Executive Summary
The main objective of this research paper is to carry out a comprehensive analysis about the Coca-Cola Company. In so doing, the paper would focus on exemplifying an appropriate company background of Coca-Cola, considering the financial overview of the company, and most importantly, formulating a problem statement of the company along with the historical background of the problem as well as the main players and actors who contributed to the problem.
Furthermore, the paper would illustrate the potential challenges, issues, and prospects of the company with consideration of the discussion of the related literature, alternative solutions and their implementations, and implications for future use. Finally, the paper shall focus on accumulating pertinent recommendations in conjunction with a relevant conclusion.
Company Background: Overview
Bloomberg Businessweek (1) suggests that the Coca-Cola Company produces, allocates, and delivers nonalcoholic beverages and syrups internationally and it is predominantly renowned for the production of sparkling and still beverages; to specify, the business’s sparkling beverages comprise of nonalcoholic ready-to-drink beverages with carbonation, for example, energy drinks, and carbonated waters and flavored waters.
Some of its other products from still beverages comprise nonalcoholic drinks without carbonation, together noncarbonated saccharine savored waters with enhanced quality, cloister free energy-drinks, lucrative juices, and lovely savored drinks, including ready-to-drink teas, high quality coffees, and superior sports drinks; moreover, the business also offers fountain syrups, and other healthy food supplements those are favored by the health conscious customers.
With the glory of running such as a successful business for over centuries, this US-based company possesses a very bold supply chain offering diversified products to consumers all over the Saudi Arabia creating a passion that fastens the billions of its enthusiasts.
Problem Statement
Coca-Cola Company the worlds leading multinational company are continuing its global operation in more than two hundred countries in the soft drink and beverage sector with stronger brand position. Through out the global operation Coca Cola Company has evidenced huge crisis from the national and international legislation, competitors, and diversified culture and disturbed its operation and profitability but none can keep any stopple to its progress.
Middle East and GGC countries are also a vital market for this multinational company (MNC) but also suffered from different crisis starting from the gulf war while US sanctions prohibited their national MNCs to do business in some Arab counties that seriously injured the company in this region (ECOS 10). Later on gulf crisis, the MNC faced some other crisis concerning the religious sentiments of the Arabs. In a promotional campaign poster with Muslim retailer is saying her prayer in front of Coca Cola’s monogram in the wall rather than the Kaba while another computer graphics presented “No Makkah- No Mohammed” – that generated serious public protest in the Arab world that leads to a of Coke in Saudi Arabia (Slide Share Inc 1).
Starting from Arab Israel conflict in sixties, Coca-Cola evidenced a long ban in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and after long interval Coca Cola reentered in the Saudi Arabia market in 1988 by joining venturing with previous center part Olayan Group but the operation don’t goes smooth (The Olayan Group 1).
The Coca-Cola Company Inc would like to explore its operation in Middle East specially to strengthening its Coca-Cola Bottling Company of Saudi Arabia (CCBCSA). In Saudi Arabia, with this view the management has engaged this researcher to present a report on the company.
Research Objectives & Research Question
The main objective of this report is to examine the operational performance and strategies of Coca-Cola in its global operation and especially in Saudi Arabia to understand and identify the crisis and challenges that belongs to the company and how the company’s strategy would respond to them.
This investigation continues on the strategic implication of the company in global operation with the aim to sustaining its market leader position among their competitors’ in the global market with their product and services with high degrees of attentiveness and particularly argued privileged levels of profitability.
This report has aimed to explore the effectiveness of global strategies by considering strategic tools and parameters and assess how the Coca-Cola Company prolonged its leading position. To do so, this report also deals with few imperative research questions as follows:
- How does theoretical framework of the strategic planning works on development of Coca-Cola Company?
- How Coca-Cola Company designed their strategic planning to become a leader in international soft drinks and beverage market?
- To what degree the implementations of existing and alternative policy can success Coca-Cola Company’s mission and vision in Saudi Arabia?
- What extent do the Coca-Cola Company assessed on competitive advantage?
- To what extent it is possible for the company to implement their strategy in global recessional economy.
Historical Background of the Problem or Contributing Factors
Williston (2) pointed out that the Coca-Cola Company has elongated complex historical background with allegation of aligning with Nazi party during World War II and its German operation evidenced blamed for anti-Semitism.
In 1936, the Coca-Cola Company sponsored the notorious Nazi showcase Olympics which most of the countries refuse to take part and up to 1939, the company operated forty-three bottling plants along with six hundred distributor channels within Nazi Germany. In the post era of World War II, the company’s global operation seriously hampered for its wartime disputed strategy and brand Coca-Cola faced worldwide boycotts in many counties.
During the epidemic of war Max Keith, the German operator of Coca-Cola developed Fanta, which the company buyout in sixties and the legend marketing campaign of the company successfully rub out the blame of Nazis integration from the public mind but history never, excuse Coca-Cola for its notorious role.
The Coca-Cola Company started its operation of bottling in Saudi Arabia during 1950 but the establishment of Israel, US favor to Israel and the company’s secret pact with Jewish spread out boycotting Coca-Cola and the Saudi Arabia Operation propounded in 1963 (The Olayan Group 10).
The Coca-Cola boycotts in the Arab world seriously damaged the companies’ bottling plants in Middle East and several studies demonstrated that the mass peoples’ boycott of US goods in this region has donated at least 55% turn down of US exports towards the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) during 1998 to 2002.
