Abstract
Homeland security and efficient border control measures are highly significant for the United Arab Emirates. The condition of regional tension in the Middle East and increased militancy movement in the region has made the borders of the country extremely vulnerable to foreign as well as regional threats. The region currently faces threats from conflicts and war in Yemen. The research aims to investigate the current stage of border control and homeland security in the United Arab Emirates. The methodology adopted for the study is secondary and primary data analysis, which is evaluated to understand the areas where the threats are imminent on the country and how the citizens perceive these imminent threats.
The paper uses both primary and secondary data to understand who the security threats are perceived by the citizens of the country and how the media and other bystanders view the issues. Further, the paper looks into the rise of security issues that the country faces and how it has affected it. On evaluating the awareness of residents of the United Arab Emirates about the importance and protection of border control and homeland security it is found that the residents of the country are aware of the impending threats to the nation but believe proper measures are being taken to counter such threats.
Introduction
Background of the Problem
From the perspective of ‘no country is immune from the crisis’, the United Arab Emirates has put a priority in developing its border security apparatus for its natural resources. The United Arab Emirates has experienced a variety of transformations and improvements in many sectors. In 1971, the United Arab Emirates was 62nd in the Human Development Index. In 2010, this indicator increased and made the country the 30th in the Human Development Index (CPC 2015). In terms of economic development, specifically in the airline sector, the country exceeded Singapore (CPC 2015). Today, the United Arab Emirates has the seventh-largest GDP per capita (CPC 2015). The infrastructure of the country has undergone significant changes.
The country’s sudden modernization led to the implementation of one of the most well-developed infrastructures in the world with the massive usage of social media and mobile industry *(CPC 2015). The country now enters the global arena. It has become a significant participant in global affairs. The United Arab Emirates has been increasingly assertive in the political developments in the Middle East, especially against Iran, Muslim Brotherhood, and other extremist Islam groups (Katzman 2015). Its open economy and borders have helped the country to prosper economically but also has increased threats to security (Katzman 2015). Economic prosperity and open economy coupled with anti-extremist stand have made it a target of many aggrieved neighboring countries and extremist Islamic organizations (Katzman 2015).
Since its creation, the United Arab Emirates experienced rapid growth of the economy (CPC 2015). The boom in oil prices predominantly caused this growth (Katzman 2015). The recent oil boom occurred in the period between 2002-2008 (Saif 2009). This boom resulted in the rapid development of economies of six countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council including the UAE. The oil boom was a result of other countries’ lack of resources and the ability of the UAE to satisfy that need. It was the second oil boom since the 1970s (Saif 2009). Besides, the country had forceful progress in the property market. United Arab Emirate economy has increased by seven percent every year since the year 2000. The aim of the state is not to be dependent on energy resources.
According to H.H Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid; diversity seems to be the new mantra for the UAE. The United Arab Emirates has planned to develop several new sectors such as the Islamic economy and innovation. Also, H.H Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid mentions that’s our aim is to build strong and stable economy diversity by the year 2021(D’Mello, 2015). Also, H.H Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid said, “We have put in place all the necessary plans to take that contribution to as high as 80 percent in 2021 through intensive investment in the industrial and tourism sectors, air and maritime transport, import and re-export, as well as supporting a range of projects and initiatives based on the knowledge economy” (D’Mello, 2015).
Although the oil resources make the country prosperous, the United Arab Emirates cannot rely on it because all-natural resources are exhaustive. The country faces two major challenges including the diversification of the non-oil sector of the economy and governmental policies (Saif 2009). The government of the United Arab Emirates supported the diversification of the economy. The country aims to accomplish this goal via the improvement of three sectors: finance, tourism, and education (Saif 2009). Consequently, a substantial amount of assets is further contributed to the development of other spheres of activity such as infrastructure, improvement of science, a public-private partnership, and education.
The rapid expansion and development of the United Arab Emirates make it a significant figure both in the Middle East and in the world (Katzman 2015). Still, the country faces a variety of internal and external challenges (Katzman 2015). The primary external challenges concern the potential geopolitical instability in the region (World Economic Forum 2007). The military threat from Iran is about the territorial dispute over few islands in the Strait of Hormuz as well as the persistent threat of terrorism posed by that country in the region and around the globe (Linden 2007). Although Linden believes that the UAE does not face threat from the Al Qaeda or the Islamic extremist organizations, primarily because they do not have their base of operations in the country, the country faces threats from the regional instability brewing in the Middle East (2007, 82).
For instance, after the Second Gulf War, the countries of the Arab world realized the need to create a safety region that cannot undermine the security of the Arab countries. Al Nahyan writes, “No single Arab country can individually achieve political and national security out of the other Arab Countries whether on the region or national level” (2000, 34). This peculiarity of the Arab countries predetermines the dependence of the country’s security on the situation in the region.
Terminology
In this paper, from here on, the term border will be used in its legal sense. Here border would imply the territorial boundary between two neighboring countries that are controlled by international and regional laws. Homeland is associated with the cultural identity of the nation though for this research we will add here to the legal parlance of the definition that implies that there are of the land within the boundaries of the country is the homeland.
The dictionary term “border control” refers to a set of measures that predetermines country’s approach to the provision of security of its borders (“Border Control Law & Legal Definition”). Border control may be referred to as the psychical expression of a state’s sovereignty. Border control monitors everything including animate and inanimate objects that enter or leave the country. The primary function of border control regulations is to protect the country.
Homeland security is a condition of the country when it is free from danger or threats. The term “homeland security” is used to define measures the particular country uses to protect the country from external threats such as terrorism, smuggling, or drug trafficking.
According to the online version of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary, terrorism is defined as “the use of violent action to achieve political aims or to force a government to act.” In the following paper, the term terrorism is used to describe potential threats to homeland security in the United Arab Emirates.
Smuggling is “the illegal transport of goods, especially across borderlines. Smuggling is engaged in to avoid taxation or to obtain goods which are prohibited in a certain region.” Smuggling is one of the threats and challenges to the border control and homeland security in the United Arab Emirates.
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime’s definition of drug trafficking presupposes that it is “a global illicit trade involving the cultivation, manufacture, distribution, and sale of substances which are subjects to drug prohibition laws.” The efficient overcoming of this problem is also significant for the United Arab Emirates as far as any illegal activity undermines the safety and status of the country.
Border control problem
Disputes over the border and its control have been present from time immemorial. Each state defines its border following its principle of sovereignty and hegemony. Barakat points out that several countries in the region have fought over a dispute over boundaries (Barakat 2005). For instance, the United Arab Emirates and Oman have decided to sign an agreement to define the common border between the two countries in 2007 (WAM 2008). Furthermore, Barakat also points out that there were political borders between countries in the Gulf region as they followed administrative boundaries since the Ottoman rule (2005).
The security issues in the Gulf States arise both internally and externally. In GCC countries, there has been a rise in the “new border approach” to propagate national and regional security (Ulrichsen 2009). These oil-rich countries have tried to strengthen internal and regional policies that would lead to greater cohesion internally to create a long-term inclusive and sustainable politics (Ulrichsen 2009). However, in the post-Cold War era, the approach to control border security has become increasingly cooperative. With the rise of transnational terrorism, a cross-border criminal network, and global issues related to climate change, there has been an increased collaboration between nations to develop a strong internal and external strategy that is mutually beneficial to nations (Ulrichsen 2009).
However, this change has not occurred in the Middle East, where security discourse is predominated by the presence of “regime security” and “national security” (Ulrichsen 2009). Thus, the paradigm of Gulf security will shift towards an open economy and political transparency (Ulrichsen 2009). According to Karasik, bilateral agreements was the key solution to solve several border disputes, the most threatening problem within the GCC – such as those between Saudi Arabia and both Oman and the UAE (Karasik 2013). Saudi Arabia, for example, refused to recognize the new federation because of an unresolved border dispute with Abu Dhabi over the Al Buraimi Oasis (Morton 2013).
The United Arab Emirates aims to strengthen its border security to the optimum to assist in rapid economic development. The challenges and threats to border security undermine the United Arab Emirates’ confidence in the future stability of its borders because of the continuous volatility in the Middle East region. For instance, the civil war in Syria and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIS) trying to become a hegemon in the Arab region are among them (Inbari 2014). Consequently, there is a need to assess the current condition of border control, possible threats, and ways of their prevention and further development. As mentioned by Al Nahyan, the ability of the country to restore and protects its political independence and social norms leads to political and economic stability (Al Nahyan 2000). In its turn, this stability depends on the organization and division of the governmental power in the United Arab Emirates (2000).
The affluence of the country due to its rich oil resources and export revenue has made it a target of criminal and terrorist activities. The UAE has tried to shift its economic focus solely from oil-sector to non-oil sectors such as tourism and infrastructure, as the country invested “in industrial and tourism sectors, air and maritime transport, import and re-export, as well as supporting a range of projects and initiatives based on the knowledge economy” (D’Mello 2015). These factors may be considered as signs of immense potential for future growth and improvement. However, the prosperity of the country has attracted a lot of undue attention and posed a threat to its border security (Ulrichsen 2009).
