Abstract
This study is designed to provide a broad range of proposed GST in Hong Kong. The provisions of GST and other taxation laws applicable to taxation that have filed in chapter 1 to 7 are discussed in details. This study also explained the provisions of the IRD that relate to the Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong. This study, generally, criticised the proposed Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong.
Introduction
Tax administration of a particular country is a significant concern as the issue of development solely depends upon the fact how efficient and working the tax mechanism of a particular country. Countries of the world have different taxation policies in the light of their particular economic structure and socio-economic consideration. “Taxable capacity of a country depends upon the sum of profits, wages and rents” (Shoup 1960, p.192).
While discussing about the taxation system of a Particular country, GST or Goods and Services Tax is an important topic. Different countries of the world have introduced the system for developing their economic advancement. Developed countries are making the example that Goods and Services tax is tremendously helping to boost their economies. Hong Kong is an important place in the Asia–pacific region for trade and commerce due to its laissez faire policy and infra-structure development. As it is considered the hub of trade and commerce, foreign investors find Hong Kong for developing their industrial and commercial relations worldwide.
One of the reasons for choosing Hong Kong as an ideal place for businesses is its simplified taxation system. The existing tax mechanism of the country does not levy Goods and services tax. As the country has faced a budget deficit and economic disturbance in the recent years, it has decided to introduce Goods and Services tax (GST) in the taxation system. To this end, Government has proposed an enactment for the introduction of the said instrument entitled Arrangement for Avoidance of Double Taxation and Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with Respect to Taxes on Income. The said legislation was signed on August 21, 2006 and took effect (for Hong Kong residents) from April 1, 2007 (Stender 2006, p.1).
Problem Statement
As a part of its tax reform initiative, Hong Kong has proposed this tax legislation. After forming a committee, the Government has entrusted them with the responsibility of drafting a proposed tax instrument. Accordingly, the committee has prepared a draft copy of the said tax legislation and subsequently Government has arranged the means for the publication of it with an ultimate intention of giving this into effect. But, the instrument is crippled with numerous problems. It is seemed that while enacting this draft legislation, committee did not consider the need and interest of the people; rather it was more devoted in developing the ways and means for generating more revenues in public fund.
The provisions as drafted in this instrument articulate that all the goods for consumption and necessary services would be subject to tax, i.e. every commodity used in the day to day life of the citizenry are levied. Again, the exports and imports goods have also been levied. This hinges on the development of businesses and investment. The rate of Goods and services tax (GST) is too high as an initial rate. The legislation was not consulted with the businesses and professional bodies. But, for the necessity of the successful implementation and determining the merits and loopholes of the legislation, consultation with the businesses, professional bodies and citizen group was badly necessary (Dowell 2004, p.67).
Definition of Key Words
While attempting research over the topic, several keywords have been used in the present study. The key words as has been used warrant explanation for the conveniences of proper understanding and duly evaluate the key messages of the study. The key words that have been used in the study are as follows:
- Inland Revenue department (IRD): This is the central board of revenue in Hong Kong which is empowered to oversee, monitor and regulate the entire revenue functionaries in Hong Kong.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): This is referred to the tax levied in almost in every economy of modern times and is levied on every goods that are consumed in each stage from production to the final disposal in the hands of customer.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): It has semblance with the goods and services tax to some extent. But, certainly, it has some characteristics which differ from goods and services tax or any other type of tax.
- Securities and Futures Commission (SFC): It is one of the auxiliary bodies in the tax administration of the country. It closely helps Inland Revenue department for the disposal of its functions.
- Special Administrative Region (SAR): It is considered that Hong Kong is one of the provinces and economic capital of china.
- Taxation: Taxation means the process of levying or taxing. There are some certain considerations for levying tax. The key considerations of Levying or imposing tax are determined in the context of a given economic structure.
- Sale Tax means the tax that are levied upon the goods or product used for the human consumption. The rules and rate of determining sale tax are prescribed in pursuance of the legislative instruction of a given country.
- Exemption indicates the meaning of tax relaxation or invoking the benefit of reduced rate tax payment. This is applied where there is a question of increased tax rate or certain products are kept away from the ambit of tax jurisdiction.
Objective of the Study
The objective of the present study is to identify the defects and loopholes of the proposed tax legislation in Hong Kong. Through this attempt, the researcher intends to explore the deficiencies and things to be done for the improvement of the legislation and make it an enactment dealing with public welfare. The study also intends to specify the means of procuring more benefits from the enactment and accordingly recommend the suitable guidelines for its successful implementation. Ultimately, the study aims to provide the scope of ensuring maximum output for the true benefit of the common people and making a wider avenue for the more development in Hong Kong through businesses and investment by virtue of this legal instrument.
Methodology
This an analytical as well as empirical study with a view to discovering the defects of the proposed legislation and finding out the possible outcome for ensuring the merit and efficacy of the proposed legislation. To gain success, the researcher has proceeded with a different outlook in order to reach the key considerations of the topic. To this end, the researcher has taken the help from different sources in order that relevant data and information collected can help to make the topic a quality paper which has the potentials to make a radical change in the tax administration in Hong Kong. For this, researcher has taken the help from different texts, journals and internet. The information gathered from that sources have greatly helped the researcher to synthesize the relevant facts and reach in the decisive findings.
Historical Background of GST
A favorable tax regime is important for a country as it helps in promoting economic development. A regular and stable tax system enhances the stability of a fiscal policy and provides the force to introduce and implement the long-term economic policies for the essence of economic sustainability. To introduce a better and world class tax regime, Hong Kong has long been striving to reform it. Accordingly, the tax department has also been sticking to review the tax mechanism and bring requisite changes in it. Hong Kong greatly relies on its tax department as 60% of the total government revenue is collected from tax revenue.
Speaking from an international standpoint, the existing tax base in Hong Kong is too narrow as its source is merely confined to salaries tax and profits tax. So, it is the timely approach to broaden the tax base. To address this problem and introduce a better tax regime, Government has set up an advisory committee in 2000 to examine the feasibility and justifiability of a broad-based tax regime. The committee in its recommendation argued for introducing a Goods and Services Tax Goods and Services Tax (GST)) in Hong Kong.
Asian Financial Crisis
Asian financial crisis is a turning point of recent history in the Asia -pacific region. After the crisis took place in the years of 1997 and 1998, the idea of a Goods and Services Tax (GST) got a momentum position in Hong Kong. The economy of the country is mainly depended upon land sales, lease exchanges, revenues from the sale of government assets. The recent statistical data estimates that in the fiscal year of 2005-2006 , 6% of the total population amounting to 34 thousands hundred taxpayers paid about 75% of salary tax, while in 2003-2004 fiscal year 1% of businesses contributed more than 60% of the total profits tax collections(GST for Hong Kong 2006, p.1). Due to budget deficit, the government in 2000 took a plan to experiment the feasibility of a broad based tax like Goods and Services Tax (GST). Subsequently, Government established a Task Force to find out the core reasons of budget deficit. The Task Force in its report found structural issues being responsible for the deficit (Kibria 2006, p.6).
