Disease Description
Arterial hypertension (AH) is one of the most widespread chronic disorders among the adults. About 1 billion people around the globe suffer from the disease (Wise & Charchar, 2016). AH does not merely decreases the quality of life but also increases the risks for the development of cardiovascular diseases (heart attack, stroke, congestive heart failure), leads to disability, and reduces life expectancy.

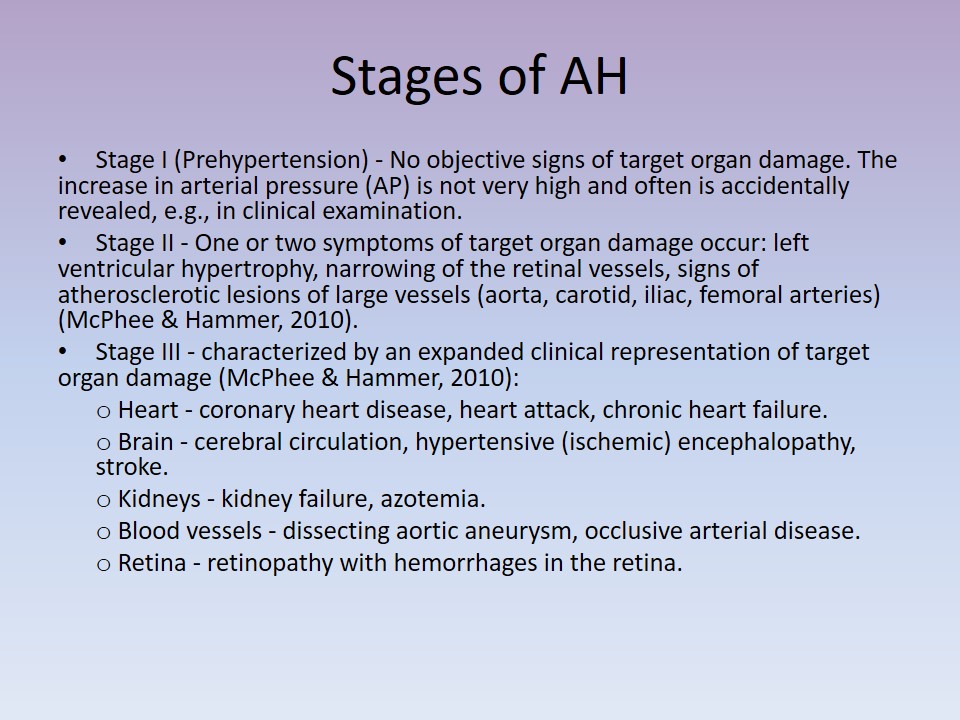
Stages of AH
- Stage I (Prehypertension) – No objective signs of target organ damage. The increase in arterial pressure (AP) is not very high and often is accidentally revealed, e.g., in clinical examination.
- Stage II – One or two symptoms of target organ damage occur: left ventricular hypertrophy, narrowing of the retinal vessels, signs of atherosclerotic lesions of large vessels (aorta, carotid, iliac, femoral arteries) (McPhee & Hammer, 2010).
- Stage III – characterized by an expanded clinical representation of target organ damage (McPhee & Hammer, 2010):
- Heart – coronary heart disease, heart attack, chronic heart failure.
- Brain – cerebral circulation, hypertensive (ischemic) encephalopathy, stroke.
- Kidneys – kidney failure, azotemia.
- Blood vessels – dissecting aortic aneurysm, occlusive arterial disease.
- Retina – retinopathy with hemorrhages in the retina.
