Introduction
In 1948, Burma attained her independence from Britain and the General Aung Sann regime embraced democratic ideologies. Nonetheless, the 1962 coup d’état ruined democratic processes (Keling et al. 2010). Currently, the country has made relatively huge democratic milestones, but the military still has a strong influence (Williams 2015). Arguably, the democratic process in Burma borrows a lot from the radical democracy theory (the proponents of the theory state that the role of democracy is to oust hierarchical and oppressive power from the society) (Dahlberg 2013).
This paper, therefore, examines the extent of democracy in Burma with the reference to the political engagement of pro-democratic leaders, the Burma political system, political history, political instability, the influence of the military on the state, elections and civil society, the judiciary, and constructive engagement into the economy.
Political background
Recently, Myanmar has made considerable political reforms. Political unrest has revolutionized Myanmar’s political system from a military-based socialist regime to an emerging democracy. However, the military effect is still evident in the Myanmar political system (Steinberg 2015). For instance, the 1990 elections were followed by unprecedented use of military intervention to suppress the opposition. The opposition boycotted the 2010 elections citing gross election malpractices (Priya 2014).
The 2015 general elections were considered the freest and fair nationwide elections. Since the parliament first convened in 2010, elections are the only multiparty elections. There was 70% voter turnout, and the opposition, NLD party led by Suu Kyi, secured a majority of both upper and lower houses of parliament seats. As such, the ruling party got the minority of the parliamentary seats (Mahtani & Myo 2015). With such an outcome, political experts foresee governance challenges. There are possibilities of agitations for political power-sharing. Additionally, more political reforms and sectarian violence are looming.
Political instability
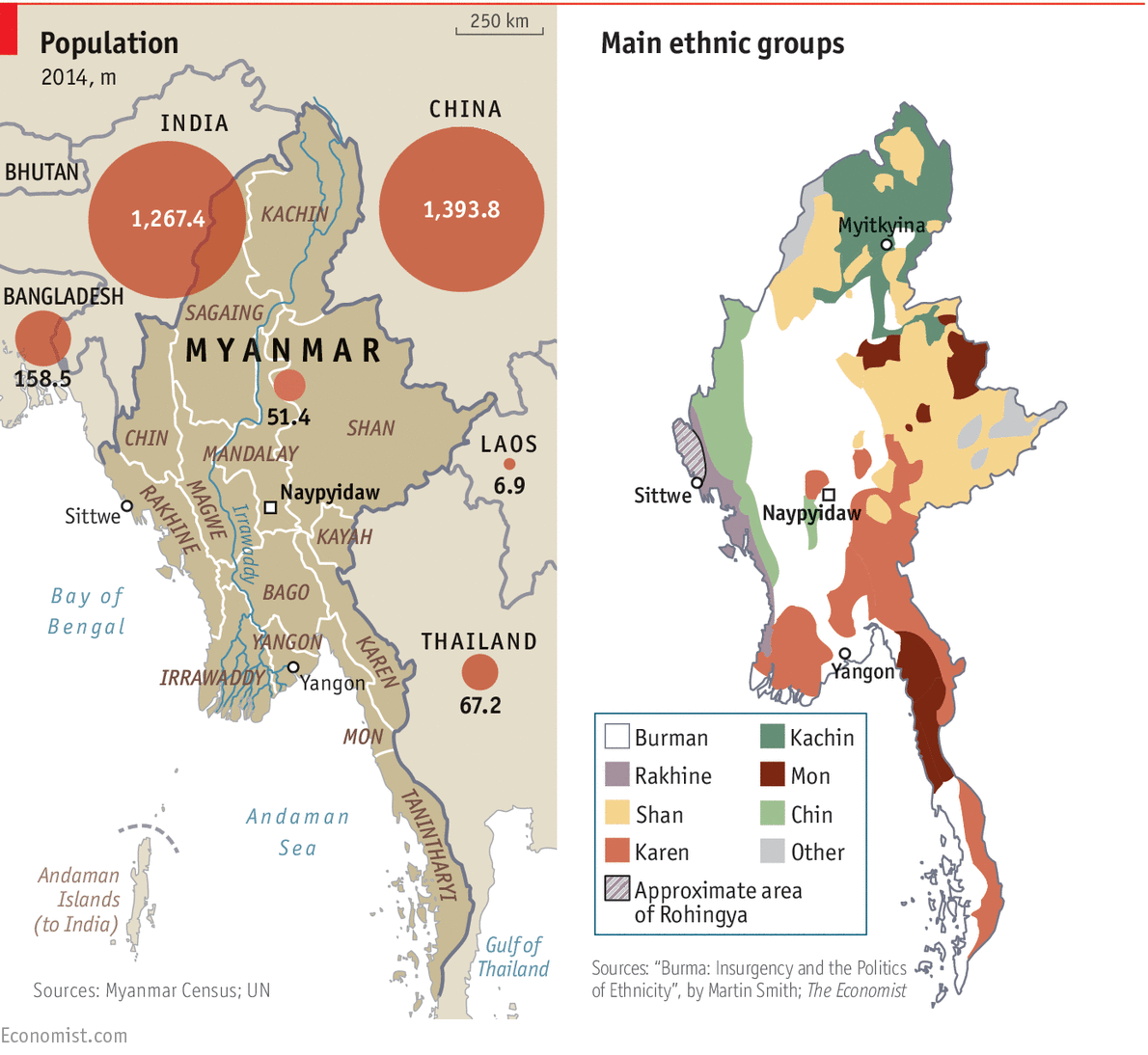