Purpose of the Study
The purpose of the research is to assess the future strategies support of the United Arab Emirates to protect its political and economic stability via the improvements of the border control and homeland security.
The study of the thesis aims to analyze the implications, potential threats, and solutions concerning homeland security issues such as drug trafficking and terrorism. The paper has put some of the objectives under consideration. For instance:
- Provide relevant information about strategic border security issues in the United Arab Emirates;
- To analyze the potential threats and imminent challenges related to border security;
- To evaluate the awareness of homeland security issues on the residents of the country as well as employees of border control systems.
Theoretical Framework
Scholars believe that there are no homeland security theories at all (Bellavita 2012). Christopher Bellavita argues that there is no universal theory of homeland security for countries and their government (2012). The existence of a universal theory is impossible due to the variety of factors that influence the choices of the border control approach of a particular country (Bellavita 2012). The United Arab Emirates, like many other countries in the Middle East, have developed their economy to the abundance of natural resources.
For this reason, the region and neighboring states also predetermine the border control measures. The pattern of development of security issues in the Middle East has been historically volatile and evolving. The predominance of regional conflict such as the Gulf War of 1991 entails external threats while domestic conflicts reflect an internal threat to the country (Maoz 1997). The Iran-Iraq War and the Gulf War of 1991 escalated regional tension and jeopardized regional security (Maoz 1997). Several civil wars that afflicted the region are the massacre of the Kurds by Iraq, the civil war in Sudan, and the Yemen Civil War (Maoz 1997).
These regional conflicts have affected the safety and security issues within the region. Further, military escalation of the USA in the region to combat the transnational terrorist organizations such as Al Qaeda and then its attack on Iraq to oust the autocratic Saddam Hussein regime have created security threat for the UAE as it had allied with the US to help in these cooperative anti-terrorism operations. Further, the regional instability between the UAE and Iran poses a serious threat to the country. The state-financed Islamic militancy, Hezbollah’s trans-border operations, growth of the ISIS have posed a serious threat to the border security of the UAE (Malek 2015).
The threat ISIS poses is a risk in the long term as well. This can be explained by the spillover effect and the desire to control all or, at least, most monarchies in the region. At present, ISIS is becoming more powerful in Yemen, not to mention in Syria and Iraq. If the global community, as a whole, and the Gulf countries, in particular, do not find enough resources for stopping the terrorist attacks and hostile activities of the organization, there is a growing risk that ISIS will become influential in the United Arab Emirates. The threat is connected to the diversified population of the country and a large number of expatriates in the UAE. Moreover, there were instances of attempts to set up the caliphate in the United Arab Emirates in 2015, which means that ISIS is already trying to undermine the current regime and affect the monarchy, thus establishing the reign of terrorists and jeopardizing national security.
The recent socio-political turmoil in the form of the Arab Spring has raised fresh challenges for the country (Malek 2015). The future challenges that are faced by the country are regional instability and China’s role in the region will create a fresh challenge to the country (Malek 2015). The importance of China’s role is connected to that country’s interest in oil and investment in infrastructure projects. Because both oil and infrastructure are the foundations of the UAE economy, the growing financial role of China in the region is alarming.
Rentier state theory (RST) tries to explain the impact of external payments on the state’s relationship with the society and impact on governance (Gray 2011) Gray defines RST as “a political economy theory that seeks to explain state-society relations in states that generate the large proportion of their income from rents, or externally-derived, unproductively-earned payments” (2011, 1). The RST has two definite approaches – first is the relationships between the government and its citizens and second, is the relation between the ruling families. In the UAE, the revenue from oil comprises almost eighty percent of the overall income of the country.
However, the government has managed to develop a flexible system of taxation (no taxes are imposed on individual earnings). Since the 1990s, the UAE government has tried to deviate its dependence on the oil sector. The second factor concerns the relationships between ruling families. Thus, no family owns oil. It is a state resource, and it belongs to every individual in the country (Aartun 2002). The economy is a crucial aspect that defines the need to implement an advanced border control. The rentier state theory aims at the evaluation of current potential and challenges to the economy and their relation to homeland security. A rentier state is a state that depends on the existing natural resources to receive wealth and revenues (Sadik 2010).
Zicchieri also argues that using a rentier state theory is not relevant to the United Arab Emirates (Zicchieri 2016). He believes that most rentier countries offer minimal support for the non-rent sectors of the domestic economy. The United Arab Emirates’ interest in public and private sectors demonstrate that Zicchieri’s thoughts should be taken into consideration (Zicchieri 2016).
Still, the investigation of Aartun demonstrates that the government of the United Arab Emirates uses the oil-based economy in the maintenance of stability in the country (2002). The research also shows that the United Arab Emirates is estimated to be one of the most stable countries in the Middle East region (Aartun 2002). However, the current rapid development of the country is necessary to implement the most efficient systems of border control. Situations in Yemen prove the existing insecurity in the region.
Since 2015, the United Arab Emirates became involved in the long-lasting and exhausting conflict in Yemen. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia became the primary opponent of the rebels in Yemen while the United Arab Emirates supported Saudi Arabia (Abdullah 2015). War, according to Abdullah, is costly and politically unproductive (2015). The instability within the region is expected to grow further due to the state of war and is expected to make it more volatile.
Efforts have been made to ensure greater security within the country. The UAE Armed Forces General Headquarters has signed a deal with an Abu Dhabi based national security company of DH271 million called the HARES project to provide the total border security solution to the country in 2005 (Kumar 2008). The project aims to provide “highly automated target detection, identification and tracking border security system designed to integrate the fully automated system to respond to external threats for the UAE border” (Kumar 2008). Such an integrated solution system is expected to lessen the threats to the homeland and border security that the UAE faces.
The security threat to the UAE is imminent, and the reasons for the threats are various. Some believe the economic prosperity of the country is responsible for the threat and others blame regional instability for the rising issues related to border control. Moreover, the growing role of the ISIS organization in the Gulf region and the attempts to set up the caliphate in the UAE pose the same threat. The UAE, therefore, makes greater efforts to control the threats that the country faces through its borders. The security issues have gained great importance in the country’s political landscape and efforts are being made to control the security hazards that the country faces.
Research Questions
Border security has gained immense importance in the UAE due to the growing political instability in the Gulf region, as well as the risks of a spillover effect in the UAE connected to the highly diversified population coming from politically unstable countries. That is why the security in the country is evolving with changes in the socio-political and economic condition of the country. The process of globalization and the effect of international events has rendered the Gulf region vulnerable to militant movements and therefore made the security of the UAE volatile. The rising regional volatility has made the UAE’s borders susceptible to infiltration.
Further, there is a distinct need to differentiate between the internal and external forces that act as the hindrance towards the security of the country. The threat that the UAE faces is from both internal as well as external forces. Therefore, the security measures cannot be restricted to the external sphere as is usually done in the western idea of security (Ulrichsen 2009). Following the concerns regarding the current state of unrest and volatility in the UAE regarding threat across its borders and brewing of threat from within the country, concerns regarding the country’s security become imminent. Therefore, the first question that the research tries to answer is regarding the current state of border control and homeland security in the country.
What is the current state of the United Arab Emirates’ homeland security and border control?
Border control is no longer implies only land borders. It may imply borders over international water or airspace. As the danger of terrorist attacks has become omnipotent, especially after the 9/11 attacks on the US, threats over the airspace have become a serious concern for many nations and the UAE is no exception. Given this rising concern regarding the UAE’s airspace, as the country has one of the maximum numbers of airports and air traffic, the next question assumes its relevance.
What are the fundamental concerns and challenges connected with homeland security?
The United Arab Emirates is facing many concerns and challenges that are connected with homeland security. For instance:
- Terrorism: Terrorism is another threat to the border security of the United Arab Emirates. The situation in the Middle East countries is unstable due to wars.
- Drug trafficking: The smuggling of illegal substances is the other threat to the border security.
- Illegal weapon and equipment smuggling: trafficking of equipment that can be used for the manufacturing of nuclear weapons.
- Cyberspace: Cyber-attacks can affect the state on the national level. Passwords manipulation, corrupted programs, malware, fishing belong to the active practices of cyber-attacks.
- Identity verification and management: Those are the four primary biometric technologies include fingerprint, iris, facial, and hand identification. Iris recognition is considered the most advanced technology.
What are the most useful ways for the elimination of threats?
There are no such ways to the elimination of threats, but what the State does is minimizing the threats. From the perspective of ‘, no country is immune from the crisis’ the state has established the Authority department of crises and disasters – National Emergency and Crisis and Disasters Management Authority (NCEMA) – to control and maintain the risk at a lower level.
