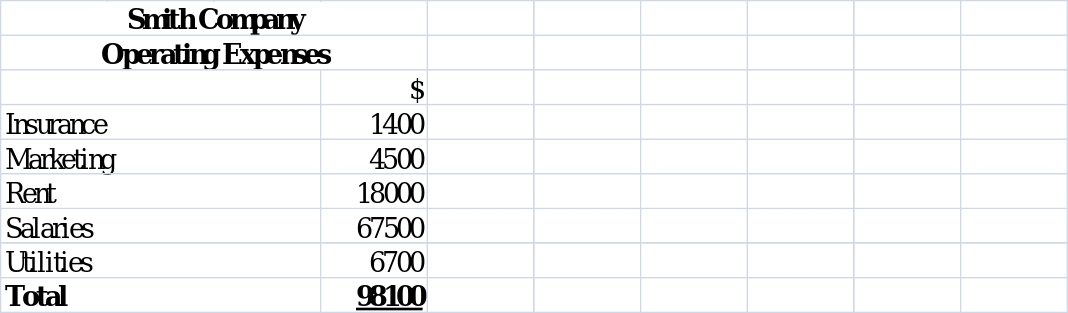
Preparation of the income statement of Smith Company first requires the calculation of the company’s operating expenses and the retained earnings at the start of the trading period ended December 31st, 2012. The operating expenditure is computed as shown in the worksheet hereunder.
Working: Operating Expenses.
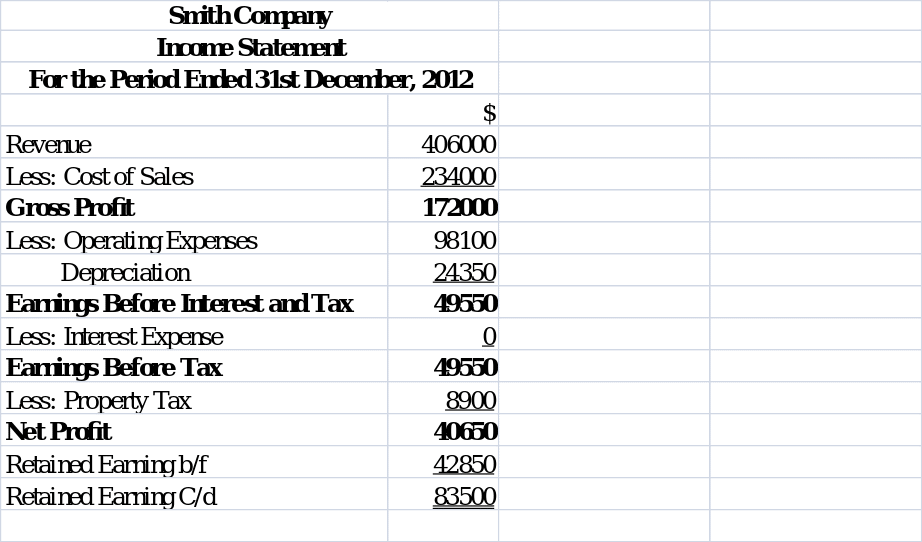
The retained earnings have been established by comparing the total debits and credits of the trial balance.
Retained Earnings b/f = $760850 – $718000 = $42850
Income Statement.
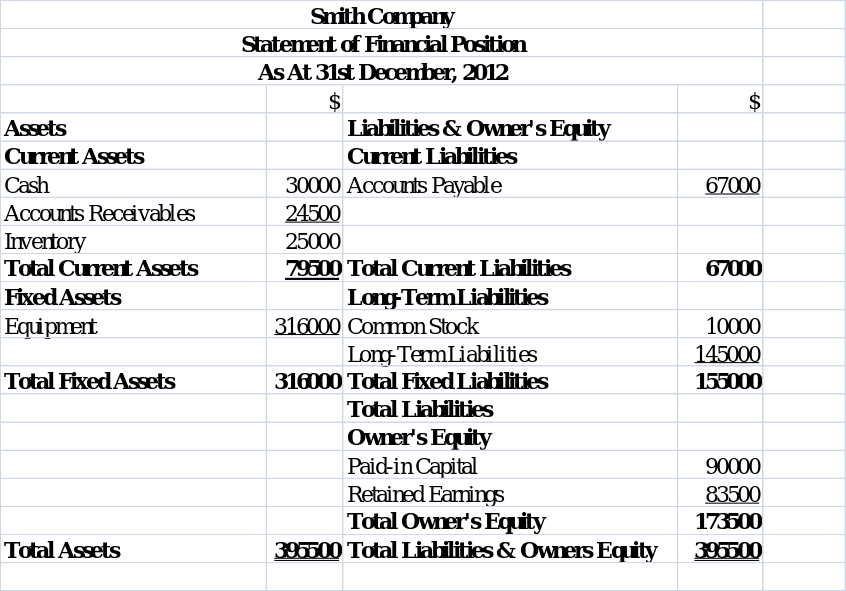
Statement of Financial Position.
