Technology is ubiquitous and has invaded every aspect of our personal and professional lives. Social networking sites have gone ahead and even blurred the lines between personal and professional lives. Technology is used for various purposes but the most common use can be found in information sharing and communications. The Internet has revolutionized the way we use technology, especially when used to communicate with each other to share information. So phenomenal is the internet that it has been compared to the industrial revolution of eighteenth-century Europe. Every organization, whether it is small, medium, or large, has in one way or another been affected by technology. Although we are aware of technology and its various uses, it is interesting to understand how it is implemented in an Interior Architecture or Design firm.
Communications are at the core of today’s business world, with businesses interacting with other businesses (B2B) and interacting with their customers (B2C). An IT administrator who works at an architectural firm informed me that most firms today have a networked environment, which helps leverage IT investments by allowing multiple devices to interconnect with each other. For example, all computers and laptops in the firm are connected to a network device called a switch, which allows these computers to “talk” to each other as well as other devices called servers, printers, plotters, and mobile devices. Below is a diagram of a typically networked environment in a small or medium architectural practice that uses technology.
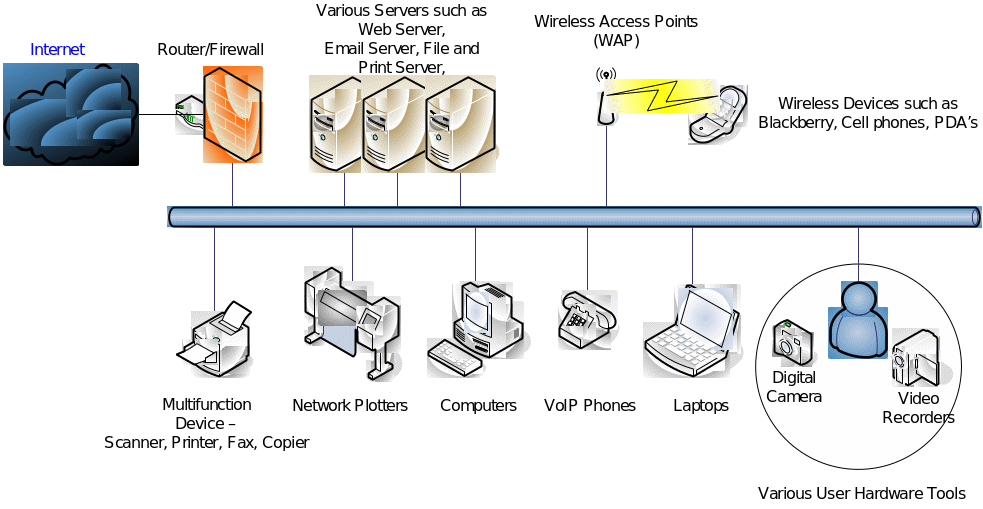
The most commonly used network environment is the client-server architecture. Servers are powerful computers used to host enterprise applications and share various business-related documents and software while clients such as laptops and printers use the services offered by these servers. Important business information such as customer and supplier names and contacts, architectural drawings, quotations, project-related files are stored in servers called file servers which are regularly backed up. These file servers allow business information to be easily available and accessible to various architects and project managers and serve as an important source of historical information, also called Business Intelligence. Laptops and computers are loaded with business applications such as Microsoft Office, Instant Messaging, email applications, and other designing software such as AutoCAD and CADKit. In a digitized environment, all details of the business operation are stored electronically, which allows them to be compiled into a single document. For example, a site visit by a surveyor to a customer’s location may involve pictures taken from the digital camera. This information is moved from the camera in a digitized format to the laptop and eventually stored on the server for the engineers, architects, or project engineers to be used for determining the scope of the project. Similarly, videos taken using a video camera may be used for a certain award ceremony may be used for advertising on the corporate website. Emails and instant messaging are other forms of technology that have made instant communication possible. Sending quotations or requesting purchase orders, or approving quotes using email is considered a valid and official method of business communication.
Despite the various forms of textual communication, voice communication is still an important mode of communication. What is not apparent, though, is that the underlying technology of telephony has fundamentally changed over the past few years. Usually, phones are connected to a Private Exchange or PBX, which routes outbound and inbound calls depending on the telephone and extension dialing. This required a separate network from the computer networks and associated maintenance overheads. Using the Voice of IP or VoIP technology, phones can use the same network infrastructure as the computers. Thus there is no need to have separate network or maintenance contracts. This translates into direct saving and improves the ROI on technology investment for these small or medium firms.
