The term macroeconomics is mostly confused with microeconomics and so there is need to first put up a clear distinction of the two. The online Business dictionary site, by the Walden University, defines macroeconomics as the “Study of the behavior of the whole (aggregate) economies or economic systems instead of the behavior of individuals, individual firms, or markets (which is the domain of Microeconomics)” (Vienneau 612).
This definition puts someone’s mind into an understanding since there is always a difference and yet a very close relationship which may raise confusion when handling the two subjects; macro-economic and micro-economics.
Dornbusch and Fischer, in the book ‘Macroeconomics’, introduces macroeconomics as a subject that “is concerned with the behavior of the economy as a whole – with booms and recessions, the economy’s total output of goods and services and the growth of output, the rate of inflation and unemployment, the balance of payments, the exchange rates” (5).
Dornbusch and Fischer also adds that, it “..deals with the increase in output and employment over periods of time which is the economic growth and with the short-run fluctuations that constitute the business cycle” (5).
Dealing with the economies and the trends in which they have been taking since times in memorial until now when technology growth is so dynamic that being left behind is almost inevitable, Journal articles are thriving in the market.
‘Business Day’ for example is a journal that is published in America in New York City Times in English. It is a well known newspaper and circulates most in America with updates on the daily economic occurrences, successes and failures, including the new technology in the market. Purchasing is done by online subscriptions and is also available in paper formats.
One question that one would easily ask when confronted with this kind of a question would be; that is it the only paper in America? And why is it the most marketable paper in the New York City? What are the market strategies used to make it more marketable and most selling paper than the rest? The answers to these questions will be the major concentrations of this subject macroeconomics since it handles the trends in economic developments, fluctuations, and the prospective future of the economy.
The article is selling at a highly in America meaning that the demand and supply almost rank at per or sometimes goes beyond the normal where the available articles in paper formats for example is not enough hence being a disadvantage to those who are comfortable with the paper format only. With the online subscription however, most clients’ demands are met hence becoming better way to access the article without being overtaken by the large number of clients.
The way the demand and supply for the journal operate within America is so unpredictable since no one can give an exact state of the demand or supply at whatever one time unless on a general estimate (Vienneau 612). It is for this reason why the following possible curves will at one particular point or the other exist or will be expected:
The Law of demand and supply
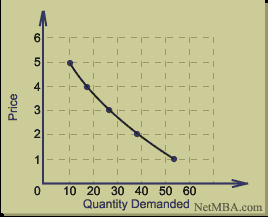
The law of Demand and supply are the factors that determine how the market of any product will behave. They operate together in that; the rise in demand while the supply is constant means higher equilibrium in prices and quantities. This is represented in the following diagram taking a demand schedule for the ‘Business Day’ as follows, then the following curves:
The demand curve will be as follows:
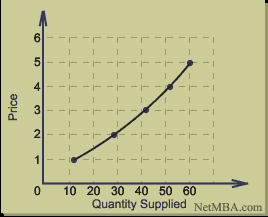
The same applies to the supply curve where the aim of the supply curve is to denote the quantities supplied (x – axis) and the prices (y-axis). The supply schedule below will set the supply curve: Supply Schedule The figure below represents the supply curve
The decrease of demand while the supply remains constant, then it means lower equilibrium and quantities; constant demand and supply would denote lower equilibrium price and high quantities. Low supply on the other hand while the demand remains constant will reveal high prices and low quantities.
When the supply goes down, the product in supply; the ‘Daily Business’ for example will have many customers demanding it which has always made been taken as an opportunity for the few who had extra stock to make more money with an immediate increase of the prices.
Contrary to the prices, the quantities goes down since the little available will be consumed within a short time. The curve showing the demand behavior is sometimes affected by various reasons which can make it to shift and hence causing the prices to change.
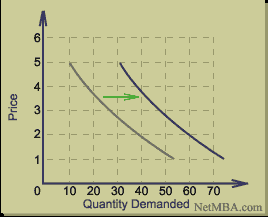
This can be because of customer preferences and tastes that may change with time. For the Article above (Business Day) for example other papers may have published more preferred news than others. When clients decide to buy other papers apart from the ‘Business Day’, then the seller of this particular article will looser business causing shift of the demand curve from the normal position to another on the right or on the left. Using the above demand schedule, the graph below is a representation of a shift of demand:
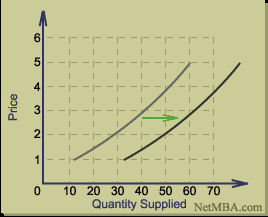
The curve representing the supply is also faced with some shift the right or to the left depending on the behavior of the prices and the quantities supplied at one particular time or day. The changes can be to the right or to the left as follows using the above supply schedule:
Equilibrium
This is a state where there is enough supply for the available clients. When such an instance occurs, the business is said to be at equilibrium since there are enough customers to buy the available products. With the case of the ‘Business day’ article for example, the equilibrium will be reached at an instance where all the papers produced within a day are all bought and all the clients have received a copy. The graph below is a representation of the equilibrium state (Brekken 1).
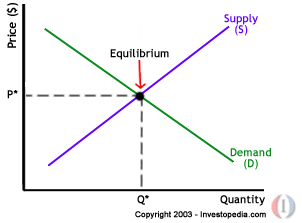
Movement along the supply or demand curves
Supply and demand sometimes may keep behaving differently along the curves which are dependent on the way the prices keep changing against the quantity of goods availed at different points of the curve. The following graph is a representation of such a movement along the curve.
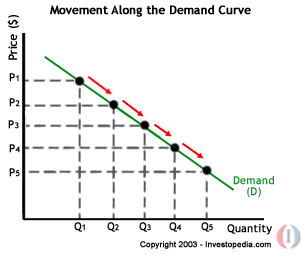
When there are changes taking place along the supply or demand curves, the indication that the prices and the quantities being supplied is evident and that this is a representation of what takes at different points along the two curves.
In conclusion therefore, the behavior of the economy is determined by the way demand and supply behaves. Since the demand and supply must always work together in a business environment, the study concerning the same provides a comprehensive knowledge and ideas on how to handle a business venture to both students and teachers.
Works Cited
Brekken, Isaac. “Business Day.” The New York Times. 2011. Web.
Dornbusch, Rudiger, and Stanley Fischer. Macroeconomics. 5th ed. McGraw Hill, 1990. Print.
Vienneau, Robert. “On Labour Demand and Equilibria of the Firm.” Manchester School 73.5 (2005): 612-619. Print.