Introduction
The case of Magna PC provides a valuable illustration of the importance that the company’s strategy has for its success and financial efficiency. Magna PC specializes in manufacturing and designing private label PC for large electronic retailers, who sell the PCs under their own branding. The company faced difficulties when the actual net sales data showed significant differences from the budget. This study will focus on defining the causes of Magna’s failure by exploring which strategical aspects the company can implement to be more successful.
Main body
Firstly, considering the nature of the company’s activity, the main goal of the company’s strategy is to achieve a competitive advantage through lower prices for customers. Thus, most of the company’s repeat customers are large retail companies primarily interested in finding a supplier with lower prices to increase their profits from the computers’ sales. Furthermore, as a manufacturer, Magna PC is also responsible for the products’ quality to final buyers and users. Thus, the company is interested in maintaining a low percentage of faulty PCs returned by consumers and increasing the level of consumers’ satisfaction with manufactured products.
Furthermore, the Magna PC’s competitor company DataMax PC uses similar techniques and processes in production, but DataMax PC’s profits are proportionally higher than Magna PC’s. The significant difference between the two companies is that DataMax PC has one manufacturing plant, while Magna PC has “four PC factories of similar size” (Sheehan & Kobussen, 2020). The information suggested that each factory has its own quality assurance departments, and the level of goods rejected and returned to the supplier is 4,5% compared to 3% in the budget. It can be that for the competitor company being in one factory saves additional costs for parts’ testing.
Next, Magna PC experiences significant difficulties in managing the high turnover rate. The company’s employees are trained primarily to perform a simple chain of sequential actions. Semiskilled work negatively influences employees’ morality and motivation to work as it seems that the company utilizes talents for machine-like labor. Increasing the level of employees’ skills and reviewing the organizational culture in favor of a more friendly approach can result in employees’ increased involvement in work. Furthermore, as replacing an employee causes additional expenses, managing a low turnover rate will positively influence the company’s financial results.
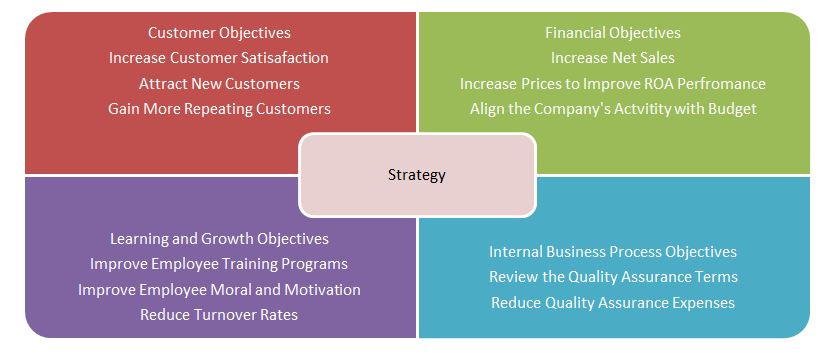
Creating a balanced scorecard can significantly improve the process of assessing the company’s performance. The table combines the collected information in an accessible visual system form (Figure 1). The company’s new strategy measures should focus on four primary fields, inducing relationships with customers, financial statements, employees’ learning and growth, and optimization of the company’s internal processes. Thus, most of the company’s obstacles are sourced in the complex strategy of selling high-quality products at lower prices for further reselling by retail companies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Magna PC targets clients who resell the production; creating custom PCs for large business companies will improve the financial efficiency through increased sales without significant additional investments. Improving the employee training programs to get more high-skilled employees for the company will reduce the turnover rates and save on hiring expenses. Lastly, reviewing the quality assurance terms can save on additional expenses across all four factories. For example, the company can outsource the quality check of supplier’s parts to third parties to ensure that its quality assurance departments do not carry out unnecessary work other than testing Magna PC’s products.
Reference
Sheehan, N T., & Kobussen, G. P. (2020). Using the balanced scorecard to assess and enhance Magna PC’s performance. IMA Educational Case Journal, 13(2), 1-2.