Introduction
Adaptive responses are initiated by the body to prevent the pathophysiology of diseases from adversely affecting organs and tissues. Every immune disorder is characterized by unique immune responses, which could also vary among individuals. This paper aims at reviewing this week’s learning materials with regard to mind maps and discussing the pathophysiology of the diseases presented in the three scenarios highlighted in the questions. Finally, it provides a mind map of tonsillitis.
A review of the mind maps of dementia, endocarditis and GERD
This week’s learning materials presented important maps that could be used to explain various factors with regard to dementia, endocarditis and GERD (Silverthorn, Ober, Garrison & Silverthorn, 2009). Dementia is a term used to describe a collection of diseases that affect human brain, which are characterized by reduced ability of individuals to think and reason. The pathophysiology of dementia involves the destruction of neural networks that are important in memory and stimuli processing (Fox, 2008; Silverthorn et al., 2009). The epidemiology of the collection of diseases shows that it correlates with age and it can affect persons across the world. Its diagnosis is based on laboratory tests, cognitive tests and ultrasound imaging. The main symptom and/or clinical presentations of dementia are significant mental retardation and hallucinations. Immune adaptive responses are geared toward repairing damaged neural networks (Germann & Stanfield, 2002).
The epidemiology of GERD shows that the disease affects about 10-20% of the population. The pathophysiology of GERD is characterized by damage of the esophagus, which is initiated by the hydrochloric acid from the stomach. Clinical presentation of the disease is a burning sensation in the esophagus. Endoscopy and differential diagnostic approaches are adopted with regard to diagnosis of the disease. A risk factor of the disease is consumption of food that could activate cells in the stomach to secrete acid. In fact, persons with high chances of developing the immune disorder should keep away from acidic food (Fox, 2008). Patients suffering from GERD should also avoid acidic medications. An adaptive immune response involves mechanisms that are geared toward preventing the release of acid into the esophagus (Germann & Stanfield, 2002; Huether & McCcance, 2012).
The pathophysiology of endocarditis is characterized by bacteria and fungi, which cause inflammation of the endocardium. “The disease affects both children and adults across the globe” (Huether & McCcance, 2012, p. 98). Some of the risk factors include congenital factors and exposure to pathogens. Clinical presentation of endocarditis is swelling of the heart muscle, fever and chills. Diagnostic approaches include blood culture, CBC and transesophageal echocardiogram. Immune adaptive responses include production of antibodies to destroy pathogens and to reduce inflammation of the endocardium (Silverthorn et al., 2009).
Scenario one: Tonsillitis
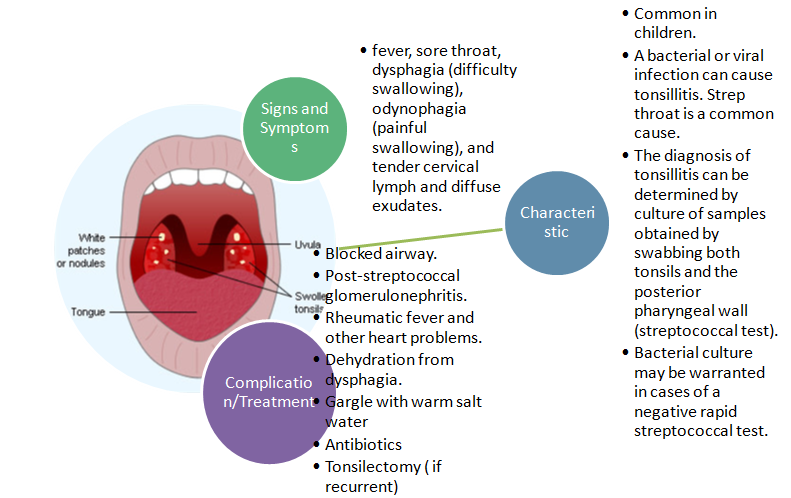
In the scenario, the patient, Jennifer, presents with signs that imply that she is suffering from tonsillitis, which is a condition that is characterized by infection and inflammation of the tonsils. The glands play important roles in defence because they are part of the lymphatic system. In fact, they are involved in filtering microbes and other substances before they could harm the body. During an infection, lymphocytes within tonsils produce phospholipase A2, which kills viruses and bacteria and leads to the development of fever. Following an infection, the glands appear red and swollen. Signs of the patient in the scenario are 4+ tonsils, dysphagia, sore throat, diffuse exudates and tender cervical lymph (Huether & McCcance, 2012).
Scenario two: allergic contact dermatitis
The 27-year-old patient appears to be suffering from an allergic contact dermatitis as a result of continuous exposure to abrasive chemicals and/or solvents. This is an example of occupational exposure to hazardous agents. The disorder is a type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction, which involves the involvement of immune cells. With regard to the disorder, T cells are activated to develop cell killing abilities. The T cells also produce lymphokines that are involved in activating macrophages that secrete enzymes and ROS to destroy infected tissues. Signs of the condition include itching and localized swelling (Huether & McCcance, 2012).
Scenario three: Three situational depression/adjustment disorder (AD)
The patient retired recently and it appears that she is suffering from an adjustment disorder, which does not have a definite pathology. However, there is a consensus that AD is caused by an alteration of biological events that are important in adjusting to stressful occurrences. The following signs characterize the condition: low concentration, anxiety, lack of sleep, depression, and low mood (Huether & McCcance, 2012).
Mind map (Tonsillitis)
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that the pathophysiology, epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, and clinical presentation of diseases vary among disorders of the immune system. More importantly, the adaptive responses that are started by the immune system to fight infections differ based on the infection. Advanced nurses need to understand the pathophysiology of immune disorders and their signs in order to make the right diagnoses and initiate correct treatment approaches.
References
Fox, S. I. (2008). Human physiology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. Web.
Germann, W. J., & Stanfield, C. L. (2002). Principles of human physiology (Vol. 1). San Francisco, CA: Benjamin Cummings. Web.
Huether, S. E., & McCcance, K. L. (2012). Understanding pathophysiology (Laureate custom ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby. Web.
Silverthorn, D. U., Ober, W. C., Garrison, C. W., & Silverthorn, A. C. (2009). Human physiology: an integrated approach. Hoboken, NJ: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. Web.