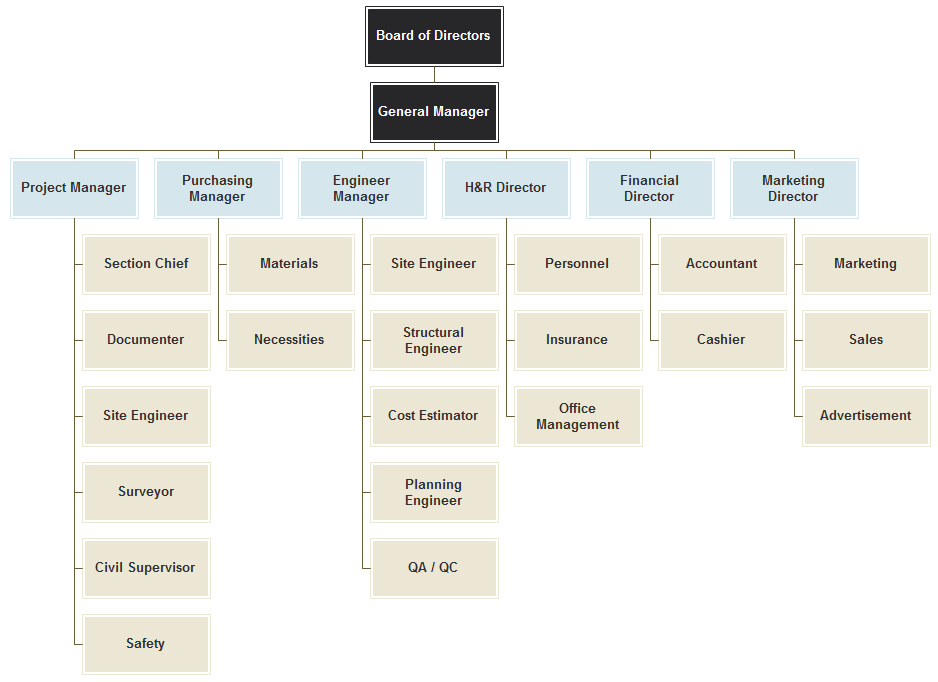
This is a standard organizational chart for a construction project. The key stakeholders here are the project manager, purchasing manager, engineer manager (chief engineer), HR director, financial director, and Marketing director. The type of organizational structure used for this project is the functional structure, where every portion of the organization is grouped according to its purpose. It is an efficient structure that requires very little in terms of maintenance and is standard for many construction companies (Lohrey).
Types of communication channels (“Communication”):
- Formal written
- Informal written
- Formal verbal
- Informal verbal.
Number of communication channels = [N x (N-1)] / 2 = [27 x 26]/2 = 351.
Risk Management
Risk management is a very important part of the construction process, as there are many potential factors that may hamper or outright ruin the project, depending on the severity of the risk. Identifying these risks, developing risk management plans, and identifying the risk owners is paramount to safeguarding the results of the project and minimizing potential damage, should any of these risks ever occur.
Construction risks could be split into six categories (Menard):
- Technical risks. These risks include the possibility of damaging the material, equipment, chances of trauma among the workers, improper design and planning, improper site investigation, and changes to project scope and requirements. Counteracting these risks is usually done through a thorough inspection of the construction process before, during, and after the completion of the project. As all construction processes are conducted by subcontractors, the responsibility for any accidents and associated risks lie on them. In order to account for any potential delays, the project’s estimated completion time must be set 2-3 months before the deadline.
- Logistical risks. These risks account for any delays or damage to the materials and equipment during transportation. To account for this, the construction site must always have a surplus of materials and equipment in order to continue work despite the delays. Otherwise, the project risks facing unexpected downtimes. In this scenario, the suppliers are the risk owners.
- Environmental risks and Force Majeure. These types of risks account for bad weather patterns, rainstorms, drought, cold, as well as major accidents of environmental or technogenic nature, such as floods, fires, and earthquakes. Flame extinguishers and proper safety protocols and measures should protect the construction site from any related incidents. Should an accident occur, the responsibility lies on the safety organization detail.
- Management-related risks. These risks usually stem from ineffective management and labor organization, which leads to delays, unexpected downtimes, accidents, and general prolongation of the construction process. This happens if the managers and coordinators of the project are not sufficiently skilled in conducting the operations they were assigned. Counteracting these risks would involve high-quality planning of the processes and efficient work of the HR department, as they are responsible for hiring new employees.
- Financial risks. These risks include changes in inflation, local taxation, prices for materials, tools, equipment, and other related factors. They can significantly inflate the overall price of the project. However, since the stadium construction project is funded and covered by the government, it is likely for them to cover for any external financial risks.
- Socio-political risks. Social and political activity on a local level may significantly hamper the completion of the project. If the stadium is to be constructed in a densely populated area of the city, it may cause protests against the construction due to noise and construction debris. It would require written approval from the occupants of adjacent houses and apartment blocks to begin the construction.
For this project, prioritized risks would include technical risks as in risks of damage to the construction, the equipment, and trauma-associated risks, logistical risks, and environmental risks.
Works Cited
“Constraints in Construction Projects.” Designing buildings. 2017. Web.
“Communication Channels Made Simple.” PMC Champion. 2013. Web.
Lohrey, Jackey. “Organizational Structure of a Construction Company.” Chron. Web.
Menard, Shannon. “The Types of Risk in Construction Project.” eSub. 2017. Web.
“Resources in Construction Projects.” Steel Deck. Web.
“Sports in the United Arab Emirates.” Ten Guide. Web.