Social Darwinism is a social order that borrows ideologies from Darwinism. In this respect, the social order alleges that only individuals with suitable survival features deserve to live under certain conditions. In other words, social Darwinism advocates for natural selection.
Social Darwinism before the 19th century
The social Darwinism progress before the 19th century was preceded by the concept of Darwinism. In this respect, the aspect of the evolution of animals and humans was greatly respected. In fact, the existence of human beings was entirely based on survival. In this regard, some communities and individuals were perceived to be superior to others as they had higher chances for survival.
This can be evidenced in societies that took a leading role in civilization, while others lagged behind in their social, cultural and economic development. Prosperity and personal liberty among individuals and communities were perceived as a milestone in the development of social Darwinism.
Social Darwinism during the 19th century
Social Darwinism was founded by an Englishman known as Herbert Spencer. During the 19th century, Spencer perceived social Darwinism as a theory of social ethics (Slattery, 2003). Spencer was categorical that human’s survival and prosperity are determined by adaptation to certain socio-economic and natural conditions. In this context, Spencer’s reference to the theory of natural selection became popular.
Social Darwinism became more evidenced in Britain during the late 19th century. The reference to social Darwinism in Britain during this period was evidenced in policies and practices that exhibited social structures at homes and community levels.
An example of such practice includes social cruelty and imperialism that were justified by social Darwinism. Spencer’s theory is of the idea that the history of human prosperity and social evolution was to be determined through competition among social groups.
Social Darwinism also became popular in the United States during the 19th century. This was due to the fact that the United States is a capitalistic country, where intellectuals and ruthless businessmen wanted to justify their actions. Intellectuals and business men believed in surviving under conditions that offered opportunities. In this respect, the concept known as “only the fittest survive” became popular.
It was during the late 19th century that the philosophy of hereditarianism became popular. Hereditarianism was perceived to be a major element of social Darwinism. In this respect, the biological aspects of an individual are perceived to influence intelligence and character.
Moreover, the philosophy argues that biological features of an individual can be determined by environmental changes. In this view, an individual’s adaptability to certain environmental conditions is harnessed.
Social Darwinism in modern times
Social Darwinism became one of the development principles that became basic for many governments formed in the 20th century. This was before the beginning of World War 1. One exemplary application of social Darwinism was evidenced during the colonialism era.
Governments and countries that wanted to prosper during that era, justified their quest for resources and development through social Darwinism. In this context, social Darwinism supported colonialism in other countries (Hawkins, 1997).
Weaker social groups were conquered by those deemed to be strong. Stronger societies, countries or governments confiscated resources from less developed countries. Moreover, military rule and actions were subjected to weaker social groups and communities (Haas, 1997). On the same note, capitalism was used by societies, businessmen and intellectuals who justified their exploitation escapades against the poor (Haas, 1997).
A more explicit example of modern social Darwinism was evidenced in America during the early 1900s. Some American states passed laws against immigration since some immigrants were perceived to be unfit. These restrictive laws included the use of sterilization to ensure certain communities did not reproduce.
Proponents of social Darwinism before the 19th century
Charles Darwin
Darwin was an English naturalist and developed Darwinism in the year 1959. Darwin was instrumental in describing his theory of natural selection. However, Darwin was cautious in applying natural selection to human beings.
Herbert Spencer

Spencer was a philosopher from Britain and is regarded as the leader of social Darwinism. Born in 1820, Spencer applied Darwinian Theory when describing human development in a socio-economic context. Spencer’s work on social Darwinism was first evidenced in the 1850s.
William Graham Sumner
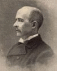
Sumner was a sociologist from Yale. Sumner ideologies were based on economy dynamics from a laissez faire perspective. From his ideologies, Sumner oversaw the need for socio-economic development based on evolution of natural events.
Synopsis on people and changes of socio-Darwinism during 19th century
Sir Francis Galton
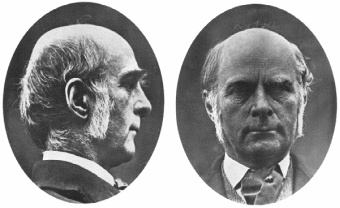
Galton was scientist from Britain and he was the first to associate social Darwinism with hereditarianism in the 1860s. His main focus was on biological inheritance and its influence on an individual’s intelligence and adaptability.
John Fiske

Fiske was a historian from the United States and an advocate of social Darwinism. His contribution to social Darwinism was evidenced in his foreign expansion ideologies. He also believed in military activities against weak nations. This socio-Darwinism ideology oversaw the justification of imperialism in the 1890s.
Oliver Wendell Holmes

