Introduction
Teamwork is a very important and relevant contributor to the success of any business around the world and this is why top business executives are paid a lot of money to utilize the skills of teams and make important business decisions that are critical to business performance (Brayden, Teppo & Whetten 2010, 1-20).
The success of an organization does not only depend on how good a team leader is but also how good the various teams that consist of employees are able to come together and integrate their skills and talent for the benefit of their organization.
The success or failure of a business usually depends on how good employees who are part of a team are able to come together develop ideas play their part and additionally how good managers or organizational leaders are able to make quick and relevant decisions resulting from the input of the team to increase positive outcome (Taylor, 2010).
Today’s business environment is very volatile and therefore it is imperative that both leadership and employees work together hand in hand in order to ensure that organization can successfully peruse their mission and vision while at the same time compete with other competing companies.
Thus, by acknowledging and building consensus that business environment is highly dynamic and volatile, it demands organizational leaders to come up with mechanisms that allow the company to quickly embrace change and this is attained by dividing the staff into teams and assigning them duties that will ensure that decision making capability of leaders is maximized (Shah 2008).
New trends emerge in the business world and may either present themselves as either problems or opportunities depending on how personnel within the organization respond.
From that rationale, the creation of value and satisfaction, which consumers demand end up pushing companies to develop strategies that govern their marketing mix and overall business strategy and go a step further to create general corporate strategies that will preside over their whole business processes to make sure they succeed in today’s fickle business ambiance (Campbell, Stonehouse & Huston 2002, 177-184).
Trends should not be seen as not threats but rather frontiers of new business possibilities and it is the duty of organizational leaders and their staff to work together as a team to make decision making for managers more certain and free of risk.
It is with the same intent that the manager intended to use the help of his team to launch a new division that manufactures liquid soap brands for the market by using the potential of the entire team and the rational decision making process to make critical marketing business decision. The liquid soap division will consist of brands that will cater to the needs of consumers who require liquid soap for both the kitchen and bathroom.
Decision making approaches and impact on strategy
A participatory approach was used and the entire the team was required to fully participate by being part of the problem solving process but the last decision was left to the team leader/manager to carry out (Jones 2010, 44).
Such a technique of team work and decision making is known as consensus building whereby subordinates who are part of a team come up with multiple ideas and discuss their viability together with the team leader but leave the last decision to the team leader.
The way in which groups interact whether informal or formal will obviously impinge on the way a business functions and the way strategic choices are made in both the short and long-run. Successful companies like Google and Apple focus their development efforts by encouraging groups and teams to brainstorm and develop ideas that form a basis for the decisions which are made by top management (Koontz & Weihrich 2009, 58).
Following this premise, the companies have adopted quite aggressive business models because managers are able to make quick decisions simply because the groups usually supply them with all relevant knowledge and information that allows the managers to quickly evaluate the pros and cons of each strategic choice to choose the best action.
It is as a consequence true to assert that the way groups and managers interact and the different approaches of making decisions within organizations can ultimately affect the future of an organization.
Marketing companies, for example are required to be quite flexible due to the volatile nature of consumers and competitors and thus, this is why many marketing companies have their staff working in groups simply because the conception of ideas and the need for quick decision making is quite critical for the success of a company in the market.
According to Kotler and Keller (2011, 144), the most important aspect of teamwork and decision making in a marketing environment is simply to ensure that all decisions and team work efforts are made with the consumer on mind. Additionally, it is important that there is a very clear channel of communication between the team members to ensure that each member is up to speed and is armed with relevant information.
The consumers are the pivot of all decisions and ideas that a business comes up with in the course of doing business. Keeping this aspect in mind, the team leader ensured that the team clearly knew that the customer is the goal and the main criteria of measuring how effective the teams efforts and decision making process was (Jones 2010, 135).
This is whereby the team leader empowers his team to use their knowledge, skills and talent to in order to gather factual options that will assist in the decision making process.
When employees explain all their options and contingent plans, the team leader him/herself is then expected to use his managerial skills to choose the best option that emanates from the output of his/her team.