Methodology
This research is divided into two distinct parts. The first area looks into the secondary data on the border and homeland security and ascertains the various measures that have been undertaken by the government to eliminate threats tot eh nation. The second area looks at the primary level analysis that tries to understand how the common citizens of the country perceive the threat that their country faces.
Qualitative research is employed because its methods are the most appropriate for the evaluation of homeland security and border control issues in the United Arab Emirates. A qualitative approach is used to evaluate the available literature related to the topic. Qualitative research is utilized for the collection of data concerning the personal opinions of ordinary people and representatives from the government (Trochim 2006). In this way, data collection is conducted in the form of interviews. It is essential to note that ordinary people are the subjects of indirect interviews, while the representatives from the government are considered as expert opinions due to their educational and professional background. The current research is essential for the realization of the connection between the population of the United Arab Emirates and the homeland security and border control. The questionnaire of ten questions was sent to fifty individuals (Appendix C). The survey contains questions concerning border control issues.
The inductive approach will be used for the evaluation of the results of the questionnaire. This type of approach is efficient for several reasons. First, it is useful for the analysis of various data and making summaries of them (G. Thomas 2015). Also, the inductive approach assists in seeing connections between links and sources. As Thomas writes, “The general inductive approach provides an easily used and systematic set of procedures for analyzing qualitative data that can produce reliable and valid findings” (G. Thomas 2015, 123).
The snowball sampling or chain sampling is a method used for the logical arrangement of known factors. The results of the qualitative research will provide implications for future studies in the area of homeland security of the United Arab Emirates. The results of the research are analyzed further in Chapter VI. Quantitative methods are used to explain the nature of the problem. Besides, quantitative research assists in the evaluation of the effectiveness of some methods for border security improvement such as iris recognition. Interdisciplinary research has been used for data accumulation from various fields. In Appendix B, one can observe that questions from different fields such as the economy and homeland security are used in the questionnaire. Data from the economy are used for the evaluation of the need to improve border control in the country.
Importance of the Study
The significance of the study is predetermined by the need to improve our border control security and applying new technology. By applying new technology such as Iris recognition will speed up the time that truck driver has to wait to cross the border. For example, the case that happens in 2012 was a Truck drivers’ tempers were getting shorter early Tuesday afternoon as the queue of trucks waiting at the UAE border to cross into Saudi was getting longer (Mick O’Reilly 2012). According to Theodore Karasik, “Biometrics, E-Government, CCTV, UAVs are all part of keeping border security”. At border crossings, biometric facial recognition software is now playing an integral role in filtering possible criminal elements (Karasik 2013).
Still, border security remains one of the most important issues that the UAE government faces. The high level of infiltration and open borders has increased the number of illegal immigrants, terrorists, and smuggling activities through porous borders. The lack of border security from the existing mechanisms raises the need for a better border control system (Al Altar 2014). The problem with the currently operating border security system is the fact that no regionwide measures are being taken to improve it. Because of the shared history, as well as the common religious and cultural background of the population of the Gulf region, the borders are nominal, and no significant attention is paid when it comes to controlling them (Al Altar 2014). That is why it is essential to investigate what can be done by one country to improve the situation in the whole region as well as minimize the risk of threats in the national context.
Scope and Limitations
The research examines threats and challenges that are most urgent nowadays such as cyberspace, terrorism, and drug trafficking. Furthermore, the unstable situation in the Middle East likes ISIS in Iraq and the civil war in Syria.
The limitations of the study refer to the lack of comparison of homeland security and border control in the United Arab Emirates and neighboring countries such as lack of information about the sleeper cells inside UAE and when they about to make they move. It could be useful for the evaluation of the situation in the region. The sleeper cells are a part of the Muslim Brotherhood that is a Sunni Islamist organization that is focused to establish Khilafah. They are connected to the issue of border security because the potential and open activities of the sleeper cells point to the imperfections in physical security at the borders as well as the incomplete state of terrorist databases.
Furthermore, the entry of sleeper cells into the country highlights that the legislative background of the border control system is imperfect, and numerous gaps allow the spies and terrorists to easily immigrate and remain unnoticed. The main goal in the UAE is to be collecting sensitive military information that posed a serious threat to UAE security. In the year 2012, an 11 significant member of the Muslim Brotherhood was arrest with more members by the end of 2012 (Baik 2013). According to Bailk” The Muslim Brotherhood is an Egyptian organization, established in 1928 in Cairo, which calls for the restoration of the Islamic Caliphate and doesn’t recognize the current nation-states in the Arab world. It was banned in Egypt following a failed bid to assassinate then-President Jamal Abdul Nasser in 1956. It was made legal in 2011 following the fall of President Hosni Mubarak’s regime” (Baik 2013).
Homeland security and border control are of primary significance for the United Arab Emirates at the current stage of the country’s development. Since the beginning of the twenty-first century, the country’s economy increased almost by seven percent annually (World Economic Forum). The primary source of prosperity is the oil-based economy. At the current stage of development, the United Arab Emirates aims to develop a domestic economy and decrease its role as a rentier state. The geopolitical instability in the Middle East region is the key threat to successful improvement. Consequently, there is a need to evaluate border control and homeland security.
Summary of the Chapter
Nowadays, homeland security and border control are two central issues for the United Arab Emirates. The major cause of concern is the rapid development of the country’s economy and its overdependence on oil. As an oil-based economy, the country has enjoyed robust economic growth that has increased by around seven percent annually (World Economic Forum). Nevertheless, because of this factor, the United Arab Emirates has faced a significant challenge in failing to develop non-oil sectors of the economy properly. At present, it is a rentier state, working on decreasing its role as such. Finally, because economic issues are complicated by geopolitical instability in the region, there is a necessity to focus on evaluating homeland security and border control to contribute to the successful development of the United Arab Emirates in the future.
Literature on Border Security
The issue of border control is significant to all countries. It can be viewed from different perspectives. For instance, a poor border control system is commonly perceived as the cause of ethnic conflict, especially in the case of people settling in border areas in politically unstable countries. It is, as well, connected to the risk of armed conflict and attempts to establish an ethnically and culturally homogeneous body of power by a well-armed group in the case of believing in disrespecting minorities’ rights. Finally, border security is a problem that is closely connected to political stability due to the risk of potential partitioning of states by hostile neighboring countries (Gavrilis 2008). Nevertheless, nowadays, the issues of border control and border security go beyond social and ethnic matters. They are connected to guaranteeing different aspects of homeland security because border control is related to controlling the inflow of illegal immigrants, including bandits, terrorists, and smugglers, thus diminishing the risk of rebellion.
The effectiveness of border control systems and border security is a multidimensional phenomenon. It is closely connected to the level of a country’s development as well as the way people perceive authorities. From this perspective, it is believed that states with higher rates of economic development allocate more resources to upgrading their system of border security to be more advanced and efficient. On the other hand, poor countries face other challenges and cannot invest in strengthening borders, thus increasing the further risk of border system ineffectiveness. Furthermore, it is critical to point to the international image of the country. From this perspective, powerful and influential states are at higher risk of terrorist and smuggler attacks and require better border protection. On the other hand, countries with insignificant influence at the international level are at a lower risk of similar threats, and it is believed that they do not need strong and secure borders (Gavrilis 2008).
Still, it is critical to understand what is meant by the security of borders. In most cases, people tend to believe that secure borders are those with highly developed physical security, such as modern checkpoints as well as being located in strategically important and geographically vulnerable places across the state. This assumption is partially true because even the most technologically advanced physical security system is likely to be inefficient in cases where the adequate organization of border security institutions and a proper legislative base is lacking. In this way, the difference between secure and insecure borders derives from the efficiency of legislation and border management. In this way, it is essential to be aware of the fact that borders can be managed by both checkpoint installations and military forces in cases of instability or increased risk of attacks and threats to homeland security (Gavrilis 2008).
That said, there are two ways to run a border control system. On one hand, there is an option of controlling boundary installations and making all related decisions at the highest levels of state authority. This centralized approach is effective due to the proper allocation of funds and an opportunity to develop a system of strict control measures. Nevertheless, making top-down decisions imposes the risk of inadequate understanding of current border control issues, thus imposing a threat to homeland security.
On the other hand, there is an option for decentralizing the mechanism of border security. In this case, the freedom to make vital decisions is granted to boundary security forces. Keeping in mind that they are commonly aware of most security issues and existing gaps in a border control system, this approach is more beneficial if adequately supported by the highest authorities (Gavrilis 2008). However, it is limited because, to implement this system, it is critical to have confidence in the operation of the boundary administration system. This means that decentralization can potentially be implemented in more developed states because most of their systems are effective and well designed (Gavrilis 2008).