Formation of Advisory Committee
In 2001, an Advisory Committee on New Broad Based Taxes was introduced in order to ascertain the suitability of introducing new types of broad based taxes. It was held that with the introduction of consumption tax being levied, the tax base of Hong Kong could be broadened. In addition, International Monetary fund in 2004 emphasized upon the Hong Kong Government to consider Goods and Services Tax (GST) for the sake of improving its taxation system.
Abolition of Estate Duty
Estate duty has been abolished in 2005 which has come into effect on February 11, 2006 though it had a positive role in redistributing income between rich and poor. In addition, Revenue (Profits Tax Exemption for Offshore Funds) Ordinance 2006 has been promulgated in March 2006.Additionally, in 2006, Government has arranged a draft legislative instrument entitled “Arrangement for Avoidance of Double Taxation and Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with Respect to Taxes on Income”. The said legislation was signed on August 21, 2006.
Importance of Hong Kong as a Heaven of Commerce
Hong Kong is considered as an ideal place for trade and commerce. It is also treated as a heaven of trade and commerce in the Asia- Pacific region for the following grounds:
Good Governance. Hong Kong is an important place for the investment and deal trade and commerce in a healthy way. Decades long, it has been gaining an increasing global fame for the ideal environment in regional and international trade and finance. It is considered as the second largest foreign direct investment recipient country in Asia, next to China. Of course, there are various reasons for being Hong Kong as the most congenial place for cross-border trade and commerce. Good governance is effectively working in Hong Kong as there is rule of law, effective civil service, corruption free public administration, independent judiciary and freedom of press.
Open Market Policy. Hong Kong has a simplified taxation system, skilled manpower, world-class banking system, ICT advancement and All these are contributing to make Hong Kong a prominent place of commercial dealings. One of the reasons of becoming a place of such importance is its open market policy. As a result, Hong Kong has been benefited with huge foreign investments (Rowse, 2003).
Geographical Location. Geographical location, secured and multi-cultural environment and improved communication facilities have attracted the foreign investors. In fact, the concentration of businesses and professionals resulting from geographical location and infra-structural development has strengthened the position of Hong Kong as the hub for business, logistics, finance and services for the region.
Vision of Government. The Government of Hong Kong possess the vision of keeping its business-friendly environment for the mutual interest of the gradual economic growth of Hong Kong as well as help other countries in developing their position in international trade and commerce(Rowse 2003). Everything necessary for the efficient and sound operation and management of a foreign company is present in Hong Kong. So, in the context of international trade and commerce, Hong Kong is gradually getting its momentum position.
Concentration of Export-oriented Industry. Another reason for its significant as a point of trade and commerce is its labour-intensive and export-oriented industries, such as electronics, textiles and clothing, toys and plastics. It maintains a level playing field for foreign and local companies.
There are three types of companies: the limited liability company, the company limited by guarantee and the unlimited company (Luxembourg Chamber of Commerce 2007). The most companies registered in Hong Kong is limited liability company. Such company are limited by shares and may be either private or public company. To operate its functions and activities, each limited company must obtain a business registration certificate. Businesses can mostly be carried out in the form of a sole proprietorship or partnership.
Improved Service Delivery. Hong Kong is prominent for its improved service delivery. It provides, sector-specific issues arrange meetings with professional associations and appropriate companies or organizations and provide PR support during the launch of a new company and foreign companies think Hong Kong as an ideal business place (Yahya 2008).
Simplified Taxation System. The formula of a sound economy in Hong Kong is its low taxes and low government spending. Hong Kong in its commercial policy puts maximum concentration on protecting the interest of Citizens and companies.
Provisions of Proposed GST
Before revealing the discussion as to the provisions of Goods and Services Tax (GST), it is reasonable to give a detail account about the existing tax administration and types of tax prevalent in the current tax mechanism in Hong Kong.
Tax Administration
The entire tax mechanism of the country is regulated through three separate agencies. These agencies in Hong Kong are predominantly engaged to deal the revenue issues of the country. Among all the agencies the most prominent one is the Inland revenue Department. The two other agencies are The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) and The Trade Department. The Inland Revenue Department (IRD) is the central revenue agency to deal the necessary tax matters in Hong Kong. It oversees monitors and regulates the entire dealings of tax affairs of the country. It is also responsible to supervise the functions and commercial dealings of foreign enterprises in Hong Kong.
The Department is also entrusted with the responsibilities of supervising and collecting corporate and personal tax. The Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) is responsible to monitor, oversee and regulate the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong and the gradual advancement of investments outside Hong Kong. Due to the continuous efforts and policy implementation of the agency, it is gradually improving in matters of manufacturing real estate and any other productive property.
It is commendable that another revenue agency, i.e. Trade Department in Hong Kong plays a pivotal contribution in maintaining tax policies as well as ensuring sound taxation system and help accelerating the economic promotion and development of the country. The Trade Department issues information regarding import and export licensing requirements. Thus, it helps in improving foreign trade and commerce which has been contributing to the growth of trade and commerce as well as boosting the economy of the country.
In order to earn a better result, Inland Revenue Department (IRD) has made many significant changes in its organizational structure. The Department has introduced Information and Communication Technology and has trained its staffs to increase their professional efficiency and make the tax regime more functioning and effective. In its ICT usage, Inland revenue Department (IRD) has included e-filing, e-enquiry, e-payment, e-stamping and the enquiry of business registration particulars through websites.
As a part of its continuous effort, IRD in 2005-06 has further attempted to identify and develop more convenient and user-friendly e-services for the conveniences of its taxpayers. In addition, the department has facilitated its staffs technical database resources and training materials which have excelled their professional standard. The year of 2005 is marked for a significant incident in the history of Hong Kong taxation, for its huge amount of tax collection by Inland Revenue Department (IRD) which has been recorded as high of $145 billion (Yee-ming & Alice 2006, p.1).
Types of Taxation
Every economic system has some distinct features as the determinants of different economic system vary due to different economic considerations. As a result, different economic systems espouse different economic policies. There are several types of tax in the existing tax mechanism of the country.
Corporate Tax
In accordance with the existing tax policy of Hong Kong, all earnings and profits are subject to tax from whatever sources they are accrued. So, the corporate earnings are also subject to tax, i.e., the financial gain earned from trade or business within the territory of Hong Kong is levied in accordance with the provisions of tax legislation. The tax rate is 17.5% since assessment year 2003-2004 in case of incorporated company while the rate is 16% since assessment year 2004-2005 in case of unincorporated company (Mergers, pp.3-4).
Besides, Non-residents in Hong Kong are also governed under the relevant tax legislation of the country in the same way alike the citizenry of the country. So, the income of Non-resident earned by means of trade, commerce, profession within the territorial limits of Hong Kong is under the ambit of tax. In addition, profits earned from exhibition of films, television programming and royalties for the use of a patent trademark, copyright, know-how or other intellectual property are levied. In order to levy corporate tax, following three tests should be satisfied as has been decided by the Privy Council in the Hang Seng Bank Case (Horwath Hong Kong 2003):
- The company must be carrying on a trade, profession or business in Hong Kong;
- the company must be generating profits from that trade, profession or business of a type which are subject to profits tax i.e. trading profits / fees as opposed to non taxable capital gains or dividends; and
- those profits must have a Hong Kong source i.e. they must derive from or arise in Hong Kong.