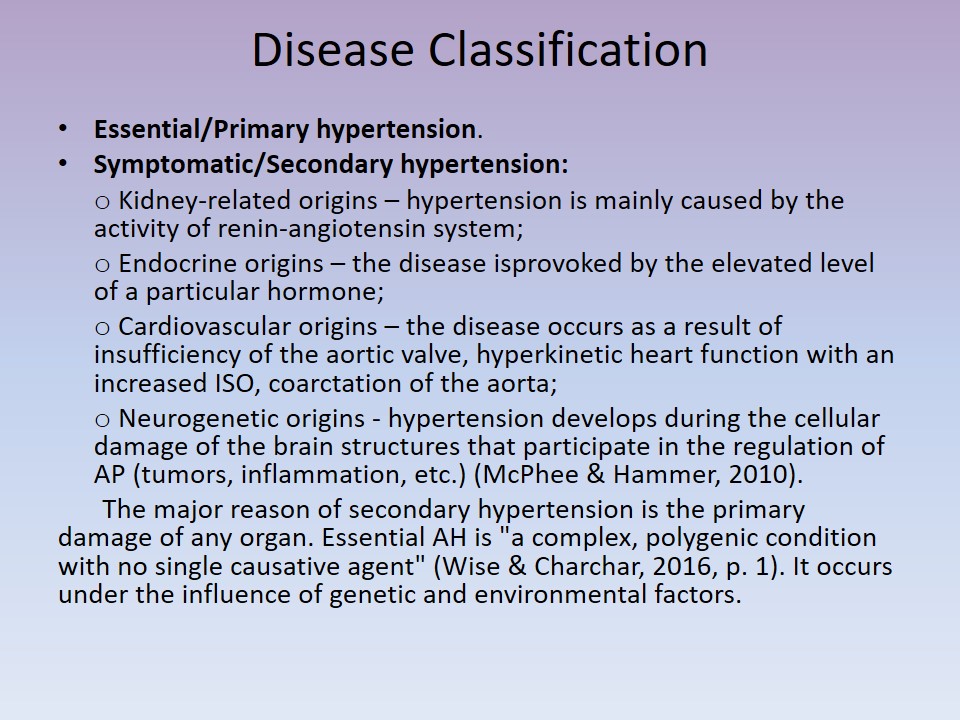
Disease Classification
- Essential/Primary hypertension.
- Symptomatic/Secondary hypertension:
- Kidney-related origins – hypertension is mainly caused by the activity of renin-angiotensin system;
- Endocrine origins – the disease isprovoked by the elevated level of a particular hormone;
- Cardiovascular origins – the disease occurs as a result of insufficiency of the aortic valve, hyperkinetic heart function with an increased ISO, coarctation of the aorta;
- Neurogenetic origins – hypertension develops during the cellular damage of the brain structures that participate in the regulation of AP (tumors, inflammation, etc.) (McPhee & Hammer, 2010).
The major reason of secondary hypertension is the primary damage of any organ. Essential AH is “a complex, polygenic condition with no single causative agent” (Wise & Charchar, 2016, p. 1). It occurs under the influence of genetic and environmental factors.
Factors Affecting Pathophysiology of the Disease
- High AP – Systolic blood pressure > 140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg.
- Age and gender – males over 55 years old, and females over 65 years old.
- Smoking.
- Cholesterol (blood content> 6.5 mmol/L).
- Diabetes.
- Hereditary predisposition – family history of early cardiovascular disease.
- Dyslipidemia – low HDL cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol.
- Obesity.
- Passive lifestyle (Malekzadeh et al., 2013; McPhee & Hammer, 2010).

Pathogenesis: Sympathetic-Adrenal System
The tone of the sympathetic nervous system is regulated by the centers of the brain, in particular, ventrolateral medulla where a2-adreneric receptors and imidazoline receptors type I and II (I1 – and I2 receptors) are contained. During the stimulation of a2-adrenoreceptors and I1 receptors, the tone of sympathetic system decreases and AP reduces (Hemming & Egan, 2013). The stimulation of I1 receptors also leads to water and sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule of kidney.
Activation of sympathetic-adrenal system plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of AH. At the initial stage of the disorder development, the content of catecholamines in plasma is elevated in most of the patients with the essential AH (Braunwald & Hollenberg, 2013). At the same time, patients with the normal level of catecholamines in the blood usually have the reduced number and sensitivity of a2-adrenoreceptors and the increase in postsynaptic influences of a 2-adreneric receptors that result in the strengthening of vasoconstrictory effects of catecholamines.
Additionally, hypersecretion of renin caused by the increased sympathetic activity, activation of the renin-angiotensin system, as well as the increase in total peripheral vascular resistance, and the volume of circulating blood, contribute to AP rise (Ayada, Toru, & Korkut, 2015).
The increased activity of sympathetic-adrenal system may be related to the central regulation disorder, a high number of angiotensin II receptor antagonists, regular high-calorie diet, stress factors, and sedentary lifestyle.

