Introduction
The use of technology has triggered innovations and enhanced the skills of children and adults. In fact, technology is one of the modern necessities because it improves interactions, communication, and the utilisation of tangible and intangible resources. However, its use among children has generated contentious debates because some researchers claim that technology affects creativity, causes addiction, and exposes them to negative social activities. Additionally, it has significant effects on the social attributes of children.
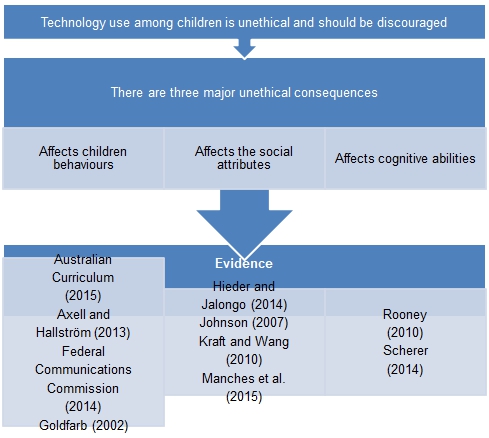
The research is aims to evaluate the ethical issues in the use of technology among children. It will examine literature that shows the long term effects of introducing technology at an early stage in human development. Recent studies and evidence from medical, early childhood, and psychology journals will be analysed to demonstrate the unethical consequences of technology in children. The research will show that technology affects the social, cognitive, and adaptive skills of children.
Technology use and Children Behaviours
According to Kraft and Wang (2010), technology shapes the behavioural attitudes of children. The researchers claimed that the affected attitudes and behaviours show in adolescence and early adulthood. When children are introduced to new technological experiences, they get intimate with what they see and feel. Additionally, children imitate what they see in computer games, videos, and other technologies. They identify with the beliefs and attitudes of characters and practice what they see with others.
Although Hieder and Jalongo (2014) argue that some levels of exposure to technology enhance the creativity of children, others introduce defiance, hostility, and violence among children. Some of the contents in the internet are very dangerous to the children. Cyber bullying, explicit contents and violent games are accessible to children and other internet users.
These materials expose children to some of the social vices. They affect the psychological wellbeing by encouraging violence and immoral behaviours. The presence of undefined, unedited, and unmonitored access to technology influences children to change their behaviours. Although the access to technology allows children to learn and acquire many skills, it affects them if not monitored.
According to Australian Curriculum (2015), there has been a significant correlation between technology use among children and physical impairments. The study showed that children who are exposed to technology at an early age are vulnerable to developmental delays and other serious health issues. Obesity and cardiovascular disorders are some of the most popular because of reduced physical exercises.
Additionally, movement deprivation and sensory overstimulation may affect a child’s normal development and extend to early adulthood. In fact, Johnson (2007) argued that if children are not monitored, they can spend hours using technology. This can cause serious sleep problems that may interfere with the normal development of motor skills. Repeated exposure to violent contents affects the decision-making capacities of a child by invoking aggression and beliefs in hostility. Children attempt to imitate the beliefs and actions of the characters.
They become emotionally attached to the experiences of technology. In some instances, children have been reported to abuse their families and friends when replicating what they saw in movies and videogames. Families and early childhood professionals should engage in policy formulation to identify the best strategies that can protect children from the negative effects of technology.
Technology and Social Attributes
According to Rooney (2010), technology affects the social attributes of children. The researcher argues that technology may affect a child’s socialisation capabilities because it encourages spending time alone. Additionally, most technologies are addictive. For example, video games, internet, and other technologies are very addictive. According to Manches, Duncan, Plowman and Sabeti (2015), technology encourages children to be introverts. Most children use technology as their companions.
The behaviour reduces the rates of physical interactions. Children avoid socialising with others because they are always on their computers or other devices. The gadgets take up most of the children’s leisure time. Additionally, social networking sites, which were developed to enhance interaction and file sharing, affect the self-esteem and public speaking skills. Most children who are introduced to technology at an early age find it hard to express themselves. Most of the devices are very engaging.
This attribute makes it very hard for children to spend time with their friends, peers, and family members. For example, social media sites allow the children to have very many virtual friends. However, they affect the physical relationships that are essential to building trust and values. Parents have an ethical obligation of monitoring the use of technology among children to avoid alienating the children from some of the important social attributes and experiences. Additionally, society should revaluate the appropriate age to expose the children to technology. Some of the video games should also be banned to prevent bad influence among children.
According to Goldfarb (2002), overuse of technology among children has been associated with human detachment and mental illness. The effects may start with mood disorders, loss of attention, and a choice of solitude over social interactions. Additionally, children may get delusional and experience emotional outbursts. Aggression can also be experienced in situations where a child is being compelled to attend social events.
In such cases, children become defiant and start developing psychological problems and low esteem. Empathy is also affected by prolonged exposure to violent games and movies. The basic communication skills are seriously affected by technology because children lack a standard guide for speech development, listening skills, and compassion. Early childhood centres should focus on introducing proactive strategies to address the rising cases of social disorientation among children.
Technology and Cognitive Abilities
According to Alex and Hallstrom (2013), technology has been found to have positive and negative effects on the cognitive abilities of children. One of the ethical consequences of technology is enhancing creativity and innovation. Technology comprises different interfaces and interactive platforms that encourage users to think critically and creatively.
Additionally, the interfaces expose children to exercises that require coordination, attentiveness, and alertness. However, Johnson (2007) observed that technology simplifies some of the basic tasks that are associated with cognitive skills. For example, simple arithmetic tasks should be done without using any calculation gadget. However, the invention of the calculator created dependency in the gadget and interfered with the development of basic cognitive skills.