Personal Income Tax
Apart from any firm or company, income may be taxed in the hands of an individual (Sawday 1939, p.86). Any income which is derived by a person from his estate or any other source is subject to personal income tax (Newton & Bloom 1991, p.47). “One of the major problems concerning personal income tax in most cases is that the statement of the said personal income is not properly reported” (Consequences, Newton & Bloom. Cited in Newton 1991, p. 125). Personal Income tax in Hong Kong is determined on the basis of the income earned by the individuals. The relevant provision of tax legislation suggests that Individuals are taxed on income derived from employment, offices and pensions in Hong Kong. “Non-residents are also subject to the salaries tax if they reside in the colony for more than 60 days in a tax year. The salary tax is assessed on the range from two to 25 percent of net income after deductions and allowances, subject to a ceiling of 15 percent of gross income” (HKTDC 1998).
Interest Tax
Interest tax is a kind of tax which is charged on the total interest obtained or received in Hong Kong. “The rate of interest tax levied is 17%” (HKTDC 1998). Of course, there are a number of exemptions in regard to interest tax. For instance, interest of individuals on deposits is exempted from tax if they engage such capital in doing business with financial institutions.
Property Tax
Under the existing tax legislation, property is also subject to tax. In this case, the tax rate is determined at 17% of annual income derived from property. In determining such rate, 20 percent of total income is reduced for the purpose of considering the matters of repairs and maintenance, land and buildings used for such income (HKTDC 1998). Provisions of Property tax in Hong Kong exempt personal residences and property owned by a corporation carrying on a business in Hong Kong from being levied on the ground of taxable property.
Stamp Duty
Stamp duty in Hong Kong is levied at the rate of which limit may be extended up to 3.75% on the conveyances of immovable property which is payable by each party to the contract in the equal shares subject to the provisions of commercial negotiation. The rate of duty is computed in reference to the degree of higher consideration or the market value of the asset being transferred (Roy 2006, p.4).
Withholding Tax
Withholding taxes are applicable in cases of royalties or other similar payments to a non-resident party. The rate ranges from 5.25% to 17.5%. The higher rate is charged where the payer and the payee are related and the said intellectual property was owned by a person within the territory of Hong Kong. The rate may be reduced in case of the fact that the recipient is entitled to the benefits of one of the few comprehensive double tax agreement where Hong Kong is a party (Gandhi 2007, p. 45).
Other Taxes
Tax provisions of the country have extended its jurisdiction in some other areas. Government policy in regard to vehicle has set tax provisions. So, under the relevant policy and tax enactment, there is a registration tax in Hong Kong on automobiles, motorcycles, trucks and buses. 0.1 % capital duty is applied while authorized share capital increase.
Essentials of Goods and Services Tax
It is very much conspicuous that the essential ingredients of Goods and Services Tax (GST) are: (i) it is applied in all domestic consumption of goods and services and (ii) It is paid by the final consumer. Of course, unlike single-sales tax, Goods and Services Tax Goods and Services Tax (GST) have no cascading effect.
Provisions of Proposed Goods and Services Tax
Sales tax has some other equivalent meanings. It is also treated as Goods and Services Tax (GST) and value added taxes (VAT). Goods and Services Tax (GST) and Value Added tax (VAT) are the same in the meaning that both are applicable in case of consumption by the private individuals. So, the sales tax or Value added Tax (VAT) is different from that of income tax or any other type of tax But, there are some certain distinctions between Goods and Services Tax (GST) and VAT (Value Added Tax) and other taxes.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is applied on the net value added to a particular good or service while Single-stage sales taxes are applied once either in manufacturing or production or wholesale distribution or in retail sales stage. Again, Goods and Services Tax (GST) is applicable in all services, but sales tax is restricted to a limited range of services. The Asia Pacific region is randomly adopting the Goods and Services Tax (GST)). Examples of some front liner countries adopting Goods and Services Tax (GST) in the Region are Australia, New Zealand, Japan and Singapore. From a thorough analysis over the provisions of goods and services tax in Hong Kong, the following characteristics have been appeared (Runil 2007, p.23):
Continuity
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a continuous process as it relates to the collection of tax at each stage of production and distribution. Though the intermediary customers are to pay tax, ultimate burden of tax is shifted on the final customer.
Principle of Taxable Supply
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is based on the concept of “taxable supplies” i.e. things provided are subject to tax. In order to get the privilege of claiming credit in a business transaction, every person making taxable supplies exceeding a legislatively specified sum or engaged in certain business must be registered for Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Shifting of Tax Burden
Under Goods and Services Tax (GST), the tax burden is shifted away from income and run towards spending. As the principles set out, under Goods and Services Tax (GST) everyone is to equally pay as well as suffer the equal hardship.
Rate
There is a difference of rates in Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in the context of a given country’s economic policy. Some states apply reduced rates, exemptions and numerous special arrangements in accordance with their policy demands. Again, New Zealand and Singapore have successfully implemented a single rate Goods and Services Tax (GST) with very few exceptions (Goods and Services p.2).
About Tourist
The proposed Gods and services tax (GST) in Hong Kong asserts that if the tourists buy goods for their consumption outside the jurisdiction they would be paid at the time of purchase and the same is refunded to them when they are on the international departure and it is proved that goods are being exported.
Self-Assessment Tax
It is a self-assessment tax. The entire dealing of Goods and services tax (GST) depends upon the free-will of the taxpayers to comply with the relevant tax legislation. This compliance make the taxation system simplified, while multiple tax rates and tax exemptions make the process complex and burdensome.
Individual Perspective
The nature of Goods and services tax (GST) as has been enshrined is mainly concentrated on focussing from two perspective : a. individual perspective and b. business perspective.The proposed Goods and Services Tax(GST) would have the following characteristics in case of individuals :
- The taxpayers would get the privilege of a reduced tax rate.
- an one-off supplement would be provided to the households Social Security benefits; 3. an annual cash Goods and Services Tax(GST) allowance on a per-household basis for low-income households not receiving CSSA;
- a universal annual “Goods and Services Tax(GST) credit” for each household to be used against water and sewage charges for an initial five-year period; and
- a universal annual “Goods and Services Tax(GST) credit” per household to be used against rates for an initial five-year period.
Business Perspective
In cases of businesses, Goods and Services Tax(GST) has the following features :
- a cut in profits tax;
- abolishing the capital fee to encourage more businesses to incorporate in Hong Kong;
- reducing the motor vehicle first registration tax and duties on liquor, petrol, diesel, aircraft fuel and methyl alcohol;
- cutting charges for import and export declarations;
- abolishing the 3% hotel accommodation tax;
- increasing tax-deduction limits for charitable donations; and
- one-off set-up assistance to small and medium-sized businesses that volunteered to register for Goods and Services Tax(GST).
System of Taxation and GST in Hong Kong
System of Taxation
In order to make a fruitful discussion over Goods and services Tax in Hong Kong it is necessary to give a an overview about the current taxation system in Hong Kong.For the purpose of determining the issues of tax, taxation system of the country rely on two principal considerations; taxable source and non-taxable source.