Most architects, project managers, sales engineers are usually traveling for consulting with their customers or attending seminars. Having access to calendars, emails, phones, the internet, instant messaging, and other business applications is a mandatory requirement (BlackBerry website). Most architectural firms provide their employees with Blackberry’s or other forms of mobile devices. This ensures that they are in constant touch with their customers and peers, through voice and emails. There are times when they want to access certain information and this wireless mode of connectivity is a very important business requirement. With the evolution of wireless technologies, even within the firm, users use laptops installed with wireless devices and blackberries to communicate with other devices through the wireless access point (WAP). This is called anytime, anywhere computing. The objective is to empower the user and give them the ability to communicate with colleagues and to access data or network resources such as printers wherever and whenever they want (Gale Group 2004).
Technology has played an important role in the design process and has revolutionized how architecture firms implement their projects. A typical design process may include concept, design, procurement, building, and documentation (Adobe Systems). Software design tools have been used extensively for designing but since the early 1990’s AutoCAD has evolved to what is now an industry standard. Each tool has its strengths and its weaknesses and since most applications today use industry-standard application interfaces, they are compatible with each other. For example, an image can be exported from AutoCAD or Microstation into Photoshop, which can then be used to prepare a sketch to be used as a reference in customer discussions (Adobe Systems). Since most architectural firms use AutoCAD, some firms to differentiate themselves have invested in more architectural-friendly software tools such as ArchiCAD, which allows clients to be involved in the design process (Earl G. Graves, 2006). This saves several hours of design time because the architects can be assured that the design would be approved faster than if they produced the design without customer involvement during the early phases of the project. Design applications are is in a constant state of evolution and intelligent 3-D modeling software such as Building Information Modelling (BIM) from Autodesk have reshaped the way construction is accomplished (Earl G. Graves, 2006). An important observation here is that outputs generated from most applications are saved in electronic format which is saved in file servers and other collaboration servers. Architects and engineers can view these files simultaneously and make suggestions or recommendations to the design, without even having to print out the design.
The designs produced need to be effectively presented and communicated to the customer effectively to bring the project to fruition. For example, to see how a specified building will look on a proposed site, instead of using the sketch of a building on an image of the proposed site, Photoshop can be used to place the building sketch over the image of the proposed site. This level of presentation is required to convert a concept into a finished product (Adobe Systems). Architects and project managers use laptops loaded with tools such as Microsoft PowerPoint and overhead projectors to give presentations to customers. Pictures speak louder than words and a few slides of the presentation can speak more than an entire report. Similarly, project managers in these firms use Microsoft projects to draw Gantt charts and schedule work, using Microsoft word to write reports for their customers. Besides just presenting designs, architectural firms need to present themselves to their customers and other business such as their suppliers as someone that can be relied on. Websites can be used in dynamic and innovative ways for presentation, acting as a kind of dynamic brochure. Websites are hosted on servers called web servers and use the internet to allow their worldwide audience to their website. Web sites are a collection of web pages that are written in HTML, Java, or other web software. Websites serve as a single point of contact for all or most new customers, who usually do a comparative study between various architectural firms, before investing time and money. An architect informed me that their firm bagged orders from countries as far as Dubai and South Africa although they were located in the UK, all through their website. A dynamic website has text but also slides, videos, testimonials from their customers, forums, and blogs for a two-way interaction which helps build confidence in their potential customers. Another form of presentation that today’s architectural firms use is a high-density (HD) display in their offices. These HD displays are connected to a computer through the network which provides all the pictures, videos, and related information. This form of technology is used to inform visitors of various projects successfully managed by the firm, awards won, and best practices followed by the firm, which is helpful because visitors learn a lot about the company as they wait for a meeting and is a good replacement for paper brochures and magazines.
Technology is constantly evolving on all fronts and users are finding new ways of employing these evolving technologies to differentiate themselves from the competition. Networks have evolved from wired to wireless to 4G communications and yet they coexist to meet varying customer needs. Applications are evolving to include a whole range of collaboration tools allowing not only teams to work together but also engage customers early on during the project. Presentation tools are evolving to make a design more and more realistic and 3 dimensional, so customers can get a real feel of what to expect for their investments. The constantly evolving technology is breaking old barriers and allowing modern firms to be more productive.
Reference List
Adobe Systems Inc., 2005, Engineering and Architectural Workflows for Photoshop CS2 .
BlackBerry Enterprise Solution. Web.
Earl G. Graves Publishing Co., Inc, 2006, Building materials: architectural firms embrace technology solutions.
Gale Group, 2004, LAN evolution’s third phase: remote, mobile users – local area networks. Web.