Introduction
A world financial services company, Lehman Brothers was involved in the banking business, trade, and research, managing investment among others. It declared bankruptcy in 2008. It was a prime trader in the treasury securities (market) of the United States. The firm’s many subsidiaries are headquartered in New York (International Business Times 1). The company filed for bankruptcy in the year 2008, a thing that virtually led to the global financial (system) meltdown following the fact that individuals in the entire world had hugely invested in this firm. It was the United States of America’s biggest filed bankruptcy case which caused an estimated loss of jobs for 25000employees and $613 billion in debts (Kelly & Saito 9).
Bankruptcy
This can be termed as a lawfully announced impairment or inability of an organization or an individual to reimburse its creditors. Creditors may institute a (bankruptcy) petition against a corporate debtor or a company with the aim of recovering a section of what they are to be paid or commence a restructuring but in the greater part of cases; however, bankruptcy is instigated by the debtor.
The uniqueness of the housing bubble was that it also entailed a new faction of (economic) actors: individuals who managed to buy a home at least for the first time. Contrary to the conventional way of an individual purchasing a home and drawing out a mortgage, these innovative players could only part with their money on the condition that the market (housing) kept moving up. He further notes that the case could be renegotiated and the new actors would go on with owning their homes.
The instances where the market declined, nonetheless, they would be forced to close out; and the securities attached to this form of mortgage would no doubt trade at a loss. It was established that even observers had the same opinion that the fall (of Lehman Brothers) was a turn around. Commentator Robert Lucas observed that the collapse of Lehman had a major significance (Zingales 10). Blinder, a famous economist, everything went down with the demise of Lehman. After the bankruptcy of this firm, no other investment appeared viable to the populace. Lending was stopped, and the economy was in turmoil.
Lehman’s bankruptcy elicited panic that resulted in intimidating not only the financial system of the United States but as well the (financial) system of the entire globe. Some writers argue that the downfall of Lehman Brothers was as result of its very hard line (leverage) policy in the perspective of a main financial crisis while others are of the opinion that the cause of this crisis was a result of poor regulation, absence of transparency, and market contentment resulting from good returns occurring in a number of years.
In the case of Lehman (and other investment banks), Zingales (12) explains that this problem was aggravated by two factors: the extremely high level of leverage (asset-to equity ratio) and the strong reliance on short-term debt financing. Financial leverage is a measure of how we use debts and equity to finance our assets. As our debts rise so does our financial leverage. most of the managers prefer using equities due to the less risk involved an easier way of calculating financial leverage is by dividing the net assets by shareholders equity.
Adrian and Shin(14) states that the balance sheet of Lehman Brothers as of November 2005 that short positions were around quarter of the asset while share holder equity was around 4%this raised leverage to around 25 bringing to the conclusion that Lehman Brothers were doing their business using debts which was risky. Short term debt financing also called repos are types of lending agreement the borrower finances the purchase of a financial security using the security itself as the collateral but incase the price of collateral declines it forces the borrower to absorb the losses accumulate if the debt burden is so heavy it can encourage them to default. Lehman brothers tried to reduce their over reliance on the two factors above but there was nothing they could do to reverse the situation. (He, Xiong,21).Lehman succumbed (Zingales 12).
How Lehman Brothers Bankruptcy impacted on Individual Wealth
Facts has it that stock initially held by Lehman’s hedge fund customers (preceding the bankruptcy) experienced unpredictably huge liquidity declines subsequent to the bankruptcy weighed against the otherwise (similar) stocks not embraced by hedge funds but exposed to the Lehman brothers. The overall price impacts of trade in these stocks rose as did their bid ask spread. Liquidity overall dropped sharply for all stocks but evidence shows that the effect of Lehman fund holdings was greatest among the relatively less liquid assets.
Lehman Brothers’ hedge fund customers were unable to fulfill this stabilizing role because they were constrained in their ability to trade their positions as shown in figures 1 and 2 (Aragon and Strahan 28). Thus, most of the individuals who had invested in this firm made huge losses as a result of the filing and this made them lose sizeable wealth.
The main problem with those who used their assets as collaterals when borrowing from Lehman Brothers did not know that the company used the same assets as collateral when seeking for debts from other companies and thus in the end your assets had more than one party to lay claim to. Everyone passes around the security, then the music stops, the company is in verge of collapse there is one chair to sit on and too many people who want to sit on it thus crises sprung up.(International Business Times 4).
