Executive Summary
The purpose of this report is to analyze external and internal environment of Amazon.com to assess the firm’s competitive position in the online retail industry to develop a strategic plan. However, this report concentrates more on market size, market growth rate, industry trends, five forces model, competitors, key success factors, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis, products and services , leadership, organizational structure, resources and capabilities, core competencies, growth analysis, profitability and valuation analysis
Background of Amazon.com
Jeffrey Bezos established this company in 1994 and introduced its virtual doors on the World Wide Web in 1995 to start as an online bookstore and the aim of Bezos was to transform this company into the largest and most customer friendly one-stop shop on the Web (Amazon, 2011, p.3; and Bezos & Risher, 2000, p.2).
At the initial stage, the management has developed separate websites for different countries to sale books and this project experienced huge loss (about $600.0 million in losses in 1999); as a result, the investors was reluctant to invest for the future development considering high cost to develop brands, the slow growth rate and return on investment (Bezos & Risher, 2000, p.2).
However, this company incorporated in the NASDAQ stock exchange in 1997, and started to diversify its business by introducing other new products like DVD, CDs, MP3 format, Kindle, software etc. from the fiscal year 1999 (Kha, 2000; Nitschmann, Quilter-Whitley & Wegner, 2005; and Bezos & Risher, 2000, p.2).
In addition, the net sales revenue of this firm has increased dramatically after diversification of its business though recession hits this industry in 2009 and slowdown its growth, for instance, its net sales revenue was $34,204 million and $48,077.0 million in 2010 and 2011 respectively and annual growth rate was 39.6% and 40.6% in 2010 and 2011 accordingly (Amazon, 2011).
According to the annual report 2011 of Amazon.com, it implements its strategy properly to offer a secure, enjoyable shopping experience online; so, it experienced success while North America sales growth rate was 43%, 46%, and 25% in 2011, 2010, and 2009; on the other hand, the International sales growth rate was 38%, 33%, and 31% in 2011, 2010, and 2009.
Table 1: About Amazon.com.
External Analysis
Discussions of external environments give Amazon.com with the information necessary to improve its strategic intent and strategic goal, which influence policy formulation and execution actions as external environment affects growth and profitability level of the company.
General Environmental Analysis
The general environments are basics in society that influence the industry of which a company operates though companies cannot control all situations directly, but it should consider to understand the characteristics of the industry to adopt suitable strategies to compete efficiently (Demir, Ikhimokpa & Nguyen, 2006; Porter, 2004; Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001 and Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008).
Demographic Segment
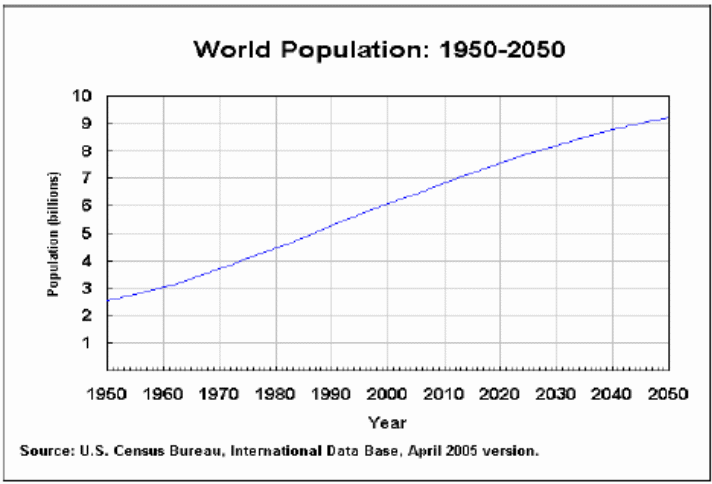
This part directly affects the online retail industry as it provides some indications where growth will occur; however, the target market of this industry spread out all over the world, so, it should required to consider the world population to assess the prospect of the business in the future. However, the world population is rising at a significant rate and the following figure shows actual position –
Economic Segment
The people of developed countries have more facilities to purchase products using internet while customers of developing countries can also be potential market for the industry as number of internet users are increasing who would like to take the facilities of advance technology, for instance, China, Bangladesh and India can be potential market within very short period.
Political/ Legal Segment
The online retail industry is complex since it involves many factors those affects on the profitability level of this industry, such as, data protection policy, taxation policy, entry barriers, regulation of the foreign governments, war and terrorism, unfriendly political relation between the governments, unstable political situation in many countries, claims from customers, shipping agents, brokers, privacy policy, and so on.
Socio-Cultural Segment
The social and cultural issues play an imperative role in the running of the industry; the fact the society and cultural issues vary all over the world indicates that the sales of the industry varies in different countries.
Whilst the sales remain highest in American and European context, the increasing developments of progressive societies like China, India, Bangladesh, and Brazil means rising sales in those areas. Conversely, sales in conservative and outmoded societies, like a few Asian, African, and Arab world countries remain few.
Technological Segment
Technology plays vital role in this industry because the process of the business, transaction system, order processing, supply chain management, development of customer relationship and brand awareness, competitive position, ensure quick and quality service, and all other important issues depend on technology.
Global Segment
The global market size is gradually increasing with rising access of Internet and IT amenities; therefore, the prospect of the industry is high.
Summary of General Environment Analysis
Main political factors such as taxation policy of the government of foreign countries, the strength of separate countries’ financial position in different years, legal actions taken by the competitors, adoption of advance technology, purchasing power of the customers, and the appearance of new technologies are the key examples of situations in the external environment those affect this company.
Driving Forces
Diacon & Donici (2011, p.2), IMAP (2012, p.5) and Nielsen (2008, p.2) argued that online retail industry of the developing countries has bright prospects considering population density and numbers of internet users.
At the same time, Diacon & Donici (2011, p.2) stated that technology is the most significant driving forces in online retail industry because it changes rapidly, which cam adversely affect on the companies in this sector while buyers always want better, simpler, along with more user friendly technology.
The shopping trends of the customers have changed for the recessionary impact though it needs less effort and save time of the buyers; as a result, the customers of international market would like to avoid online purchase to save shipping expense (Diacon & Donici (2011, p.1).
Industry Analysis
Industry analysis will mainly focus on Porter’s five forces model, competition, structure of the industry, market size, rivalry between established competitors, impact of growth on profitability, demand, key success factors etc.
Description of the Industry
IMAP (2012, p.5) reported that Internet users growth rate does not demonstrate a direct connection with online retail market growth, but it has influence to change of customer behavior; on the other hand, Nielsen (2008) stated that growth of this industry depends on the number of internet users though only 10% of total users (627 million) purchase over the Internet.
However, the report IMAP (2012, p.5) provided number of internet users while Nielsen (2008) concentrated on the change of customer behavior by showing total internet users along with online purchasers in global context, which shows in the following tables –
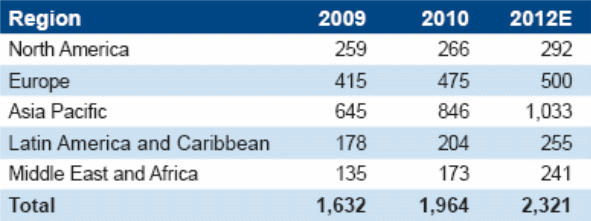
However, PRWeb (2012) analyzed the data of IBIS World (2012) to describe this industry; however, IBIS World (2012) categorized this industry into ten main goods categories, such as, the Online Cars & Automotive Goods, Clothing & Accessories; Electronics, Food & Beverage, Furniture & Furnishings, Health & Beauty products, Books & Music, Stationery and Online Travel & Accommodation.
Industry Dominant Economic Features
It includes many characteristics, for instance, market size and growth rate, existence of potential competitors and the relationship between them, differentiation, innovation, supply chain management, development of technology, demand situation, scope of vertical expansion, financial perspectives, and so on (Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; Kotler & Armstrong, 2006 and Porter, 2004).
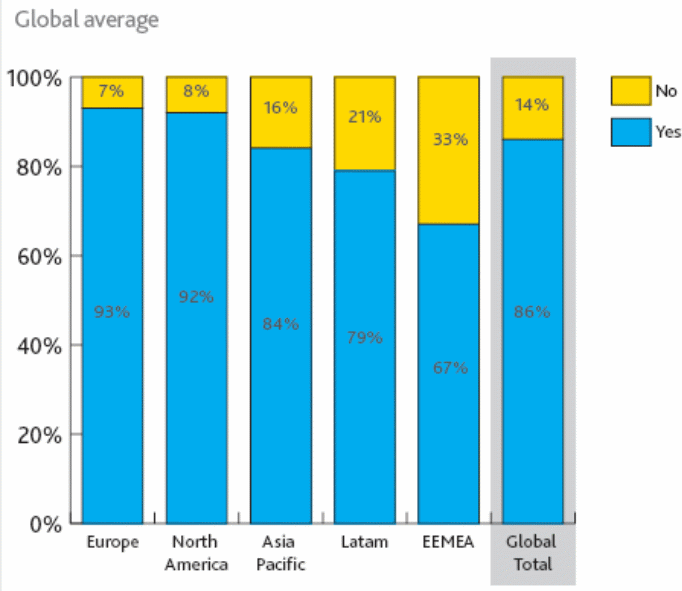
However, online purchasers would like to save their time and efforts; therefore, more than 65% US-based Web buyers purchase the products online; in addition, IMAP (2012, p.6) provided data of Datamonitor by stating that global online retail sales are expected to become more than $778.60 billion by the fiscal year 2014.
The companies of this industry mainly used online stores as their operational format and there are many companies in this sector, such as, Amerisourcebergen Corp, Costco Wholesale Corp, Aldi GmBh & co OHG, Best Buy Co, Inc. Lowe’s Companies, Woolworths Ltd., Finatis S.A. (France), Wal-Mart, Tesco, Amazon.com, eBay Inc..
Market Size
IMAP (2012, p.5) stated that global financial crisis has changed the purchasing power and willingness of the customers, which declined the retail sales by 3.70% in 2009 to $13.90 trillion; on the other hand, online retail sales grew by 14.5% in 2009 to reach $348.60 billion in spite of recession.
However, IMAP (2012, p.5) reported that electronics was the biggest sector in global online retail sales, holding more than 22.6% market share of this industry; on the other hand, the marketers of other products also drive to introduce online purchasing system to increase sales revenue.
However, IBIS World (2012) stated that the market size of the online retail industry is boosting gradually since the number of internet users is increasing, for instance, about 100 million customers of the US market purchase products in this way each year and online retail spending reached $36.3 billion for the quarter in this country.
At the same time, IBIS World (2012) reported that online retail profits would boost at an average yearly rate of 9.60% to total $310.10 billion among this profits about 9.40% to total $291.90 billion would contributed by the US customers.
Market Growth Rate
According to the report of IMAP (2012, p.5), the growth rate of online retail sector is satisfactory, but still it occupies only 2.5% of total global retail sales; however, the United States is the largest market for online retail with 37.20% market share and the customer spent $129.80 billion and $130.1 billion in 2008 and 2009 respectively.
However, Wauters (2011) stated that the US and other European countries’ online retail market grow rapidly; he further added that European countries are trying to experience annual growth by 10% within the fiscal year 2010 to 2015, though actual growth in these regions were more than 18% in 2009 and 13% in 2010.
However, the following figure shows the online retail industry growth rate comparing with traditional retail industry and the subsequent table provides the growth rate of the US market for 2010 and 2011 –
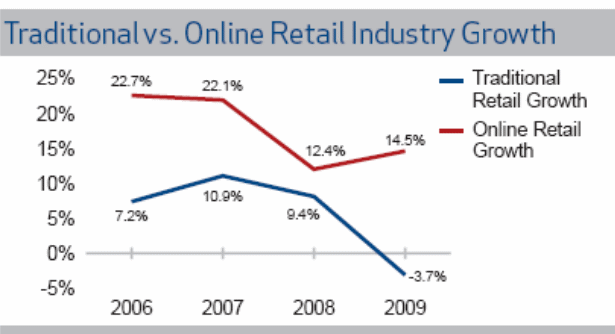
Table 2: Online retail industry growth. Source: IMAP (2012, p.10).
Table 3: the growth rate of online retail industry in the US market for 2010 and 2011. Source: ComScore (2011).
Competition Analysis
Morillon (2010, p.1) stated that online retail industry has spread on the global mainstream demand while the customers of the western countries spend at least two hours every day; therefore, the new companies is entering this sector to capture new market with new or existing product and service line.
For instance, Amazon.com, ebay, Facebook, Google and other companies become popular and occupied market shares of old brands like Microsoft, IBM, HP or Apple etc. (Morillon, 2010, p.1); however, the following figure shows the search engines market shares worldwide –
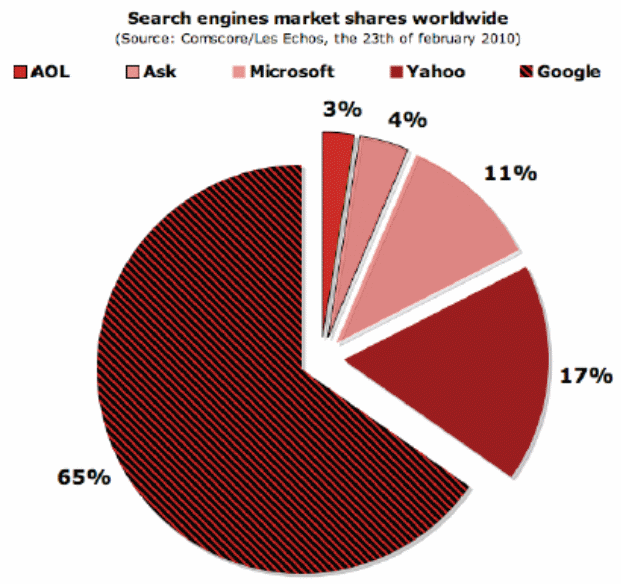
Industry Competitors
Major competitors in the online bookstore market are Amazon.com, Target.com and Barnes & Noble; however, key players in the hardware and software markets are Microsoft, IBM, Dell, HP or Apple; in addition, main rivals in the consumer electronic products are Apple, Amazon.com, Sony, Samsung, etc.
However, this industry is highly diversified and competitive, where the competitors start with small product line drive to enter market with new products and most of case the companies vertically integrated; however, the following figure compares of profits of the competitors for 2000 to 2008 –
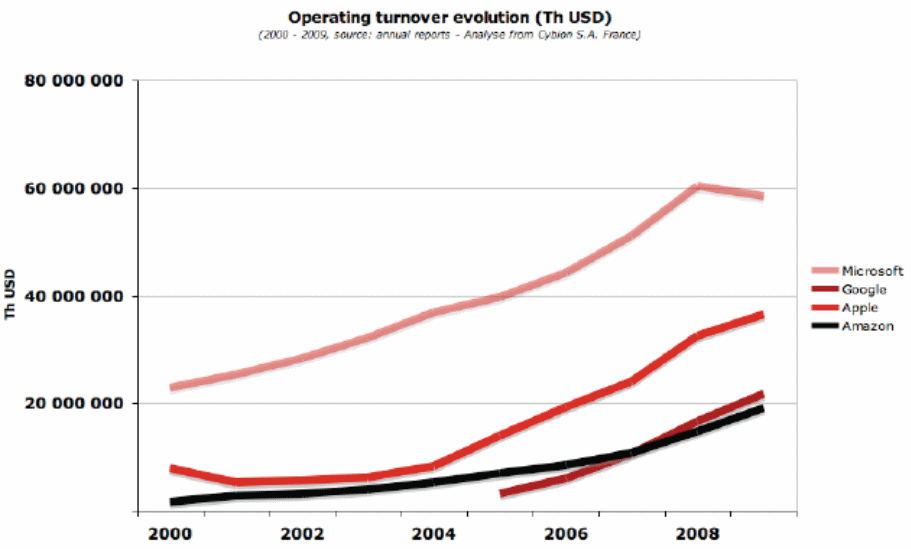
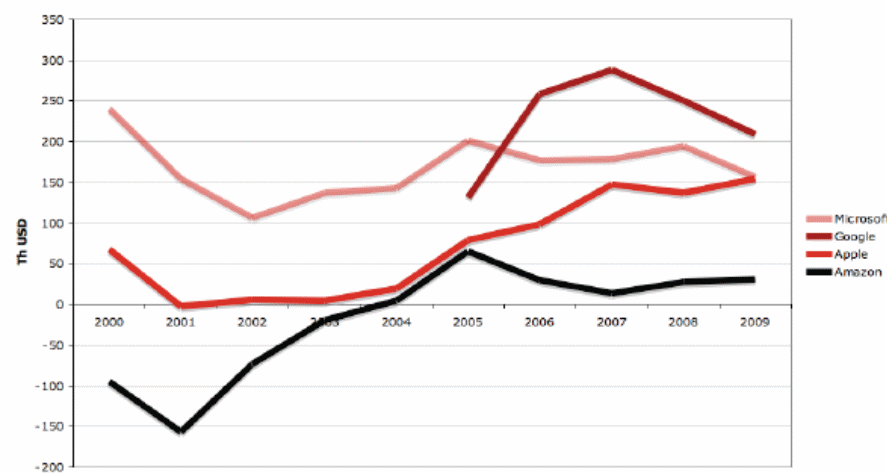
Rivals Anticipated Strategic Moves
In this online retail industry, there are many influential factors those affects on the capital expenditures and environmental regulations; for instance, violation of data protection acts bring unfortunate situation for the customers as well as for the companies.
Most of the companies in this industry follow merger and acquisition strategies to enter new market and share technologies along with resources to become major player in the market, for instance, Amazon.com acquired numbers of companies like Joyo.com, dpreview.com, Junglee.com, Audible.com, Fabric.com etc. and B&N has acquired the Tikatok and Fictionwise, which has leading market position in the e-Book
Summary of Competitive Analysis
The online retail industry will become more popular in the western countries as well as in the developing countries in Asia, because a number of internet users are increasing who want to lead simple life; therefore, new companies would like to start business with limited resources and old companies would penetrate new zone.
At the same time, the competitors must observe unparallel competition because of adaptation of advantage technology by few companies; in addition, the trends to acquire companies to share resources of other companies would be popular strategy to the rivals.
Key Success Factors
The key success factors of the industry include the benefit of having the whole world as a market, without any need to set up business in different countries. Rising number of people now choose to shop online rather visiting outside, which is another success factor of the industry; moreover, other success factors include convenience, efficiency, less costly and quick services.
Industry Trends
Netimperative (2009) pointed out ten trends of this industry and stated that online retail industry experienced 13% growth in 2009 but it faced post recessionary impact; therefore, it becomes essential factor for the market players to identify the trends of their customers and change the customer behavior to save the industry from global financial crisis.
However, most of the companies in this industry make prior research to start business, for instance, the CEO of Amazon highly observed customer decision-making process and their demand sector to introduce online service, which gave him the chance to achieve competitive benefits over rivals and experience first mover advantages.
In this context, Netimperative (2009) identified trends including change business strategies for financial downturn, experience barriers to penetrate new market, hard to attract new customers, increase demand and expectation of the customers, boost loyal customers, and consider monetizing web sites by linking with third parties to reach target market.
Five Forces Analysis
The popular five forces model of competition has developed by Michael E. Porter and it is now using as a significant management tool for evaluating a firm’s industrial formulation in strategic procedures and this model generally provides an insight through which an organization can develop such strategies (Porter, 2004; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; and Kotler & Armstrong, 2006).
Porter has analyzed those five factors, which format each industry and its related market that indicates the competitive intensity along with the potential profitability and magnetism of that industry; so, companies can modify important criteria as this model deals with the dynamic factors of an industry; however, the following figure demonstrates the Porter five forces model for this industry –
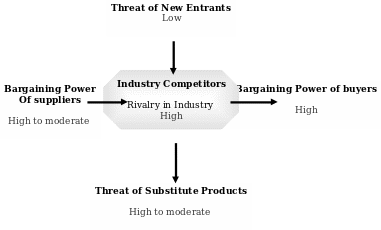
Threat of New Entrants
Porter (2004) stated that the existing players in the market are not the only threatening factor for the company, but the potential newcomers can also create competitive challenges in the free market economy, and it is very common phenomenon that more and more firms will penetrate new market to gaining competitive benefits.
However, the threats of new entrants is very low in online retail industry because of number of factors such as need strong supply chain management system, advance technology to manage different system, require highly efficient human resources, most importantly need huge investment to penetrate this industry with large products and service range.
At the same time, the entry barriers differ for several factors, for instance, the company of developed countries would face comparatively less problems if the entrepreneurs able to arrange fund and can use this fund properly to adopt technology along with other activities; however, the companies of developing countries has to face more legal barriers to penetrate new markets.
On the other hand, it is difficult for the new companies to gain competitive advantages, as it should require sufficient knowledge about specialized product management and supply-chain techniques; in addition, it should require large marketing budgets to build brand and create customer base, which make it very difficult for the new entrants to sustain into this industry.
However, Amazon.com and Apple along with other competitors in this industry will enjoy the first mover advantage, which give competitive advantage over the new entrants; on the other hand, new companies have to suffer numbers of entry barriers in the online retail industry (Nitschmann, Quilter-Whitley & Wegner, 2005, p.11).
Power of Suppliers
Most of the companies in this industry are highly diversified; therefore, these firms need to maintain good relationship with the suppliers considering the fact that few suppliers are reliable for ongoing servicing of merchandise and content, supplies of books and other technical instruments.
At the same time, the firms of this industry concentrate on this issue more carefully in order to avoid unnecessary delay to deliver products to the customers, and maintain efficient management system as contract with suppliers can frustrate for several reason, such as, bankruptcies of the suppliers for financial downturn, or other natural crisis.
According to the above figure, the bargaining power of the suppliers is high to moderate because of many reasons, for instance, relationship with licensors (those responsible for sourcing, services, manufacturing), government policy of the international market, and instability of the price of raw materials, global economic downturn, and changes of shipping costs and transportation facilities and so on.
In this situation, Amazon (2011, p.14) stated that suppliers are the most important factors to this company as they can create serious problem for the company; thus, it would not like to make long-term agreement with the suppliers to take their products and services and to increase credit limit.
Power of Buyers
As there are many companies exist in this industry, the bargaining power of the buyers is comparatively high; however, this power depends on a number of issues, such as, price of the products, quality of services, the switching off costs, available service providers purchasing power of the customers, recession, and so on.
However, the bargaining power of the consumers also vary considering buyer volume, brand identity, quality, decision making policy of the customers, substitute products, pull-through and so on (Mirow, 2005, p.10; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; Kotler & Armstrong, 2006; and Porter, 2004).
On the other hand, this is highly competitive industry where the companies always like to change strategies to attract more customers while pricing strategy of the company plays vital role to attract more customers and create loyal customer base; therefore, the switching off costs become low automatically, which increase the power of the buyers.
For instance, Amazon.com, Border, B&N and other relevant companies offer similar products particularly books and education related products at the same price level for which it gets easier for the customers to choose their preferred piece of item from any one of them; however, This leaves the buyer with high price sensitivity (Nitschmann, Quilter-Whitley & Wegner, 2005, p.12).
As a result, buyers played a dominant role in determining pricing strategies; however, Amazon provides an alternative for the same products at the same or cheaper prices (Amazon, 2010; and Nitschmann, Quilter-Whitley & Wegner, 2005, p.12).
Threats of substitute products
Substitutes products and services mean those products, which are being used or will be used in future to meet the same purpose as met by the identified product manufactured in other industries; however, the price of the substitutes influence the demand of the product of branded company (Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008 and Porter, 2004).
Existence of close alternative product retrains a company to boost its price in the industry; however, there are several factors, which determine the threat of substitutes, for instance, customer loyalty, customer intimacy, switching costs, position of the manufactures, performance value of the substitute and recent trend (Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; and Porter, 2004).
Amazon.com deals with wide range of products and services; therefore, all the products accessible by this company need to compete with various similar products from the rivals; such as, the substitutes of books are easily available from local book suppliers and international competitors like B&N and Books-A-Million Inc, and Borders Group provide similar service (Nitschmann, Quilter-Whitley & Wegner, 2005, p.11).
At the same time, Amazon.com also offers kindle, DVDs, CDs, MP3 downloads, video games, and other consumer electronic products and in this sector, there exist a number of substitutes those serve similar purpose, for instance, nowadays smart mobile phones can serve above mentioned services besides telecommunication services (Amazon, 2011; and Amazon, 2010).
However, there are too many substitutes but the customers like to purchase quality products and most of them mainly consider the brand name along with cost efficiency; therefore, the threats of substitutes is comparatively high because when book is concern the readers firstly think about the content and writer of the books, but not think about the company.
Intensity of rivalry
According to the Porter’s five forces model, this force explains the competitive strength among the existing firms running their operations within the industry; however, the conventional economic point of view, higher competition among the firms tends to decrease profitability (Porter, 2004; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; Kotler & Armstrong, 2006; and Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001).
In addition, it is universal fact that the firms try to gain a competitive advantage over other competitors and the intensity of the desired competition generally differs from industry to industry; however, many firms operating in the same industry raise competitive pressure as they target similar customers (Porter, 2004; Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; and Kotler & Armstrong, 2006).
Moreover, the intensity of rivalry is depend on several factors , such as, market expansion, market share captured by the major players, Higher fixed costs in terms of economies of scale, low switching expenses, branding, strategic risks, cultural, philosophical, and historical diversity also intensify rivalry (Johnson, Seholes & Whittington, 2008; and Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson, 2001; and Kotler & Armstrong, 2006).
However, the online retail industry is extremely competitive due to the existence of a large number of companies with plentiful offerings, such as, Books-A-Million Inc, Borders Group Inc, Sony, Kobo Books, Google, Apple, B&B, Samsung, Overstock.com and so on; moreover, there are many small and large companies at both national and international market; however, following figure shows some statistics–
Table 5: Comparison between Performances of Major Competitors.
The above table compares the performance of the competitors those offer online retail service (particularly bookstores); however, this table identifies the key problem, which arises from the presence of such an intense level of competition and recognizes that because of so many other bookstores, the annual profit margin of other competitors get lower than expectations. However, the following figure compares the cash flows of the major competitors –
Table 6: Comparison between cash flows of Major Competitors.
Summary of Industry Analysis
From the discussion of porter five forces model foe the online retail industry, it can be said that the threats of new entrants is low, but rivalry among existing firms are very high as penetrate in new market is difficult for the new companies and there are too many large competitors offer similar services in the online retail industry.
On the other hand, this report also focused that the bargaining power of the buyers depends on several factors where decision-making process of the customers, global economic downturn, reduce purchasing power, brand image of the existing companies, switching off costs and so on; however, the power of the customers in this industry is comparatively high.
In addition, this paper pointed out that the bargaining power of the suppliers are moderate to high and the quality of the service and efficient delivery depend on the suppliers; at the same time, the players of this industry need to concentrate on the risk of substitute products.
Internal Analysis
This report will include internal factors of Amazon.com those influence the company to gain competitive advantage and increase profit margin, such as, it will include the mission of the company, structure of the business, strategies of for the future development, and internal strengths and weaknesses.
However, there are too many positive internal factors those will focus on the internal strengths analysis section; however, these are brand awareness, human resources, sales volume, experience, technology, financial position, product line and customer base, innovation, corporate governance, supply chain management and so on.
At the same time, this paper will discuss weaknesses of this company including excessive operating expenses, negative impact of merger and acquisition, affect of high diversification of the business, costs of infrastructure development plants and special offers to attract more customers.
Organizational Analysis
Robbins & Judge (2004) stated that organizational analysis should include leadership approach, human resource management, strategic planning and implementation process, return on investment and economics of scale, customer relationship management, process management, organizational structure, etc. However, the following figure demonstrates it moiré clearly –
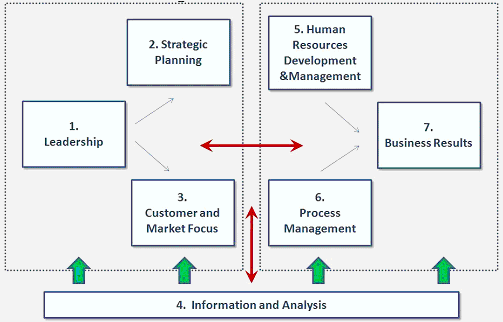
Corporate Mission
The corporate mission of Amazon.com is to become World’s most customer centric company; to develop a place where customers can come to find and discover anything they would like to purchase online.
Products and Services
According to Amazon (2010), Amazon.com is a platform of almost 110,000 books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books; moreover, it has modernized the physical book market with online downloadable e-books and has introduced an upgraded service called Kindle; it also offers an advertising service that facilitates the sellers to promote their products, allowing them to upload their catalog and set cost-per-click rates.
On the other hand, Amazon (2011) has suggested that the business is highly diversified, and is undertaking many differentiation strategies on the products and services; for example, it offers a range of facilities, which includes Amazon- Studios, Alexa- Internet, A2Z-Development, A9.com, Amazon.com, Amazon Web- Services, LoveFilm, Zappos.com, Woot, Junglee.com, Audible.com, Endless.com, IMDb, and many other essential services.
Leadership
According to Deutschman (2007), the leadership style of Jeff Bezos is not entirely democratic; however, he pretty much leaves the workers alone unless they are confused, and in case of confusion, appointed proficient moderators solves the problem and he never meet the employees; on the other hand, he is both stubborn and flexible, obsessed about consumers, not co-workers, and simpleminded.
In addition, Deutschman (2007) also added that Jeff Bezos employ people in the organization extremely cautiously, pay no attention to other people’s advices, never pursues the short- term source of money, and does not communicate his plans too often.
Organizational Culture
Employee retention is one of the key challenges for the company while brilliant employees play vital role for the business expansion; however, Amazon always recruits talented and highly qualified staff considering organizational culture to get highest outcomes (ILR School, 2012).
Structure
Anderson & Palma (2005) argued that organizational structure is one of the most important factors to implement the Multi-product Strategies and this structure is different from the single product firms as multi-product firms using the Multidivisional (M-form) Structure, which has also three variations; however, from the product and service line of Amazon, it can assume that it is a Multi-product firm.
However, the organizational chart of Amazon.com is complicated and different from single product firms because this company has separate departments for business operations in global market; however, the following figure shows the organizational structure of Amazon –
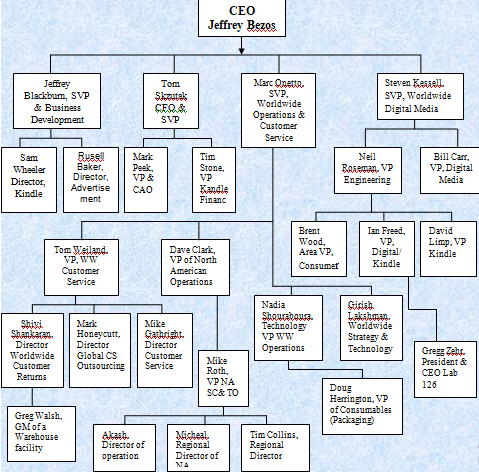
According to the annual report and the above figure, Jeffrey Bezos is the President, CEO, and Chairman of the Board of this company; however, he established this company in 1994 and started online business from 1995.
Additionally, he is responsible to control the management system and other board members; however, Jeffrey Blackburn is the Senior Vice President (SVP) who manage advertisement department and Kindle department by two directors, Tom-Skzutak is chief executive officer and SVP maintains finance department, Steven Kessell (SVP) controls Worldwide Digital Media and manages his function by two departments (Amazon, 2011).
Moreover, the above figure described that Marc Onetto is also senior vice president of this company who is responsible for global customer service and he needs to control four separate departments those maintained by four different directors (Tom Weiland, Dave Clark, Nadia Shouraboura, & Girish Lakshman).
Strategy
Innovation: Johnson (2010) stated there is no fixed time frame to structure a successful company while Amazon.com built excellent brand image within 20 years of its operation; however, he argued that innovation of product and service line is one of the main force to bring high-profile success for this company by meeting the demand of both buyers and sellers.
On the other hand, Amazon.com always gives highest efforts to ensure customer satisfaction by providing quality products and services to four groups of customers; however, to ensure quality and demand to identify a new area of potential growth, the marketers of this company collect information of the market and contact with customers using IT community.
At the same time, Johnson (2010) further pointed out that it should not invest in new business sector as it has not long experience; however, this company successfully introduced several products and services, such as, the Kindle e-book reader (it sold an estimated 500,000.0 Kindles in 2007), Amazon’s web-services platform and so on.
However, Amazon.com has experienced huge success in global market because of innovate service, quality, price, management plan, and technology; therefore, its growth rate is outstanding, for instance, in 2011 sales growth rate of this company was 40.6% and in 2010 this rate was 39.6%;
Product line and customer base: Muller (2007) argued that Amazon is a huge global brand, which familiar for two key grounds, such as, it was an early exploiter of online technologies for e-commerce and was one of the unique dotcoms and the first online retailers; thus, it was able to develop a large customer base (more than 30 million customers).
According to the annual report 2011 of Amazon.com, it has four main customer groups and a numbers of subsidiaries; however, it brand image has developed with books, but it has diversified its business and introduced different services for the customers including electronics, toys, games and so on
Human Resources: This Company has more than 56,200 full-time and part-time employees along with independent contractors and temporary personnel who are working to increase profits and to overcome any challenge in this competitive online retail industry; however, recruitment of the number of employees is depend on the seasonal factors as some times the company has to deal with large orders.
However, it is prime duty of the employees of Amazon to serve the company with their highest effort and integrity to increase loyal customer base in global market; in addition, the experience and knowledge of the staff could assist the company to increase its sales volume by implementing strategies (Amazon, 2011, p.4; ILR School, 2012).
Summary of Organizational Analysis
From the above discussion, it can be said that the management efficiently control the companies and take right decision to improve the performance, such as- innovation and expansion strategies are main influential factors of its success.
Analysis of Firm Resources
It will include tangible and intangible resources, capabilities, Core Competencies and Sustainable Advantages, etc.
Tangible Resources
Johnson, Seholes & Whittington (2008), Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson (2001) and Kotler & Armstrong (2006) stated that tangible resources mainly include physical assets, financial and human resources; however, physical assets include constructions, property, equipment, furniture, leasehold improvements, machines, fixtures, product capacity and so on.
In addition, return on capital employed mainly determined by the financial resources; on the other hand, sales per worker determined by the total workforce employed and their productivity;
Summary of Firms Resources
Intangible assets include knowledge, ideas, capacity for innovation, goodwill, etc.
Table 7: Intangible assets of Amazon.com. Source: Amazon (2011).
Capabilities
Amazon.com is renowned and very successful in its showcase of almost 110,000 books, magazines, newspapers and e-books; however, it restructured the physical book market with online downloadable e-books and provided online book-selling service, which help the company to create brand image and develop large customer base in this industry.
According to the annual report 2011 of Amazon.com, diversification of the business from online book selling to other products was one of the prime factors to become successful within short period of its operation and it has capability to target developing countries by offering lower price.
Core Competencies and Sustainable Advantages
Summary of Firms Resources
This part divided its resources into two groups where fixed assets described in tangible assets and goodwill, and knowledge analyze in intangible assets.
Financial Analysis
The following table shows present financial position of the company –
Table 9: Financial Overview 2009 to 2011 of Amazon.com.
Profitability Analysis
Current ratio
Table 10: Working Capital and Current Ratio analysis of Amazon.com.
Since current ratio illustrates the margin of safety or cushion reachable to the creditors, it is a familiar and swift evaluation of the liquidity of the corporations; moreover, it is an index for Amazon’s financial constancy and practical solvency and a directory of the strength of its working capital.
As demonstrated in the table above, from 2009 to 2011, there has been an unexpected decrease in the current ratio of Amazon (1.3 in 2009 and 2010 consecutively, and 1.17 in 2011).
Even though the current ratio was stable in 2010, it fell in 2011; it is notable that this kind of fall in the ratio demonstrates the deterioration of the liquidity position of the business, and it is significant that the liquidity position of Amazon has weakened over the past financial year.
On the other hand, if there was an enhancement in the current ratio, it was very likely that the liquidity position of this online business would fortify with time; however, as the liquidity position of Amazon is deteriorating, it is necessary for the company to concentrate on this issue before it is likely to affect the company more severely.
Table 11: Working Capital and Current Ratio analysis of Apple Inc.
As shown in the table, there has been a gradual decrease in the current ratio of the company from 2010. The ratio increased from 2.641140745 in 2008 to 2.742482183 in 2009, and then suddenly started to diminish from 2010 with a figure of 2.011292346 and finally to 1.931886381 in 2011; as this kind of fall in the ratio demonstrates deterioration of liquidity position of the business; it is notable that the liquidity position of Apple has weakened over these years.
This fall in the current ratio of the company could be a result of the poor economic environment during the global financial downturn in 2010 and the continuation of its aftermath in 2011.
Gross Profit Margin
Table 12: Gross profit margin of Amazon.com.
The gross profit margin (GPM) is the proportion of turnover, which a corporation conserves following the direct-expenses linked to generating the materials traded throughout a certain phase; additionally, a mounting profit margin means that the corporation has good pricing strategy (it is proficient to lift prices with small or no consequence on sales) or that it possesses an intensifying productivity.
Nevertheless, as illustrated in the table above, there has been small decrease in the gross profit margin from 2009 to 2011, which was consecutively 22.5672202, 22.34533973, and 22.44108409 – decreasing gross profit margin could indicate that variable costs have risen while selling price has remained constant; it could also mean that Amazon has cut prices to make an augmentation in sales.
It is important to argue that even though in 2011, the gross profit margin has increased in contrast to the previous year’s gross profit margin; still it is quite lower than that of 2009.
Moreover, some analysts suggested that owing to the upcoming financial downturn and Euro zone crisis, it is unlikely that this gross profit margin will strengthen for the business in the next few years. Under this circumstance, it is wise for Amazon to re think about its existing business level strategies before the situation of the gross profit margin worsens.
Table 13: Gross profit margin of Apple Inc.
Although the gross profit margin of the Apple Inc has increased from 13,197 in 2008 to 17,222 in 2009, and 25,684 in 2010, all of a sudden, it fell again in 2011 to 20,516 – it is notable that a decrease in the GPM could specify that variable costs of Apple Inc have ascended while selling price has stayed unvarying.
The increase in the variable costs of Apple could be a result of increase in the number of highly paid temporary workers, rise in the price of raw materials, high inflation, or even a momentary rise of cost at any stage of the production process; however, it could also mean that Apple has cut prices to make rise in sales.
Acid test ratio
Table 14: Acid test ratio of Amazon.com,
Acid test ratio is a rigorous measuring device, which settles whether an enterprise has adequate short- term assets to cover its urgent liabilities without selling inventory; more essentially, the acid test ratio is much more arduous than the working capital ratio, chiefly for the reason that the working capital ratio permits the addition of inventory assets.