Unfair treatment of the minority has characterized the political leadership in Burma and, therefore, political unrest, anti-government rebels, and nationalist leaders have been involved in fighting for reforms. As a result, the political situation in Burma has been unstable for a long period. The 1962 coup d’état resulted in a military takeover that led to short-lived relative stability. The barbaric suppression and strong military rule led to major political unrest in 1988. The military junta did not relinquish power, refusing to step down after losing in the 1990 elections. The arrest of opposition leaders and monks further created more instability (Oxford Burma Alliance n.d.). Currently, constructive engagements have relatively stabilized the country.
Democracy theory
Radicle theory of democracy
Chief proponents of the radicle theory of democracy include Ernesto Laclau and Chantal Mouffe among others. Precisely, this theory calls for radical democratic citizens and pro-democratic leaders to point out oppressive elements in society and radically fight for human rights and the rule of people (Dahlberg 2013). Myanmar citizenry, monks, political leaders have staged rather radicle fights against the military-led government for years.
However, Myanmar democracy still lags behind due to both military rule and socio-economic policies (Callahan 2014). Although the 2015 multiparty election was relatively free, cases of political arrests were still reported. Additionally, the electoral process, civil liberties, and inclusion still rank poorly. For instance, the 2015 analysis of global democracy revealed that Myanmar is still ‘Not free’ (Puddington 2015). As such, the international communities, including the US still put pressure on Burma to embrace democracy and release political prisoners (AFP 2016).
Historical overview
During the time of British colonization, especially after the Second World War, there were insurgencies of armed minority nationalists. General Aung San took over leadership after independence and Burma adopted a parliamentary democracy system (Keling et al. 2010). The government implemented the parliamentary system for 14 years. However, there were widespread army mutinies and armed rebellion among some communities (Devi 2014). Consequently, rebels controlled nearly all Burma’s borders by the late 1950s and the role of the army became crucial (Keling et al 2010).
