Introduction: Research Topic and Problem
- The United States pays a certain attention to the improvements in the sphere of education.
- African American Students have a huge academic potential and a number of educational challenges.
- Academic advising in HBCUs should be developed to help students and promote educational understanding.
Problem
Students are in need of academic advising that can be of various types discussed by theorists and writers a lot; still, the gender-related gap in academic advising and its impact on student retention, success, and satisfactions are poorly discussed topics.

Purpose and Significance
Purpose: to identify and examine the impact of such domains as advising session, advocacy/accountability for student welfare, knowledge and availability on academic advising by evaluating undergraduate student’s perceptions of male and female advising in HBCUs.
Significance: four domains and their development in terms of the existing gender issues are poorly discussed in the literature; therefore, it is necessary to discuss these issues and explain how students can improve their academic achievements and what roles teachers should perform in academic advising.

Theoretical Framework
Now certain theories could be applied to the study under analysis.
The framework is developed on the basis of the theories introduced in case studies offered. For example, the following ideas could be offered:
- Interactionalist Theory of College Student Departure.
- Theory of Involvement.
- Psychological Model for Student Retention.
At the same time, educational development theories developed by Crookston could be used in the study to understand what academic advising is and what the roles of advisors are.

Definitions and Terms
- Academic advisor– a person, who aims at helping students to achieve their academic goals, plan their studies, and make decisions.
- Advisement frequency – a number of advisor-student meetings.
- Attrition/retention – a number of students, who attend courses.
- Academic success/achievement – the possibility to get GPA equals 2.00 and above.
- HBCUs – stands for Historically Black Colleges and Universities
- Developmental advising – a type of advising when student’s development and initiatives are appreciated.
- Prescriptive advising – a type of advising when the authority of an advisor is evident.
- Student persistence – student’s desire to study and achieve academic goals.
- Student retention rate – the number of students, who decide to return to colleges and universities and continue their education.

Literature Review
HBCUs Essence
- Education is a serious issue for consideration in America. Racial inequalities cannot be neglected even in the sphere of education.
- HBCUs provide Black students with an opportunity to study and develop their skills and knowledge.
- HBCUs support the promotion of the opportunities for Black students, the discussion of old problems and challenges, and the introduction of the answers and solutions.
- Academic advising is an integral part of education at HBCUs.

Academic Advising
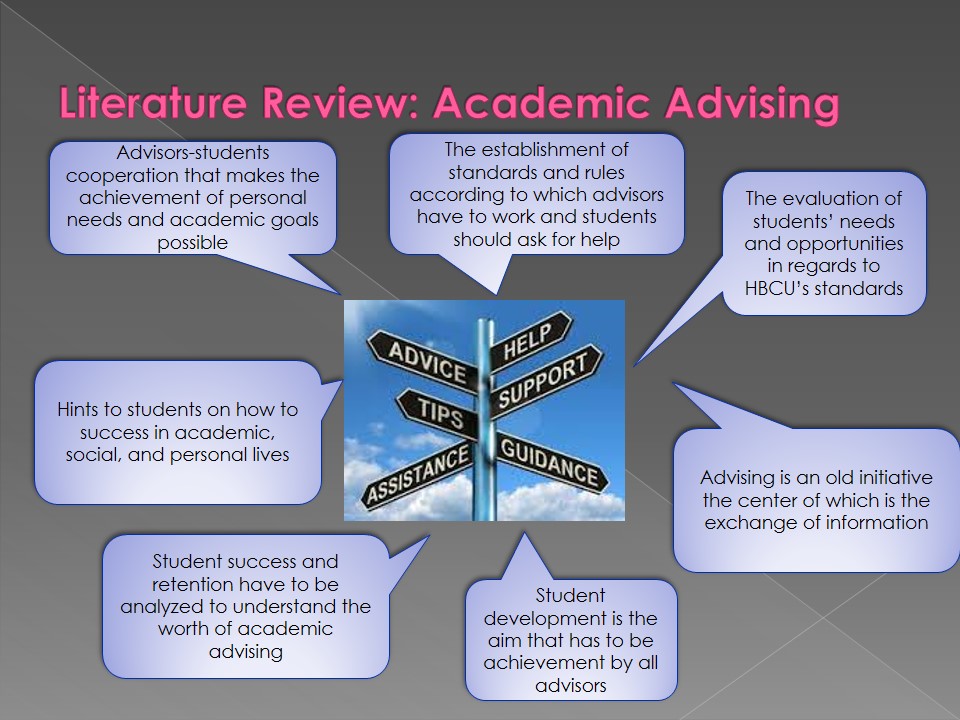
- Advisors-students cooperation that makes the achievement of personal needs and academic goals possible.
- Hints to students on how to success in academic, social, and personal lives.
- Student success and retention have to be analyzed to understand the worth of academic advising.
- The establishment of standards and rules according to which advisors have to work and students should ask for help.
- The evaluation of students’ needs and opportunities in regards to HBCU’s standards.
- Advising is an old initiative the center of which is the exchange of information.
- Student development is the aim that has to be achievement by all advisors.
Types of Advising
Developmental Advising is a preferable approach astudents mong many where the core is the promotion of student’s development, success, and abilities. Students have to be motivated by advisors.
Intrusive Advising is an alternative approach where the roles of students are diminished, and the majority of activities and first steps are taken by advisors.
Prescriptive Advising is the type of academic help that is offered without a certain involvement of students in academic work. The authority of advisors is the core within the frames of which students ask questions and get help.