Taxable source
Inland Revenue Department, the central revenue authority in Hong Kong considers the following things in determining the relevant points of tax or revenue matters. All the profits arising out of the transactions performed or executed inside Hong Kong is subject to tax. The criteria of determining the source of businesses’ depends upon various considerations. The profits are fully taxable on the fact that both the contract of purchase and contract of sale are executed in Hong Kong.
When either the contract of sale or of purchase is performed within Hong Kong; profits earned from the transaction is subject to tax. In addition, if a sale contract is made to a Hong Kong customer or a purchase contract is made for purchasing commodities or goods to a Hong Kong supplier or manufacturer, the contract is supposed to be held in Hong Kong and the profit is taxable. Again, in case of the fact that a purchase or sale contract is made even from Hong Kong over phone or by fax, the transaction is presumed to be done in Hong Kong and subject to the jurisdiction of tax (Guidelines 2003).
Non-Taxable Source
If the activities of business in Hong Kong are limited to the following matters, the profits of the business would be non-taxable (Guidelines 2003):
- Issuing or accepting an invoice to or from an ex-Hong Kong customer or supplier of the group on the basis of terms already concluded by an ex-Hong Kong associate.
- Arranging letters of credit.
- Operating a bank account, making and receiving payments.
- Maintaining an accounting records.
GST in Hong Kong
From a perusal of the provisions of Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong, following characteristics have been appeared.
Unstable Economic Structure
The purposes of implementing a Goods and Services Tax (GST) in Hong Kong are: to stabilize public finances, sustain economic growth and ensure future prosperity (Reforming Hong Kong 2006, p.2). Government has not designed the said taxation system to generate more revenues in its fund. But, most of the citizens are against this as Government has not made enough consultation with professional bodies and political parties before publishing the Consultation Document. For the lack of Government efforts in making the citizens well-convinced about Goods and Services Tax (GST), strong demonstration was made from the peoples’ corner as being proved to them as unpopular and economically rigorous. This instrument does not match with the concept of a stable financial structure (Pinaki 2005, p. 29).
Impractical
Considering the practical difficulties and economic instability and necessity of reforms in the tax administration, the Hong Kong government issued a consultation document outlining proposed reforms by introducing a simple Goods and Services Tax (GST) structure to the current tax system in Hong Kong on 18 July 2006 (A Goods and Services, p.3). The proposed Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework would adopt a broad based tax system and levy on all expenditure items with limited exceptions applicable to some financial services, residential property sales, rentals and exports of goods and services (A Goods and Services, p.2). Actually, it has no practical value.
Unreasonable
GST Goods and Services tax (GST) would be charged on all taxable imports of goods. The proposed Goods and services structure (GST) also provides that Goods brought into the territory of Hong Kong for the purpose of consumption would be subject to GST. Of course, Goods which are passed through transit would not be taxed. Importers and exporters would be required to lodge goods declarations with Customs before taking delivery of their goods. Of course, registered exporters would be treated as being governed by the provisions of paying tax and are required to lodge goods declarations with Customs before shipping their goods. But, A summary of the proposals for a Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong (2006) states that,
“the goods which would otherwise be exempt or zero rated would not be “taxable” imports and accordingly they would not come under the provisions of goods and services tax (GST). Temporary imports and returned goods would not be subject to GST. It is proposed that the Goods and services tax (GST)-free threshold would be set at $3,000 for goods in cases where it would be brought by individual incoming travellers15 and $4,000 for imported cargo16. If the threshold allowance were to be exceeded, the full value of the imported goods would be subject to GST” (p.8).
From a perusal of those provisions regarding export and import matters, it is deemed that the legislation is quite unreasonable.
Less Exemption and More Encompassing
It is apparent that this instrument has covered more items, but has relaxed a few from the ambit of tax. From a minute analysis from the proposed goods and services tax (GST) legislation, it is clear that Hong Kong would adopt a broad based tax system and would levy tax on all expenditure items, with very few exemptions. So, only some financial services, residential property sales and rentals and exports are exempted.
Zero-rating Arrangement
In pursuance of the proposed Goods and Services Tax (GST) structure, zero-rating arrangement would be applicable to all financial sectors which would render the Hong Kong as a significant point of financial supplies (A summary of the proposals for a Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong 2006. p.18). Consequently, the shape of Hong Kong would be radically changed and would be turned into a new horizon of economic world. Of course, these financial supplies would be ensured in consultation with the financial regulators and financial industry in order to avoid abuse to the producers of same kind of products. This consultation is certainly a safeguard and effective check for the effective implementation of viable tax legislation.
Effects of Goods and Services Tax
Of course there are some negative impacts of taxation. “There is no tax which has not a tendency to diminish production” (Shoup 1960, p.45). In the same way, it has been argued that “income taxation discourages work, sales and value-added taxes discourage consumption, and capital gains taxes discourage investment” (CSI Summary 2006, p.2). Even that levying or imposing and collecting tax is important for the effective operation of state mechanism.
Economic Effect
The implementation of Goods and Services Tax (GST) may affect the economy on a short term basis due to increasing consumption and inflation (A Goods and Services, p.4). Of course, this inflation depends upon the particular economic situation of a country and Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate. Lower rate of Goods and Services Tax (GST) can help in mitigating the short-term economic effects.
Political Effect
From political point of view, this instrument would be subject to more hardship. Politically, Government would face a great difficulty as this change would increase civil service administration costs, which would be problematic in the current political and economic climate. Of course, Government at its minimal effort can reduce the personal allowances to eradicate the budget deficit and contribute in the development scheme of the country.
Societal Effect
As the provisions enunciate that all the people would be subject to tax, there is no doubt to assert that it would severely impact upon the society. People would not accept such legislative decision imposed upon them as the rate is too higher and logically it is a preposterous and a meaningless attempt. The fact of becoming all the people subject to tax would certainly create a societal instability and dissatisfaction among the people against such ridiculous decision of the government.
Defects of Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Hong Kong has a very narrow tax base. Government still has not been able to establish a sound taxation system. The reasons behind this shortcoming is: it is confined to a very limited number of persons as only around 37 percent of the territory’s 3.5 million working population taxpayers (Simmons, p.1). In addition, the tax base is levied in limited range, i.e. the provisions of the existing tax mechanism enunciates, few taxes are levied on goods and services, and no tax on dividend income, income from overseas sources, and capital gains.
But, this is uncommon in any developed economy. Government has not been able to include more people in its taxation scheme by reducing the level of personal allowances. This level is much higher than other developed economies. But, “Government is doubted for the introduction of this sales tax instrument. Such introduction may hamper the plan to sustain the momentum of economic recovery and allow the economy time to recover from earlier economic setbacks” (Hong Kong Budget 2004, p.4). Because, the inherent defects of goods and services tax are seemed to be too much harsh for the people (Raffel 2003, p.8). The defects as has been manifested in this proposed legislation may be summed up as follows:
Registration
The proposed legislation suggests that there will be a high registration threshold whereby businesses with annual turnover over HK$5 million need to register. Of course, Exports of goods and international supplies as well as financial supplies will be zero-rated while sale and rentals of residential properties will be exempted (Gilbert 2005, p.24). Such provision is sufficient to discourage businesses and investment in the country.
