The question of what effects bitcoin would have when it becomes a widely adopted form of payment for goods and services globally leads to highly speculative answers. There are positive and negative outcomes that can arise from the adoption. To understand the eventual outcomes, it is also important to have a general view of bitcoin’s journey to becoming a relatively popular alternative payment option. A general verdict of the digital currency’s outlook is that it is graduating to become similar to traditional currencies.
The current difference is that bitcoin is not yet dispensable by retail bank institutions or businesses, but there are establishments that are supporting such functions in some non-formalized ways. People can bank their bitcoins or even invest them. Another similarity that is developing is in exchange forums.
The normal currencies have forex services that allow people to change one currency to another. As bitcoin becomes popular, its value is also becoming predictable and people can use the coin base to make exchanges. There are payment processors serving the bitcoin network too.
According to a report by Jessop, bitcoin’s rise in popularity since 2007 has been due to convenience for particular types of transactions online (1-7). The alleged originator of Bitcoin was Satoshi Nakamoto in 2007, but the formal journey as a payment option began in August 2008 when three individuals, Neal Kin, Vladimir Oksman, and Charles Bry, opted to seek a patent that would protect the encryption application they had developed.
The individuals also registered a domain name that would help to coin the name of the alternative payment option. They registered the domain on a website that allowed anonymous registrations. By that time, the alleged founder had released a white paper report explaining the idea of a purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash that could be used in every part of the world for transactions.
Important features of bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital currency that is generated with encryption techniques that regulate its availability and verify transfers. The currency operates without a central bank. Bitcoin is the name for a single unit while many units of the digital currency are called bitcoins. Bitcoin comes from the encryption processes of a specialized application that requires significant computing power to accomplish.
People and businesses around the world generate Bitcoins by running computers in different parts of the world to solve mathematical problems using a type of software. No one, in particular, develops or prints a bitcoin currency. Without a central bank, there is no way to create more bitcoins deliberately as other currencies currently do in central banks around the world.
The creation of Bitcoin is known as a mining activity because computers work constantly to solve the mathematical problems, and the result is the presentation of encrypted keys that are used as coins. Overall, the computers work in a networked environment. The distributed network forms the bitcoin exchange platform, thereby allowing individuals and businesses to process transactions in bulk or singles that are made using bitcoin.
A conventional currency is based on promissory notes, where a person knows that depositing the currency is equivalent to getting a promise of payback in the future. Payback can be in gold or other accepted valuables, as well as in notes and coins of money. For bitcoin, the foundation is mathematical.
Therefore, there is no way of having custody of bitcoins in the physical sense. Besides, a bitcoin is a record that exists on a distributed ledger. The ledger is the block chain, which consists of all bitcoins mined. Volunteer networks of computers that are operated by real people share the block chain. Therefore, ownership of bitcoin implies that one has rights to transfer the control of a record. The rights move to another person as indicated in the block chain after the transaction.
Bitcoin uses the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm. It is a way that allows third-party verification of the authenticity of every signature. On the other hand, the signer retains the exclusive ability for coming up with a signature and the data being signed is the transaction that transfers ownership. These features happen automatically in the program development for facilitating easy usage. End users only need to press on transfer buttons and sign in or out, similar to the way they would do on secure websites like PayPal. The framework ensures that no direct manipulation of transactions by a single party is possible. It also maintains the integrity of the block chain (Rykwalder par. 3-4).
Advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin when adopted as an alternative payment for goods and services
Bitcoins work electronically when buying goods and services. Anyone who has the implementation of Bitcoin wallets can accept or issue payment with bitcoin. Therefore, allowing many people to have bitcoin wallets is the only requirement for ensuring smooth transactions from the consumer’s side. They can be implemented in many payment methods, such as mobile payments and wireless payments.
Bitcoins cannot be manipulated in their generation method because the authentication and generation frameworks for mathematics rely on detached processes that have to coordinate results in a way that would be impossible for a single entity to control. The Bitcoin software is open source, thereby allowing people to examine and correct flaws, as well as create applications that enhance its capabilities. Therefore, different governments and businesses can find better ways of enhancing the convenience of paying through bitcoins.