The Olayan Group is Saudi Arabian multinational company consisting with fifty business entries served for manufacturing, distribution as well as project financing and the Coca-Cola Company reentered in Saudi Arabia through a joint venture in 1988 under the banner CCBCSA. Olayan Group engaged its highest effort to recover Saudi Arabia Market after twenty-five years absence by enforcing corporate crisis management, entrepreneurship, and persistent commitment to growth including national and global values.
The excellent operation of CCBCSA has enabled the Coca-cola to recover 30 % of the beverage and soft drink market of KSA with inspiring growth in the GCC counties within 2000 by producing Coca-Cola, Fanta, and Sprite. CCBCSA introduced state of the earth technology in its production plant including IT integrated management at 30 distribution channels all over KSA and above 1400 employees that serve a strong customer base (The Olayan Group 1).
Saudi Arabia: Crisis Management
TRACCS (1) argued that the crisis management drives still prolonged to Coca-Cola after the reentry of the company in KSA while in 2000, the Life Magazine bring into public views a Coca-Cola promotional photograph a Cameroonian Muslim salesperson saying his Namaz keeping Mecca and Kaba at his back but bending his head in front of Cocoa-Cola cooler.
The portrait has captioned with the slogan that “Muslims always look for spiritual refreshment”, it is not clear whether the happing was an intentional hit to the Islamic sentiment or a malicious blander of the R&D of Coca-Cola, but the fact faired worldwide Muslim protest. The anti-Islamic propaganda of the company swiftly spread out in KSA, different Muslim activists and student organizations in the US University campuses urged to boycott of Coca-Cola in KSA.
The situation was deteriorating quickly but the local Agent of Coca-Cola, the Olayan Group tactically take control on the fact and communicated with the headquarter of Coca-Cola to make safe by a written exculpation along with apology from the Life Magazine by obviously mentioning that Coca-Cola never done any thing with that photograph.
Within two days headquarter arranged such a document from the Life Magazine and published a protest in the Newspaper from New York, the same copy was translated into Arabic and published in the local Newspapers and distributed in the University campuses in KSA and thus the crisis was managed.
Saudi Arabia: Crisis Management
In 2000, Coca-Cola slapped with a diverse religious crisis in Saudi Arabia while some Muslim identified that the computer graphics of reversed Logo of Coca-Cola looks like Arabic alphabets and spelled as “No Makkah-No Mohammed’”. This time same storm of protest flourished in KSA and argued for boycotting US products and Coca-Cola at the most wanted object of attack and the market of Saudi Arabia become destabilized.
The local agent has called to mitigating the crisis responding to negative propaganda against the Coca-Cola along with setting a stopple to such false allegation. The local agent urged to the media due to the irrationality of the false allegation offensively caused from baseless rumors, they formed an investigation team with legend pundits and linguistic professors.
The report of the investigation pointed that the logo of Coca-Cola had designed long before in 1880 while the company operates only in the domestic market as a soft drink while there were no question to integrating anti-Islamic thoughts. Both the electronic and print media responded positively, some of the newspapers published cover concerning the real fact that contributed Coca-Cola to overcome the raised scandal against the company.
The Main Players or Actors Who Contributed To This Problem
For the presented case – 1, it is clear that clear that the local agent of Coca-Cola has successfully managed the risks with the help of headquarter but the fact that goes through promotional campaign in Cameron is malicious evidence for which the main player is the R&D department of Coca-Cola that has forgotten to respect diversified culture. Being a large MNC, Coca-Cola has to take care of maintaining ethical and social responsibility as an integral element of its strategic management process for the operation both home and abroad.
Godiwalla (5) added that the socio-cultural environments in which the MNC operates are continuously changing with time where the MNC needed to respond properly for it ethical and along with CSR issues while the socio-cultural environments consists with major three levels as global, regional and home country.
It is natural that sometimes the home country at headquarters’ couture could be far different and conflicting to the operating country; in that case, MNCs must take care to the host country’s culture and ethic and in this aspect where Coca-Cola evidenced enough lacking to meeting the industry norms in KSA.
In the both cases, to publicize the scandal in media, there are possibilities to have the involvement of competitors. The most renowned competitor of Coca-Cola is the Pepsi who has enjoyed the Saudi market along in the absence of Coca-Cola, but for Saudi Arabia and the Middle East both the competitors are most friendly to protect common interest due to different boycotts in this region.
Another possible main players or an actor who contributed to this problem is Macca-Cola. Rarick (1) exposed that the Macca-Cola came in the Saudi Arabia market in 2002 addressing the un-Islamic attitude of Coca-Cola and the owner of Macca-Cola is a Muslim political activist from French.
Mecca-Cola used the name of the birthplace of the founder of Islam, which has considered as a holy place for the Mohammedans, and emotionally blackmailed the religious sentiment. It also branded another product Zamzam Cola that already gained enough popularity in Iran, Bahrain and other Arab countries just patronizing anti-American sentiment in this region.
Another new player also trying to gain a share in the soft drink market of KSA by using religious sentiment named ‘Qibla-Cola’, which is an US, based company, but Islamic leveled.
Challenges, Issues, and Prospects
Due to an US leveled MNC; the Challenge of Coca-Cola Company is unavoidably concerned with the challenges of USA in Saudi Arabia. CCI (1) pointed out that it is the pick time for America to take into account how the people of rest of the world observe present America, what are major changes of public perception towards Americana during nineties, how the isolation and social life of American are changing, and anti-American moves are flourishing globally.