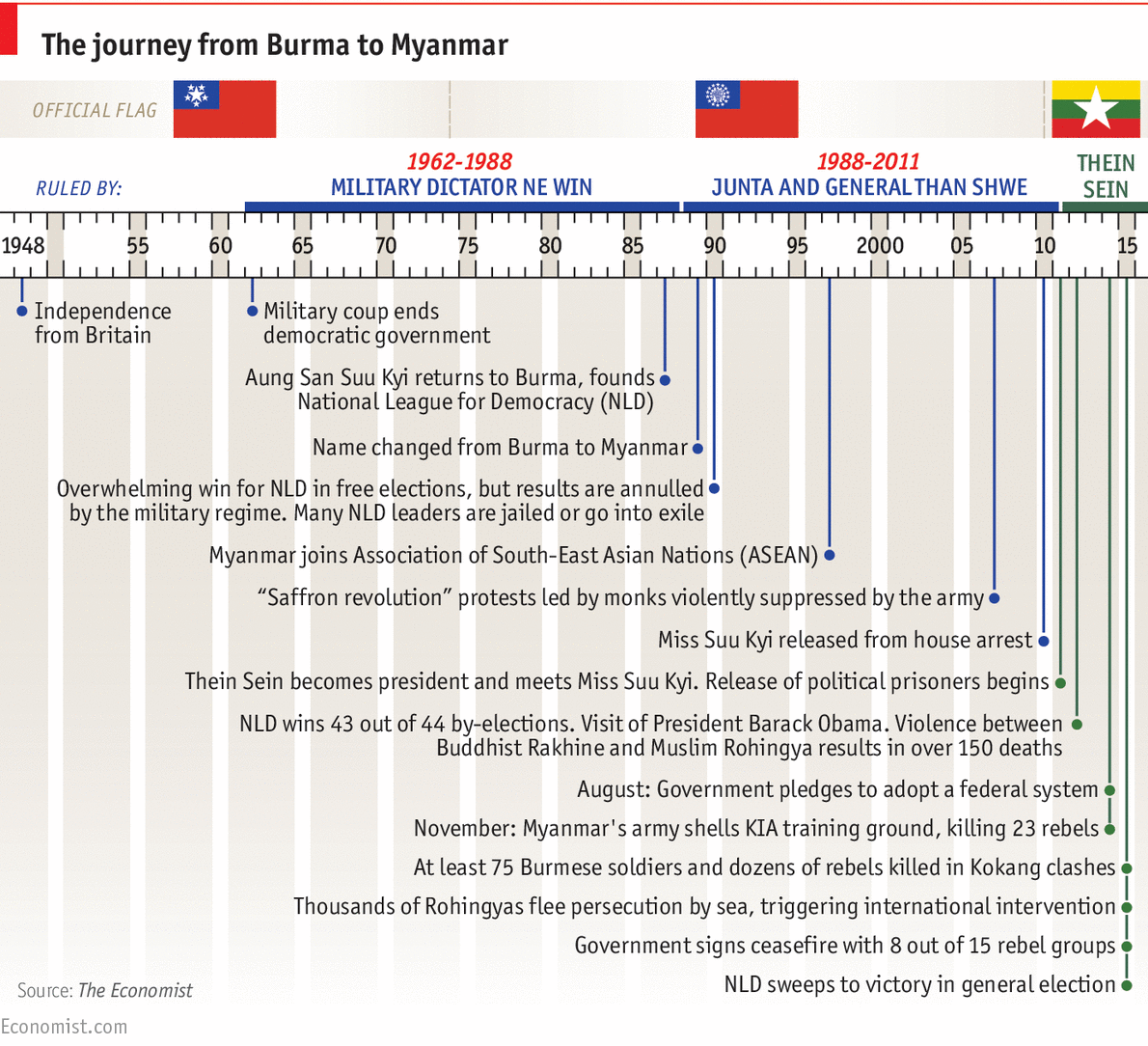
On March 2, 1962, a coup d’état led by “General Ne Win erupted, disrupting the implementation of the parliamentary democracy and consolidation replacing it with socialism” (Keling et al. 2010, p. 132). Consequently, Myanmar’s international relations were adversely affected. The government forced closed-door policy towards foreign countries leading to self-imposed isolation.
The retrogressive political and socio-economic policies propelled the people to rebel against the government. Between 1974 and 1989, the level of the uprising became extremely vivid (Devi 2014). The government responded with strong brutal measures that led to the death of thousands of people. In 1988 in particular, the government security forces killed thousands of protestors during the 8888 uprisings (Keling et al 2010).
Consequently, the credibility of the government was extremely stained, and it received international criticism. Further, the 8888 uprisings mass murder awakened nationalist movements that demanded the resignation of major government officials.
The government had failed terribly in uniting people, stabilizing the economy, and improving the international relationship.
Aung San Suu Kyi co-founded and headed the National Democratic League Party, which was officially established in September 1988. The party marshaled resources to fight for human rights, implementation of democratic processes and regulation of military power in government control. Notably, former government officials that were pro-democracy like Aung Gyi, a military general joined the movement (Keling et al. 2010).
NLD participated in the 1990 election and took 392 out of 485 seats. However, the government-assisted SLORC in denying NLD victory. Further, the government accused the NLD leaders as traitors leading to the arrest of many, including civilians. In 1991, about 25 members of parliament were arrested allegedly for threatening Myanmar national security (Keling et al. 2010).