Considering that the company division is a newly born venture it is necessary for the team leader to be vigilant and aggressive to ensure that the whole team’s shares one vision and that the expectations of the entire team are in tandem with that of the team leader and the organizations corporate, business and functional goals.
The advantages associated with participatory type of teamwork approach is that the organization and the manager can collect many ideas and develop many strategic options that are likely to increase positive outcome within the organization. Additionally the process of decision making is made simpler by the fact that consensus building takes place prior to the final decision being made.
Team Working approaches and impact on strategy
A participatory approach was used and the entire the team was required to fully participate by being part of the problem solving process, According to Buchanan and Huczynski (2010, 131), it is vital that a team leader ensures that the vision of the entire organization is clearly known by the entire team/staff from the initial stage because any ambiguity may become a future source of conflict and discomfort amongst the team members in the future and may henceforth compromise the chances of success for the new division and affect the decision making process.
Consumers are driven by needs, wants and desires and hence their consuming behavior can be attributed to these. Companies that define consumer needs and motives with a high degree of accuracy usually end up being the market leaders and enjoy a huge market share and revenue streams (Michael, Yasemin & Joseph 2009, 123).
Managers are often aware of how important consumer motives are and therefore ensure that their brightest minds who make up the team come together and create ideas that will further the performance of the company.
Being the team leader, communication was made clear that all other team members collectively come together so that the process of problem identification and problem solving can start using the rational decision making process.
The rational decision making process is a problem solving technique that allows managers and the respective teams to carefully and sequentially make decisions based on facts that present themselves as a result of the problem solving process (Koontz & Weihrich 2009 69).
Business executives in working with the leading companies are usually trained to use logic and facts in the process of making decisions by identifying problems and opportunities and creating multiple solutions/strategies to tackle the problem. Managers/ team leaders thereby use the rational decision model to reduce the number of risks and uncertainty because this process is highly factual and logical in nature.
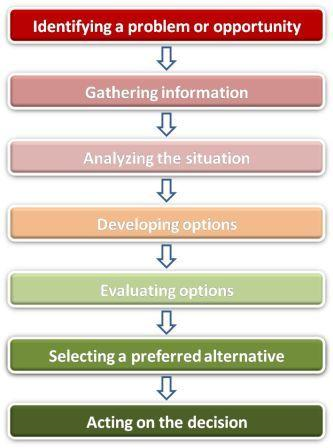
Figure 1: The Steps involved in the Rational Decision making process.
By bringing together the skills and talents of all individuals of the team, the team leader expected that it would be possible for the team to create a good marketing strategy that would allow the new company to effectively price, place, and promote its products to compete with other existing companies (David, Cindy & Masco 2008, 5).
As a result, the five members of the team were each assigned to deal with each facet of marketing and gather relevant intelligence on pricing, product, and promotion and distribution trends of related liquid sap product within the industry. The data that would result from this process would prove crucial in the rational decision making process.
The launch of a new product is not easy at all and for new products/ new divisions to succeed in selling products as soon as they enter the market it is important for the managers and their teams to ensure that all relevant data is gathered. Knowing this the team was to gather competitive intelligence that would be used to finalize the marketing mix of the new liquid soap.
With the task of each and every team member already clarified the group was given a time frame of one week to bring back their feedback. Every suggestion of product design, price, placing and promotion strategy was to be backed by tangible evidence of pros and cons to justify why team members so it as the best alternative.
This will therefore require every team member to identify problems and opportunities that present themselves, gather all the relevant data pertaining to either the problem or opportunity, critically analyze the volume of information that was gathered and then using the information to develop options that are most suitable.
According to Kotler and Keller (2006, 415), it is important for business executives to create numerous options so that management can make more informed choices. After the numerous options are made the rational decision making process requires that the numerous options that were developed are analyzed and that actions which are weak or unsuitable are filtered and eliminated.
It is at this process the managers/team leader to become an effective decision maker and use his/her skills to choose the best decision.
The team was required to sit together and analyze the various options but this process was slowed down due to the fact that one team member left the tem before she had a chance to finish carrying out her research on pricing. Being an effective team leader the team leader quickly decided to split the remaining task of gathering pricing data from the market.