Educational Development Theories
There is no certain theory that could be applied to academic advising and gender-related issues. The development theory involves the discussion of the ways that promote students’ growth, progress, and success and the possibilities to improve the already gained achievements and qualities.
- Cognitive theories: the considerations of changes students undergo. The best representatives are Perry (need assessment) and Piaget (physical experience).
- Psychological theories: the development of interpersonal relations and understanding of the needs. Erikson’s stages of development could be considered.
- Typological theories: the evaluation of the already identified theories and achievements. Myers and Holland are the best representatives in this field.

Variables
Four domains of academic advising are the variables of the study:
- advising session-
- (students and advisors have to meet and discuss the goals and possible opportunities of their collaboration).
- advocacy/accountability for student welfare-
- (advisors have to understand the level of their responsibility in regards to the expectations of students).
- knowledge-
- (advisors have to demonstrate a high level of knowledge and understanding of their duties).
- availability-
- (advisors have to realize that students can ask for help anytime and be ready to answer their questions and give hints).

Instruments
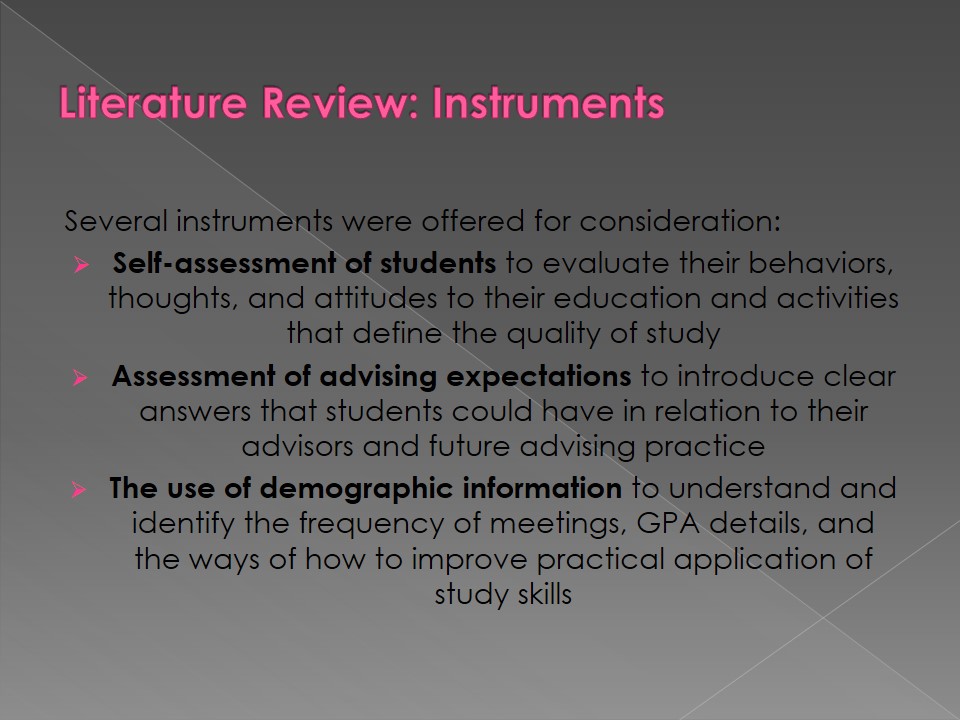
Several instruments were offered for consideration:
- Self-assessment of students to evaluate their behaviors, thoughts, and attitudes to their education and activities that define the quality of study.
- Assessment of advising expectations to introduce clear answers that students could have in relation to their advisors and future advising practice.
- The use of demographic information to understand and identify the frequency of meetings, GPA details, and the ways of how to improve practical application of study skills.
Gender-Related Issues in Advising
Academic advising is properly organized in case such issues as culture, gender, and social status of people are taken into consideration.
Educational and personal disparities should not be a problem for American students.
Academic advising is prejudiced by male cognitive and psychological theories. Female opinions are neglected from time to time.
Gender-related issues touch upon the advisors and students regarding the possibility to get their education and make free choices.
The existing gender gap influences the quality of advising and predetermines the possibilities of students to work with male and female advisors.
Retention between male and female Black students varies as well, and it is necessary to comprehend the reasons for why a gender remains to be a crucial factor in education.