However, linking the failure of Lehman to the level of asset prices is less clear. If liquidity is a priced risk factor, then shocks to market liquidity could lower asset prices, and raise expected returns going forward (Viral & Pedersen 5). But in the Lehman case there is anecdotal evidence that some hedge funds faced a short squeeze because securities lenders exposed to Lehman recalled their loans, forcing those borrowers to repurchase shares and putting upward pressure on prices (Aragon and Strahan 8).
As evidenced by Aragon and Strahan (28) the hazard analysis he conducted showed that the hedge fund failure rates increased across the board in 2008- the year 2008 indicator enters with a co efficient of 1.5 higher meaning that failure rates increased by at least 50% in 2008 relative to the earlier years as shown in Table 1. This increase goes beyond what one would predict based on the performance which itself was very poor during that year (Aragon and Strahan 14).
This market meltdown did not only cause losses to the shareholders and customers of the organization but also caused huge losses to the company executive officers who had invested much in these companies. Evidence given by Bebchuk, Cohen and Spamann (11) shows that the chairman of the board and CEO of Lehman held, directly or indirectly, 10.8 million shares as of January 31, 2008.
When Lehman filed for bankruptcy on September 15, 2008, those shares became worthless. Compared to the peak stock price of $85.80 on February 2, 2007 this amounted to a paper loss of $931 million. Ending up with such losses shows that CEOs failed to perceive the risks their firms faced thus their risk-taking must have been driven entirely by excessive optimism or even hubris, not by perverse incentives (Bebchuk, Cohen and Spamann 5).
Other evidences of such huge losses are as documented by the Press Release by Dave Mandelkern for the San Mateo county treasurer where they made a loss of 155 million American dollars due to the concentration of Lehman Brothers bonds held in the Pooled Investment Fund managed by the San Mateo county treasurer- tax collectors office. This loss was devastating to the many agencies investing their surplus funds in good faith with the county treasurer-managed pooled investment fund as required by the law. Included in this loss was 38 million US dollars which belonged to the K-12 school districts throughout San Mateo County thus the loss was felt throughout the country and the rest of the world (Bebchuk, Cohen and Spamann 8).
Among the many known losses due to bankruptcy, the state of Florida was among the major victims. More than 440 million dollars vanished from the pension (fund) that reimburses benefits for someone million public workers and retirees. These losses could lead to permanent loss or delay in the payments of salaries and benefits and this affects these citizens’ well beings.
The overwhelming impacts of the collapse (of Lehman Brothers) spread like bush fire to various regions of the globe. In the UK, for example, more than five thousand workers lost their employment, while nearly twenty thousand in the United States suffered the same fate of losing their source of livelihood. Close to 2,500 (Lehman) workers in India will also lose their jobs in the near future. The glory in (global business) for Wall Street is no more. Three of its main (autonomous) brokers have gone underground with only two left.
Market price impact: This was experienced in the entities active in capital markets even tot hose with no direct relation to Lehman’s brother because the filing of the bankruptcy intensified pressure of the entities to reduce their balance sheet. The extent of the exposure made banks to seize the group collateral and attempt to liquidate resulting in further downward pressure on the assets that in turn forced leveraged institutions to liquidate to meet margin calls putting further pressure on assets. This aggravated the huge losses that were already made by investors.
Lehman’s filing for bankruptcy had a more dramatic impact on money funds. On September 16th, 2008 primary fund, a $62 billion fund announced that because of the total loss it suffered on its$785 million holding of Lehman Brothers debt it was forced to put a seven day freeze on redemptions, since the net asset value of its shares fell below $1(Lingales 14). As asserted by Collins, a consultant on investment matters, this bankruptcy as well impacted on the pension fund such that the extensive (market) disruption was expected to be experienced in assets engrossed in changes implementation in the strategy.
He further notes that there are a number of more precise knock on issues that affected the pension funds going by where they were invested, which incorporates issues such as cash funds operation among others (Collins, 1). With the firm operating through out the world its difficult to cover every individual and now, Lehman’s orderly resolution will take some time, and it is unclear who the real losers were and how much was lost. In business the loss of an important player could offer franchise-enhancing and profitable opportunities to those that survive.