Levy upon Export and Import Goods
The provision of levying tax upon export and import goods is quite irrelevant as it suggests the trend of pricing upon the goods of human consumption. This provision can help the common people stand against the government.
Inclusion of Whole Items
The provisions of this act stipulate that all the goods and services would be subject to tax. Consequently, people have been worried as to their consumption and expenditure of necessary commodities in their day to day life. Such provision has made a negative impression upon the people regarding the said tax legislation.
GST in the Global Taxation
Goods and services tax (GST) is broad-based and capable of ensuring a stable revenue system. In modern economy, more than 120 countries [see Figure below] have introduced Goods and Services Tax (Budget Consultation 2004, p.1). Singapore follows a fixed Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate of 5% which is equally applicable to all products and financial services even in the case of the exemption of some products (GST for Hong Kong 2006, p.2).
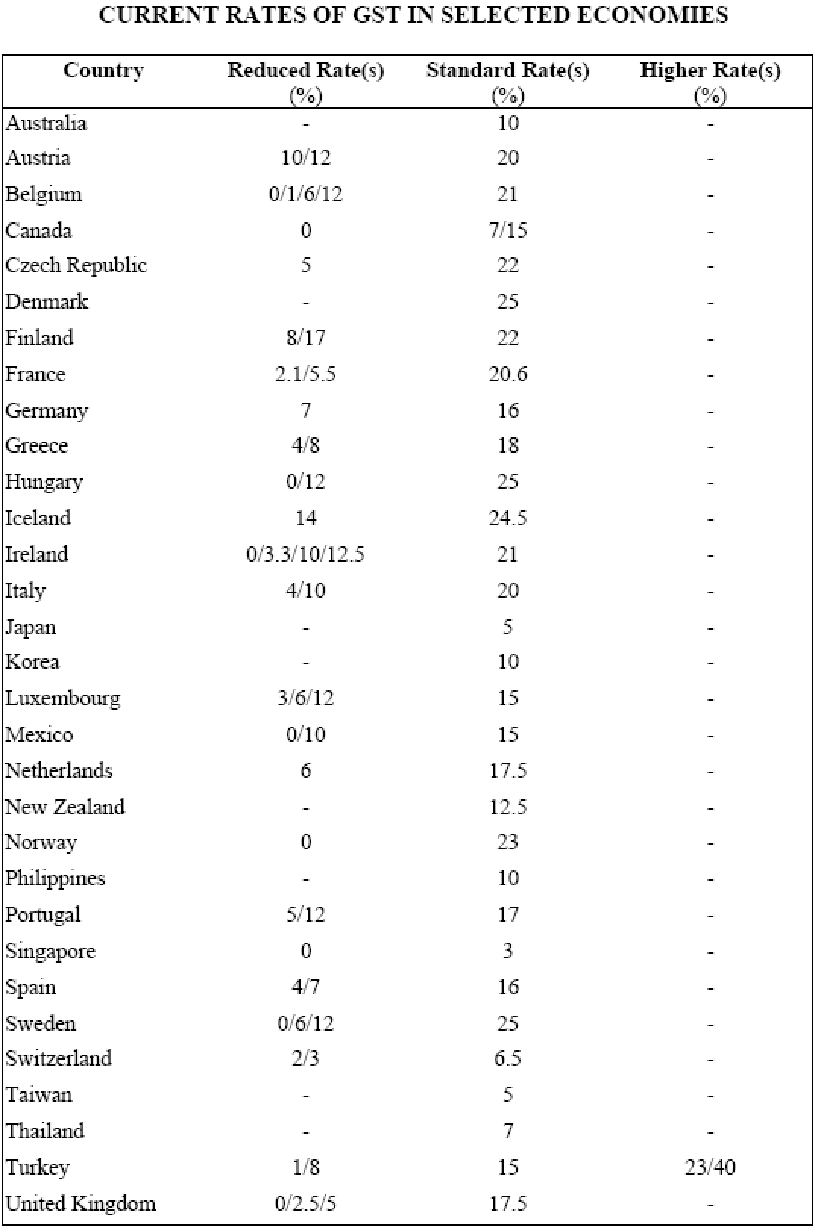
The Australian government launched an education, awareness and compliance program to help businesses cope with a Goods and Services Tax (GST), with AUD500 million set aside to assist small and medium sized businesses to prepare for the levy (GST for Hong Kong 2006, p.2). So, to make the legislation effective and reach it to the citizens’ doorsteps Government of Hong Kong should also introduce such program as without citizens’ participation and public discourse, no program can see the ray of hope and success. In addition, Canada, New Zealand and several other countries of developed world have adopted GST in their economies which is accelerating their sustainable economic growth.
Criticism of GST in Hong Kong
Recently, Hong Kong has taken the approach to introduce sales tax. But, introduction of this act implies a perilous consequence, as the rate would never be decreased rather increased which would affect the economy in a larger extent. In addition, this increasing tax would not strengthen the economic structure in anyway (West 2000). For the following reasons, it is considered that sale tax is not a fair and just policy:
Threat for the Growth of Trade and Development
Much debate has been taken place regarding the proposed Goods and Services Tax (GST).The current global economy is the result of globalization which has been derived from the laissez faire concept. The laissez faire policy does not suggest that there cannot be any tax on the goods and services; rather it speaks about a flat rate of income tax equally applicable to all goods and services in a single market for the total population of the world. Though some proponents argue in favor of sales tax, it is quite irrelevant to the laissez faire principle. The introduction of sales tax can jeopardize the normal growth of trade and development.
Unpopular flavour
Speaking about the proposed sales tax or Goods and Services Tax (GST), critics point out that it would jeopardize the economy and contribute to yield an unstable taxation system in the country. Karlsson (2006) states the Henry Tang’s speech as follows:
“Although the public understands that Goods and Services Tax (GST) [General Sales Tax] can broaden our tax base, it is clear from the views collected that we have not been able to convince the majority to accept Goods and Services Tax (GST) as the main option to address the tax base problem” (Karlsson 2006).
But, the ratio of income taxpayers is notoriously negligible; around 35% of the total workforce pay income tax. Again, this act articulates that people of average income or vulnerable section of the society would be subject to increased tax rate. One of the impediments covered by this enactment is that it puts “tax on every commodity of daily necessities” (A Goods and Services, p.4). This is a burden on the people as people would be suffocated in bearing the tax on ever commodity they consume and the national context would be much troubled. Introduction of sales tax in such situation would not be unaaceptable and efficacious.
Groundless Effort
After a year of review and consultation with the concerned quarters, Govt has launched the plan to the nation though it has been vehemently criticized for its unpopular flavour. The Government decided to generate around $3.8bn in its budget from the proposed tax legislation (Newhouse 2006). Actually, the tax reform attempt through Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been proved as a baseless shooting and huge loss of public exchequer. It severely lacks the practical value and utility.