Setting up a bank account is difficult compared to how easy it is to come up with a bitcoin address. Besides, the process does not include any fees. Therefore, bitcoin payment can significantly increase the uptake of formal payment. A user can have as many addresses to use for payment, and there is no use of names as identities. Besides, the payment process is transparent because every transaction that ever happened in the network is on record in the block chain.
Government entities can make their addresses public so that anyone can tell how many coins they have. Private individuals can see all coins at a particular address, but they cannot tell its owner. The biggest advantage is that transferring bitcoin is free, irrespective of the amount and the distance. Besides, as an electronic transaction, the transaction reflects instantly in the networks that process Bitcoin payments.
Some of the disadvantages of bitcoins are just the advantages flipped. For example, the anonymity makes it hard for governments to track laundering activities and proceeds of bitcoins can be from many illegal activities. It is not easy to freeze bitcoin addresses, as it is to freeze bank accounts.
Another problem that comes with anonymity is that if someone gains access to a bitcoin address and steals the bitcoins by transferring them, then the money cannot be recovered. However, the culprit can be found using investigative techniques and be compelled to issue a refund (Sparkes par. 10). Bitcoins are finite in number, which makes them valuable with every increase in demand.
Economic Impact of Adopting Bitcoin
Bitcoin is currently valued at about US $340, and the price has been increasing. It is, therefore, the strongest currency in the world. Adoption of Bitcoin would mean that all countries in the world have a chance to have strong currencies without having to pay heavily for pegging costs.
Currently, countries like the UAE peg the value of their currency to the US dollar to maintain balance of trade and improve the attractiveness of their economies. Pegging allows investors to enjoy similar monetary environments like the United States. Bitcoin adoption would mean that even third world countries that lack that ability would still enjoy the benefits of a strong currency whose value relates to global economic conditions (Carmody par. 5-6).
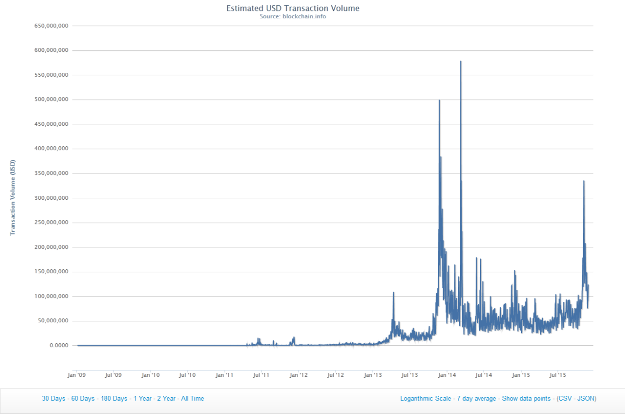
Transaction volumes for bitcoin picked up in 2011 after being relatively minimal since formation in 2008. At the time, the average monthly figure was less than 1 million dollars. By 2013, transaction values had reached figures ranging from 20 million dollars to 54 million dollars. The highest recorded transaction volume of all time is about 570 million dollars. The graph below shows the value of bitcoin transactions (Carmody par. 2-8).
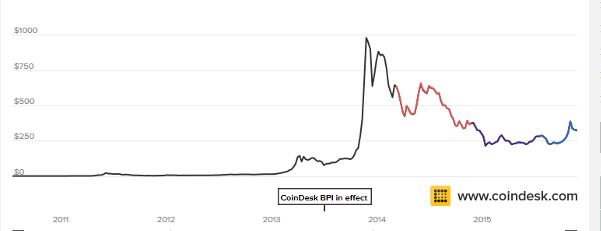
There are several exchanges tracking the price of bitcoin with other currencies. The notable ones are Bitmap, Bitfinex, Coinbase, itBit, Mt.Gox, and CoinDesk BPI. The graph below shows the fluctuation of exchange ranges since tracking began.
Continued mining of bitcoins implies that soon the real value of the currency will be apparent. Given that bitcoin is the only cryptographically based currency to achieve mass adoption, its real value is significant for its adoption. It is like cash because individuals do not have to sign their names or transaction records when making payments. It is also like credit cards that facilitate convenient wireless payments.