In the United Arab Emirates, security and border control have assumed great priority due to the unstable in the gulf region such as ISIS (Katzman 2015). The emergence of ISIS as a force in Syria and northern Iraq has changed UAE’s perspective towards Iran (Guéraiche 2016). Due to the spread of radical Islam and the fear of Shi’a expansion in the Gulf, the UAE has taken a conciliatory stand with Iran. In 2014, Sheikh Mohammed Bin Rashid Al Maktoum, the ruler of Dubai announced that “we have no problems with the Islamic Republic of Iran” (Guéraiche 2016, 75). The issues of homeland security and border control in the United Arab Emirates have been developed over time since 1971 (Karasik 2013).
However, with the development of recent events, international coordination in border control has become important to the country (Guéraiche 2016). A recent study suggests regional cooperation in military strategy has become an important issue for the GCC countries (Salim 2015). The primary responsibility of the country is to evaluate potential challenges and threats and prevent them such as challenges related to identity management and verification (Al-Raisi and Al-Khouri 2008). Nevertheless, new threats will always appear. The article “Iris Recognition and the Challenge of Homeland and Border Control Security in UAE” examines the new way of improving border security in the United Arab Emirates (Al-Raisi and Al-Khouri 2008, 117).
Modern warfare has breached the walls of conventional border-based warfare. Now there is no physical border over which war is fought. This faceless border and enemy has become more difficult to identify and ascertain. Proper identity management and verification are crucial for efficient border control. Iris recognition is a new method of biometrics that aims at improving security systems. The primary advantage of iris recognition refers to the fact that it gives immediate results. Although fingerprint, facial, and hand are efficient for the same purposes as well, it takes time until results will be viewed. The authors of the article discuss the significance and the role of this change for homeland security and border control in the United Arab Emirates (Al-Raisi and Al-Khouri 2008) the United Arab Emirates is in need for the new biometric system due to the increase in traveler’s number (Proença 2009).
According to Proença, 9500 people have been caught by the Iris recognition system while traveling with forged identities (Proença 2009). Moreover, the need for iris to speed up travel entry through the United Arab Emirates due to more than a 6500 passenger enters the United Arab Emirates via airport, land, or seaport (Daugman 2004). Apart from identity identification systems, the United Arab Emirates realizes the importance of other methods of border protection (Daugman 2004). For this purpose, flying remote control drones were manufactured to monitor the territory of airports (The National 2014). These pieces of writing are important for the research as far as they demonstrate the current condition and possible improvements of the border control and homeland security in the United Arab Emirates. However, the practical enhancement of the border control measures is nothing without the proper legal implications.
The legal system of the country plays an essential role in border security (Fitzpatrick 2008). The United Arab Emirates realizes this fact and implements a system of strict laws. Such laws aim to prevent terrorist attacks. The article “Export Control and Combating Terror Financing” has been published on the official site of the Embassy of the United Arab Emirates in the United States of America. The article presents information about the United Arab Emirates’ policies concerning export control and combating terrorism. According to the article, the United Arab Emirates supports all sanctions imposed by the European Union. Also, the most significant export control laws are described in the paper. The article provides readers with information about the collaboration between the United States of America and the United Arab Emirates (Fitzpatrick 2008). The United Arab Emirates has reaffirmed its intention to promote peace in the world by stating that the county has plans concerning the establishment of free of nuclear weapons zones in the Middle East (Katzman 2015).
Malek points out, that the UAE’s non-proliferation credentials are well recognized internationally. This makes it an important layer in regional and international non-proliferation and disarmament efforts” (Malek, Praise for UAE stand on non-proliferation 2014). The UAE has strengthened its nuclear and another radioactive security framework since the 2014 Nuclear Summit (National Security Summit 2016). The UAE has taken several recent steps towards increasing the security of its nuclear arsenal. The country has established a nuclear power program and has also accepted a bid of $20 billion from a South Korean company to build commercial nuclear power reactors in Barakah by 2020 (“Nuclear Power in the United Arab Emirates” 2016). The UAE decided to enrich its uranium arsenal after Iran announced its decision to enrich in 2009 (Flietz 2015). Though many believe that this was the beginning to an end to the non-proliferation agreement of the GCC countries with the US, this step is considered essential for regional safety and security (Flietz 2015).
Such intention is of extreme significance for the United Arab Emirates’ homeland safety as far as it can be achieved only when the whole region is stabilized. This fact makes this aspect of the country’s activity important for the current research.
The United Arab Emirates aims at a continuous enhancement of its border control measures. According to the article “UAE Sets $10 Billion for Homeland Security,” the government of the United Arab Emirates decided to double investments in homeland security. Such a decision is motivated by the economic development of the country and the growth of the population (WAM 2014). It should be noted that the cyberspace is a new dimension that requires precise control of homeland security (Neaimi and Lutaaya 2015). The increased cyber attack on the financial sector has made it an important issue for the country (Brouwer 2015). The United Arab Emirates has become an object of numerous cyber conflicts because of the developed economy (Neaimi and Lutaaya 2015). Consequently, there is a need to develop an efficient system of cybersecurity. As Neaimi and Lutaaya describe it, “The fundamental drivers to the cybersecurity market age geared towards increasing the digital risk from cyber users by creating greater vulnerabilities because of more pervasive utilization of engineering and cloud computing” (2015, 295).
The above literature review provides us an insight into several important aspects connected with border control and homeland security in the United Arab Emirates. It should be noted that the county develops homeland security in several directions. First, the government encourages the implementation of recent technologies for efficient security at borders such as Iris recognition. The state is concerned with the legal aspects of border control and law enforcement such as export or importing prohibited equipment. However, the United Arab Emirates spares no financial resources for the improvement of border control measures. For example, the United Arab Emirates Sets a budget of $10 Billion for developing Homeland Security (WAM 2014).
Aspects Related to Border Control and Homeland Security
Area Reporting and Geographical Location
The United Arab Emirates includes seven smaller parts. They are Sharjah, Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Fujairah, Dubai, Umm al-Qaiwain, and Ras al-Khaimah. (UAE Government,” Seven-emirates”)
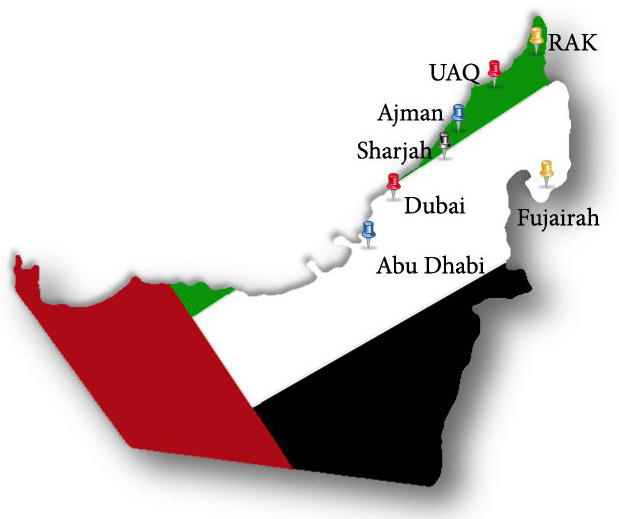
The general area of the United Arab Emirates is more than 80,000 square kilometers. The United Arab Emirates extends for one kilometer along the Gulf of Oman, and more than a thousand kilometers along the lower Gulf. The total coastline of Abu Dhabi is more than 450 km while Dubai’s coastline encompasses 70 km (Middle East Research Institute 2015). The three largest emirates are Abu Dhabi (67340 square kilometers), Dubai (3885 square kilometers), and Sharjah (2590 square kilometers). Abu Dhabi is the most western emirate (Middle East Research Institute 2015).
Dubai is located in the east. Sharjah is situated on two sides of the Ras Musandam peninsula. A range of mountains known as the Hajar Mountains divides the whole peninsula. The highest peak of the Hajar Mountains in the United Arab Emirates is two thousand five hundred meters (Middle East Research Institute 2015).
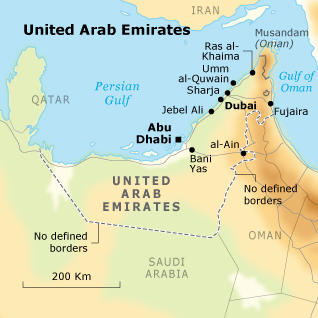
Knowledge of the area is significant for the evaluation of the country’s potential in terms of border control. The following map depicts the location of the United Arab Emirates and its neighbors. This situation is valuable for border control. The strategic position of the United Arab Emirates is advantageous from both military and political perspectives. That is why it may become the target of terrorist attacks.
In addition to the strategic position of the United Arab Emirates, the country is vulnerable from the perspective of geographical location, as well. This can be explained by the natural barriers to improving the effectiveness of the border control system, such as mountains, deserts, and coastline. These areas are easier to reach because it is more complicated to construct an adequate control system in such natural environments. Furthermore, it is more difficult to control illegal immigration (having the aim of further terrorist attacks) in these territories due to the necessity to allocate vast financial and human resources to make control measures operational.