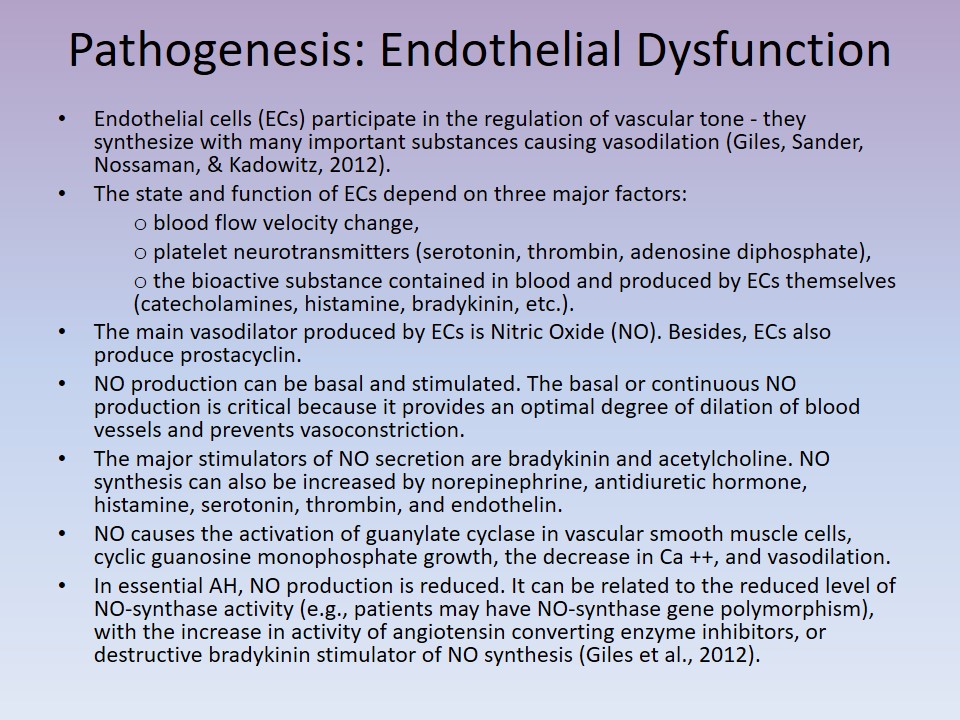
Pathogenesis: Endothelial Dysfunction
Endothelial cells (ECs) participate in the regulation of vascular tone – they synthesize with many important substances causing vasodilation (Giles, Sander, Nossaman, & Kadowitz, 2012).
The state and function of ECs depend on three major factors:
- blood flow velocity change,
- platelet neurotransmitters (serotonin, thrombin, adenosine diphosphate),
- the bioactive substance contained in blood and produced by ECs themselves (catecholamines, histamine, bradykinin, etc.).
The main vasodilator produced by ECs is Nitric Oxide (NO). Besides, ECs also produce prostacyclin.
NO production can be basal and stimulated. The basal or continuous NO production is critical because it provides an optimal degree of dilation of blood vessels and prevents vasoconstriction.
The major stimulators of NO secretion are bradykinin and acetylcholine. NO synthesis can also be increased by norepinephrine, antidiuretic hormone, histamine, serotonin, thrombin, and endothelin.
NO causes the activation of guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle cells, cyclic guanosine monophosphate growth, the decrease in Ca ++, and vasodilation.
In essential AH, NO production is reduced. It can be related to the reduced level of NO-synthase activity (e.g., patients may have NO-synthase gene polymorphism), with the increase in activity of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, or destructive bradykinin stimulator of NO synthesis (Giles et al., 2012).
Pathogenesis: Target Organ Damage
- Hypertrophy of heart (mainly the left ventricle) is a consequence of pressure overload, effects on the myocardium of neuro-humoral factors (catecholamines, AT-II of, aldosterone, etc.), inherited disorders (including hereditary predisposition to essential AH).
- Peripheral artery disease implies remodeling of arteries. It proceeds in two stages:
- The stage of functional vascular changes defined by vasoconstrictor reactions in response to transmural pressure and neurohormonal stimulation.
- Morphological phase which is characterized by structural vascular lumen decrease due to thickening of the medial layer.
- Vessels become rigid as the content of the extracellular collagen is increased in them. The major arteries are exposed to atherosclerotic lesions while the small vessels, arterioles, and capillaries, are reduced. Vascular depression with a decrease in blood flow and the development of venous congestion and stasis develops in the tissues (Braunwald & Hollenberg, 2013).
- Renal disease – hypertensive nephropathy or hypertensive nephrosclerosis. It takes a few stages of development:
- First, there are functional changes in the kidney blood vessels. Increased AP leads to an increase in the ultrafiltration and excretion of excess sodium contributing to the normalization of AP.
- The spasm of afferent arterioles gradually leading to their remodeling occurs as the reaction against the high blood pressure in the kidney.
- Then, the hypertonicity of afferent vessels develops.
- Arteriosclerotic vascular changes, functional overload of the glomeruli and tubules gradually leads to atrophy and diffuse sclerosis of the kidneys (McPhee & Hammer, 2010).
- The brain is affected due to remodeling of both large and small vessels.