Additionally, the computers and phones have spelling-aids that help users to complete words while typing. In fact, most of the gadgets have auto-correct functions that detect spelling mistakes and correct them immediately. According to the Federal Communications Commission (2014), the high dependency on technology to carry out some of the basic human activities affects a child’s cognitive abilities.
The traditional methods of early childhood education involved improving handwritings, understanding the correct spellings of words, and learning to read, write, and recite course contents. Additionally, children were expected to understand the mathematical rules of small numbers. However, technology has interfered with the early childhood education and normal cognitive development. Children are becoming less analytical and completely dependent on technology.
The advent of technology has also been characterised by the invention of short, grammatically incorrect words to save time and space. The language found in many texts and chat messages is characterised by shortened words, unconventional punctuations, omission of words, and non-adherence to grammatical rules. In addition to poor communication skills, technology causes attention deficit. According to Swing Gentile, Anderson and Walsh (2010), children with an extended exposure rate to technology were more vulnerable to attention problems.
In fact, the level of technology exposure correlates with a reduction in classroom engagement. Additionally, it leads to the development of health-related complications that interfere with normal learning capabilities.
According to Mössle, Kleimann, Rehbein and Pfeiffer (2010), children with higher exposure rates performed poorly at school even after eliminating the social, cultural, and family backgrounds. Consistent exposure to technology leads to episodic fatigue, which is damaging to the psychosocial wellbeing of children. The government, parents, and educational agencies should establish appropriate guidelines to regulate the exposure rate and technology contents.
Conclusion
There are serious ethical issues associated with the use of technology among children. Although technology has emerged as a positive contribution to socioeconomic developments, it has serious ethical issues when exposed to children at an early age. Early exposure affects their social attributes and encourages the development of negative behaviours that show in early adulthood. Additionally, technology affects classroom engagement by causing attention deficiency and health disorders.
References
Australian Curriculum. (2015). Applying social and ethical protocols and practices when using ICT.
This article provides information on the ethical practices that should be noted when dealing with technology. It provides excellent data for use in the assignment. However, it does not clearly indicate whether the ethical implications apply to children.
Axell, C., & Hallström, J. (2013). Representations of technology in the ‘Technical Stories’ for children of Otto Witt, early 20th century Swedish technology educator. International Journal of Technology & Design Education, 23(4), 817-834.
Axell and Hallström argue that technology has been introduced to children by schools and reading materials. For example, textbooks and children’s books are full of persons who use technology in one way or another. The data collected contributes to how children access technology. The article also helps in giving the pros of using technology.
Federal Communications Commission. (2014). Children’s Internet Protection Act.
The article highlights the Children’s Internet Protection Act, which aims to protect children from the harmful influences of technology. The article also highlights some of the ethical issues that are associated with the use of technology, especially among children.
Goldfarb, B. (2002). Visual Pedagogy. Media cultures in and beyond the classroom. Durham: Duke University Press.
Goldfarb takes an academic look at the influence of technology on children and education. The author provides both the negatives and the positives of technology on the cognitive abilities of children.
Hieder, K., & Jalongo, M. (2014). Young children and families in the information age: applications of technology in early childhood. New York, NY: Springer
Hieder and Jalongo analyse the family unit and how technology is incorporated into this unit. Additionally, they discuss the impact of technology on young children in the family unit. The authors state how relationships are affected by technology.
Johnson, D. (2007). Does technology change how schools teach ethical behaviors?
The article by Johnson highlights the impact of technology on education. Specifically, the author takes time to analyse how technology has been used in schools to help children learn faster and more efficiently.
Kraft, E., & Wang, J. (2010). An exploratory study of the cyber bullying and cyber stalking experiences and factors related to the victimization of students at a public liberal arts college. International Journal of Techno ethics (IJT), 1(4), 74-91.
This source is very different from the rest because it analyses children who have experience with advanced technology. The authors explain how the Internet and technology, in general, have led to cybercrime. Consequently, children have been victimised.
Manches, A., Duncan, P., Plowman, L., & Sabeti, S. (2015). Three questions about the Internet of things and children. Techtrends: Linking Research & Practice to Improve Learning, 59(1), 76-83.
The authors highlight the different ways in which interaction between children and technology has changed over time. The article provides excellent data for the assignment, as it explains in detail the ease of access to all kinds of data, both good and bad. It also explains the ease with which children can access data using technology.
Mössle, T., Kleimann, M., Rehbein, F., & Pfeiffer, C. (2010). Media use and school achievement–boys at risk? British journal of developmental psychology, 28(3), 699-725.
The article evaluates the correlation between excessive media use and academic performance. It demonstrates how overexposure to games and other media affects academic achievements.
Rooney, T. (2010). Trusting children: How do surveillance technologies alter a child’s experience of trust, risk and responsibility? Surveillance & Society, 7(34), 344-355.
Rooney explains that technologies can alter a child’s character. In turn, the child can grow with the new characteristics. Rooney asserts that in many cases, these characteristics are negative and make the child unsociable.
Swing, E. L., Gentile, D. A., Anderson, C. A., & Walsh, D. A. (2010). Television and video game exposure and the development of attention problems. Pediatrics, 126(2), 214-221.
The research evaluates the implication of television and video game exposure in cognitive development. The researchers show a significant correlation between prolonged exposure and the development of attention problems.
Appendix: Research Map