Continued arrests and brutal treatment by the military-led to the fleeing of the minority to neighboring countries. Refugees went on agitating for democratic reforms and formed the Democratic Alliance for Burma (DAB). The party, together with other pro-democracy people like Suu Kyi, received support from Southeast Asian countries and the US. Additionally, international institutions like the United Nations have strongly supported fighters for human rights. Nonetheless, the military-based government frustrated efforts to the realization of democracy, particularly when it arrested Suu Kyi and other pro-democracy leaders (Keling et al. 2010).
In spite of the local and international pressure, the military government held on to power. In an attempt to change people’s perspective, the party named “changed to the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) in 1997” (Keling et al. 2010, p. 132). However, more agitations for democracy occurred. In 2007, unpopular government policies pertaining to oil led to more protests that resulted in killings and arrest of many monks that were associated with the Saffron Revolution. Further, more accusations followed the government’s inaction and undermining relief from international communities following the 2008 cyclone (Xu & Albert 2015).
Political System
For over fifty years, a military government that had only two consecutive leaders at the helm governed Burma/Myanmar. These leaders were the center of power that ruled with iron fists, were final authority on all issues. Besides, they also had a huge number of military sycophants. Any emerging oppositions were fast purged. Some members of the military who were purged earlier became the cornerstone of the pro-democracy movement in Myanmar since 1988 (Clapp 2015).
Myanmar 2008 Constitution provides for a multiparty democratic system. Institutions of power are however controlled by the military and its leading sycophants. As such, Myanmar has experienced pure turbulence characterized by civil war, military dictatorship, long jail terms and withholding of retirees’ pensions to bar them from engaging in the country’s political affairs (Ijtemaye 2014).
An executive heads the country since 2011 after the collapse of the State Peace and Development Council that had ruled since 1988. From 2011, however, the pro-military government has initiated a series of administrative and political reforms, but without clear roadmaps. These reforms have led to enhanced democratic practices, including “the release of the pro-democracy champion Aung San Suu Kyi who had been in house arrest for several years” (Clapp 2015, p. 1). It had embraced dialogue, released over 200 political prisoners, created human rights commissions, promoted the work of civil society, and introduced new labor laws and practices, including support for strikes (Xu & Albert 2015). Further, the government relaxed rules on press censorship and currency regulations.
Under these reforms, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) agreed on the leadership bid of Myanmar in 2014. The US government lifted sanctions, the then-Secretary of State – Hillary Clinton visited the country in 2011, and President Obama followed a year later. Two years later, Kyi’s National League for Democracy won 43 seats from the open 46 seats for the contest. Today, Kyi is a member of parliament and could become the president.
On 8 November 2015, Myanmar went to the ballot, and Kyi’s party resoundingly took the victory with a large majority in both the upper house and the lower house. This victory was however attained after the government removed restrictive laws that led to previous election boycott. Kyi’s party now controls both houses. While majorities would like to see her at the top, the government has ensured that Kyi is ineligible for the presidential race because of a constitutional provision prohibiting any individual with foreign children (her two sons are Britons) from participation. Further, it is imperative to note that not all political prisoners have been released and clashes persist in some regions.
Major Political Parties
Major political parties in Myanmar include the ruling pro-military party – USDP, NLD, Rakhine Nationalities Development Party, National Unity Party, Shan Nationalities Democratic Party and other small, fragmented ethnic-oriented parties (The Economist Group 2015).
These parties define the meaning of multiparty democracy in Myanmar. Between 2010 and 2015, the country has held two major elections and a by-election (see the below figure), but NLD chose not to take part IN the 2010 election because of restrictive laws. This implied that democratic space in Myanmar was yet to be relatively free and its political future was unknown (Wilson 2015). In the recently concluded election of November 2015, NLD won majority seats in both houses.
The Presidential Electoral College of Myanmar is responsible for choosing the country’s president. The members of the Electoral College are drawn from the upper, lower houses and military appointees. Consequently, the president is responsible for appointing the cabinet ministers, who must be approved by the national assembly.