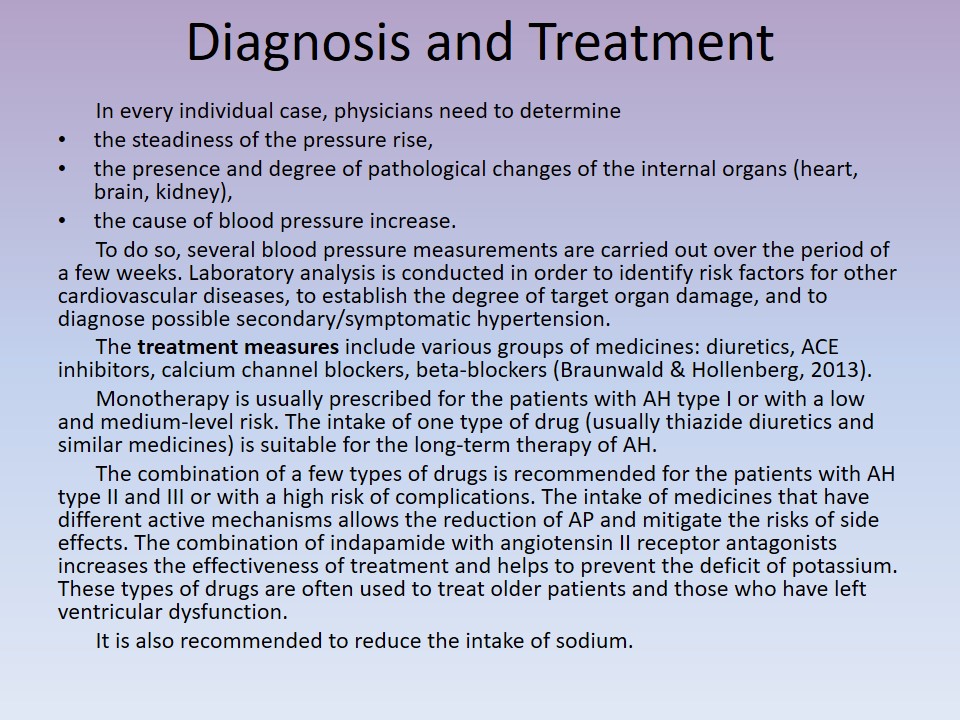
Diagnosis and Treatment
In every individual case, physicians need to determine:
- the steadiness of the pressure rise,
- the presence and degree of pathological changes of the internal organs (heart, brain, kidney),
- the cause of blood pressure increase.
To do so, several blood pressure measurements are carried out over the period of a few weeks. Laboratory analysis is conducted in order to identify risk factors for other cardiovascular diseases, to establish the degree of target organ damage, and to diagnose possible secondary/symptomatic hypertension.
The treatment measures include various groups of medicines: diuretics, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers (Braunwald & Hollenberg, 2013).
Monotherapy is usually prescribed for the patients with AH type I or with a low and medium-level risk. The intake of one type of drug (usually thiazide diuretics and similar medicines) is suitable for the long-term therapy of AH.
The combination of a few types of drugs is recommended for the patients with AH type II and III or with a high risk of complications. The intake of medicines that have different active mechanisms allows the reduction of AP and mitigate the risks of side effects. The combination of indapamide with angiotensin II receptor antagonists increases the effectiveness of treatment and helps to prevent the deficit of potassium. These types of drugs are often used to treat older patients and those who have left ventricular dysfunction.
It is also recommended to reduce the intake of sodium.
References
Ayada, C., Toru, Ü., & Korkut, Y. (2015). The relationship of stress and blood pressure effectors. Hippokratia, 19(2), 99–108.
Braunwald, E., & Hollenberg, N. K. (2013). Atlas of heart diseases Hypertension: mechanisms and therapy. New York, NY: Springer.
Giles, T. D., Sander, G. E., Nossaman, B. D., & Kadowitz, P. J. (2012). Impaired Vasodilation in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension: Focus on Nitric Oxide, Endothelial-Derived Hyperpolarizing Factors, and Prostaglandins. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension,14(4), 198-205. Web.
Hemmings, H. C., & Egan, T. D. (2013). Pharmacology and physiology for anesthesia: foundations and clinical application. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders.
Malekzadeh, M. M., Etemadi, A., Kamangar, F., Khademi, H., Golozar, A., Islami, F., … Malekzadeh, R. (2013). Prevalence, awareness and risk factors of hypertension in a large cohort of Iranian adult population. Journal of Hypertension, 31(7), 1364–1371. Web.
McPhee, S. J., & Hammer, G. D. (2010). Pathophysiology of disease: An introduction to clinical medicine. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical.