Mission, Vision, and Values
Vision and mission statements, as well as organizational values, not only can be regarded as integral parts of the corporate culture but also as indispensable components of strategic management. If used intelligently, they may contribute to the company’s sustainable growth and longevity.
According to Sherman (2017), one of the major attributes of success in strategic management is when the intended corporate behavior matches the actual one. Many examples are illustrating how the disconnection between the two impacted enterprises in a negative way. For instance, Lumber Liquidators states that they value safety and aim to deliver it in every organizational process, yet, some time ago, it was revealed that the company ships products exposed to toxic substances (Sherman, 2017).
As a result, of such revelations, customer loyalty and trust may significantly decrease and cause declines in profits. Despite a large number of unfortunate examples of inefficient value management, some companies can do it well. One of them is LEGO.
In his article, Sherman (2017) writes that about thirteen years ago, LEGO had been going through a period of decline in sales and product demand due to changes in the market and customer preferences. The company tried to improve the situation by diversifying the product range, but then things got worse instead − by offering too many products to consumers, LEGO deviated from its core values and mission. Nevertheless, the sales increased almost tenfold as soon as the organization started to move towards restoring its core values which include simplicity in the product line development and low-quality service. As Sherman (2017) observes, the given strategy allowed LEGO to increase customer appeal, improve employee commitment, and better financial performance.
The example of LEGO demonstrates that the connection between proclaimed vision, mission, and value statements and organizational behavior is important. Thus, to enhance performance, companies should, first of all, develop a clear understanding of what they are, what they aim to achieve, and why they want that. Moreover, they need to identify the criteria and standards which seem to be of primary significance, and then try to comply with them in everyday business activities and communicate them to stakeholders.
So what are the major benefits of having a clear mission and vision statements? Researchers suggest that they determine the company’s commitment to financial goals and long-term survival in the market, its identity, and the overall foundation for building competitive advantages, its value-adding capabilities, and the target population (Kofi Darbi, 2012). Overall, mission and vision define the orientation of the company in the market.
When speaking of corporate values, they allow aligning internal organizational resources with external social and economic demands. Overall, creation and conceptualization of values are two of the main strategic tasks of any leader − through these activities they can determine the fashion of organizational interactions with consumers and partners, and ensure a high level of stakeholders’ engagement. It is possible to say that corporate values may be aimed to address a small range of specific needs of a limited stakeholder group and be successful wherein. It all depends on the scope of operation and organizational purposes.
However, according to the core ideas proposed in the stakeholder theory, consideration of stakeholders’ interests and needs on the broader scale is much more beneficial for companies’ profitability and sustainability (Vidal, Berman, &Van Buren, 2015). Therefore, it is possible to say that by valuing social responsibility, innovation, and environmental protection, organizations may achieve greater success by increasing their ability to attract potential consumers.
External Environment: Technological Environment in Healthcare
Healthcare is considered to be one of the most slowly changing industries, yet it is associated with great potential for improvement (Quora, 2017). Technology may play a significant role in fostering favorable transformations in clinical settings. It may impact either customer service, practical skills of health providers, team communication, knowledge management, or the overall hospital environment. However, every change, especially of a structural and systematic character, requires significant efforts and investments, and, for this reason, many hospitals fail to embrace change or even do not try to do so. However, the benefits of integrating advanced technology in healthcare business are tremendous. In this essay, we will discuss some of them.
Nowadays, information and communication technology has become an intrinsic part of everyday life. According to Carr (2003), while during the 1970s-1980s information technology (IT) allowed managers to increase competitiveness and supported organizational growth, effectiveness, and efficiency, it now has become a commodity. It means that IT is no longer regarded as an innovation that helps companies to stand out among their competitors in the market and rather has become a necessary means of business maintenance and conduction.
Although infrastructural technologies are essential to the information and knowledge management and help to solve various managers’ and employees’ tasks, organizational leaders cannot expect that they will obtain opportunities for gaining competitive advantages once they have purchased an advanced IT equipment. Nowadays, the competitive advantages are developed and maintained by those who have a “superior insight into the use of new technology” (Carr, 2003, p. 43).
Nevertheless, appropriate implementation of IT and communication technology can impact hospitals’ performance in a positive way. For starters, it can contribute to greater cost efficiency. It is observed that “up to 50% of patients miss their scheduled appointments, costing clinics $150 billion a year” (Quora, 2017, par. 2). It is one of the main problems for clinical settings which can be addressed by using communication technology, e.g., automatic reminder text or online messages. This entails extra administrative and organizational work, but the results may be rewarding. The outcomes of technology use may include greater customer satisfaction and smaller volumes of financial loss due to missed appointments.
Technology may favorably impact the quality of service and medical practice by enhancing diagnostic procedures and practitioners’ skills, as well as allowing better doctor-patient connectivity due to innovative remote care opportunities and telemedicine (Szczerba, 2014). Just a relatively few hospitals carry out robotic-assisted surgeries or follow other most recent trends in biotechnology, pharmaceutics, etc. However, the most innovative and advanced settings are usually at the top of the competitor list in the industry. In fact, by implementing new ideas and technologies, such organizations help to change current views on healthcare and, in this way, bring positive changes to the world.
Microsoft CEO, Steve Ballmer (2009), states in his talk at Stanford University, that innovation supported by advanced technology is one of the major qualities of successful entrepreneurship and is a necessary aspect of modeling the world. While the majority of people only follow the course of development, an innovative entrepreneur thinks a step ahead. A dynamically changing environment prompts the need for change, and the main task is to forecast these needs for improvement and strive to achieve desirable changes. It is possible to say that the given assumption is also relevant to the healthcare business that is highly affected by the technological environment.
“Grow” Strategy vs. “Hold” Strategy: The US Fast Food Industry
Key Threats
Significant shifts in customer preferences: the preference of healthy yet convenient food options is the current trend that impacts product demand in the fast food and restaurant industry (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017).
High level of price-based competition: the US fast food market is now oversaturated, and the given factor motivates companies to cut prices to survive (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017).
The demand for high-quality customer service increases: nowadays, visitors value both the quality of food and the overall purchase and communication experience; therefore, companies need to invest in staff training and education (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017).
The industry performance largely depends on various external economic factors: per capita disposable income, consumer spending, and consumer confidence largely affect product demand and sales; to mitigate these threats, organizations should adjust pricing policies to consumer demands and purchase abilities.
Key Opportunities
Product diversification: nowadays, health-conscious consumers represent the major group of potential customers; the shift in consumers’ preferences provides the opportunity for fast food companies to target these consumers and increase profits by diversifying the current product range and offering some healthy food options (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017).
Investment in technology: it can contribute to the increase in employee productivity by improving the speed and quality of service (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017).
Entry into new international markets: the orientation to international expansion is often included in the long-term strategies of fast food companies (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017); entering a new market allows businesses to generate multiple benefits such as access to new customer groups, increase in exploitation of organizational core competencies, decrease and spread of financial risks, and achievement of cost-efficiency.
Recommendations
The analysis of the industry by using the GE/McKinsey Matrix reveals that it is associated with high growth potential. The attractiveness of the fast-food industry can be defined as moderate as it allows investing in new segments (i.e., healthy and diet food) and improve organizational profitability by increasing productivity. Thus, not only may the company defend its current strengths in this environment but also develop the capacity to outperform competitors.
In combination with the organization’s current competencies and business advantages, the identified environmental factors may facilitate its sustainable growth. For this reason, a more aggressive strategy can be recommended for the client.
Since the US fast food market provides a slow-growth environment for companies (Fast Food Restaurants in the US, 2017), the Model of Grand Strategy Clusters suggests the organization implement the following strategic moves: concentric diversification, conglomerate diversification, and joint venturing. Concentric diversification implies the development of new products which will be thematically and contextually related to the current organizational product range.
This strategy will help the company to target new customer groups without deviating from its current brand vision and image. Conglomerate diversification and joint ventures are the two strategies for the expansion of business in both domestic and international markets. Conglomerate diversification means the acquisition of enterprises based on their financial performance, while the joint venture implies the establishment of synergies with other businesses.
It is possible to say that in case the company will decide to expand the business to distant and unfamiliar markets, it should focus on the development of partnerships (joint ventures) with local organizations that have sufficient operation experience. In this way, the firm will be able to mitigate financial risks and build knowledge about the situation in the hosting cultural, political, legal, and economic environments needed to understand the conduct of local competitors, increase own competitiveness, and, in this way, attain privileged access to customers and suppliers.
The Platform Wars: Profit Margins vs. Market Share
Both market share and net profit are important indicators of organizational growth and sustainability. However, in some cases, it may be difficult to have both. The market share values show the volume of products the company sold in comparison to the total number of sales administered by all other firms in the industry, while net profit, as well as profit margin, reflect the overall profit of the organization per each dollar of sales.
The profit margin impacts the stock price of the enterprise. It is a dynamic index that fluctuates every quarter (Dediu, 2010). Conversely, market share is usually characterized by greater stability and is closely linked to the firm’s commitment to R&D endeavors and quality initiatives. Thus, it can be considered a better indicator of the company’s sustainable growth which is very important in the ever-changing environment of the console and gaming industry. Therefore, while trying to improve performance in both categories, we will nevertheless prioritize market share values.
After running the simulation The Platform Wars: Simulating the Battle for Video Game Supremacy, we concluded that by slightly increasing the console price per unit (up to the US $260-270) and keeping the royalty percentage and the number of subsidized games at low levels, the company can achieve a better competitive level and will be able to gain a high market share value (Figure 1). Thus, based on the simulation results, it is possible to conclude that the preservation of the prices below the average industry price (i.e., US $267.05) can lead to desirable results because a low pricing strategy is usually associated with larger volumes of sales. The findings indicate that it may be preferable to bet on a larger amount of sales than trying to gain a greater profit per unit.
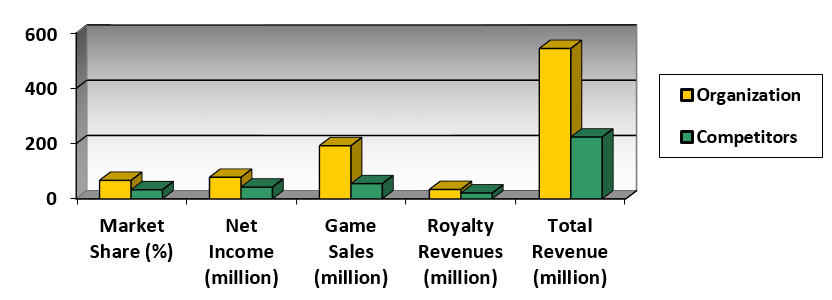
Overall, the low pricing strategy helps to achieve better market share and profit margins, and, what is more important, it helps to become a confident leader in the market. At the same time, it is observed that with the increase in the royalty and subsidized games values, the organization-competitor ratio in many categories become more balanced:
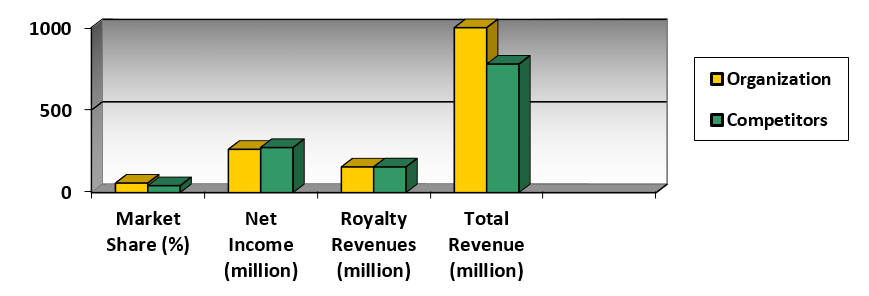
Although product differentiation is frequently used by manufacturers in highly competitive industries to support profitability, it may not always be so efficient. The findings demonstrate that sometimes it is better to invest in smaller amounts of products and focus on their quality. However, it is important to start the strategy design with the evaluation of the external situation in the market and collecting all relevant data.
References
Ballmer, S. (2009). The future of Microsoft, the future of technology (entire talk). Stanford eCorner. Web.
Carr, N. (2003). IT doesn’t matter. Harvard Business Review, 5, 41-49.
Dediu, H. (2010). Which size matters? Market share vs profit share. Web.
Fast Food Restaurants in the US: Market research report. (2017). Web.
Kofi Darbi, W. (2012). How do high-performing organizations define their mission in Ghana? African Journal of Economic and Management Studies, 3(2), 184-204. Web.
Quora. (2017). How technology is evolving to make healthcare better. Forbes. Web.
Sherman, L. (2017). Corporate mission statements don’t really matter, unless you want to be a great leader. Forbes. Web.
Szczerba, R. (2014). Tech trends shaping the future of medicine, part 1. Forbes. Web.
Vidal, N.G., Berman, S., & Van Buren, H. (2015). Stakeholder theory and value creation models in Brazilian firms. Revista Brasileira de Gestão de Negócios, 17(55), 911-931.