Holmes was a Supreme Court jurist in the United States and a reformed social Darwinism in the 1890s. Holmes advocated for use of new ideas and innovation for mankind survival. The jurist oversaw the need for being innovative due to the underlying changing circumstances evidenced in a developing world.
Social Darwinism since the 19th century
Since the 19th century, social Darwinism continued to be advanced from many levels as evidenced below.
1914-1918: This period is known for the World War 1. Social Darwinism was applied by German militants knows as the Nazis. The Nazis were advocating for National Socialism.
1939-1945: This period oversaw the Nazis use eugenics to show how other communities and races were inferior and unfit to live among the Germans. This period marked the onset of the World War 2.
1955-1970s: During this period, the social Darwinism theory took a biological dimension. For example, biologists and anthropologists from Britain and America tried to analyze human behavior using the DNA.
From this perspective, human adaptability and domination over others was argued from a biological perspective. Such biologists include the British scientist James Watson and American Richard Herrnstein.
There are several differences between nationalists and communists. This can be evidenced from the history of China during the years between 1911 and 1940, when China was facing a colonization threat from Japan.
It is important to note that China has been known as a country driven by communists’ ideas, while on the other hand Japan is purely made up of nationalists and capitalists (Jowett, 1997). In this context, the political issue separating nationalists and communists is the western imperialism.
Nationalists are subject to western imperialism. In this regard, the Japanese were nationalists and capitalists seeking a certain national agenda (Jowett, 1997). This agenda was to strengthen the Japanese economy through capitalism. The Japanese had to do these through the landlords and capitalists.
On the other hand, the Chinese are known for their communist ideologies. The Chinese believe that social equality should be a national agenda. In this respect, all workers and especially the peasants are highly respected. The peasants are viewed as the pillars that form the basis of national wealth. In addition, democracy is not regarded by communists.
According to Jowett (1997), history alleges that Japan’s aggression against China was a significant show of might over China. This is a basic principle of nationalism, where a nation becomes more important than community members.
The nationalists believe in a capitalistic system of economy. In this regard, the Japanese became landlords and businessmen in China’s colonized territories (Jowett, 1997). This means that private ownership of land is entitled to any individual with financial capabilities. In this context, capitalistic governments are run through taxes.
Communists believe in communal property. The economy is not propelled or controlled by a certain social-class. Communists believe in comprehensive responsibility and non-private ownership in assets such as land. Assets such as land are owned by the community.
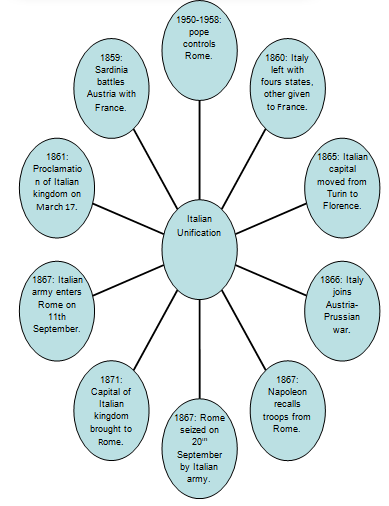
Fig 1.0 A mind map of Italian unification events.
Democracy is the most beneficial among other political systems in modern times. Unlike other political systems, democracy allows people to exercise their rights without suppression from representative government (Cohen, 1997).
On the other hand, communism ensures that every individual within the society is accorded equal rights. However, this political system is retrogressive and limits productivity among potential citizens (Cohen, 1997). It is difficult for individual citizens to agitate for personal rights under the communist regimes.
Fascism is another retrogressive political system that allows dictatorship. Under fascism, citizens are not represented in the government. In fact, fascism is a clear depiction of a military rule (Cohen, 1997). Fascism advocates for nationalism and loyalty to one supreme leader.
Today, democratic nations are advancing and developing at a higher rate. This is not evidenced in countries under communism system. Democracy allows governments to offer incentives to citizens who are innovate and productive. Individuals are able to prosper without any limits. Moreover, individuals are not responsible for not providing to fellow citizens.
On the other hand, communist states are slow in technological development (Cohen, 1997). The observance of human rights is highly ignored by communist governments, since there is no provision of individual human rights. Any individual who prospers in communist states is perceived as an oppressor of the poor. Basically, communist governments always strive to provide basic amenities for its citizens.
Fascism allows capitalism among individuals, but allows the government to interfere with such progress without any legal remedy. In any case, capitalists and wealthy people have a direct influence on government affairs (Cohen, 1997). In most cases, the influence is subject to creation of a social gap in the society.
References
Cohen, C. (1997). Communism, fascism and democracy: The theoretical foundations. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Haas, E., B. (1997). Nationalism, liberalism and progress: The rise and decline of nationalism. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Hawkins, M. (1997). Social Darwinism in European and American thought, 1860-1945: Nature as model and nature as threat. Cambridge, CB: Cambridge University Press.
Jowett, P. (1997). Chinese civil war armies 1911-49. Oxford, OX: Osprey Publishing.
Slattery, M. (2003). Key ideas in sociology. Cheltenham, GL: Nelson Thornes.