Until and unless America would change its foreign policy, the US brands would face raising challenge of decreasing sales revenue like coca-cola.
Connecting to the Twin Tower attack on September 11, 2001, the US and Saudi Arabia has been deteriorating and that like a cold war situation while USA blame KSA for financing the terrorists as Al-Qaeda’s chief is a Saudi citizen.
The public perception in this region is that the Al-Qaeda is a creation of America and the terrorist attack of September 11, 2001 was a preplanned drama of Americans that was staged to undermine the Arab world to exploit their petroleum resources. The American aggression in Iraq, Afghanistan, threats to Iran all those are interlinked to the US-KSA relation those directly impacted US brands like Coca-Cola in this region (MEPC 7).
Rather than the political issues there are some other challenges those Coco-Cola has been facing in Saudi Arabia and rest of the globe.
Favaro, Tim, and David (1) pointed out that the retailing soft drinks have a great challenge during the recession due to the exaggerated home values seriously impact on the customers. During the recession, the interest rate turns to zero and credits are available for free of cost while the raising unprecedented levels seriously decrease the consumer’s spending.
The soft drinks have to have face challenges by responding uncompromisingly accumulating new outlets, introducing new concepts, driving to the international market and organizing online presence retaliates could take the challenges. As a leading soft drinks Coca-Cola has to drive in the market with such challenges.
The Coca-Cola Company (5) pointed out that the soft drinks industries are acknowledged as dead set against recession, but the present U.S. recessionary economy has sink it’s teeth into the profits of world’s prevalent beverage giant like Coca-Cola.
Coca-Cola Company proclaimed that its sales were downturn in December 2008 due to some of its supply chains are facing worst monthly returns among the last five years and if the situation continue any more then there is doubt to say that the biggest fast food has been impacted by recession. Coca-Cola has also argued that elevated food prices, reduced speed of customer expenditure coupled with the downturn of housing market that resulted lower sales in global operation.
The company also identified pure water resource, raising health consciousness of customers, increasing competition in the global market, shifting beverages business environment, exchange rate, energy crisis, increasing cost and decreasing profitability and their major issue of challenge.
USCIB (1) pointed out that Coca-Cola Company has been overcome the punch of credit crush while the Chairman and CEO of Coca-Cola Muhtar Kenthe also added that the company has noteworthy growth in 2008 particularly where 73% of the revenue and 81% of its profit from overseas market.
The soft drink industry possibly would gain an enhanced situation with no serious impact of global financial crisis as well as considerable increase in food prices but Coca-Cola has been positioned against some recession due to job cut and reduced income globally.
Under the recessionary economy, people consider more than twice before spending their money about the justification of expenditure while Amidon (13) mentioned that under the recessionary economy the return on assets of Coca-Cola has reduced 3% in 2008 in relation to previous year 2007.
Amidon (5) also reported that Coca-Cola has gained a profit slight higher than its expectation but overall growth rate decreased notably. In 2008, due to the global financial crisis and its consequential recession, the company reported a remarkable loss of US$ 874 million while the company’s debt-to-equity ratio decreased 0.979 or 97.9% in global operation.
It is important to note that the soft drinks industry is indeed prospective in Saudi Arabia because the public demand for such beverages remains more or less inelastic in most of the cases except of any sudden influence by recessionary impact.
In context, Coca-Cola Company has a number of prospects for carrying out its business operations in Saudi Arabia for enlarging non-carbonated category, which is growing in a fast pace (the international non-carbonated drinks market grew by 7.5% in first quarter of 2005, whereas in 2007, Coca-Cola announced a 7% augmentation in its Powerade-sport-drink and 14% augmentation in Minute Maid juice).
Conversely, apart from Saudi Arabia, Coca-Cola has achieved significant growth in main emerging-markets like Russia, China, and Brazil as demand for soft drinks and beverages at those nations raised rapidly in current times owing to their economic-growth (unit volume increased by 11% in 2006 in North Asia, Eurasia, and Middle East due to mainly for growth of China and Russia).
In recent years, with number of international sporting events rising, the prospect of Coca-Cola to sponsor those events and to enhance its brand name is increasing as well; it is arguable that this method of brand promotion is a good technique to reach the target customer.
To illustrate this argument, it is essential to state that the company has recently sponsored the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing, 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, Canada, and 2010 FIFA Football World Cup of South Africa that altogether brought a huge success for the company’s image.
Discussion of the Related Literature
Coca-Cola operates on a local-scale in every community of KSA and the world constructing widespread-accessibility with local-focus owing to potency of Coca‑Cola’s organizational structure that encompasses more than 300 bottling-partners internationally who work closely with customers like grocery-stores, restaurants, street-vendors, convenience-stores, movie-theaters, and amusement parks, who in turn sell its products to final-consumers at a rate of 1.6 billion servings-a-day. This reflects the fact that this company indeed possesses a very strong organizational structure as illustrated in the figure below:

Figure 1: Organizational Chart of Coca-Cola
Source: Self generated from Girard (5)
Coca-Cola’s products are consumer products, and are rather responsive to consumer’s disposable income; therefore, the company’s management reports two possibilities that serve to figure out its arrangement related to this factor – first, consumers think soft drinks as inexpensive pleasure and so even in temporary environment of steady or slightly dwindling disposable income, consumers are unlikely to relinquish soft drinks.
Second, Coca-Cola scrutinizes disposable income in over 200 countries including Saudi Arabia where it sells soft drinks; this information suggests that disposable income is gradually rising around the world and that individual consumers are eventual buyers of soft drinks; additionally, Coca-Cola interprets this to mean more purchases of consumer products, particularly in countries where consumer product purchasing has been negligible.
