Explain the function of prototype and a requirement prototype
A prototype is a model of a final product. A prototype is used as a communication tool between system designers and customers. The first function of a prototype is to show the customer that the designer understands the system requirements. The second function is to communicate the system’s requirements to the team of designers. In this case, one designer can use a prototype to communicate the system requirements to a team of designers.
In general, a prototype clarifies the understanding of the designer and the customer about the system requirements and the expected outcomes. A designer’s prototype allows the customer to access the designer’s understanding of the project requirements. The customer can make changes to the designer’s prototype in the event it does not meet his expectations. On the other hand, a customer’s prototype clarifies the system requirements to the designer. A requirement prototype shows all the system requirements before the onset of the project. It is useful in communicating all project requirements between the system designer and the customer.
What is a rapid application development?
Rapid application development (RAD) is a methodology in software development that makes use of iterative techniques and prototyping to enhance quick completion of software projects. The methodology adapts techniques that reduce the overall conventional time taken to develop softwares. A typical RAD has four phases. They include requirement planning, user design, construction, and cutover phases.
What is meant by scheduling?
Scheduling is planning and allocation of time and resources to various activities in a project scope. In system design and analysis, scheduling refers to the chronological planning of the occurrence of various activities in the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
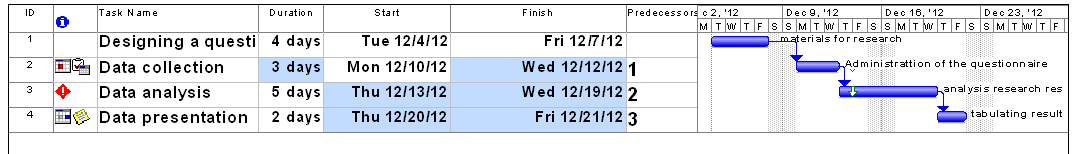
Illustrate a Gantt chart with the aid of a diagram
Figure 1 shows a Gantt chart for a 14-day statistical research project. The duration of activities is exclusive of weekends.
Risk management
Risk management is the process of identifying, accessing and elimination or reduction of risks in system analysis and design. Risks are eventualities that may hinder the completion of the project scope or the attainment of the final project’s objectives. Complete elimination of risks is not possible and thus risk management entails minimization of risks in the project management process.
How to estimate a time required for a project?
Accurate estimation of time duration for a given project demands comprehensive knowledge of the project scope by the project manager. The project scope entails all the activities and resources required for the completion of a project. The first step in the estimation of time required for a project is the identification of various tasks that make up a complete project. The project manager is then required to prioritize the project tasks by estimating the required time for each of them. The final estimate of time for the whole project is the summation of time taken for each task of the project. PERT formula can also be used for accurate estimation of project time. PERT is an acronym for Project Evaluation and Review Technique. The formula is given as:
Te= (To + 4Tm + Tp) / 6
Where:
- To is the most optimistic time required to complete the project,
- Tm is the most likely time required to complete the project and
- Tp is the most pessimistic time required to complete the project.
Prototyping is useful during the analysis and design phases if users are involved in the evolution of the prototype. However, it has some disadvantages. Describe three disadvantages or risks.
The first disadvantage is the general tendency to avoid formal documentation of the system design. Formal documentation allows inclusion of all requirements of the project before commencing implementation. This is essential in effective scope management. Documentation also allows the common person to understand the system through reading of the written instructions. The second disadvantage regards sharing of data with other systems. Prototyping does not provide information on how data will be shared with other systems. This makes it difficult for the designer to implement inter-system data sharing. The third risk is the tendency of bypassing the SDLC checks. SDLC checks are used in modular software development to ensure stage wise debugging of errors.
After identifying some of the requirements for a system, one needs to check that his understanding is correct. Describe two ways in which this can be done
The two methods used for testing an understanding of the system requirements are prototyping and Joint Application Design (JAD). Prototyping allows the designer to translate system requirements into a working model. Well-understood system requirements should translate into an effective working version that meets final project objectives. Failure of the prototype to meet final project objectives implies insufficient knowledge of the system requirements. JAD allows wider consultation of the system designer with other experts in Information Technology (IT). Well-understood system requirements should resonate with the views of other experts.
What are the database design concerns at the Logical Level? At the Physical Level?
The logical data model deals with the actual functions of the database in question. It is concerned about what the database will do once it is developed. Logical modeling entails collection, assessment, and analysis of information on business requirements and processing them into a functional logical database.
On the other hand, physical level of a database modeling entails actual implementation of the results of logical modeling. It involves defining object schemas for each logical model attributes. In general, physical modeling is concerned about the organization of storage formats in objects such as columns and tables based on logical modeling results.
Discuss the interview process. Include in your discussion types of interview, question types and what type of information you expect to discover with each type.
Interviews are used to collect information, facts and other people’s opinions about a given research topic. In general, the interview process consists of the interviewer and the interviewee. The interviewer asks the interviewee questions and records the responses of the latter. There are four different types of interviews: structured interviews, semi-structured interviews, in depth interviews and focused group discussion.
Structured interview is based on already scheduled interview questions. The interviewer asks scheduled questions and records the interviewee’s responses. Semi structured interview is less formal than structured interview. It consists of open-ended questions, which provides a room for more views and opinions of the respondents. In depth interview is less formal than semi structured interview. It entails interview questions that prompt a discussion between the interviewer and the interviewees.
In depth interview is used when the researcher is seeking in-depth information about a given topic of research. Focused group discussion is an in-depth interview involving many people in a discussion. The researcher asks questions, which demands responses from a group of interviewees. The researcher records opinions of each group participant. The most effective data collection method in focused group discussion is tape recording.
In general, there are two types of interview questions: Closed ended and open-ended questions. Closed ended questions have multiple-choice answers for the respondent to select his preferred responses. They do not provide room for respondent’s opinions outside the research questions. On the other hand, opened ended questions have no preset answers. The responded is free to give his opinion. Open-ended questions are used when the researcher is seeking varied opinions about a given topic of research from the respondents.