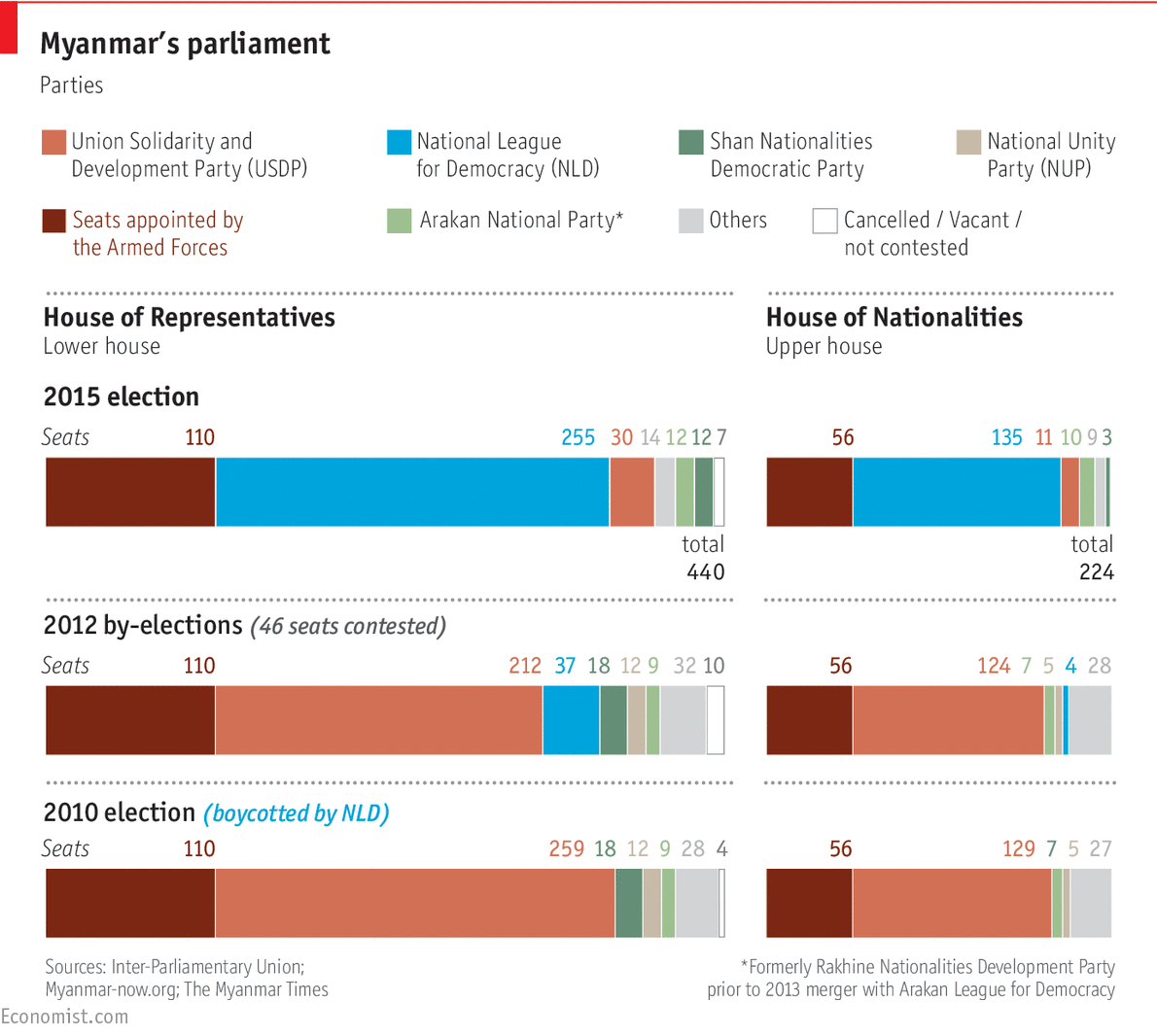
The current political system can accommodate several other small ethnic parties, which are eligible to contest for some seats. Major and small parties and even individuals with diverse political ideologies and positions on several issues currently depict Myanmar national politics. Consequently, objectives are different and to some extent, not carefully crafted to respond to critical issues facing the country. In fact, this observation applies to more obvious political approaches to issues related to ethnic clashes, regional insurgencies, and social and religious tensions. Further, the country’s politics is characterized by the failure of the leading political parties to address key issues, including land disputes.
While Kyi’s party won majority seats in all houses, this does not automatically translate to the presidency because of restrictions and technical relations between the parliament and the executive. At the center of this power, the arrangement is the country’s most powerful political force, the military that generally controls pathways and the formation of the country’s presidency and powerful council ministers (MacDonald 2015).