Nevertheless, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo’s real ‘buyers’ have been neighbouring bottlers who are either franchised or owned, particularly in the case of Coca-Cola; it is arguable that whilst Coca-Cola and its competitors release their franchises, those bottlers in turn develop the ‘channel’ in the course of which these comprehensive beverage brands attain the local customers even in the rural areas.
Environment Analysis of Coca-Cola in Saudi Arabia
In order to convey an assessment of Coca-Cola’s operations in the Saudi Arabian business environment, it is imperative to consider a number of factors such as the country’s demographics, economic, political, socio-cultural, technological factors:
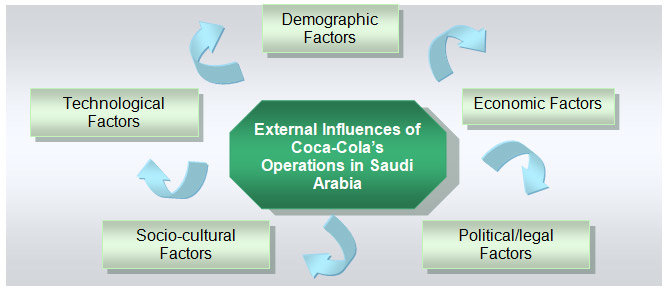
Figure 2: External Environment of Coca-Cola Operation
Source: Self-generated
Demographic Factors
It is crucial for Coca-Cola Company to examine the demographic features of the country to ensure that it is undertaking effective tactical steps. In 2010, Saudi Arabia had a total population of 25,731,776; the average age of the total population was 24.9 years (with an average of 26 years in men, and 23.4 years in women) and a populace growth rate of 1.548 percent annually.
Recently, the birth rate of the country is 19.43 births per 1000 people and death rate is 3.34 deaths per 1000 people; moreover, the net migration rate of Saudi Arabia is -0.61 migrants per 1000 people. The urban inhabitants represent 82 percent of the total population with a rate urbanisation of 2.5 percent; the life expectancy of the total population is 73.87 years and total fertility rate is 2.35children per woman.
According to Indexmundi (1), the government expends about 5.7percent of the total gross domestic product for education purposes of Saudi Arabia and it is arguable that the literacy rate of the total population is 78.8 percent. The following table shows the age configuration of the total Saudi Arabian population:
Table 2: Age Configuration of the Saudi Arabian Population
Source: Self-generated from Indexmundi (1)
Whilst carrying out the operations in Saudi Arabia, another vital issue is for Coca-Cola to make sure that it has the appropriate preparations and competencies to serve people from every ethnic background. The table below illustrates the languages, literacy rates, ethnic, and the religious groups present in the country:
Table 3: Religious and Ethnic Groups
Source: Self-generated from Indexmundi (1)
Economic Factors
Since the impact of the global financial crisis was not excessive in the KSA, Coca Cola’s operation over there had no severe hindrances by this economic determinant. However, the company suffered significantly by the recession from its operations in the rest part of the world.
The 2010 fiscal year substantiated to be rather complicated for the company because of the continuance of the recessionary affect that the company faced in 2008 to 2009 period creating difficult general retail environments for all of its trading entities. As per Yahoo Finance (1), during this time, the share prices of the company faced a sudden slump as shown in the figure below:
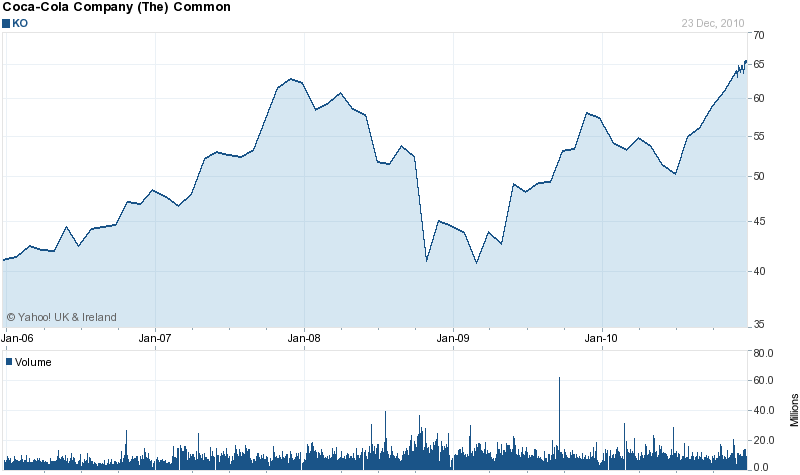
Figure 3: Basic Chart of Coca-Cola
Source: Yahoo Finance (1)
In spite of these tough situations, Coca-Cola engendered a quite remarkable development in the income and started to revive back its stock prices.
Political/legal Factors
The political matters can play a significant role in the entire process of Coca-Cola’s KSA operation, consequently affecting its producing, allocating, and retailing activities to the final consumers; the changes in political environment could affect this industry accordingly through both direct and indirect link.
Governmental instabilities, strikes, political violence, state of emergency, etc can for example, severely affect the business environment of the soft drinks industry in the country. On the other hand, the company always need to comply with all the lawful barriers including complying with the Islamic laws, environmental and labour legislations, and many other rules and regulations as well.