Danger of losing significance
Hong Kong has long been reputed as an important place for the traders and businessmen for their commercial transaction due to the flexible and non-interference policies of its government. Last year Hong Kong has earned more than US$13.5 billion from the foreign investors (Lee 2006). Tax legislation of the country does not levy sales tax. Recently, in order to avoid the fiscal ups and downs Government has decided to broaden its tax base at the rate of 5% which would exclude financial transaction such as mortgages and loans and include almost every necessary components of day to day life (Lee 2006).
There is little doubt that with the adoption of such taxation policy, country would certainly lose its significance as a centre of trade and commerce. Consequently, Hong Kong would face a great difficulty in matters of economic depression and low investment which will lead to the collapse of economic foundation of the country.
Against the Notion of Public Welfare
Government under the proposed tax act plans to collect HK$20 billion each year from the sales tax and reduce the personal salaries tax, the corporate-profits tax and enhance the quality of public services. But moderately speaking, this proposed legislation preserves the interest of rich people and affects the poor masses as the current 17.5% corporate tax would be replaced by the proposed 5% rate (Lee 2006). It is logically believed that people are entitled to get the maximum opportunities of Government services and Government is ready to provide every assistance, coordination and essential services to its citizenry and protect them from all sorts of hazards and jeopardy. But, the introduction of sales tax is quite inconsistent with the notion of public welfare and principle of good governance. It is imperative on the Government to reconsider the issue for protecting people’s interest.
Complicated Legislation
A low and simplified taxation system is better for a country. In this concern, Hong Kong has a long standing reputation in the economic world. One of the reasons of more foreign investment is the adoption of laissez faire policy and simplified taxation system by the Government of Hong Kong. So, the scheme of broadening tax base is quite irrelevant consideration and a possible threat to the future prospects and gradual development of the country. The proposed tax legislation regarding sales tax would make the tax mechanism complicated and import economic instability in state administration.
Impractical
The entire concept of “broadening” Hong Kong’s tax base is merely an academic solution or confined to the theoretical outlook. It lacks practical implication and overlooks the possible impacts of such groundless decision. The budget deficit in Hong Kong has been caused due to the collapse of the property market (Lee 2006). This approach of filling the budget deficit by enacting a reverse legislation and affecting the people cannot be viable. Again, tourism industry would be greatly hampered and as a hub of trade and commerce Hong Kong would lose its significance. Consequently, the ultimate consequence of introducing this legal instrument would carry a hardship and depression in its economy.
Adverse to the Businesses
Economy of a particular country relies on the soundness of its business transaction. Commercial transaction, i.e. trade and commerce of the country is regulated and promoted with the close assistance of businessmen. So, without their participation and cooperation, economy of a country cannot be developed and provide an outstanding result. In order to get the proper output, business policies for the regulation and promotion of economic development must be categorically designed. Relevantly, it is a matter of great concerns that business policies or concerned legislation of a country must conform to the interest of the businessmen.
But, as regards the provisions of proposed tax legislation, businessmen have been worried considering the fact that they would in more proportion be subject to tax rather than the consumers. This has made them skeptic as to the perilous consequences and prospects for the development of the businesses for their better sake. Again, the persons who had not to pay tax have understood that they are also going to be levied by the force of Goods and Services Tax (GST). So, these marginal people as well as businessmen have taken their positions against this.
Non-Responsive Government
Government has not contributed its best effort to disseminate the positive impact of this act. It has been proved that the Government is much callous in reaching the correct message among the public. Government could easily choose the option to make people understand as regards the significance of the said Goods and Services Tax (GST) to boost the economy of the country. There are several examples in the countries of the world that have been able to develop their economy with the introduction of GSTIt is little more than a decade that Australia has recorded a successful example in adopting Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2000.
Australian Prime Minister John Howard, in order to persuade the people in supporting Goods and Services Tax (GST) used “logical fallacies” technique in 2000. While using this technique, John Howard added that “as the current taxation system is not seemed proper for the up gradation of Australian community, it is necessary to change the taxation system in order to reach our dream, goal and becoming a major financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region” (Heung-man 2007, p.10).
But, Government of Hong Kong did not take such efficacious means to convince the people as to the merit of the legislation. Existence of a different economic policy is another reason for the unpopularity of this enactment. Because, “though Singapore has been successful through the introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) and has increased the ratio of Goods and Services Tax (GST) now stands about 19%” (Heung-man 2006, p.14), there is a much difference between the two economies.
The economic policy adopted in Singapore is unlike to that of Hong Kong, i.e. states interference in the regulation of all sorts of economic affairs while Hong Kong has the different approach, i.e. follow the laissez faire. So, the traders and businessmen become perplexed at the Government decision on the ground that the taken policy might collapse the potentials of trade and commerce. But, inevitably, in some cases it is essential to make state interference on the national economy.
Overlooking Citizens’ Interest
Modern state philosophy suggests that citizens should be afforded a certain degree of conveniences, facilities and privileges within the possible limits of a given state. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been portrayed to the citizens as antagonistic to this vision. As a result, being the instrument as adverse to the interest of people, public demonstration was staged claiming its unenforceability.
Rigorous for Common People
It is impossible for any state; howsoever developed and efficient management of its economy, to equate all the people in the same economic footing. For the multifarious variables including economic policies of the state, people cannot achieve the same economic status. Marginal or destitute people suffer from economic hardship and become subject to oppression and deprivation. To speak from a logical point of view, the provisions of this act would severely affect them as the concerned provisions articulate that all the citizens are liable to pay tax for the reason that they are the beneficiaries of public services. In addition, as the workforce is limited in number and total populations are not able to earn, enforcement of this legislation would bring a serious effect in the national arena.
Threatening for retail competitiveness
The proposed Goods and Services Tax (GST) would loosen Hong Kong’s retail competitiveness compared with cities in the Pearl River Delta. Many Hong Kong residents have already made a number of regular purchases outside the SAR (Special Administrative Region). So, the impact of the introduction of a consumption tax would not be an aspiring outcome (Broadening Tax Base 2004, p.1).
An Instrument of Manipulation
“The common phenomenon regarding Goods and Services Tax (GST) prevalent in various countries is that the subsequent Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate is much higher than the rate was initially introduced” (Broadening Tax Base 2004, p.2). The tax levied on personal income or profits derived from business transaction is more visible than sales tax. As it is physically invisible, People cannot realize the burden of sales tax.
So, policy makers are taking the opportunity of manipulating the citizens through the introduction of sales tax. In fact, though it is considered that sales tax is designed to help developing the economy of a country; in true sense, it does not contribute in accomplishing such purposes. In fact, this increased rate of Goods and services tax (GST) would harshly affect economy and an adverse relation between citizens and government which would generate dissatisfaction, non-cooperation and ultimately produce mal-governance in state administration.
Increased Administrative Cost
In the view of taxation authority, “complex Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime would increase staffing costs” (A Goods and Services, p.3). This expenditure is unnecessary and extra loss of public fund replacing the existing simplified taxation system. Virtually speaking, this unnecessary expenditure through the introduction of proposed tax enactment is ridiculous and against the principle of public policy.
