Sampling and Recruitment
Convenience sampling will be used because of the specific study design and its aims. The researcher plans to choose the study participants using online resources, information from clinics, and private contacts to have the needed number of participants.
All possible participants of the study will be contacted by the researcher; the researcher will provide them with the information about the study, its aims, and objectives, as well as papers needed for ethical considerations (such as forms to provide written consent or right to withdraw). The participants will also be asked to explain their refusal but only if they find this appropriate (the information can be useful for the research as a future reference when conducting a study).
The researcher plans to use SPSS Statistics 21.0 for data analysis (Assi, Thomas, Haffar, & Osselton, 2016).
Study Design
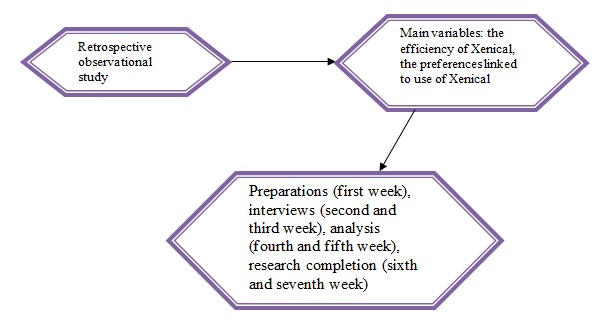
A retrospective observational study design is used for this paper. Observational studies are used to understand the effects of the treatment and its influence on participants (Howell, 2016). An observational study is not an experiment but rather research on the current issues and its outcomes or influences. Furthermore, the retrospective design of the study implies that the participants will not be controlled during their treatment but rather interviewed about the treatment outcomes (Howell, 2016).
It is a descriptive, cross-sectional study that will focus on surveying and interviewing the participants about Xenical, the process of weight loss, and Xenical’s influence or lack of influence on weight loss. Furthermore, the researcher also aims to interview the participants about the impact of local features and context on the use of this medication.
Variables and Factors
The main variables observed in this study will be the following: the efficiency of Xenical for weight loss in the UAE populations and the preferences linked to the use of Xenical compared to other medications for weight loss. The secondary variables are the influence of local context on the availability of Xenical and the use of other medications (legal and illegal) by the population of the UAE and the influence of combined therapy (Xenical plus physical activity) on the efficiency of the treatment.
The factors observed in this research are the following: gender, height, weight, age, location, the duration of treatment using or not using Xenical, the availability of Xenical in the area, the availability of other medications for weight loss (legal and illegal) in the area, the availability of other means used for weight loss in the area (medical interventions at clinics, sports facilities, etc.). The factors that can influence the main variables are the social and financial backgrounds of the participants, the pharmacists’ attitude towards weight loss medications, the presence or lack of physical exercises, and lifestyle interventions. According to Shamsher et al. (2016), many pharmacists in the UAE do not recommend clinically tested weight loss medications due to the existing belief that they cause severe adverse side effects. This can negatively influence participants’ decision to use Xenical or any other tested and approved medication.
Contextual Conditions
The contextual conditions include access to medicine, the availability of cheaper substitutes, cultural/religious, and societal attitudes to weight loss medications, and weight loss in general (Tomoaia-Cotisel et al., 2013). The researcher aims to gather information about these factors to evaluate how they influence the use of Xenical.
Study Procedure
The study procedure will be the following: the participants for the study will be selected; the participants will be provided with information about the study and the researcher. After providing their written consent, the participants will be interviewed and surveyed about Xenical, other weight loss medicine, and their impact on the process of weight loss. The researcher aims to analyze the data using the software presented above and individually studying answers to open questions.
Definitions
According to the CDC (2017), “weight that is higher than what is considered as a healthy weight for a given height is described as overweight or obese”. To evaluate whether or not a patient is obese, BMI (Body Mass Index) is used.
Xenical (Orlistat) is clinically tested and approved medication for the treatment of obesity (Azadbakht, Gojani, & Heidari-Beni, 2015). Surveys are structured sets of data that allow the researcher to use statistical controls in data analysis (Greenfield, 2016).
Examinations and Data Gathering
When the potential participants agree to participate in the study, the author aims to begin the surveys and interviews one week after all papers containing written consent from participants are received. The interviews and surveys will be conducted within two to ten days, depending on the participants’ ability to take part in them. The qualitative and quantitative data collected for the research will be analyzed within three to seven days; after that, the researcher aims to review the analysis to ensure that there are a few biases as possible. This will be the end-point of data-gathering.
Time Schedule
The first patient will be included in the study within two days after the preparations for the research are complete. The last patient will be included approximately on the seventh or tenth day after the study preparations. Each patient will be the understudy for one to three days. The last patient is estimated to finalize the study in two or three weeks after the study preparations are complete. The estimated total duration is approximately two months.
Flow Diagram
References
Assi, S., Thomas, J., Haffar, M., & Osselton, D. (2016). Exploring consumer and patient knowledge, behavior, and attitude toward medicinal and lifestyle products purchased from the internet: A web-based survey. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance, 2(2), 1-16.
CDC. (2017). Defining adult overweight and obesity. Web.
Greenfield, T. (2016). Research methods for postgraduates. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
Howell, D. C. (2016). Fundamental statistics for the behavioral sciences. Toronto, Canada: Nelson Education.
Shamsher, A. A., Nadeem, N., Nadeem, V., Mutib, K. O., Mutib, N. O., & Charoo, N. A. (2016). Herbal and prescription weight loss products: Awareness among pharmacists about efficacy and safety. Journal of Pharmacy Practice and Research, 46(4), 331-337.
Tomoaia-Cotisel, A., Scammon, D. L., Waitzman, N. J., Cronholm, P. F., Halladay, J. R., Driscoll, D. L., & Shih, S. C. (2013). Context matters: The experience of 14 research teams in systematically reporting contextual factors important for practice change. The Annals of Family Medicine, 11(1), 115-123.