Socio-cultural Factors
The Saudi Arabian population is a quite conservative and sensitive in terms of adoptions of religious values. Being a multinational-Company, it has been in many instances quite difficult for Coca-Cola to adapt all the socio-cultural issues of the country and behave in accordance to the societal and communal attitudes towards marketing activities and advertisements of the company.
Technological Factors
The company believes that in this rapidly changing competitive world it is essential for its Saudi Arabian division to adapt the latest technological infrastructure to gain competitive advantage. Therefore, its IT department constantly works for ensuring the greatest technological assistance in this market. Moreover, it is imperative to note that the company has hi-tech instruments that help it in rapid production in KSA.
Core Competencies of Coca-Cola
Apart from the fact that the company possess a well-built organisational culture, many other factors exists that enhances the company’s position not only in Saudi Arabia, but also in the global context. These factors include the core competencies of Coca-Cola Company that provides it with competitive advantages over the rival businesses. Some such core competencies have outlined below.
- Marketing: Coca-Cola has considered as one of the instigators of contemporary marketing model; throughout its long history of marketing activities, it has pioneered many innovative advertising techniques and styles to capture market and it was the first company to offer a gimmick with its product. In 1900, this company started presenting its signature drink as a delicious and refreshing formula and this slogan has repeated for over the century of advertising Coke in the globe; in fact, through its powerful marketing campaigns, it has created an image that has reflected in what customers think of when they buy Coke;
- mySAP: Coca-Cola turned to the Strategic Enterprise Management (SAP SEM) competencies of mySAPTM Financials and mySAPTM Business-Intelligence (mySAP BI) to manage the task of running its regular operations by using the mySAPcomTM platform internationally; SAP SEM solutions has integrated strongly with Coke’s transaction system to consolidate financials, power financial-planning, and provide comprehensive view of corporate financial performance across the organizational-structure. This strategic approach of the Coca-Cola Company has played a significant role in enhancing its position in Saudi Arabia and in the global context.
- Innovation: Coca-Cola has been able to survive and grow in an ever-changing market because of its capacity to methodically innovate and distribute new products; in 1990s, it showed earnings growth of 15 to 20 percent per year, and it was apparent that the market was changing – to cope up with these changes, Coca-Cola transformed into a total beverage company.
- Size: the large organizational structure of the company allows it to employ huge distributors in KSA who have the capacity to deal with stadium, universities, and school systems to include them in Coca-Cola’s customer base; these distributors possess capability to carry out massive-purchases that significantly lowers cost; moreover, Coca-Cola’s has come up with an effective customer management-scheme to remain competitive.
- Distribution channels: by means of a powerful distribution network throughout KSA and the global village, there are rather a very few places left in the world where the products of this company has not reached yet. To simplify, even though Coca-Cola is an industry giant with a global presence, the fact that the availability of its products remain unswerving even in the remote places of the world has ensured by the widespread supply chain of the company.
Strategic Analysis of Coca-Cola Company
Kotler and Armstrong (79) argued that strategic options are coordinated and interrelated set of proceedings that has designed for utilizing the core capacities and competencies for achieving the competitive advantage. Therefore, according to the standard model, Coca-Cola generates numerous strategic options in Saudi Arabia by some systematic phases from business-level to co-operative strategy, which has shown in the following figure.
Figure 4: Primary phases of formulating strategy
Source: Self-generated from Kotler and Armstrong (79)
- Business-level strategy: Coca-Cola Company could generate this type of strategy for KSA by using Porter’s generic strategy as below-
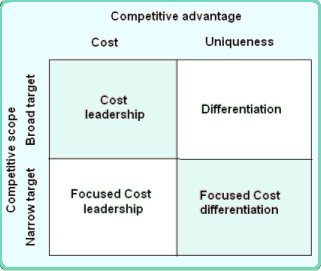
Figure 5: Porter’s generic strategy for Coca-Cola Company
Source: Self-generated
If it follows the cost leadership strategy, Coca-Cola will be able to provide its beverages at the lowest costs in relation to other competitors’ like PepsiCo or Mecca Cola; on the other hand, if it follows the differentiation strategy, it can deliver unique attributes and features to the target customers. Here, Coca-Cola can offer the finest colas, juices, carbonated, and non-carbonated drinks or other items through unique tastes, flavors, and nature that would be much better than some other competitors like PepsiCo does. The formulation of differentiation strategy has shown as the following-
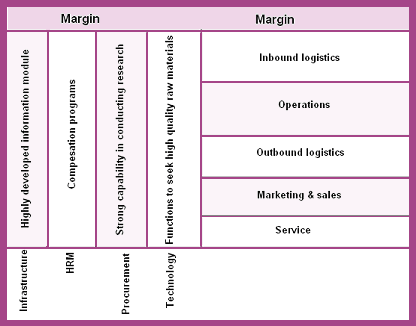
Figure 6: Porter’s generic strategy for Coca-Cola Company
Self-generated from Kotler and Armstrong (79)
- Competitive dynamics: at this stage, Coca-Cola can attempt to create competitive dynamics for its KSA business that comes from a series of competitive actions and responses among the competitors within the ready- to- drink beverage industry which may be affected by a number of reasons, like- similarity of resources, relative size of the company, innovation, quality and so on.
- Corporate- level strategy: this strategy is important to decide the structure of the company; this concept focuses on diversification that involves the Coca-Cola retail segment offerings and the diversified sales mix of its beverage items.