Moreover, it is stated that enterprises with acid test ratio of less than ‘one’ could not compensate their current liabilities and they must be viewed at with intense level of vigilance; in addition, if the acid test ratio is to a great extent inferior than the working capital ratio, it denotes that the current assets are exceedingly reliant on inventory.
As shown in the table above, from 2009 to 2011, there has been an appalling and gradual decline in the acid test ratio of Amazon (1.03 in 2009, 1.02 in 2010, and 0.84 in 2011 successively). As the acid test ratio had become less than one in 2011, it is apparent that Amazon could not compensate its current liabilities and it is ought to be dealt with intense level of watchfulness in order to avoid adverse impacts on the business as a whole.
Most importantly, it is necessary for the company to consider the various methods, which are applicable in such a condition for improving this ratio and lowering the latent risks very quickly.
Net Profit Margin
Table 15: Net profit margin of Amazon.com.
Net profit margin is one of the most essential factors for determining the position of the business currently in order to assess its overall performance in a year.
High net profit margin ratio demonstrates how successful the corporation is at changing sales into profit, and that the corporation is capitalizing on some competitive-advantage, which can give it some supplementary capability and suppleness throughout the difficult financial periods; conversely, low net margin means the firm is not generating enough sales or it is not keeping your operating-expenses under control.
It is quite surprising that for Amazon, throughout 2009, 2010, and 2011, the net profit margin has decreased so much that it took on a very low figure (4.61 in 2009 decreased to 4.11 in 2010, and finally to 1.8 in 2011).
Such a decline in the net profit margin ratio throughout the three stated financial years might point out cost binges, which necessitate competence development; in addition, the Amazon, having a low ratio, might need to take on debt to pay its expenses.
All these factors indicate that once again it is very much crucial for the company to seriously deal with developing its policies to enhance the annual turnovers; however, the company should also focus on the ways in which it will be able to lower down the costs of goods sold, which is quite high in case of Amazon.
Table 16: Net profit margin of Apple Inc.
From 2008 to 2011, this ratio has increased constantly in the case of Apple, showing an optimistic attribute for its operations as good net profit margin ratio demonstrates how victorious the business is at altering sales into returns, and that the business is exploiting some viable benefits, which could give it several added potentials during the complex fiscal phases.
In this context, such a gradual rise in the net profit margin of Apple Inc is greatly positive trait for the top management of the company in order to ensure a healthy business pose right after the recovery of the global financial downturn. The net profit margin of Apple rose from 23.86 in 2008 to 28.12 in 2009, and 28.42 in 2010, and finally to 30.86 in 2011.
Return on assets (ROA)
Table 17: Return on total assets of Amazon.com.
Return on assets is one of the major profitability-ratios that determine the sum of profit generated per dollar of assets owned; it also assesses corporations’ aptitude to create profits before leverage with assets, rather than utilizing leverage in form of shareholders-equity or other debt-liabilities; generally, the higher this figure is the more efficient the corporation is in exploiting its assets.
In one word, ROA is a meter of how lucrative a corporation is comparing to its total assets, and increasing ROA gives an idea that the firm is competently handling its assets to engender earnings; for Amazon, it is arguable that from 2009 to 2011, return on assets (ROA) of the company decreased consecutively from 8.17, and 7.48, to 3.41. Consequently, once again, in case of Amazon, this ratio is not quite attractive as well – this is because diminishing return on assets could denote to the fact that a definite signal of difficulty exists all- around the corner, particularly for growth businesses.
The consequence of this could be a financial-disaster for Amazon, because in recent years Amazon is determined to bring about sales growth – this normally leads to huge upfront investments in assets, comprising accounts-receivables, inventories, manufacturing tools, and conveniences; in such a condition, if a fall in demand occurs, Amazon cannot sell assets to pay bills because of over-invested assets.
Total assets turnover
Table 18: Total assets turnover of Amazon.com.
Total assets turnover ratio (TATR) is used to evaluate the company’s capability to exploit its own assets to engender sales and revenue; it is a sign to the company’s operational effectiveness, or capacity utilization; an inferior ratio indicates incompetent exploitation of assets, where as a comparatively higher ratio indicates rigorous use of assets by the company.
Total assets turnover of Amazon has risen successively from 1.77 and 1.82 to 1.9 in 2009, 2010, and 2011; it is notable that as total asset turnover considers a business’s competence in utilizing its assets in creating an augmentation in the income, the superior the figure is the better; consequently, here, this raising trend of the ratio will bring future-success.
Such an increasing drift of the total assets turnover ratio of Amazon in recent years points to the fact that the company is constantly trying to develop its economic efficiency along with time to achieve economies of scale through more smart use of the existing capital and competencies.
If this objective of the company becomes successful, it would be able to further lower its operational expenses in upcoming financial years and lessen the selling prices of its products to the final customers – this would induce a rising number of people to purchase Amazon’s products, raising its sales in turn.
Return on capital employed
Table 19: Return on capital employed of Amazon.com.
The Return on Capital Employed ratio (ROCE) is used to assess how much income the corporation earns from the investments, which the shareholders have given in the corporation; in addition, the ROCE also points to the fact that whether or not the corporation is generating sales and adequate turnovers in order to make the best utilization of its capital assets.
Corporations could boost ROCE by declining expenditures in order to amplify profit margin ratio, and even by purchasing raw materials and items at lowers-expenses; however, as demonstrated in the above table, the return on capital employed of Amazon has lowered gradually throughout the three financial years (which was 17.51 in 2009, 16.69 in 2010, and 8.3 in 2011 in succession).
Amazon should give enough emphasize over this area in order to prevent this factor from further deteriorating
Growth Analysis
The following table shows growth rate, operating profit margin, and tax rate, etc.
Table 20: Intangible assets of Amazon.com. Source: Growth analysis from Amazon (2011).
Valuation Analysis
Valuation Analysis (for 3 years 2009, 2010 & 2011)
Traditionally, concept of valuation analysis centered on three dynamics namely, i) income after interest and tax payment, ii) cash flows at the end of year and iii) discounted cash flow rates (interest rates), considering these forces there are two key objectives of valuation analysis.
They are a) assessment of market value of Amazon.com that assigned to review market needs, income capacity or return on market portfolio, expenses, as well as relevant costs.
Then again, b) valuation analysis recommends way of feasibility and sustainability that lucrative financial status along with quality. In the light of valuation concept and its objectives, following are the sequential phases of Amazon.com valuation analysis.
Value of Assets or FCFF (Free Cash Flow to the Firm) for the year of 2009, 2010 and 2011 (Amazon.com Inc. 2009, 2011)
From aforementioned calculation table it has identified that the Amazon has performed positive cash flow for 3 consecutive years but in 2011 amount of cash flow declined significantly where as in 2010 increased.
Return on Capital or Expected Growth Rate, g: growth rate of Amazon.com has calculated in following table for the year of 2009, 2010 and 2011. (Amazon.com Inc. 2009, 2011)
In case of growth rate or the return on capital, Amazon performed relatively best in 2011 due to its highest growth rate of 32.29%.
Cost of Capital, K
Cost of Debt, Kd: considering after tax payment, calculation of cost of debt is plotted following table for the year of 2009, 2010, 2011. (Amazon.com Inc. 2009, 2011)
Cost of Equity, Ke: in the light of CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model) calculation of cost of equity is plotted following table for the year of 2009, 2010, 2011. (Amazon.com Inc. 2009, 2011)
Calculation of Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC): here is the calculation table of WACC of Amazon for the year 2009, 2010 and 2011. (Amazon.com Inc. 2009, 2011)
From above table WACC of Amazon for the year 2009, 2010 and 2011, rather than 2009, 2010 and 2011 carried high WACC and for this reason, it can be pointed out that 2009 is the most profitable year for Amazon.
Terminal Value
At the end of 2011, Amazon executed poor performance because of big amount of negative terminal value.