The just-concluded election of 2015 brought about several changes to this arrangement, and the military once again is greatly affected.
The Military and the State
As Myanmar gradually shifts to a democratic state, the military rule becomes obsolete. For several years, the Myanmar military has significantly engaged in politics. They were responsible for the two coups that led to the introduction of direct military rule in the country. The military has justified its actions through a vague praetorian argument that it is the only institution with the ability to protect the national interest of Myanmar against both domestic and foreign threats.
However, the transition to democracy has challenged its current position. For instance, the military solidarity, between the outgoing President – Thein Sein and USDP is gradually fading. It has critical interests to protect in Myanmar. First, the military is concerned about constitutional representation in the national assembly. Second, it wants to protect the executive portfolio. Third, the military strives to preserve control over the country’s security affairs. Fourth, it is concerned about the veto power on constitutional changes. Fifth, it seeks institutional independence from political scrutiny. Finally, the military wants to safeguard immunity from prosecution on crimes committed during the junta periods.
Given the magnitude of these interests, the Myanmar military is a no longer hegemonic group, but rather a critical veto power in the current political structure. Hence, the men in uniform have moved beyond political monopoly to allot themselves high-ranking, specialized positions and mutilated the country’s constitution to ensure that they remain vital players in Myanmar political structure and the country’s political leadership. In fact, the military has categorically stated that it will play this role beyond the just-concluded national election of 2015 (MacDonald 2015).
Myanmar can improve its 2008 constitution to achieve some changes through vital amendments. Military parliamentarians have always however voted against any constitutional changes that would allow for the reduction of a majority vote for constitutional amendments and any attempts to allow Kyi to run for the presidency (MacDonald 2015).
Before the election, it was argued that the military was going to keep its constitutionally protected influences, including nominating the president, deciding the president not elected by the public but by the Electoral College. With its 25% seat allocation in parliament, the military has a significant voting right and the right to propose a single presidential candidate (MacDonald 2015). In addition, the military is solely responsible for nominating ministers for the positions of Home, Defence, and Borders, who must be active, senior military men.
Currently, the military cannot or is hesitant to reinforce itself forcefully and blatantly in the political sphere unless it sees threats to its critical interests, which may emanate from the new government. Given the military veto power on constitutional amendments, parliamentary representation, executive powers, and security dominance, the military safely feels that it rule the country or at least influence the new government yet to be formed, particularly if it threatens the core interests.
This implies that the 2015 National Election was not therefore the end of the military-political engagement. Nevertheless, it marks a significant step towards the first-ever civilian-military government in Myanmar. This new arrangement is a major milestone as the military begins to cede power.
March 17 2016 could determine the future of democratic space in Myanmar. The date refers to the time the democratically elected government is most likely to take power from the military. It is a transition period. The military, the lower house, and the upper house independently would nominate their own presidential candidates (Goenka 2016).
Today, it is generally acknowledged that Aung San Suu Kyi is most likely to become the president and her party will get the Vice President’s position because the party controls the majorities in both houses. However, a source was quoted saying, “the military has already shown their intentions clearly, and the military will not accept the suspension or amendment of 59f, not at the moment” (Goenka 2016, p. 1). This position would automatically lock Kyi out of the presidency. Nevertheless, the coming government has raised the levels of optimism and hopes for democratic reforms in Myanmar even though the winner may be barred from becoming the president (Transnational Institute 2015; Genser 2015).
Elections and Civil Society
It is widely acknowledged that an active and dynamic civil society is a necessary foundation for any democracy (Gallagher 2015). In this context, Myanmar, an emerging democracy really needs civil society organizations to ensure the inclusion and protection of all stakeholders.
Traditionally, civil society had limited or no roles to play in Myanmar. However, this situation has changed as the country becomes more democratic. Today, they can negotiate peace between the government and armed militias (Asian Development Bank 2015).
Further, since 2012, civil society organizations in Myanmar have found roles in preparing the public for general elections and by-elections. They work to strengthen electoral and democracy in Myanmar. Specifically, they address issues related to human rights, political rights, and political participation by the marginalized, women, youth and conduct voter and civic education.
The recent election success was partially attributed to civil society’s role. It is expected that civil society will continue to work with other stakeholders on elections, voter education, registration, observation, and campaign regulations. Through civil society organizations, many citizens participated in a democratic election for the first time. Besides, it is expected that civil society will work towards promoting a more inclusive, open society to develop democracy in Myanmar.