- International strategy: since Coca-Cola is operating and distributing its services over countless stores and other shopping malls in many parts of the globe excluding KSA, to become a unbeatable player in the international market it should consider the following factors-
- Issues of production
- Demand condition
- Connected and supporting industries
- Its strategy, structure, and rivalry
- Co-operative strategies: In the light of the existing plans and situations, Coca-Cola can develop various types of co-operative strategies such as the following-
- By composition of strategic alliances in Saudi Arabia, Coca-Cola can combine the resources, capabilities, and core competencies with other firms for gaining the mutual interest in designing, distributing, and producing goods.
- Through joint- ventures, it can enjoy benefits by the combination of assets as it is doing now. Nevertheless, Coca-Cola should consider following things before incorporating the strategies, which includes the following-
- Internal service quality: In Saudi Arabia, Coca-Cola’s internal quality has maintained by the path of higher employee selection and training process, neat and clean workplace, quality work environment, higher salary and strong support for those who are dealing with the customer’s and franchisee.
- Satisfied and Productive Service Employees: Employees of Coca-Cola are more satisfied, dependable, and hard working because they draw higher remuneration then other companies.
- Greater service value: Coca-Cola affords more effective and well-organized customer value creation and service delivery for the Saudi Arabian market; as a result, Coca-Cola service value is greater than many of its competitors.
- Customer Satisfaction and Unique Customers: Coca-Cola always struggles to convince all of their customers in KSA; therefore, each an every customer is significant and loyal to them. They believe that if they can satisfy them they in future they will purchase their foods and refer other customers.
Present Perspective of CCBCSA
Olayan Group that formed CCBCSA joint venturing with Coca-Cola is a major giant of Saudi privates sector and engaged its highest effort to establish this US brand in Saudi Arabia through localization strategy. Khaled Olayan, the chairperson of the Olayan Group, argued that in working as an agent of Coca-Cola, this group has constructed and maintained a wonderful network of partnerships and relationships some of which are working together for more than decades; he further added that it constantly strives to strengthen existing relationships in an even better position to assure operational proficiency. The Olayan Group (3) suggested that it maintains well-trained employees, advanced technological support, impressive administrative control, as well as strong delivery systems in order to ensure better performance of Coca-Cola in Saudi Arabian market. The group believes in the fact that Coca-Cola has an outstanding brand reputation and prominent image that assists it to increase its profit gradually; in addition, it appreciates that apart from regular customers, new customers are also important to develop company’s market segments and that to retain and attract customers it has popularity for its superior customer service. In addressing the factors that the Saudis appreciate most about Coca-Cola, the group stated that people are attracted about its widely diversified product ranges starting from juices to carbonated drinks as well as the strong distribution channel that makes it possible to deliver the products even in very rural areas.
However, some arguments suggest that it spend comparatively a large part of the budget for advertisement and promotional actions that increases its operating expenses. On the other hand, it lacks sufficient strategies to address the fact that Saudi Arabia is a conformist nation in terms of religion, culture, and values and therefore, its advertising campaigns should correspond with this fact and not create any situation that is disheartening for the Saudi communities. It is arguable that in many cases Coca-Cola’s marketing activities created immense controversies in the country.
Alternative Solution as To How This Problem Can Be Alleviated
Considering the dilemmas that the Coca-Cola has been evidencing with the challenging issues in Saudi Arabia and rest of the globe, it is proper time to rethink the raised issue how to respond to them by standardizing marketing efforts across the host countries.
Sands (1) responded to this question with the single-minded views that there are states of affairs in which standardized marketing looms would deliver problem-solving approach with greater profit generation while the companies would drive with purely local approach. The localized multinational marketing strategy of Coca-Cola could successfully demonstrate that its marketing strategy is uniform through out the national boundaries but moderately diversified for the problematic regions of the excising markets
The Coca-Cola Company possible recognize the challenges and threat and would be able to identify the appropriate solution which would be applicable in the concerned market while it may simply distinguish the opportunities towards greater profitability within the standardized multinational strategy just like completely local approaches.
Coca-Cola has to pursue that for any case, while any opportunity or challenge would appear then the standardized multinational marketing strategy with completely local approach would be the right solution. It is also notable that in the concerned market, any alternative approach to overcome existing dilemmas would be localized, without local approach; none of the strategy would be successful and may connect with risk. With is logical ground the suggestive alternatives for Coca-Cola are as follows-
Alternative-1: Integrating National Identity:
In Saudi Arabia Coca-Cola face the dilemmas of boycotting American goods, to avoid anti-American moves Coca-Cola has the opportunity to integrating National identity that positively influence the buying behavior of Saudi people. In Saudi market Coca-Cola has been manufacturing under the banner of CCBCSA, which has registered in KSA, thus there is no problem to integrate national identity.
For instance, Coca-Cola can write in its Bottles “Made in Saudi Arabia – by the Arabs” and such statement could be used in the advertising that will ultimately motivate public perception in this region.
Alternative – 2: Removing linguistics dilemmas:
It has demonstrated in the case-2 of this research that the dilemmas were generated form linguistic problems from which the ‘Coca-Cola boycotting’ moves ere started. To overcome such further misunderstanding, Coca-Cola can translate its name into Arabic while there evidence that before entering China market, Coca-Cola has conducted billion dollar research to translate the brand name into Chinese. Moreover, Coca-Cola would be attentive to integrate Arabic in its promotional and advertising copies would be in local language.
Alternative – 3: Localizing Political Stands:
Coca-Cola is a multinational corporation – doing business and generating profit is its ultimate goal, it has no political agenda to establish rather than business. History tells that the company has alleged as an intellectual collaborator with notorious political affiliation staring from Hitler’s Nazi affiliation to supporting Israel.