Bitcoin adoption will eliminate rent-seeking intermediaries that currently work with money transfer transactions. Moreover, bitcoin will not succumb to barriers of national borders. The next effect is that the costs of transactions will reduce significantly, leading to the affordability of goods and services (Carmody par. 5-8).
In Africa, Latin American, and South Asia, many people have no access to credit and cannot use digital payments like PayPal. Thus, they are technically shut from online transactions. On the other hand, the world is moving fast toward electronic commerce that relies on digital payment platforms. Bitcoins will be a solution to the millions of people locked out of the formal system.
It will allow the people to exchange coins for cash that they receive as payment in their localities. Another tremendous impact will be on cash remittances. People will no longer have to rely on cash transfer services like the Western Union to send remittances back home. They will just transfer bitcoins and the recipients will walk to exchange centers or convert the bitcoins online into local currencies at the prevailing rate (Carmody par. 7-18).
Bitcoins show the potential of moving the unbanked directly into the digital currency platform, where they can store money in phones in digital form. The efficiency and security of the bitcoin network will increase value for everyone and force governments and other tax taking entities to change their tracking systems for collecting taxes, given that all transactions are similar to cash, where there is no evidence left other than the value exchange.
Overall, the economy will be very simplified as people will be able to tell the value of anything based on bitcoins and, therefore, get the true value of goods and services (Carmody par. 18-20).
Current trends in bitcoin adoption
Bitcoins are decentralizing payment systems across the world. As they become popular due to increased media focus, bitcoins will also have significant impacts on economies. For example, the ability of central banks to manage monetary policies and the overall value of money in circulation will be hampered when a significant part of the population will accept and hold bitcoins (Sparkes par. 4). Already, enthusiasts around the world are making it a personal initiative to encourage the adoption of bitcoin.
As a result, some impacts that would materialize fully when bitcoin is an official currency are being felt. Many people are using bitcoins to obtain other investment vehicles like precious stones contrary to the expectations of many that e-commerce would be the number one reason for taking up bitcoin. The travel industry is also showing signs of success as several companies start accepting bitcoins as payment. Those booking with bitcoins can avoid hefty currency transfer charges and, therefore, get more value for the same price (Fargo par. 10).
Charities are now accepting bitcoin donations, similar to the way they accept cash. Bitcoins are helping the charities reach new audiences that would be hindered by credit card and other forms of payments. Bitcoin does not require the transfer of value from one currency of the giver to the currency of the receiver. It allows unrestricted access to donate using bitcoin from anywhere in the world and by anybody.
Those implementing the system to accept bitcoins note that it is a simple as setting up conventional digital payment platforms. Once donated, bitcoins can be transferred to other currencies, used to shop online and in particular locations offline in some cases. With widespread adoptions, there will be no risk of failing to have a place to spend bitcoins and the conversion fees to local currencies will no longer be a factor (Cahalane par. 6-7).
Conclusion
In the end, bitcoin will open up international money transfers, which will limit governments’ ability to manage monetary policies. The adoption of bitcoin will also erode a significant source of income for middlemen in forex trades. Nevertheless, the positive impacts are notable.
Many people who do not have worthy credit or other means of getting into formal banking systems can use bitcoin when it is implemented in mobile money solutions and other forms of conveniences. The reduction in transaction charges overall and the simplicity of bitcoin as it functions similar to cash are the most attractive features to look out when it becomes a recognized currency. Besides, the possible applications are infinite, especially for people in poor economies currently locked out of ways of participating in the global economy.
Works Cited
Cahalane, Claudia. “Bitcoin: How The Charity RNLI is Using The Digital Currency.” The Guardian. 2014. Web.
Carmody, Tomothy. “Money 3.0: How Bitcoins May Change The Global Economy.” Geographic. 2013. Web.
Fargo, Scott. “BitPay Study: Bitcoin is Now an Every-Day Currency.” Inside BitCoins. 2015. Web.
Jessop, Nathan. “A Brief History of Bitcoin – And Where It Is Going Next.” The Next Web 29 Mar. 2015. Web.
Rykwalder, Eric. “The Math Behind Bitcoin.” Coin Desk. 2014. Web.
Sparkes, Mathew. “Bitcoin ‘Could Pose Risk To UK Economy.’” The Telegraph. 2014. Web.