Judiciary
Myanmar judiciary has never been independent and was often subjected to influence from the military government and widespread corrupt courtrooms. In fact, an investigation established that majorities were insecure on economic and social spheres and never expected it to perform roles that guarantee fair elections because of a lack of the rule of law (Asian Human Rights Commission 2010). The new government must, therefore, ensure a clean, just, and independent judiciary to promote the rule of law. Thus, it must overhaul the entire judiciary system and replace the old guards at the helm (Din 2015).
Constructive Engagement into the Economy
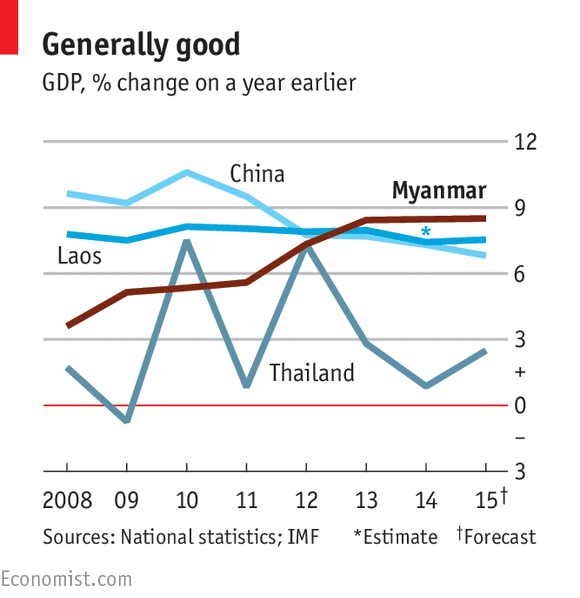
Critics have asserted that democratic and political reforms that started in 2010 have slowed down or even ended. However, Myanmar has continued to register significant foreign investment since 2010 – it has almost tripled to beat some Asian giants (see the below figure).
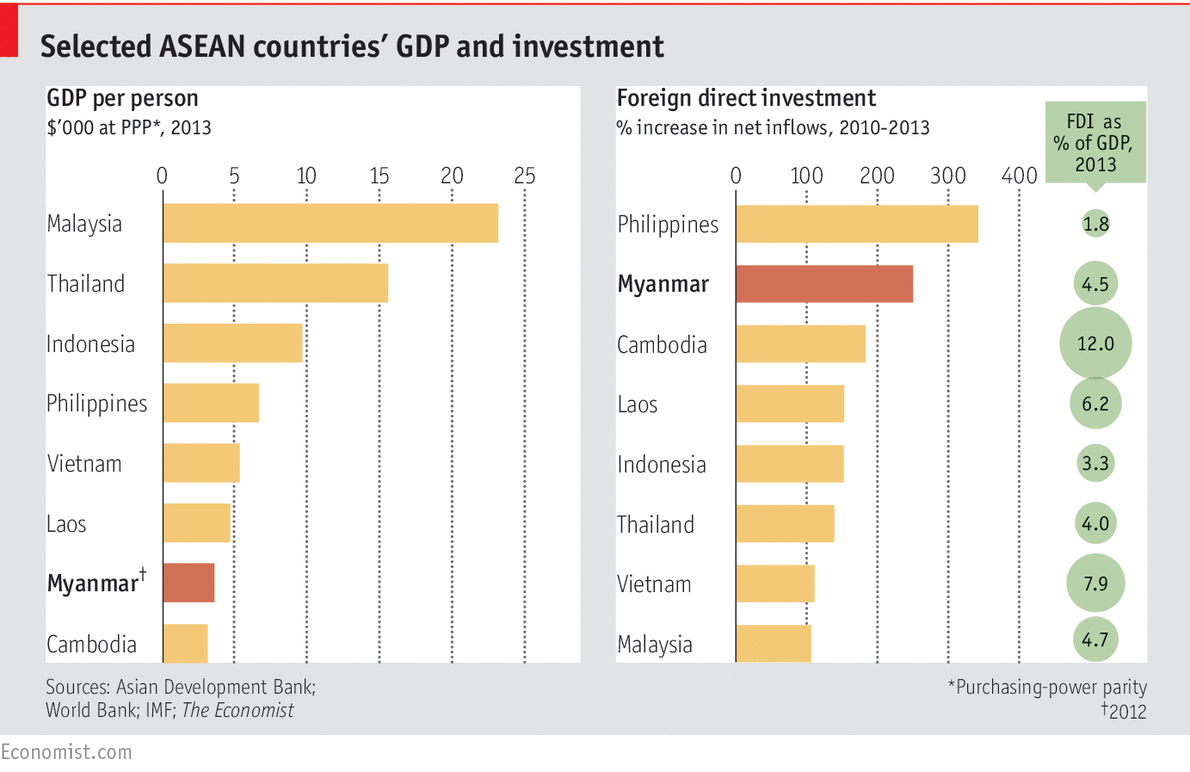
It is favored with its geographical position between China and India, a young workforce, and cheap labor. Besides, Myanmar is rich in natural resources, including jade, gold, oil, natural gas, and rubies.