Financial Strength Analysis
Debt Equity Ratio
Table 28: Debt Equity Ratio of Amazon.com
Source: Self generated
The above table demonstrates that in 2011, the debt equity ratio of Amazon was quite greater than the past two years; so, presently, its position is not quite strong in terms of debt equity ratio. Whilst in case of 2009, the debt equity ratio of Amazon was 1.63, in case of 2010, it increased to 1.74, and finally, in case of 2011, it took a more severe pace.
This ratio is an appraisal of corporation’s financial power projected by dividing its total liabilities by shareholders’ equity; it specifies what proportion of equity and debt the firm is using to finance its assets; a high ratio commonly denotes that a firm was antagonistic in financing growth with debt; so, this can result in volatile earnings because of additional interest-expense.
To help the company from deteriorating, and prevent unstable earnings due to added interest-expense, proper steps are required; for example, the company could stop to assertively finance its activities all the way through debt and as a result, it should pay interest on such financing.
Table 29: Debt Equity Ratio of Apple Inc
Source: Self generated
The debt equity ratio of Apple fell from 0.622 in 2008 to 0.501 in 2009, and then rose from 0.501 in 2009 to 0.573 in 2010, and at last fell again to 0.5437 in 2011. As stated earlier, a huge debt equity ratio usually signifies that a corporation was aggressive in funding expansion with liabilities; this in turn can cause impulsive income of Apple Inc; nevertheless; as Apple’s debt equity ratio has declined than the preceding financial year, its place has reinforced again.
It can be noted from the table above that the in 2008, Apple Inc was highly aggressive in funding expansion with liabilities, and as a result, the debt equity ratio of this year was the highest.
Even though, later on in the next year it was able to achieve the lowest debt equity ratio, it rose again in 2010 due to financing growth with debt. In 2011, although the figure was lower than the last year, it was still much higher than the 2009’s figure. All these things point to the fact the cash flow situation of Apple Inc is also not quite stable
Liabilities to assets ratio
Table 30: Liabilities to assets ratio of Amazon.com
Source: Self generated
The liabilities to assets ratio weakens whilst cash or account reachable balances shrink, devoid of an equivalent shrink in current-liabilities, or boost in a current liability devoid of an equivalent boost in cash or accounts reachable (for instance, cash spent to buy fixed assets, cash spent to give off a long- term debt, or cash spent to disburse dividends).
From 2009 to 2011, the liabilities to assets ratio rose respectively from 0.62 to 0.63 in 2010, and again from 0.63 to 0.69 in 2011; this shows that the liquidity ratio of Amazon is gradually getting worse than the previous two years.
As a resultant effect, it is very much important that the company’s strategy- makers consider the liquidity position of the corporation with extreme caution, as it needs further strengthening, without which the business position may face more troubles in near future.
To put simply, it is a ratio needed to calculate a business’s financial-risk by making sure exactly how much of the business’s assets have been financed by the debt; as a result of this, it is an extremely extensive ratio as it comprises both short and long- term debt in addition to every type of tangible and intangible assets
Table 31: Liabilities to assets ratio of Apple Inc
Source: Self generated
From 2008 to 2011, the liabilities to assets ratio of Apple Inc have diminished from 0.383566946 to 0.352219085; this shows that Apple’s liquidity ratio has abridged than the preceding financial year; screening the indication that the position of the company is currently in a better position than Amazon.
In terms of the liabilities to assets ratio of Apple Inc, the idea is clearly apparent that very low amount of the business’s assets have been financed by the debt; moreover, the current strategy makers of the company are emphasizing on the issue of additional intensification of all of its financial ratios.
Long-Term Debt to Assets Ratio
Table 32: Long-Term Debt to Assets Ratio of Amazon.com
Source: Self generated
It is notable that the long-term debt to assets ratio of Amazon has increased sequentially from 0.07 in 2009 and 2010 to 0.09 in 2011.
However, it is important to state that long-term debt to total asset ratio is the ratio, which demonstrates the economic condition of corporations and the corporations’ aptitude to confront each of its monetary necessities; most importantly, this ratio illustrates the proportion of a corporation’s assets, which are funded with lending and other fiscal necessities, which last over a fiscal year.
This means that decline in long-term debt to total asset ratio would signify that the corporation is running well, and is less reliant on debts for operational expenditure, trading-activities, and other business-needs, whilst a higher-ratio indicates that it is greatly significant to have good-income and stable cash-flow; so, it is necessary for Amazon to check debt-structure and verify its debt-capacity.
Long-Term Debt Ratio
Table 33: Long-Term Debt Ratio of Amazon.com
Source: Self generated
Long- term debt ratio shows the monetary leverage or authority of a corporation; in addition, it calculates what proportion of the general business assets are possessed by the equity and debt; the investors in debt favor this sort of ratio, as it assists them to identify what coverage is there at the time of bankruptcy.
The table above shows that the long-term debt ratio of the firm rose steadily from 2009 to 2011 (from 0.18 and 0.19 to 0.25); moreover, it is noticeable that as a firm with a higher ratio is considered riskier than one with a lower ratio, this seems to be a negative side of the business.
Management Efficiency Analysis
The CEO of this company Jeffrey Bezos had conduct market survey to assess customer demand and the position of the competitors, which influence the CEO to derive its operation in global market with diversified product line (Kha, 2000, p.89).
In addition, this company has enjoyed first mover advantage in this industry and it looked for new market that values its technological applications, for instance, the goal of the CEO was to reach internet users.
However, the CEO stated that it is easy for the competitors to reduce price; therefore, he tried to offer value added services, for example, the service of this company was faster than their competitors’ services and the customers wonder what value a virtual bookstore adds besides a small discount, which is another reason of its success (Kha, 2000, p.90).
At the same time, the aim of this company is to ensure safe and swift delivery and reduce the threat of rivals acquiring its suppliers; so, the leaders of this company has concentrated on making the operating model well-organized and reaching profitability by using its distribution in-house while retailers like Wal-Mart use third party logistics (Kha, 2000, p.90).
According to the view of the CEO of this company, distribution centers are equipped with the latest material-handling technologies including pick-to-light system to instruct the employees through the picking and packing procedures, maintain a pick profile for the fast-selling items, develops homegrown warehouse management system to gather information about velocity, length, turnover rate and so on (Kha, 2000, p.90).
Summary of Financial Analysis
The financial position of the business is not quite impressive; for example, the current ratio of Amazon was stable in 2010, but it fell in 2011, demonstrating the deterioration of the liquidity position of the business; moreover, from 2009 to 2011, there has been an appalling and gradual decline in the acid test ratio of Amazon as well.
On the other hand, from 2009 to 2011, there has been an awful decline in the acid test ratio, small decrease in the gross profit margin, decline in the net profit margin ratio throughout three years, increase in the debt equity ratio, rise in liabilities to assets ratio, decrease in ROA, rise in total assets turnover, and fall in ROCE. Moreover, there was an increase in the long-term debt to assets ratio and long-term debt ratio as well
SWOT Analysis of Amazon.com
Strengths
Brand Awareness: Strong brand awareness of Amazon.com is the key strength of this company as it has real influence on the global customers, which always help Amazon to introduce new services for the customers and increase demand of the products of this company to new customers (Amazon, 2010; & Johnson, 2010).
Sales Volume: According to the Annual report 2011 of Amazon, sales revenue from the products and services sales have boosted all over the world, which indicates this company follows effective strategies to compete in this competitive online retail market; however, the subsequent table shows total sales revenue of this company from products and services –
Table 1: Total sales revenue of Amazon.com.
Experience: Though it is an American multinational electronic commerce company established in 1994, but it is successfully operating its business in global market, diversified its business successfully, and gained experience in this sector to operate the business with strong brand image.
Technology: This is one of the most significant factors for Amazon.com, because the success of online retail market is extremely depends on the adaptation of technology with other strategies, for instance, Amazon requires to develop its products and services bearing in mind market demand and competitors’ effective actions.