Methodology
Introduction
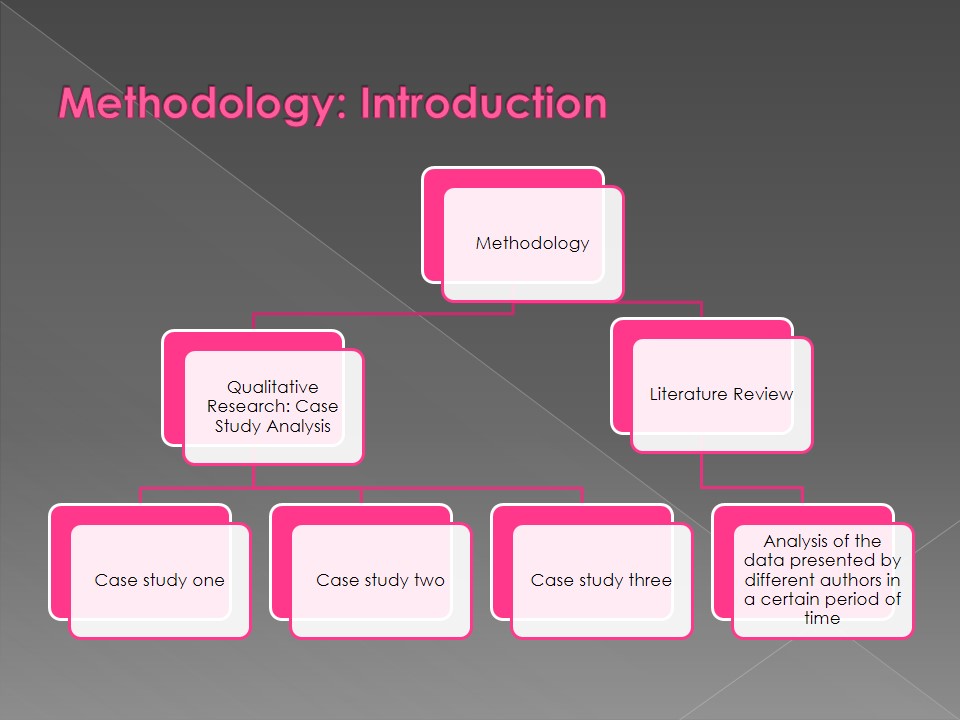
- Methodology:
- Qualitative Research: Case Study Analysis:
- Case study one.
- Case study two.
- Case study three.
- Literature Review:
- Analysis of the data presented by different authors in a certain period of time.
- Qualitative Research: Case Study Analysis:
Case Study One
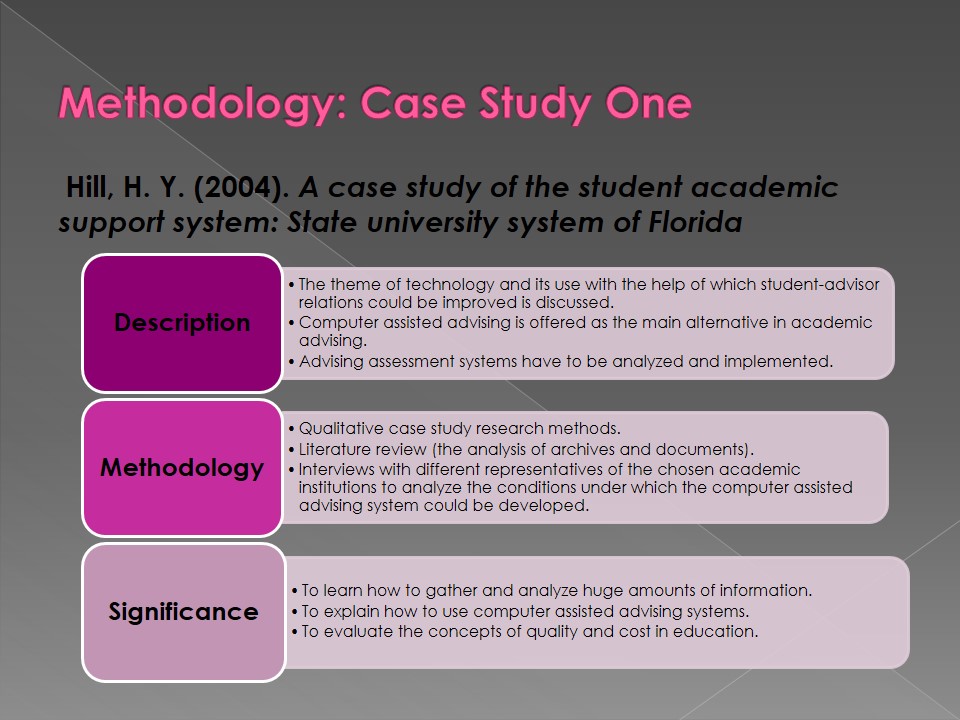
Hill, H. Y. (2004). A case study of the student academic support system: State university system of Florida.
- Description:
- The theme of technology and its use with the help of which student-advisor relations could be improved is discussed.
- Computer assisted advising is offered as the main alternative in academic advising.
- Advising assessment systems have to be analyzed and implemented.
- Methodology:
- Qualitative case study research methods.
- Literature review (the analysis of archives and documents).
- Interviews with different representatives of the chosen academic institutions to analyze the conditions under which the computer assisted advising system could be developed.
- Significance:
- To learn how to gather and analyze huge amounts of information.
- To explain how to use computer assisted advising systems.
- To evaluate the concepts of quality and cost in education.
Case Study Two
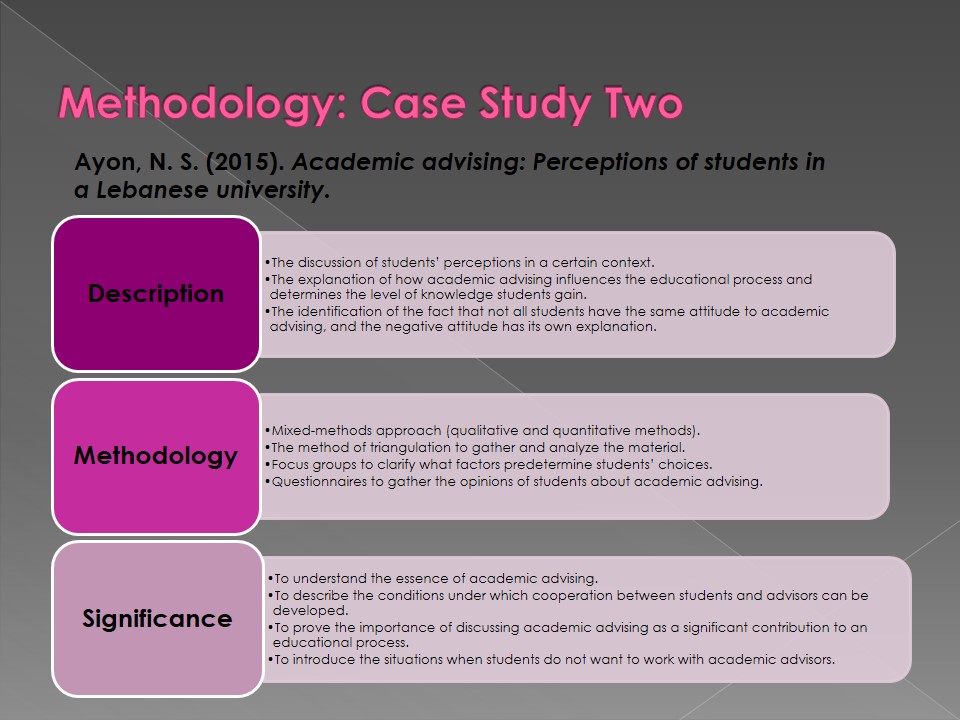