Rather than any affiliation with anarchist political stand, Coca-Cola needed to stand beside the local people. During the US aggression in Iraq, if Coca-Cola appeal to the government to stop war against humanity- what was lose to the company but he gaining could be supposed to be positive perception from the local communities and never be boycotted.
How Each Alternative Can Be Implemented
USCIB (2) reported that in the leadership award, ceremony-2008 the president and CEO of Coca-Cola Muhtar Kent explored his anxiousness to the anti-globalization and anti-American moves and he suspect that if America does not shift its position, America would be isolated from the globe with its recessional economy.
He urged the government, business communities, and the civil society to working together to recover US democratic image rather than notorious warier and such a view would contribute to implementing the Alternative-3.
Alternative 1 and 2 could be implemented by following tools-
- Attitude of the Host Country: Being an MNC Coca-Cola needed to remove all difficult of its operation in the host country – Saudi Arabia by exactly accepting the approximately and non-confrontational behavior of the Arabs;
- Local Custom and Religion: It is the strapping challenge for the Coca-Cola to become conscious the core values of the local custom of Islam in Saudi Arabia including other existing multi cultural customs as well as ethnic groups and minorities live and work in KSA;
- Special Emphasis on Religious Issues: As the Muslims are zero tolerant regarding their religion issues and respond sensitively with bad temper, Coca-Cola needed to extremely conscious to deal with such issues in Saudi Arabia;
- Recruitment challenges: Coca-Cola must lead its recruitment policy in Saudi Arabia with ‘best talents with best pay’ aspect and during the selection of proper talents; the recruiters may face barely credible challenges to guarantee the effectual service for bet fit with the organizational objectives where religious orientation also an influential aspect here,
- Assessing Social Status: Coca-Cola needed to conduct particular market survey concerning Saudi Arabia’s social structure along with life style with the aim to addressing its social values, religious sentiment, as well as interaction;
- Cross-cultural Training: It is essential for the Coca-Cola to introduce a new fortune in its operation and to do so it will conduct well-organized Cross-Cultural Training aimed to motivating the spirit of the both management and employees in Saudi Arabia.
The future implication of alternatives or any other strategy would be thrown into dark prospect while the corporate crime of the Coco-Cola Company would be analyzed and people would lose their all faith and dependency on this MNC. Alsop (8) mentioned that the Coca-Cola plant in Columbia oppress its workers more brutally than slavery, the workers started movement substance wage and duration of work.
The management did not come into any negotiation but haired the corrupt paramilitary and they faired 129 union leaders at a time. In India Coca-Cola used extreme level of pesticide into the Coca-Cola Bottle, which has identified by the Indian government and banned its production for several months while the company also involved with conflict with the local farmers.
The colorful propaganda and advertising including the literature of its corporate social responsibility does not really indicate the actual core values of the company but humanities would identify it as a corporate terrorist Thus the future implication of alternatives very significant to the company for its long run sustainability and Coca-Cola surely lead to address the alternative implications.
Implications for Future Use
A number of strategic approaches exist that the company can implicate as future maneuver in order to exercise flourishing operational attributes in all parts of its business sphere in Saudi Arabia. Some such future implications include the following illustrations:
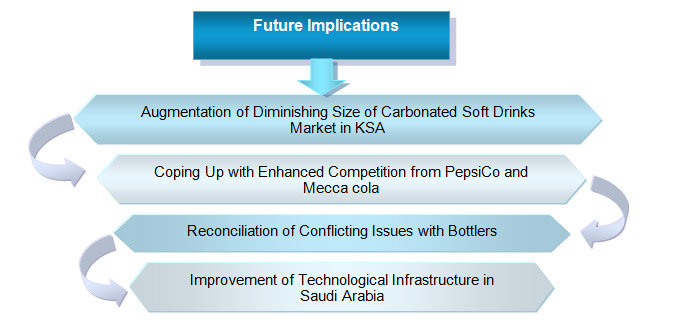
Figure 8: Future Implications for Coca-Cola Company
Source: Self generated
- Augmentation of Diminishing-Size of Carbonated-Soft-Drinks Market – Along with rising awareness amongst health conscious population of KSA, it is evidential that the market for such drinks are lowering by a certain rate; Coca-Cola will be augmenting the market size of this drink by emphasizing and investing more on its R&D to come up with something that is safe for health.
- Coping Up with Enhanced Competition from PepsiCo and Mecca Cola – In order to attain competitive advantages over the competitors of the Saudi Arabian market, the company will come up with pioneering policies that would be in accordance to an appropriate response to rivalry to achieve and maintain industry leadership.
- Reconciliation of Conflicting Issues with Bottlers – The Coca-Cola Company has a number of conflicting and unresolved issues with the bottlers in Saudi Arabia that pose a major hindrance for the business by increasing its operational expenditures. The company with very soon sit together with such bottlers and try to reconcile those conflicts by means of appropriate negotiations.