Demographics and Population
The population of the United Arab Emirates comprised 9.4 million residents in 2014 (World population review 2015). The population of the state is extremely diverse. The full list of the population of the United Arab Emirates can be found in Appendix A. Thus, approximately ten percent of the overall population forms Emiratis while the rest of the population is representatives from other countries and nations.
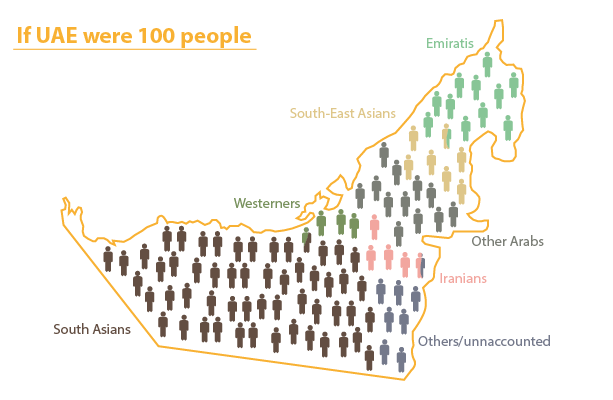
This information is proved by the fact that the United Arab Emirates has the highest migration rate in the world. It comprises more than twenty percent. Such a high rate is predetermined by the legal ability to apply to the country’s citizenship after living in the state for twenty years. The other distinctive feature about population refers to the male to female ratio. The gender imbalance is 2.2, and it is the highest imbalance in the world after Qatar (World population review 2015).
Data about demographics and population are important for the evaluation of possible attacks of terrorists. According to Krane, “UAE authorities see their biggest security threat in the groups of Indians, Iranians, and Pakistanis who outnumber Emirati citizens” (Krane 2009). The following image proves the statement of Krane (“Top 5 Nationalities Living in UAE”).
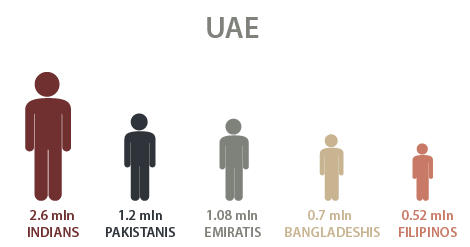
Population rise and increased migration come with economic growth. As the UAE succeeded economically, ex-pats from different Asian countries flocked to the emirates. However, this open environment also increases the influx of antisocial elements that may have entered the nation to spread terror. Therefore, the rising influx of foreign nationals may become a threat to the country.
Economy and GDP
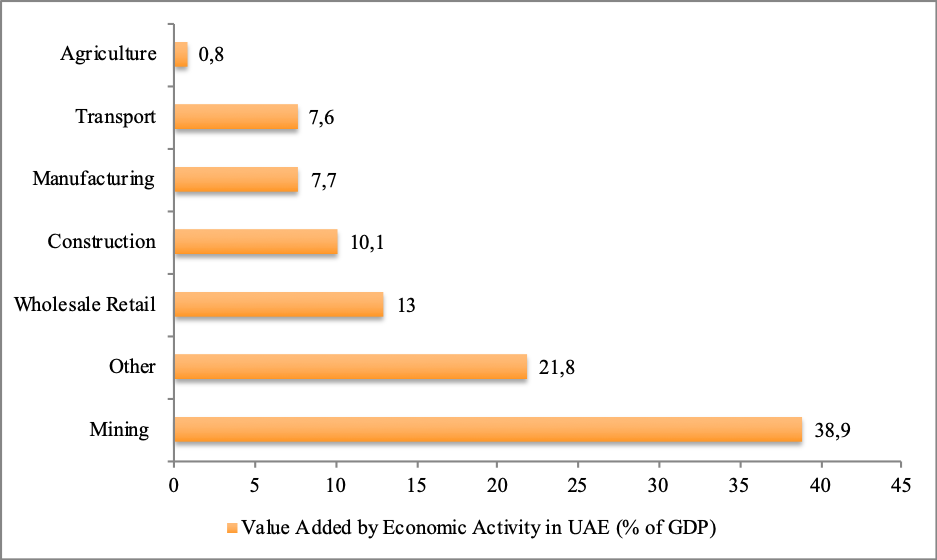
The economy of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is influenced by the system of the free-market economy that levies little restrictions on private sector activities, foreign trade, and capital movement (Shayah 2015). The GDP, as in December 2015, was $402 billion and the economy has a high per capita income growth of $66,300 and a trade surplus of 13.6% (Forbes 2016). The UAE is also the world’s eighth-largest oil exporter, and this is the principal reason behind the country’s economic development (Shayah 2015). Even though there have been efforts towards diversification of the economy, the oil sector contributes 25% of the GDP (Forbes 2016).
Figure 1 shows the mining sector, which comprises the oil sector and some other mining activities as the largest contributor to GDP (Federal Competetiveness and Data Authority 2016). The global financial crisis of 2007-2009 significantly affected the country’s economy resulting in layoffs, departure of foreign workers, and a large number of nonperforming loans in the banks (Katzman 2015). The fall in real estate prices collapsed many banks and the federal government has to interject money from the sovereign fund and increasing liquidity to bail out these failing organizations (Katzman 2015). However, by 2011, these crises were over (Katzman 2015).
The open nature of the economy ensures business competition, even though the distinction between the private and public sectors is blurred. For example, some of the companies are owned by the government, which makes the ruling parties active participants in the financial structure of the economy (MERI 2015). Anti-trust laws are restrictive as major sectors such as government agreement and industries are exempted from it (Shah et al. 2013). Although the World Trade Organization recommends the state to eliminate monopolies, such policies have to be developed (Shah et al. 2013). The UAE has expanded its foreign trade. For instance, since 2011, the country became partners with Latin America and Africa (Krane 2009).
The dependency of the economy on the oil sector and the international dependency on the oil sector of the region put the country in a precarious position in terms of national security. The Iran-Iraq war in 1980 and the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait in 1990 increased the need for tight security network among the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries (Katzman 2015). Regional unrest, due to the various socio-political and economic reasons has affected oil trade and other areas of the economy (Katzman 2015). Also, over-dependence on oil trade (trade done mainly with US dollar) increases the dependency of the economy on foreign currency, thus making it susceptible to changes in the value of the dollar. This may pose a threat to the economic security of the country.
The economy’s dependency on the oil sector increases the vulnerability of the country. This has become clear with the recent fall in oil prices that has stalled the country’s economic growth (Augustine 2016). The regional unrest and mutual distrust between the oil trading countries in the Middle East may escalate a regional war that would affect the security of the country. Therefore, the economy is one factor that contributes to diminishing security in the country. Thus, the UAE economy is connected to the issue of border security because of vast allocation toward the further economic growth of the country. From this perspective, the significance of other sectors such as border security might be ignored and lack the necessary resources for operating effectively.
Infrastructure
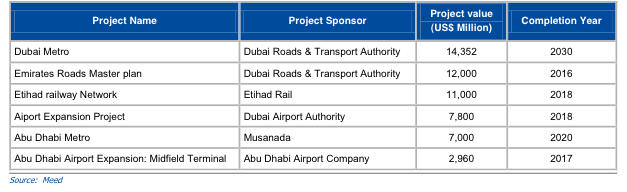
Infrastructure is the largest non-oil sector in the UAE (Fahy 2015). The government has allocated 13 percent of its budget only to the infrastructure development of Dubai (Fahy 2015). The increased infrastructure spending is intended to diversify the sector-wise share of GDP in non-oil sectors. Hence, the government has planned to spend extensively to build tourist attractions. In 2015, infrastructure investment in the UAE is expected to be more than $300 billion by 2030 (Algethami 2014). The UAE government has undertaken a $55.11 billion for six major infrastructure projects (Deulgaonkar 2015).
Figure 2 shows the expected spending on specific projects in the UAE. Transportation is essential for a tourism boost. Keeping this mind, the UAE government has targeted the completion of the Dubai Metro by 2030 (Deulgaonkar 2015). This infrastructure project cost the government $14.35 billion (Deulgaonkar 2015). Further, plans are in place to increase the railway network and the airport. Dubai RTA has plans to expand the Emirates Roads and then the Etihad Railways (Deulgaonkar 2015). Plan to expand the airports, a project undertaken by the Dubai Airport Authority, aims to expand the Abu Dhabi Airport and Abu Dhabi Metro (Deulgaonkar 2015).
One of the major airports in Abu Dhabi International Airport with Etihad Airways expansion. This extension allows serving fifteen million travelers annually (Deulgaonkar 2015). Dubai World Central International Airport and Dubai International Airport are other important airports in the country (Algethami 2014). Initially, there was a supposition that there were too many airports in the United Arab Emirates. A large number of airports were caused by the nature of relations between Sheikhs in the state. Thus, every Sheikh considers it to be a sign of prestige to have a personal airport. Nowadays, the abundance of airports is only useful for the United Arab Emirates. The country is a center of leisure, health care, and business for many people.