Dissimilarity of Opinion among Government Officials
Public have become much worried as there are differed opinions among Government officials regarding Goods and services tax (GST). This transpires mismanagement and inefficiencies of public administration which is frustrating for democratic norms and values. Because, the Government policies and decisions are of much importance and they should be circulated and disseminated with sense of responsibility. The issue arising out of differed opinion among Government officials is quite enough in the minds of the people to produce distrust and no-confidence on Government
Baseless Argument of Public Service and Protection from Economic Downfall
It is argued that many people do not contribute to the costs of public services. So, they should be equally liable to pay revenue to the public exchequer. In addition, “to avoid the future economic downfall, introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) is essential”(Reforming Hong Kong 2006, p.6). But, this can not be a valid defense as states are liable to provide the citizens best comfort irrespective of the status of the citizens.
Recommendations and Conclusion
The proposed tax legislation of Hong Kong lacks certain defects and loopholes. In fact, this legal instrument was legislated with a view to making a change in the national economy in ensuring a sound and stable financial structure. It is not unsurprising that legislation possess some shortcomings. The approach of adopting this legislation is public welfare and filling up the budget deficit for ensuring the betterment of the country. As Public welfare cannot be excused on a mere cause, Government should be more active to repair the defects and immediately enforce it. From a through study over the topic, the present study has found some ways and means for the improvement and implementation of the proposed Goods and Services Tax act which may be recommended as such:
- The capable workforce in comparison to total population of Hong Kong suggests a wide gap which is very much irrelevant to the economic development of the country. Rather the issues of terrorism, hike of oil prices are some major impediments. So, in the context of the practical situation, it is essential to introduce Goods and Services Tax (GST) for adding the benefit in its taxation system as people would provide additional revenue and ensure a stable taxation system in the country.
- Inevitably, taxation is important for the effective operation and management of state administration. The proposed Goods and services tax (GST) though to some extent has an unpopular and non-democratic flavor; it is of much significance for the interest of the people and gradual economic promotion of the country.
- In the proposed legislation the rate is likely to be levied is much higher. Considering the issue of goods and services tax (GST) over the world, it is found that the successful countries took a strategy where they initially levied at a minimal range and subsequently increased the rate on the context of the given economic situation. The proposed rate of 5% is quite irrelevant; rather it could be 2or 3 percent.
- This legislation would facilitate few tax payers to get the benefit of sales tax. Actually, the whole matter depends on the point of how the tax schedules would be revised. In order to ensure the effectiveness of sales tax and opening the avenue to the people availing its true dividend, it is necessary to review the existing tax mechanism and if necessary, steps should be undertaken to restructure the tax administration of the country.
- The strategy of the Government should be developed. Due to lack of proper strategies and policies, Government has lost its popularity. The proposed plan to increase sales tax has caused a 6 percent drop in public trust in the government (Taipei Times 2006, p.5)
- The level of personal allowance subject to tax can easily be minimized by half and a drastic reform can be introduced in the system. If this is so done, the number of tax payers would be increased from 1.3 million to 2.2 million and generates an extra $14 billion in tax revenues (Simmons, p2).
- Hong Kong has a developed economy. So, introduction of consumption tax is not a bar in accordance with the economic context of Hong Kong; rather it is a unique and timely approach for strengthening economic development. Government should wisely ponder the gravity and importance of consumption or sales tax and introduce it for the sake of enhancing the further development initiatives and facilitate the people invoking maximum benefit at the best extent.
- In the global context, Countries have taken the view to introduce Goods and Services Tax (GST) as a part of tax reform in their tax reform or promotion of revenue system program. The purpose of such reform is not to increase the revenues, but to remodel the tax system and make it more equitable. Accordingly, Hong Kong has taken the view of introducing this. But, the correct message of this reform initiative should be reached to the people through proper means.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) is considered as opposing to the interest of people and accordingly resistance is made against this. So, steps should be undertaken to make the people well-convinced and accordingly grass root basis network should be developed. For this, linkage program with educational institutions should be ensured in order to educate the students and disseminate throughout the society as regards all the necessary issues of Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Public forum should be formed to more categorically single out the loopholes and deficiencies of the proposed tax legislation. As public discourse ensure valuable suggestions, comments and guidelines, arranging such public discourse or citizens’ forum can help in developing and implementing the proper strategy
- “It would add 5 millions dollar annual turnover to its economy, exempt small and medium sized businesses from this collection, reduce or eliminate compliance costs for small and medium sized businesses”(Reforming Hong Kong 2006, pp.13-14). Of course, unregistered businesses would not be able to reclaim Goods and Services Tax (GST) on their inputs. Additionally, it can minimize complexity and compliance cost for businesses and administrative costs for Government.
- Media should be more active to contribute in producing and arranging various program and articles concerning the detailed discussion about the legislation. This would widely help the people for their better understanding over the legislation and potential outcome arising out of the legislation. Policy makers would get the sufficient guidelines to frame a more accurate and working tax mechanism.
- Undeniably, public administration of the country is regulated through Government officials; the success of public administration of a particular country greatly relies on the efficiency of the public servants or Government officials of the country. Generally, Government staffs are not familiar with the handling of tax affairs and sound management of tax administration. To improve the efficiency of tax administration capability of Government staffs should be increased with the introduction of training program. More training programs can enhance the performance capability of Government officials in ensuring well-functioning taxation system.
- It is imperative for the Government of Hong Kong to consider exemptions for the purpose of giving a definite shape of Goods and Services Tax(GST) and make it workable. Political parties should be united on this issue to introduce a better taxation system and make the people its true beneficiaries.
- All the Government functions should go with a view to benefit the mass people as they are the key component of democratic governance. Though Goods and Services Tax (GST) may be considered as a working tool for the benefit of a particular economy, alike other states, Government of Hong Kong should also pay a due regard to the interests of low income or vulnerable section of the society so that the said Goods and Services Tax (GST) may not hamper them. Relevantly, in this regard, Government should minutely consider small and medium sized business enterprises which are actually the foundation and principal means of Hong Kong’s economic structure. So, the consideration of the potential impact of financial services sector and accordingly erect a body of policy implementation is a sine qua non for the government.
- In the view of taxation authority, complex Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime would increase staffing costs or administrative expenditure. It is recommended that in order to get the benefit from Goods and Services Tax (GST), steps should be undertaken to minimize the administrative cost. Because, if a simple Goods and Services Tax (GST) system is implemented in Hong Kong, it would follow an amount of administrative cost which is currently levied from principal sources in the existing revenue mechanism (Goods and Services p.3). In this aspect, axiomatically, it can be stated that a special committee should be formed for the purpose of finding out the ways and means to develop an improved structure for rendering the better services by the tax administration so that administrative cost can evenly be minimized. If the administrative costs take away larger portion of the revenues, it would be a meaningless effort and produce no outstanding output for the benefit of the people.
- One of the impediments covered by this enactment is that it puts tax on every commodity of necessary goods that are used in day to day life.. As a result, people would be much troubled. So, exemption or reduction of tax from daily necessities to some extent may eliminate the regressivity of tax legislation. In this concern, policy makers should categorically specify the criteria of determining the daily necessities and exemptions to be applicable over certain goods and services as well so that revenue administration of the country is not hampered in anyway.