As soon as all the relevant data was gathered, each group member was required to analyze data clearly explain the implications of the data which was collected. According to Buchanan and Huczynski (2010, 122), it is the duty of the team to bring to the table all alternate options and ensure that there is full disclosure of facts so that the team leader can make the relevant decisions.
The team, therefore went ahead and shared information and data which they gathered and presented to the team leader all the relevant data necessary for creating marketing mix for the brands falling under the liquid soap division.
The entire problem solving process took the team one whole week and the team presented multiple solutions to the team leader and consensus building took place but the final decision making process was left to the manager.
Effectiveness of the team
The team’s effectiveness is highly commendable because each and every member of the team was in tandem with the vision of the division at the beginning of the practice. With the vision of the division in mind, the team operated with utmost openness and trust that was enabled by clear lines of communication (Lancaster & Withey 2006, 94).
Decision making at the lower level was left to the team members themselves thus saving time, the ability to meet regularly in the one week during afternoons made it possible to analyze the data gathered by the team members.
It is at these sessions that all team members communicated and exchanged notes making every team member fully aware of the facts and relevant information in respect to the whole project and with every team member well informed it was easier to brief the manager (Koontz & Weihrich 2009, 73).
The level of skill and talent together with operation of the team is also commendable because the competitor intelligence which they gathered made it quite simple to compare currently existing liquid soap brands overall industry trends and thus use it in the final marketing mix of the brands that were to be developed by our new division.
In summary the company’s brands will be better designed and packaged, priced, promoted and distributed to compete with the current market leader.
The only shortcoming of the team is that the level of competition and hostility between the members trying to outshine each other got on the way of achieving the mission but after the leader made it clear that such behavior is injurious to the group and not appropriate the team members apologized to each other.
Conclusion
Team work is a very important aspect in organization for the reason that organizational output depends on talent, skills and knowledge of the staff. The output of teams usually contributes to the quality of decisions that managers make. If a team is ineffective in operation then most probably a manager will have fewer facts to support the kind of decisions that he/she makes.
When poor decisions are made then this may affect future revenue streams, market share, costs and efficiency of the organization.
“A team-leader is someone who steps back from the entire system and tries to build a more collaborative, more innovative team that will work over the long term.” – Robert B. Reich American Politician and Writer The above statement suggest the synergy that managers can create by using more collaborative and participatory approaches that are rational to work together with teams to guide their decision making process.
References
Brayden, K. G., Teppo, F. & Whetten D. A., 2010. “Perspective—Finding the Organization in Organizational Theory: A Meta-Theory of the Organization as a Social Actor.” Journal of organization science volume 21 issue 1, 1-20.
Buchanan, D. A. & Huczynski, A. A., 2010. Organizational Behavior 7th ed. New York: Trans-Atlantic Publications.
Campbell, D., Stonehouse, G. & Huston, B., 2002. Business Strategy an Introduction 2nd edn. Linacre House, Banbury Rd: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Charles, W. et al., 2002. Essentials of Marketing. Natorp Boulevard: South Western Cengage Learning.
David, A. J., Cindy F. R., & Masco, C. J., 2008. “Personality predictors of teamwork behaviors and decision-making style.” Review of Business Research, 1-5.
Jones, G., 2010. Organizational theory, design, and change. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Koontz, H. & Weihrich, H., 2009. Essence of Management an International Perspective. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K., 2011. Marketing Management 13th edn. New York: Prentice Hall.
Lancaster, G. & Withey, F., 2006. Marketing Fundamentals. London: Butterworth-Heimann.
Michael P. L., Yasemin K.Y. & Joseph M. T., 2009. “A theory of change in turbulent environments: the sequencing of dynamic capabilities following industry deregulation.” International Journal of Strategic Management, Volume 1, Number 3, 186-211.
Shah. K., 2008. “Decision Making.” Submityourarticle.com. Web.
Taylor, J.T., 2010. “Making effective decisions.” Team building USA. Retireved from http://www.teambuildingusa.com/articles/making-effective-decisions/