The system of roads is also well-developed in the United Arab Emirates. The government realized the need to build an advanced system of internal roads to support the local economy and business. Construction programs commenced in 1970. In that year, for instance, the largest road construction that connected Qatar and Ras Al-Khaimah was built. Roads are necessary for the efficient moving of goods in the country. It is the second most useful means of transportation after airways (Al Nahyan, Sohal, et al., Transportation infrastructure development in the UAE: Stakeholder perspectives on management practice 2012).
Seaports of the United Arab Emirates are also the most developed in the Gulf region (Al Nahyan, Sohal, et al., Transportation infrastructure development in the UAE: Stakeholder perspectives on management practice 2012). Major ports are Port Zayed in Abu Dhabi and Jebel Ali Port in Dubai. After the gaining of independence, Dubai was the only city capable of accepting increasing imports (Deulgaonkar 2015). The port was already built in Dubai, and it became the basis for future expansions. As in previous cases, the government of the country financed the building of airports because of the need to prepare the basis for the potential development and increase of the economy. The system of infrastructure is connected to the condition of the economy of the United Arab Emirates. Consequently, there is a need to know the most developed and less developed sectors and their relation to security issues.
In addition to the expansion of roads, rails, and airways, the UAE has concentrated on the expansion of its ports. Aligning its goal to expand the tourism industry and to facilitate trade, the country is planning to build the largest cruise ship port in Dubai (WAM 2016). Further, continued investment in the port and other transportation infrastructure will boost international trade (WAM 2016).
The reason behind the surge in growth in the infrastructure of the country is due to the GCC’s stress to reduce dependency on the hydrocarbon sector (Deulgaonkar 2015). Hence, there has been an increase in capital investment as a percentage of GDP in the infrastructure sector (Deulgaonkar 2015). Therefore, the rise in investment in the country is to build infrastructure to attract tourists and boost trade.
In addition to the growth in the infrastructure expense in the construction of transportation and other tourism-related projects, the country has major infrastructure investments in the hydrocarbon sector. Oil pipelines are critical to the economy. Such critical infrastructure is essential for oil trade, which is the primary source of the country’s earnings. Therefore, the pipeline infrastructure of the country is an asset and important to national security.
The security of infrastructure has become an important issue for the UAE government. A threat to the transportation infrastructure and to that of the hydrocarbon industry is abundant (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). Protecting the critical infrastructure is a challenge for the country’s authorities and major unrest in the region puts them in a vulnerable position. Critical infrastructure for the UAE is oil, gas, water, and electricity (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). The essential infrastructure services like transportation and the critical sectors like water, oil, and gas are essential for the UAE and hence are easy targets by different threats (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). Hence, protecting the infrastructure that the country builds is essential as it depends on such sources. Attacking these critical infrastructures may put the country in a vulnerable position.
The United Arab Emirates has substantial benefits from its aviation and transport systems. In most cases, the benefits of economic development are taken into consideration. It is predetermined by the fact that economic development is the most vivid example of the positive outcomes (Oxford Economics 2009). Thus, the aviation industry in the United Arab Emirates enhances the GDP per capita. Also, well-developed aviation provides more residents with job opportunities. Finally, taxes are also influenced as the country receives more revenues.
Still, Oxford Economics emphasizes the fact that the “economic footprint” is not the only positive aspect of the country’s aviation and transportation systems. Positive influences can be divided into three sub-groups. The first one has been already discussed. The second point refers to the issue of customers’ satisfaction. Thus, all people who use services in the United Arab Emirates (passengers of planes or ships) enjoy the high-quality services and facilitate the further development and intention to meet all consumers’ needs (Oxford Economics 2009). Also, the advanced system of connections between cities and even countries leads to increasing investments and expansion of the business.
The location of the United Arab Emirates and the availability of resources predetermine the need for the continuous improvement of homeland security and border control. The United Arab Emirates consists of seven emirates that are developed in terms of infrastructure. Abu Dhabi and Dubai are the most significant emirates. The geographical condition and the economic vision of the country make infrastructure imperative. The increasing threat to its infrastructure and economy from non-Emirates and other foreign forces creates the necessity to revamp the security system in place within the country (Malek, UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure 2014).
The political unrest in the Middle East and neighboring African regions increased security instability within the country. Further, the large expatriate population of the UAE (mostly Indians and Pakistanis) poses a threat to the security of the country as the socio-political unrest in their countries make spillover to the UAE (“United Arab Emirates 2015 Crime and Safety Report: Abu Dhabi” 2015). The country, since its independence in 1971 from the British Empire, has shown significant growth. However, the 2008 financial crisis negatively affected the economy, even though it was quick to recover from it. The two major sectors of the country are hydrocarbon and infrastructure. The country has extended its infrastructure both in the critical and services sector. However, economic growth, infrastructure development, and oil resources need security from external threats. That is why security is an important concern for the UAE.
Summary of the Chapter
The United Arab Emirates is a country made up of seven emirates. All of them have achieved a significantly high level of development of infrastructure since becoming independent in 1971. This can be explained by the emphasis the government places on infrastructure projects. Among the seven emirates, Abu Dhabi and Dubai are the most developed. Even though the country has one of the most developed economies, it experienced a detrimental impact on the 2008 financial crisis. Nevertheless, due to its infrastructure potential and oil-based economy, the UAE managed to recover relatively quickly. Furthermore, the country is characterized by a high ratio of an expatriate population compared to native citizens of the UAE. Most of these are Indians and Pakistanis.
Because of political instability in both the countries of expatriates’ origin and the Arab region as a whole, the risks of sociopolitical threats in the United Arab Emirates are high. This can be explained by the spillover effect (OSAC 2015). That said, due to its geographical location, vast natural resources, diversified population, and high level of infrastructure development, the United Arab Emirates faces the necessity of constant improvement of the system of border control and homeland security to protect the country’s welfare.
The History of Border Control and Homeland Security
Background Information
The UAE was formed by six “Trucial” states when they gained independence from the British Empire in 1971 (Katzman 2015). The country adopted a constitution in 1996 (Foley 1999). Ras al-Khaimah tried to gain independence but due to the lack of resources and international support, it joined the federation in 1972 (Foley 1999, Katzman 2015). Presently, UAE is formed by the states of Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ras al Khaimah, Umm al-Quwain, and Ajman (Foley 1999). Post-independence there was a problem with the control of power and the warring Emiratis as well as opposition from neighboring states (Katzman 2015). For instance, Saudi Arabia did not recognize the United Arab Emirates as a federative country because of the disagreement about the Al Buraymi Oasis (Katzman 2015).
In 1981, the Iran-Iraq War and the 1990 war with Iraq questioned the security policy of the country (Katzman 2015). Further, during the Iran-Iraq war, there was a split in the support for Iran, when Abu Dhabi and Ras al-Khaimah supported Iraq while Sharjah, Umm al-Quwain, and Dubai supported Iran (Foley 1999). The reason for such dissent was due to the autonomous nature of the Emiratis and their armed forces (Foley 1999). In 1980, due to the increase in instability in the region, Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates formed the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) (Katzman 2015).
One of the main adversaries of the UAE is Iran. The whole of GCC has allied with the US to counter Iran that destabilizes peace in the Middle East (Katzman 2015). The strife between Iran and the UAE stated due to a dispute of many islands on the Persian Gulf. In 1971, Iran, then ruled by a US-backed shah, seized many of the Greater and Lesser Tunb islands from Ras al-Khaymah (Katzman 2015). Further, in 1992, Iran claimed Abu Musa and assumed complete control over the island (Katzman 2015). To settle the disagreement peacefully, Sharjah agreed to let Iran establish military objects in the northern part of the island while Sharjah’s civilian population living in the southern part of the region (Katzman 2015). The situation was peaceful until the 1990s but tension began when Iran refused to allow workers from the UAE to disembark on Abu Musa, despite the agreement with Sharjah (Katzman 2015). Even though this issue was solved without aggravation but it signals that Iran’s actions may be unpredictable.
Current Stage of Development of the United Arab Emirates
At the current stage, the level of development of the country (especially of Dubai and Abu Dhabi) predetermines the need for advanced border control (Saif 2009). The location of the country in an unstable region makes it necessary to be ready for possible aggravations at any time. The history of the Gulf region has proved several times that safety is more about illusion than reality there. The region itself is important for the global community because of its wealth due to natural resources.
In the last thirty years, the region, including the United Arab Emirates, became an area for such conflicts as the Iran-Iraq War, The Gulf War of 1990-1991, and the invasion of the US’ military forces in Iraq in 2003 (Al Kaabi and Al Kaabi 2011). After these events, the political power of Iraq decreased drastically, and Iran became of the main disturbing powers in the Arabian states. As Al Kaabi et al. write, “Under the pretext of wanting to establish a new reign of hegemony, Iran has been meddling in the internal affairs of the Gulf States and the region by using Shia minorities as a tool to spread its influence” (Al Kaabi and Al Kaabi 2011, 1).