- To make it successful, Government has many options to choose. The prime and foremost concern is that due to lack of publication and dissemination, it could not reap the benefit. In this regard, Government could undertake Seminars to able the Government officials understand and properly evaluate the Goods and Services Tax (GST) scheme and in certain cases recommend the measures to be taken by the Government to develop the mechanism in broadening the tax base. As the matter is concerned with the greater interest of the nation, common masses were required to be convinced well. To accomplish this purpose, Government in its conveniences can “hold seminars in estates, community centers, and the offices of professional bodies to answer citizens’ queries and Produce TV or radio programs to reach the true message of Goods and services Tax Goods and Services Tax (GST) to the citizens’ doorsteps” (Heung-man 2006, p.15).
Compensation scheme should be introduced to compensate the affected persons and groups for the introduction of Goods and Services Tax. In this regard, the standard of determining the damage to the affected persons or groups should be singled out.
Annotated Bibliography
Lee, Wendy., 2006. Tax-free may flee Hong Kong. Wall Street Journal Exclusive. (Lee 2006):
This article states about the Government decision concerning broadening the tax base of Hong Kong in order to enhance development initiatives in its territory. The gradually developing economy of Hong Kong is mostly relied on income tax and profits tax. The article also examines the impact on the Hong Kong economy caused by this proposed legislation.
GST for Hong Kong? (2006).
This article deals with the issues associated in reforming proposed Goods and Services Tax (GST). The article states to consider the points which may impact in the national economy. The writer has proposed the Government and concerned authorities to address the issues for making a successful tax reform.
Stender, Neal., et al. 2006. China Investments & Operations: Advantages of Hong Kong Holding Structure Now Include Tax Preferences, 1-7.
This article examines various issues of revenue matters both in PRC (Peoples’ Republic of China) and Hong Kong. The writer has advocated that PRC (Peoples’ Republic of China) business regulations are on the way of gradual change. Due to this, the relevant regulations and directions are becoming more complex and rigid in cases of company’s financial dealings and tax matters.
Shoup, S. Carl., 1960. Ricardo on Taxation. New York: Columbia University Press.
The tax in America was introduced near the end of the Seventeenth century to replace a still earlier tax that had atrophied in much the same way as this one was destined to do. The new tax was imposed at a rate of 20 percent on the full rental value of real estate and on an imputed income of 6 percent of the capital value of all personal property, including money, but excluding stock on land and household property. The above mentioned statements are about the taxation system in America as has been ascribed in this book. This book discusses the taxation policy as suggested by Ricardo. In addition, the book also puts focus on various types of tax including profits tax and wage tax. Besides, the book has concentrated its discussion on sales tax. It has been recommended that sales tax is important for the development of a country.
Sawday, K.S., 1939. A Practical Guide to the New Income: Tax Law. Calcutta: S.C. Sarkar & Sons Ltd.
This book has provided a detailed discussion about the Indian fiscal policy and different types of tax that were prevalent under the then tax regime. The book has discussed amongst other the criteria of determining tax rate and asserted the importance of income tax and capital gain tax in the development of Indian economy. The book has also argued that sales tax is the inevitable consideration for the sound economic policy of Indian economic structure, though practically it is seemed impractical and unimaginable thought in the Indian context.
Newton, W. Grant., & Bloom., D. Gilbert., 1991. Bankruptcy and Insolvency Taxation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
This book is well designed in context of America in order to provide a broad range of guidance on the tax aspects which must be made by companies in financial trouble. It has also discussed about the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code and the Bankruptcy Code applicable to businesses. Besides, the book has put attention on the tax consequences to creditors of loss from debt forgiveness, discharge of indebtedness, tax procedures and tax preferences and liens.
References
Dowell, K., 2004, A History of Taxation and Taxes in England from Earliest Times to the year 2002. London: Hithoran Publications.
Rowse, T. J. M., 2003. Invest Hong Kong: Government of the Hong Kong SAR. State of Business Magazine 16(1). Atlanta: Georgia State University. Web.
Luxembourg Chamber of Commerce in Hong Kong., 2007. Double Taxation Agreement between Hong Kong– Luxembourg. Web.
Yee-ming, L. M., & Alice, P. J. Commissioner’s Overview. Inland Revenue Department Annual Report 2005-06, 1-3. Web.
Mergers & Acquisitions Asian Taxation Guide. Price Water House Coopers, 1-18. Web.
Consequences of Discharge of Nonrecourse Indebtedness. Journal of Taxation 67. Cited in Newton, W. Grant., & Bloom., D. Gilbert., 1991. Bankruptcy and Insolvency Taxation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Hong Kong Trade Development Council (HKTDC), 1998. Web.
Roy, Gamlar., 2006, Mergers & Acquisitions Asian Taxation. New Delhi: Mitra Publications.
Runil, Rugers., 2007. Good and Bad for GST. Economic View. (Culcatta).
Reforming Hong Kong’s Tax System Public Consultation, 2006. LC Paper No. CB(1) 1994/05-0(01), 1-39. Web.
A summary of the proposals for a Goods and Services Tax in Hong Kong., 2006. A Proposed GST Framework for Hong Kong. The GST Framework. In Chapter 5, 1-26. Web.
Simmons, S. Richard. Widening Hong Kong’s Tax Base – A Call for Consistency, 1-3. Web.
Hong Kong Financial Budget 2004. International Tax Watch. AGN International, 1-9.
Gilbert, G. L., 2005. Hong Kong Tax Regime. the Financial Express (Dhaka).
West, Andrew., 2000. Read their lips Hong Kong: “New taxes!”. Capitalism Magazine. Web.
A Goods And Services Tax For Hong Kong. Annex F. 1-6. Web.
Raffel, K. L., 2003. Taxation Regime in Asiatic Economy. The Ananda Bajar (Calcutta).
Horwath Hong Kong. 2003. Sources of Profit in Hong Kong – Guidelines for Trading Companies. Web.
Broadening the Tax Base in Hong Kong, 2004. Position Paper prepared by “the American Chamber of Commerce in Hong Kong”, 1-2. Web.
Budget Consultation 2005-06. L.C. Paper No. CB(1)146/04-05(01), 1-2.
Pinaki, V. R., 2005. Goods & Services Tax. The New Nations (Dhaka).
CSI Summary. 2006. The Ultimate Tax Reform: Public Revenue from Land Rent. Civil Society Institute: Santa Clara University, 1-4. Web.
Taipei Times, 2006. HK government loses ground in popularity stakes. Web.
Kibria, L., 2006. Tax Regime in Hong Kong. the Financial Express (Dhaka).
Heung-man, M. T., 2006. Introduction of Goods & Services Tax (GST) in Hong Kong from a Political Perspective, 1-18. Web.
Karlsson, Stefan., 2006. Hong Kong Will Not Impose Sales Tax. Stefan Karlsson’s blog: Data Indicate No U.S. Recesssion-Yet. Web.
Newhouse, Doug., 2006. People power kills Hong Kong GST tax hike. TREND-News. Web.
Gandhi, Arun K., 2007. Sale Tax with Higher Rate. the Don (Karachi).
Yahya, Nese., 2008. A Turkish business destination: Hong Kong. Turkish Daily News. Web.