This economic growth reflects the reward of democratic processes and peace.
Conclusion
This essay has explored to what extent Myanmar is a democracy. It shows that since 2010, the country has made significant strides towards democratic processes. While it is a multiparty democracy, the military government has used all tactics to assert its influence politically in all branches of the government.
The just-concluded National Election of 2015 presented hope for democratic reforms in Myanmar to end military-controlled government. Many believe that NLD has helped Myanmar to attain a new era in democracy and peace.
However, critical issues persist in political, social, and economic spheres. Specifically, NLD must manage a smooth transition from the military-controlled government to a democratic one, judiciary, and political reforms. It is widely accepted that the current national politics cannot guarantee fair processes and even the winning NLD may have to face resistance from the military that has clearly stated it will not allow for some constitutional amendments to allow Kyi to become the president. Nevertheless, it is interesting to monitor the coming events after 17 March 2016 to witness a potential transition to a new democratic period of governance in Myanmar.
Reference List
AFP 2016, US Urges Myanmar to Free all Political Prisoners. Web.
Asian Development Bank 2015, Civil Society Briefs: Myanmar. Web.
Asian Human Rights Commission 2010, ‘Burma’s elections: An absence of minimum conditions’, Ethics in Action, vol. 4, no.3. Web.
Callahan, MP 2014, Democracy in Burma: The Lessons of History. Web.
Clapp, P 2015, Myanmar: Anatomy of a Political Transition, The United States Institute of Peace, Washington, DC. Web.
Dahlberg, L 2013, Radical Democracy in Contemporary Times. Web.
Devi, KS 2014, ‘Myanmar under the Military Rule 1962-1988’, International Research Journal of Social Sciences, vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 46-50. Web.
Din, 2015, Myanmar’s Old Judiciary a Challenge to the New Era of Governance. Web.
Gallagher, 2015, Partnering with Myanmar’s Civil Society to Build Democracy. Web.
Genser, J 2015, ‘Democracy on a Leash’, US News. Web.
Goenka, H 2016, Myanmar Elections: Can Aung San Suu Kyi Be Named Next President?. Web.
Ijtemaye, L 2014, Backgrounder – Political and Economic Reforms in Burma/Myanmar. Web.
Keling, MF, Saludin, MN, Feigenblatt, OF, Ajis, MN, & Shuib, S 2010, ‘A Historical Approach to Myanmar’s Democratic Process’, Journal of Asia Pacific Studies, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 132-148. Web.
MacDonald, AP 2015, ‘Myanmar’s military wrangle with a new political reality‘, East Asia Forum. Web.
Mahtani, S & Myo, M 2015, Myanmar Votes Amid Claims of Irregularities. Web.
Oxford Burma Alliance n.d., Saffron Revolution. Web.
Priya, P 2014, Myanmar: Revival of the Lost Kingdom. Web.
Puddington, A 2015, Discarding Democracy: Return to the Iron Fist, Freedom House, Washington, D.C. Web.
Steinberg, DI 2015, Myanmar’s military – velvet glove, iron fist?. Web.
The Economist Group 2015, Myanmar. Web.
Transnational Institute 2015, The 2015 General Election in Myanmar: What Now for Ethnic Politics?. Web.
Williams, MC 2015, Myanmar’s Troubled Path to Reform: Political Prospects in a Landmark Election Year. Web.
Wilson, T., 2015. Myanmar’s political destination still unknown. East Asia Forum. Web.
Xu, B & Albert, E 2015, Understanding Myanmar. Web.