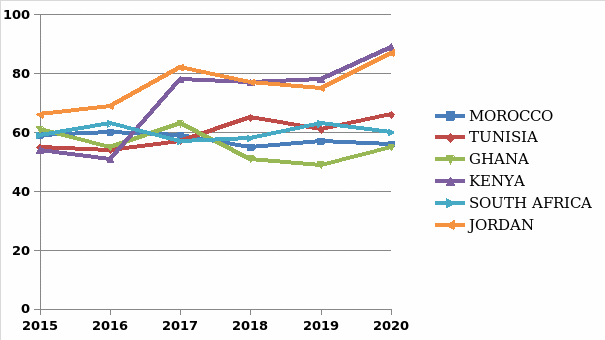
General Assessment of the Performance Trend of Selected Countries
The Global Innovation Index is used in analyzing different countries. What is taken to account is the output and input markers. It is essential to know their factors to develop a suitable Innovation index for a particular index. The Global Innovation Index (GII) analyses and ranks 131 countries worldwide. It is a well-known fact that Kenya is a growing hub for innovation; therefore, it comes as no surprise when the country experiences steady growth. In East and Central Africa, Kenya is the leading ICT innovator, making it one of the top technology hubs globally (Crespo and Cátia 5266). Together with India, Vietnam, and Moldova, Kenya has consistently been recognized and an innovation achiever for the past nine months. There have been many new businesses scrambling for space in the ICT market in recent years, and the key is rapid economic growth.
The Global Innovation Index (GII)in Jordan, however, is not steady, and the country keeps on dropping in terms of how it is analyzed and ranked. Previously Jordan had been doing in a well-placed position, but it kept on dropping in position due to various factors (Dutta, Lanvin, and Wunsch-Vincent). Many issues need to be worked on to ensure that Jordan goes back to a top innovation hub. Such may show some levels of unstableness in the economy. In most instances, the global innovation index grows as the country’s economy grows. The same notion applies to Ghana; it was on the rise, but there is a noticeable drop in the global Innovation index rating after a while. Many factors may lead to the decline in the country’s rating, including drop in the economy, being satisfied, and not adding anything to what is already present regarding innovation.
The Global Innovation Index of Morroco has remained unclear and not predictable because it keeps on changing every year. It may be rated highly one year, then the next year it slightly drops, then again the following year it goes back to where it was. Even though Tunisia dropped further in the ratings in recent years, it had similar characteristics in terms of its predictability (Dutta et al). Despite being a nation with lots of potential in the innovation sector, Morroco has been performing dismally in the Global Innovation Index, making it hard to predict their next position in the following year’s analysis.
The Country that has Witnessed a Surge
Kenya is a country that has steadily grown over the years with regards to innovation. It has turned into one of the leading innovation hubs and hence a steady rise. Being the second country in sub-Saharan Africa, Kenya has proved to be a force to reckon with. While countries like Mauritius, South Africa, Tanzania, and Botswana dropped positions, Kenya kept rising (Dutta et al). Kenya’s growth in innovation is mainly evident throughout the country’s high technological exports. It comes as a surprise why a country like Kenya could beat countries like South Africa, Morroco, and Tunisia, which have better economic status. Part of Kenya’s success in steady growth in the Global Innovation Index has mostly been credited to government support.
However, the Global Innovation Index’s main success steady growth has been accredited to the country’s easy access to investor and credit protection brought about by market sophistication. There are different unconventional banking methods in Kenya, which has led to easy financing for small-scale farmers to indulge in the market (Dutta et al). Some of the microfinance institutions that help propel Kenya to greater heights include; SMEO Microfinance Bank, Faulu Kenya, Kenya Women Microfinance Bank (KWFT), and many others. Many countries overlook microfinance, but the truth is they help elevate the economy in unimaginable ways (Gachanja et al. 16). They do so much when they promote local businesses, which help economical growth.
Kenya also has boasted creative outputs that are facilitated by various innovation linkages. The country’s creative outputs have grown immensely, which is quite a good sign as it is an indicator of good dealings and growth in Intellectual property. That is the reason as to why there is a rapid increase in monetising intellectual property rights and encouraging the application of ICT to various businesses (Gachanja et al. 19). The government has put its focus mainly on health coverage, food security, increase in manufacturing, and affordable housing. That is the government’s plan to ensure that everything is done to the absolute best, and growth is continuous.
To conclude, taking Kenya as a major example, the things a country should do to improve its The Global Innovation Index (GII) include offering absolute support in the necessary departments. The Kenya government has a hand in all the thriving sectors, including; economic growth, creative outputs that include intellectual property, ICT, and fintech. The moment the government comes in and plays its role in uplifting such sectors, everything is attainable. Countries like Morroco, Tunisia, SouthAfrica, and Jordan all have the potential to be the best. If their government awards them the support, then their Global innovation index will rise higher.
Works Cited
Crespo, Nuno F., and Cátia F. Crespo. “Global Innovation Index: Moving Beyond The Absolute Value Of Ranking With A Fuzzy-Set Analysis.” Journal of Business Research, vol. 69, no. 11, 2016, pp. 5265-5271.
Dutta, Soumitra, Bruno Lanvin, and Sacha Wunsch-Vincent. The Global Innovation Index 2020: Winning with Global Innovation. , Internet resource.
Gachanja, Isaac M., et al. “Influence of Organization Learning On Innovation Output In Manufacturing Firms in Kenya.” International Journal of Innovation Studies, vol. 4, no. 1, 2020, pp. 16-26.