Remarks on Smith Company’s Success
The success of a firm is defined in quantitative and qualitative terms. Qualitative indicators refer to non-quantifiable information used to describe the performance of an enterprise. Quantitative performance indicators refer to the quantifiable measures of a firms or industry’s success. The most used measurable indicators of performance are financial ratios (Walther, 2010).
In describing the success of Smith limited, a variety of ratios have been computed. The ratios describe, in quantitative terms, the firm’s liquidity, activity, profitability and gearing level (Walther, 2010). Liquidity ratios have been used to determine the company’s to meet its short term debts as the fall due (Walther, 2010). The current and the acid test ratio have been computed to assess Smith Company’s ability to offset current obligations as they mature. A proportion of 2:1 is acceptable.
Current Ratio = Current Assets/ Current Liabilities = 79500/ 67000 = 1.1866: 1
The computed ratio indicates that the firm may be experiencing difficulties in meeting short-term obligations as they fall due.
The acid test ratio is a quotient of the most liquid current assets and the current liabilities. In normal situations, the ratio should be 1:1.
Acid Test Ratio = [Current Assets- Inventory]/ Current Liabilities = [79500 – 25000]/ 67000 = 0.8134: 1
The firm’s quick ratio is unsatisfactory. This indicates that the company’s ability to raise quick cash is limited since much of its investment is locked in inventory.
Profitability is the widely used measure of an enterprise’s success. The profitability ratios are hence used to determine an enterprise’s ability to generate profit. The commonly computed profitability ratios include return on capital employed, return on investment, profit margin, assets turnover and gross and net profit ratios (Walther, 2010).
Return on investment refers to profit on the owners’ investment in the firm. It is a quotient of profit after tax and owners’ equity.
Return on Investment = [Profit after Tax / Owners’ Equity]* 100 = * 100 = 23.4294%
Assets turnover is a quotient of sales and capital employed expressed as a percentage.
Assets Turnover = [Sales / Capital Employed]* 100 = [406000/ 249000]* 100 = 163.05%
Gross profit ratio is calculated by dividing gross profit by sales and expressing the quotient as a percentage.
Gross Profit Ratio = [Gross Profit / Sales]* 100 = [172000/ 406000]* 100 = 42.3645%
Net profit proportion is computed by dividing net profit by revenue and expressing the result as a percentage.
Net Profit Ratio = [Net Profit / Sales]* 100 = [40650/ 406000]* 100 = 10.0123%
Smith Ltd is providing reasonable returns to owners of equity. Its assets are also efficiently being used to generate sales. Nevertheless, the operational expenses are very high leading to a reduction in the net profit.
Gearing ratios are used to establish the capital structure of a firm (Walther, 2010). The debt-equity and equity ratios have been used to establish the debt load in Smith Ltd.
Debt-equity ratio establishes the relationship between the providers of equity and providers of fixed interest capital.
Debt-Equity Ratio = [Total Debt/ Total Owner’s Equity] = [155000/ 173500] = 0.8934.
The equity ratio is computed by dividing total assets by the owners’ equity. It establishes a firm’s financial weakness or strength.
Equity Ratio = [Total Capital Employed/ Equity Capital] = [395500/ 173500] = 2.2795.
The management of Smith Company has been unsuccessful in establishing a financially strong company. The proportion of finance provided by debt owners is almost equal to that made by owners of equity rendering the enterprise risky. Similarly, equity is only a small proportion of capital employed.
Reference Page
Walther, L.M. (2010). Principles of Accounting: A Complete Online Text. Web.