International Collaboration
Nonproliferation Treaty
The UAE became a member of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NTP) in 1995 and the International Atomic Agency (IAEA) in 2003, signing an additional protocol in 2005 (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016). The United Arab Emirates displayed a desire to promote peace in the world by signing the Nonproliferation Treaty (Malek, “Praise for UAE stand on non-proliferation” 2014). The Nonproliferation Treaty means that the UAE will not become the manufacturer of the atomic bomb and weapons of mass destruction. This factor is important for the current research because it provides an insight into the country’s security issues.
The treaty did not allow the UAE to import enriched uranium preventing the possibility of nuclear enrichment (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016). Another aspect of the treaty is the ban on exporting substances that might potentially contribute to the nuclear enrichment of other states (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016). In this way, the Nonproliferation Treaty is connected to the issue of border security because the UAE recognizes a personal responsibility for national and regional safety. Strict neutral control measures make the reduction of terrorist attacks involving nuclear weapons possible.
In 2014, the United Arab Emirates discussed the creation of the zone in the Middle East that would be free of weapons of mass destruction (Malek, “Praise for UAE stand on non-proliferation” 2014). The United Arab Emirates aims to accomplish this aim to make the Gulf region safe for any international and regional transactions and collaborations. According to the information in the article, the International Atomic Energy Agency’s protocol concerning the nuclear collaboration between the United Arab Emirates and the United States of America was signed in 2013 (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016). Thus, the first state admits its devotion to avoid works related to plutonium separation or enrichment of uranium. However, it is still clear that the formation of the zone free of weapons of massive distractions is impossible now (Malek, “Praise for UAE stand on non-proliferation” 2014). This conclusion is logical because of Iran’s nuclear activities, the Yemen War, and other conflicts.
The international collaboration of the country is important to represent its status as a reliable, safe, and secure country. Besides, international collaboration is a part of homeland security as far as the country receives necessary support and protection in case of some threat. The United Arab Emirates has been demonstrating its commitment to the peaceful existence in recent years. In 2008, the country actively supported “White Paper” which meant the dedication to the ideas of the use of nuclear energy for peaceful aims (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016). In 2009, the state signed an agreement on nuclear collaboration with the US to forego uranium enrichment and contributed ten million dollars into the IAEA fuel bank — an international organization that fights with illegal enrichment of uranium (Nuclear Threat Initiative 2016).
Fighting Terrorism
The United Arab Emirates signed the International Convention on the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism in 2005. Mohamed Ali Al Shamsi supported the country’s devotion to fighting terrorism at the Fourth Review of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy. This is because the country has dedicated a lot of energy on arresting Al Queda operatives, denouncing terror attacks, improving border security, and so on (Katzman 2015). Al Shamsi described national policies of the United Arab Emirates concerning the promotion of peace (The National 2014). Fighting terrorism is a significant part of border control (The National 2014). Terrorist attacks are extremely dangerous for the country’s security. Thus, the initiatives and policies devoted to eliminating and preventing terrorist attacks are necessary for the country.
The Development of the System of Law
The UAE has restricted the trafficking of illicit goods through its borders. The law aims to stop the transportation of illicit materials on the borders (Dunne 2012). The government presented a law in 2007 that presupposed the exact and stringent regulations for export (Dunne 2012). According to Chapter 1 of this law, “new law authorizes the concerned authorities to ban or restrict the importing, exporting or re-exporting of any commodity for reasons related to safety, public health, environment, natural resources, a national security” (WAM 2007, par. 1). There was also the right to ban the export of weapons or any other military materials as well as biological and chemical substances. This law enforced the establishment of the special committee that should handle the processes of import and export. A year later, the regulations became more severe. The law contains detailed lists of prohibited materials for export or import. It describes all necessary actions in case of violations and potential fines (WAM 2007).
In 2014, the 14th International Export Control Conference called for increased security measures to enhance the nonproliferation of weapons of mass destruction (Dubai Customs 2014). The Committee was accountable to the Council of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and it, in turn, to the President of the United Arab Emirates. The enhancement of this Law Committee is of great significance for border security (Dubai Customs 2014). It conducts necessary procedures for control including the supervision of licensing, the entrance of materials, inspection, investigation, reporting, disclosure, and documentation of all transactions. There are representatives of the Committee in every emirate (Dubai Customs 2014).
Since 2010, the United Arab Emirates continued improving the system of law, especially for export control. It was done as a reaction to the severe imposition of a new wave of sanctions on Iran. The country aimed to prevent the re-export of technologies to Iran by implementing stricter measures of export control (Katzman 2015).
In 2014, the director of Dubai Customs introduced intentions of the Committee by stating, “We at Dubai Customs are committed to rigorously implementing both local and international export control regulations instituted to curb the spread of weapons of mass destruction globally” (Dubai Customs 2014). This shows the country’s emphasis on control of terrorism and illegal transactions through its borders.
The United Arab Emirates has a unique system of the approach to border control known as “strategic trade control” (Dunne 2012). The government has signed many treaties to enhance the enforcement of strategic trade controls. These agreements include the Non-Proliferation Treaty of 2006, Chemical Weapon Convention 2000, Missile Technology Control Regime, and the Global Initiative to Combat Nuclear Terrorism (Dunne 2012).
These issues are crucial to the investigation of the legal regulations connected with homeland security and border control. The United Arab Emirates, being a rapidly developing country, faces numerous challenges connected with the protection of borders. The significance of the legal system should not be underestimated in this respect. Regulations of border control procedures predetermine the country’s readiness and intention to prevent possible aggravations and violations. International collaboration and national laws of the United Arab Emirates demonstrate the country’s aim to become a superior country in terms of border protection.
Border Control
Land Border
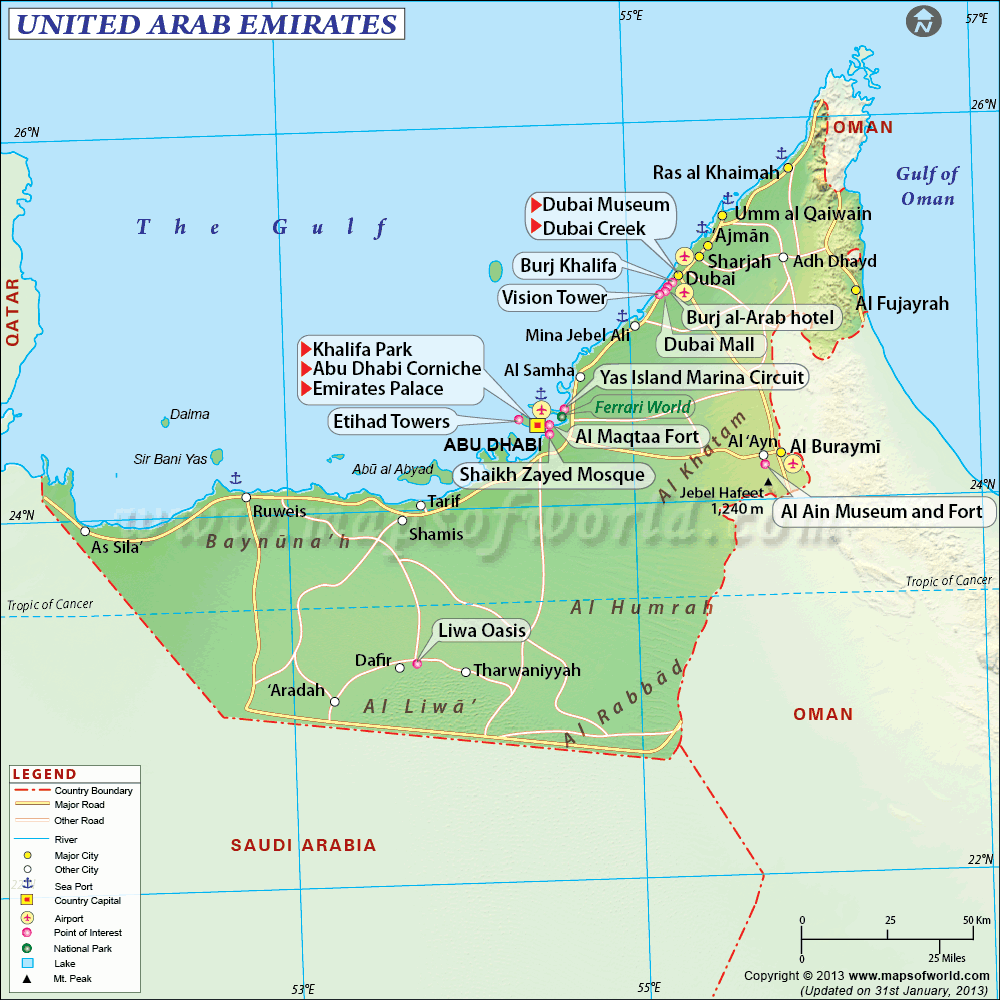
Oman and Saudi Arabia surround the UAE in the south. The Gulf borders it in the north. Land borders of the country may be observed on the map.