Conclusion
The conclusion of is that the value of the remaining holdings is essentially zero for Lehman because common shareholders are unlikely to receive anything from the bankruptcy estate, as reflected in the near zero stock price of Lehman when it was delisted (Bebchuk, Cohen and Spamann 30). Joseph Stigiltz a famous economist proposed that governments should restrict leverage that financial institutions can assume and executive compensation should be more related to long term performance and also that they should re-instate the separation of the commercial (depository) and investment banking (International Business Times 6).
With the firm operating through out the world its difficult to cover every individual and now, Lehman’s orderly resolution will take some time, and it is unclear who the real losers were and how much was lost. In business the loss of an important player could offer franchise-enhancing and profitable opportunities to those that survive.
Figures and Tables
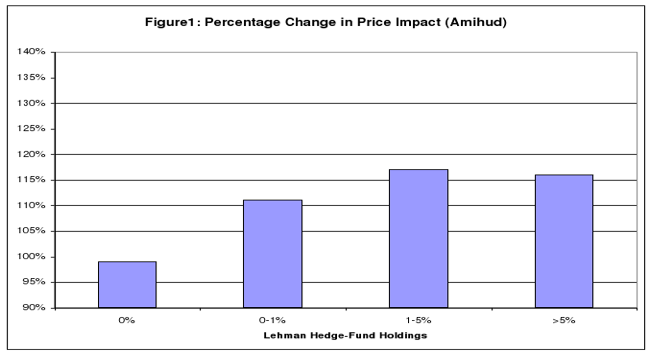
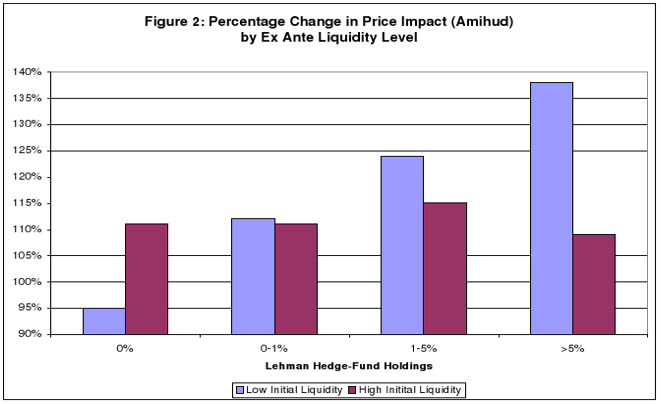
Table 1: Hazard Model predicting exit of hedge funds from the market.
This table reports a hazard model that relates the survival rate of each hedge fund to its performance and its use of Lehman Brothers as prime broker. The sample included all hedge funds in existence as of 2002, as well as all hedge funds formed after 2002 (based on TASS). Hedge funds were assumed to have failed if they dropped out of the TASS database. A coefficient greater than one indicates an increasing relationship between the co-variate and the survival probability; a coefficient below one indicates the opposite. We report a Z-statistics that are asymptotically normally distributed under the null that the coefficient equals one.
Robust Z statistics in parentheses + significant at 10%,*significant at 5%,**significant at 1% (George O Oragon et.al. Pg 37, 2009).
Works Cited
Adrian T, Shin H.S. liquidity and leverage. Federal Reserve Bank of New York & Princeton University, 2008. Web.
Aragon O. George and Strahan E. Philip. Hedge funds as liquidity providers: Evidence from the Lehman Bankruptcy. New York: Arizona State University; Boston College, 2009.
Bebchuk A. Luciana; Cohen Alma and Spamann, Holger. Wages of Failure: Executive compensation at Bear Stearns and Lehman 2000-2008. Harvard Law School, Discussion Paper No. 657, 2010.
Collins, Noel. Impacts of Lehman Brother’s bankruptcy on pension funds. 2010. Web.
International Business Times. Lehman Brothers. 2010. Web.
He. Z, Xiong W. liquidity and short term debt crises. 2009. Web.
Kelly Jason and Saitto, Serena. Lehman said to cancel ex-employees’ severance. 2008. Web.
Viral, Acharya and Pedersen, Lasse. Asset Pricing with Liquidity Risk. National Bureau of Economic Research, 2005.
Zingales, Luigi. Causes and Effects of the Lehman Brothers Bankruptcy. University of Chicago Graduate School of Business, National Bureau of Economic Research and Center for Economic Policy Research, 2008.