- Improvement of Technical Infrastructure – To ensure efficiency in manufacturing techniques of Saudi Arabia, the company will be seeking assistance from its machinery suppliers to provide it with the most up-to-date technical equipments that would be fast enough to cut down production time.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Recommendations
- It should try to be more focused in terms of compliance to the Islamic rules and regulatory barriers in Middle East countries and shape its behavioral conduct so that it is not incompatible with the religious sentiments of the local residents for which it could lose its market;
- Coca-Cola should be watchful about the expectations of the Saudi market since there is a chance of reducing customer base at an extensive and sharp rate for the recession;
- Being a multinational corporations, Coca-Cola must maintain cooperative trend rather than conflicting with the Saudi Arabian government and let the government to understand that this MNC and its subsidiary beverage companies are here to mutually benefit each other using KSA’s competitive advantage;
- It is essential for Coca-Cola in KSA to assess risks and unforeseen events connecting to external-environments and ensure mobilization of internal resources and capabilities to cope with the adverse effect of unique regulatory bindings until the progress of governmental attitude; therefore, it is necessary to have local decision-making power in Saudi Arabian office rather than waiting for headquarters’ approval;
- The long historic corporate scandal of Coca-Cola from Nazi affiliation to genocide of 470 workers in Colombia would urge just a question mark to the corporate social responsibility. Within the changing global political environment, the Coca-Cola Company needed to come from malicious corporate scandal and inhuman activity. In this regards to bring workers and employees trust the company needed to conduct schooling for its management regarding what is corporate social responsibility rather than documentation.
- History demonstrates that the company has accounted serious lode to your revenue due to its alignment towards Israeli rather than Arabs, either the company needed to stand beside majority of people rather than fewer or it needed to act naturally without any political affiliation. The company need to demonstrate more business diplomacy regarding Middle East peace process that would crease clean image of the company
- There is enough evidence that the company has lost some plants and assets in foreign counties due to the US governmental policy, while US legislation or government policy creates global conflicting situation that hamper the company’s interest, it is ought for the company to protest such governmental initiatives.
- The high-level use of pesticides into the soft drinks in India has generated the public perception that the Coca-Cola Company may not bother for public health issues but to making profit with harmful product depending on colorful advertising is ultimate objective of the company. To the instance the Coca-Cola Company may needed to beg unconditional apology to the Indian people and compensate for public health injury. On the other hand, to improve product quality the company needed to conduct more research with appreciates guidance by the academia and health specialist and it would dement huge investment on research.
- Market can adversely affect for few reasons; therefore, Coca-Cola should monitor the increased competition in KSA, customers perception about the price of new items, down slopping trend in housing, upward interest rates, limited disposable earnings, lack of confidence of customers, reduced demand for the different beverages, ineffectively hedged costs of goods, like- high labor expenses, construction costs, IT and logistics costs;
- It should impose more control on the existing supply chain of Saudi Arabia since it is running on different risks, such as- disruption of its beverages to the third- party logistics and service distortion through general transportation within its own servicing channels;
- Since the customer choices are changing in Saudi Arabia, it should introduce new products considering the market demand of the population by launching delicious drinks with distinct flavors and tastes;
- At this moment, the company has to compete against the brands such as Mecca Cola and PepsiCo as these companies are increasingly posing a great threat for Coca-Cola, which may create low switching costs for many customers.
Conclusion
Being a US-based brand that has established in 1886 with its global presence as the most popular ready-to-drink items’ seller, there hardly exist any provinces where people are not aware about the name of the Coca-Cola Company. Its products are available even in very remote places all around the Saudi Arabia and people of nearly all ages enjoy taking the pleasure of its refreshments.
In spite of all these praiseworthy features of the company, in some instances, this brand had to face public remonstrations for operational inappropriateness. This happened when the Arab world noticed a remorseful advertisement of the company engendering adverse situation for its operational activities.
Additionally, the business has also suffered from diverse complexities in the Middle East and the GCC nations long back during the gulf war. However, with the help of its strong financial position, strategic approaches, brand identity, and operational excellence it expects to uphold its reputation and implement all its future strategies.
Works Cited
Alsop, Natalie. Solidarity trip planned on Coca Cola’s crimes. 2002. Web.
Amidon, Bradford. Coca-Cola Annual Report Project. 2010. Web.
Bloomberg Businessweek. COCA-COLA CO/THE (KO: New York). 2010. Web.
Bloomberg Businessweek. COCA-COLA CO/THE (KO: New York). 2010. Web.
CCI. America, The World, and the New Challenges for Global Brands. 2004. Web.
ECOS. Sudan’s Oil Industry Facts and Analysis. 2008. Web.
Favaro Ken, Tim Romberger, and David Meer. “Five Rules for Retailing in a Recession.” Harvard Business Review. 2009. Web.
Girard, Richard. Coca-Cola company: Inside the Real Thing. 2005. Web.
Godiwalla, Yezdi. “The MNCS Global Ethics and Social Responsibility: A Strategic Diversity Management Imperative.” Journal of Diversity Management 1.2 (2006) Web.
Indexmundi. Saudi Arabia Demographics Profile 2010. 2010. Web.
Kotler, Philip, and Armstrong Gary. Principles of Marketing. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall, 2006. Print
MEPC. US Challenges and Choices Saudi Arabia: A View from the Inside. 2004. Web.
Rarick, Charles. MECCA-COLA: A Protest Brand Makes Its Mark. 2008. Web.
Slide Share Inc. Crisis Management – Coca-Cola. 2010. Web.
The Coca-Cola Company. ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS. 2009. Web.
The Olayan Group. Coca-Cola Bottling Company of Saudi Arabia. 2009. Web.
The Olayan Group. The Olayan Group in Saudi Arabia and the Middle East. 2004. Web.
USCIB. Accepting USCIB Award, Coca-Cola CEO Says Financial Crisis Jeopardizes Market Openness. 2008. Web.
Yahoo Finance. The Coca-Cola Company (KO). 2010. Web.