Ayon, N. S. (2015). Academic advising: Perceptions of students in a Lebanese university.
- Description:
- The discussion of students’ perceptions in a certain context.
- The explanation of how academic advising influences the educational process and determines the level of knowledge students gain.
- The identification of the fact that not all students have the same attitude to academic advising, and the negative attitude has its own explanation.
- Methodology:
- Mixed-methods approach (qualitative and quantitative methods).
- The method of triangulation to gather and analyze the material.
- Focus groups to clarify what factors predetermine students’ choices.
- Questionnaires to gather the opinions of students about academic advising.
- Significance:
- To understand the essence of academic advising.
- To describe the conditions under which cooperation between students and advisors can be developed.
- To prove the importance of discussing academic advising as a significant contribution to an educational process.
- To introduce the situations when students do not want to work with academic advisors.
Case Study Three
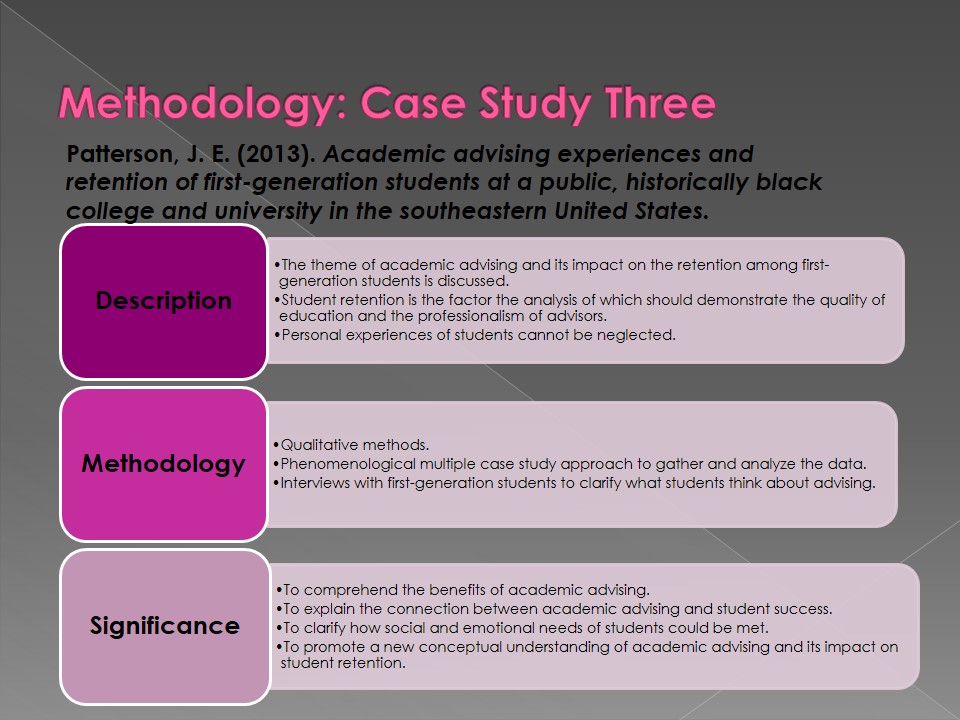
Patterson, J. E. (2013). Academic advising experiences and retention of first-generation students at a public, historically black college and university in the southeastern United States.
- Description:
- The theme of academic advising and its impact on the retention among first-generation students is discussed.
- Student retention is the factor the analysis of which should demonstrate the quality of education and the professionalism of advisors.
- Personal experiences of students cannot be neglected.
- Methodology:
- Qualitative methods.
- Phenomenological multiple case study approach to gather and analyze the data.
- Interviews with first-generation students to clarify what students think about advising.
- Significance:
- To comprehend the benefits of academic advising.
- To explain the connection between academic advising and student success.
- To clarify how social and emotional needs of students could be met.
- To promote a new conceptual understanding of academic advising and its impact on student retention.
Methodology and Purpose of the Study
Case Study Analysis is an effective method with the help of which it is possible to:
- Prove the worth and importance of the chosen topic;
- Use real-life examples;
- Decide if prejudice and personal viewpoints should be considered;
- Investigate how communication with students should be organized.
Direct participants, various contexts, and one similar topic for discussion.