At initial stage, this company has not strong customer base and the stakeholders were anxious considering annual financial statements, but now Amazon.com is one of the most influential market leader in online retail industry; consequently, to increase sales, the investors would invest large amount for technological advancement like CRM and IT sector to support its business strategies (Muller, 2007).
Financial position: on the other hand, financial position particularly profitability level of this company is outstanding, for instance, however, the following table demonstrates net profit of this company from products and services –
Table 34: Net income from operation of Amazon.com.
Corporate Governance: the Board of Directors of Amazon.com follow the section of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, and Securities Exchange Act 1934 to maintain corporate governance system with high degree of compliance with general norms of corporate practice; however, it also consider the rules of international law and the recommendations of the several reports;
Supply Chain Management: SCM of Amazon.com is outstanding to control the business in overseas market
Other: Forward going network and elimination of extra costs, availability of books with new edition and few rare books, and strong administrative control.
Weaknesses
Operating expenses: One of the main weak points of this company is high operating expense and it is increasing each year, which negatively impact on the profit margin of the company; however, the following table shows that cost of sales, marketing costs along with other costs is boost each year-
Table 35: Total operating expenses of Amazon.com.
Special offer: In order to increase sales revenue and customer base, and to compete with competitors, this company changes its strategies time-to-time and in some case it provides special offers like free shipping provisions, which increase costs up to $500 million; therefore, it adversely affect the total profits of the company.
Diversification of the business: According to the annual report 2011 and the study of Johnson (2010), Amazon is moderately diversified company, though it was developed its brand as the number one retailer for books; however, this strategy can confuse the customers and endanger its brands, which can reduce customer attention on the core business;
Rapid Expansion and Development Plant: According to the annual report 2011 of Amazon.com, this company is expanding business to provide products and services to the customers of all over the world by developing infrastructure to support its retail and services; however, it should require simultaneous change its management sectors, finance departments and other areas, which can strain internal administrative controls;
Merger and Acquisition: Merger with foreign companies could also create financial problems, as large investment is concern; however, it could demolish the image of Amazon.com particularly affect the originality of the products and services of this company;
Other: this company has faced many other problems including pricing and availability for all sorts of customers, relatively smaller budget for advertisement and promotion to compete with international competitors, high price of old-edition books and so on.
Opportunities
Joint venture: Amazon.com has the opportunity to enter new marker with new products and services in the foreign market by following different entry mode strategies; however, many large companies like Marks and Spencer (M&S) and others are interested to enter joint venture agreement with Amazon.com considering the brand image and financial performance of the company;
Market share: It has already addressed that the aim of this company is interested to increase market share and enter new markets particularly Asian and European markets, which influenced management to collaborate with Target, Toys-R-Us and the NBA; however, it entered in China by purchasing china’s largest online retailer Joyo.com and it was estimated about $75.0 million (£40.0 million).
Other: At the same time, it has the opportunity to provide quick customer service with high customer satisfaction, to build collaborations with the public sector to provide unique service and it has strong financial capabilities for further expansion in global market.
Threats
Competitors: The presence of large competitors in online retail industry are one of the key threats for Amazon.com while the market position of the competitors is strong enough, for instance, Barnes & Noble captured about twenty-five percent shares of the e-bookstore market in global context, and Apple’s operating profit margin is 33.87% whereas its only 1.79% for Amazon.com (Yahoo Finance, 2012).
In addition, it has both direct and indirect competitors or different sectors those provide similar services with their strong brand awareness and gain huge profits; according to the annual report 2011 (p.4), indirect competitors include media companies, web portals, web search engines; however, the subsequent table shows direct competitor comparison more elaborately –
Table 36: Direct Competitor Comparison. Source: Yahoo Finance (2012).
In addition, there are many small competitors those are offering similar products; therefore, some time customers fail to differentiate the brand from its competitors; however, it also increases price competition;
Global Financial Crisis: Amazon.com needs to consider the external financial risks to invest large fund in new projects in such economic condition and unstable global market; as a result, the management of this company should prepare an investment plan, which would forecast market risks and measure growth rate in case of future investment.
Recommendations
From the above discussion, it can be found that the total operating expenses increased per year though costs of good sale is related with the sales volume; however, total expense of this company has increased per year; for instance, its operating profit increased $14417.0 million from 2010 to 2011.
In this context, the management of Amazon.com should address this issue and need to reduce operating costs by cutting unnecessary expenses; moreover, it should change the suppliers if necessary though some suppliers are most important for the development of the company.
Recommendation 1
The entire paper has addressed that the growth rate of this industry decreased due to the adverse impact of global financial crisis; therefore, Amazon.com need to take initiatives to increase loyal customer base and attract new customer to save the company from recessionary impact;
Recommendation 2
Amazon.com earned 58% profits from North America and rest 42% profits from international market; therefore, this company should concentrate more on the global market to gain competitive advantage over competitors;
Recommendation 3
The figure “profit per employee evolution” shows that Apple had succeed in creating new profitable markets and Google is the most efficient company because it ears $209,000 per employees, Apple $157,00, and Amazon $31,000; this data indicates that profits from per employee is not satisfactory considering competitors’ profit margin. Thus, the company needs to develop the efficiency level of the employees and need to develop long-term strategic plan to find out some way to increase profits by using talents of the staff.
Reference List
Amazon. (2010). Annual Report 2010 of Amazon.com. Web.
Amazon. (2011). Annual Report 2011 of Amazon.com. Web.
Anderson, S. & Palma, A. (2005). Market Performance with Multiproduct Firms. Web.
Bezos, J. & Risher, D. (2000). Customer Fulfillment in the Digital Economy: Amazon.com E-tail Customer Fulfillment Networks Pioneer. Web.
Cogmap. (2011). Organizational Structure of Amazon.com. Web.
ComScore. (2011). comScore Reports $36.3 Billion in Q3 2011 U.S. Retail E-Commerce Spending, Up 13 Percent vs. Year Ago. Web.
Demir, K. Ikhimokpa, A. & Nguyen, D. (2006). Strategic Analysis. Web.
Deutschman. A. (2007). Inside the Mind of Jeff Bezos. Web.
Diacon, P. E. & Donici, A. N. (2011). E-Commerce across European Union. Web.
IBIS World. (2012). Online Retail in the US: Market Research Reports. Web.
ILR School (2012). Amazon.com: Hiring People Who Want to Build. Web.
IMAP. (2012). Retail Industry Global Report 2010. Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001). Strategic Management. (4th ed.). South-Western Thomson Learning.
Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2008). Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. (8th ed.). London: FT Prentrice Hall.
Johnson, M. W. (2010). Amazon’s Smart Innovation Strategy. Web.
Kha, L. (2000). Critical Success FActors for Business-to-Customer E-Business: Lessons from Amazon and Dell. Web.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G. (2006). Principles of Marketing. (11th ed.). Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Mirow, M. (2005) Strategies to Achieve Market Leadership: The Example of Amazon. Web.
Morillon, S. (2010). Google, Microsoft, Apple and Amazon: Financial analysis. Web.
Muller. T. (2007). Valuation Analysis: Apple vs Amazon. Web.
Netimperative. (2009). Ten online retail trends for the next decade. Web.
Nielsen. (2008). Online shopping takes off. Web.
Nitschmann, S. Quilter-Whitley, E. & Wegner, R. (2005). Barns & Nobel. Web.
Porter, M. E. (2004) Competitive Strategy. Export Edition. New York: The Free Press.
PRWeb. (2012). Online Retail Industries – e-Tailing Revenue Skyrockets as Consumers Empty their Virtual Purse. Web.
Robbins, P. S. & Judge, A. T. (2004). Organisational Behavior. (12th ed.). New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
Wauters, R. (2011). U.S. Online Retail Industry Could Be Worth $279 Billion in 2015. Web.
Yahoo Finance (2012). Direct Competitor Comparison. Web.