The United Arab Emirates has built fences along borders with Saudi Arabia and Oman to enhance border control (Katzman 2015). The country has signed the 123 Nuclear Cooperation Agreement with the US to stop the proliferation and terrorism through its borders (Katzman 2015). Such protection of land borders is necessary for the prevention of illegal activity.
The land outlets that the UAE has can be divided according to the Emirates they belong to. Abu Dhabi has the maximum number of land outlets (five land outlets), Dubai has one, Sharjah has one, and Ras al Khaima has one. The names of the land outlets in Abu Dhabi are – Al Gwifat outlet, Al Hili outlet, Al Maqdif outlet, Mazeed outlet, and Khatam Al Shaklah outlet (General Authority of Ports Borders and Free Zone Security 2013). Border security, especially over the land outlets, has been increased in the UAE.
One particular checkpoint was that of Dubai’s Hata outlet that leads to Oman that allows all nationals to cross the border to Dubai into Oman. However, other checkpoints such as Al Madheef and Al Hilli are open only to GCC nationals (Gulf News 2016). Security over border check posts was increased in Hilli Border, where until 2012, UAE residents could cross by showing their passport and not getting it stamped. However, since 2013, immigration stamp has become mandatory for all. Increased restrictions for travelers show the importance of border security for the UAE. Border security has been continually increased in the UAE to fight threats of terrorism through its borders.
Sea Border
The United Arab Emirates shares sea borders with Qatar, Kuwait, Iran, Iraq, and Bahrain. Besides, the Strait of Hormuz (the most significant import point in the area) is located along its coastline (Cordesman 2015).
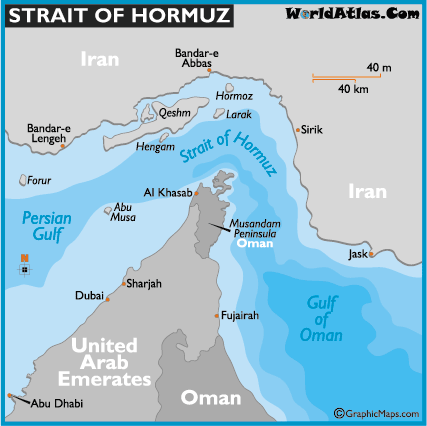
The latest innovation for the protection of ports was launched in Abu Dhabi — two flying drones that control the zone (The National 2014). The significance of sea borders in the United Arab Emirates cannot be overestimated. The state borders with the Persian Gulf (the most significant gulf in the region), and all activity should be monitored there (The National 2014). The reason for such need lays in the fact that the United Arab Emirates shares sea borders with unstable countries. Consequently, there is a need to protect all sea borders to prevent illegal activities (The National 2014). Further, the Dubai Customs Intelligence Unit at Port Rashid in Dubai collaborates with the US Customs and Border Protection Force to do a checkup of US containers that originate from Iran (Katzman 2015). The country also a signatory of the Megaports Initiative that aims to stop the proliferation of illicit products through ports (Katzman 2015).
The UAE has many ports. Abu Dhabi has four ports – Zaid Port, Musaffah Port, Magraq Port, and Al Hor Port. Dubai has four ports – Rashid port, Jabal Ali port, Al Homariah port, and Dubai Drydocks World. Sharjah has three ports – Khalid Port, Al Homariah Port, and Khorfakkan Port. Ajman has Ajman Port and Umm Al Quwain has Ahmed bin Rashid Port. Ras Al Khaimah has five ports – Saqr Port, Al Jeer Port, Ras Al Khaimah Creek port, Al Jazeerah al Hamra Port, and Ras Al Khaimah Maritime City. Fujairah has two ports – Fujairah port and Diba Al Fujairah port. Apart from increased security in the ports, the UAE has leased an Eritrean port in 2015 to increase the military base to combat Houthi rebels in Yemen (Fitzgerald 2015). Such increased military operation over the sea shows that the UAE has increased its security measures to counter rebel activity beyond its borders.
Air Traffic Control
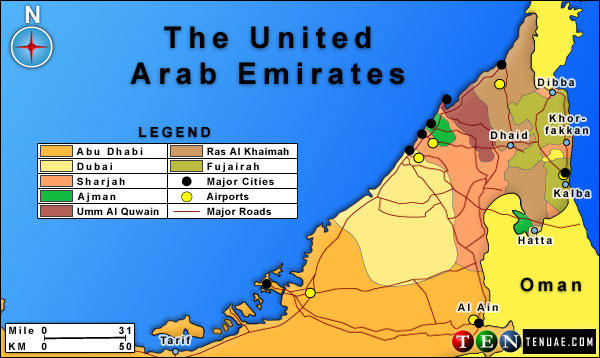
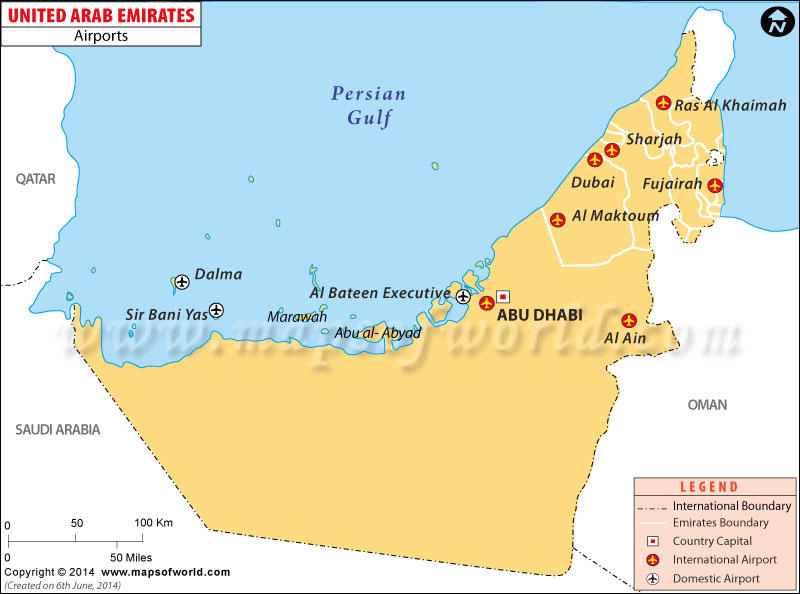
Major airports in the United Arab Emirates are presented in the following image.
The system of border controls in the United Arab Emirates aims at providing maximum safety and security for conducting all types of border-crossing services. The tourists who are going to visit the United Arab Emirates must have the entry visa that should be arranged at the place of leaving before arrival. However, some nationalities do not have to follow the described procedure. Those who belong to the list of exceptions can obtain the visa after the arrival. It is necessary to make a visa and have a sponsor for the visit for representatives of nationalities that do not fall into the group of exceptions (UAEinteract 2016). Such a system lets the United Arab Emirates improve border control and evaluate the efficiency of protection systems. Also, the country can analyze the rate of violations among nationalities that do not have to follow requirements of the advanced procedures (mostly Middle East nations) and those who have to follow all procedures.
The government of the United Arab Emirates continuously seeks new ways of improvement of security measures. Iris recognition can serve as an example of advanced verification systems (Al-Raisi and Al-Khouri 2008). These practices are predetermined by the need to identify intruders who may use new technologies.
The UAE has eight airports namely – Abu Dhabi International Airport, Al Ain International Airport, Al Bateen Airport, Dubai International Airport, Sharjah International Airport, Ajman International Airport, RAK International Airport, and Fujairah International Airport (General Authority of Ports Borders and Free Zone Security 2013). The UAE has adopted biometric technologies to revamp its airport security system (Lee 2016). The UAE launched “e-Border,” which is a multi-biometrics border management system that uses Iris recognition to identify its citizens. This is a practical way of identifying citizens as many women in the region have their faces covered. The airport authorities in the UAE also use facial recognition and automated fingerprint identification system, allowing accurate identification of its citizens (Lee 2016).
Special Case of Border Control at Madha

According to Hanzell, Madha is a landlocked island that is surrounded by Sharjah, Fujairah, and Ras Al Khaimah (Henzell 2012). It has an area of 75 hectares and has a population of approximately 2,000 people (Henzell 2012). Inside the Madha settlement, there is a small village called Nahwa that has around 40 houses. This village, though a part of Sharjah, is enclosed by Oman (Henzell 2012). The situation is controversial for border control (Henzell 2012).
The controversy about enclaves concerns the border control procedures. Thus, there are checkpoints of both Oman and the United Arab Emirates. Numerous checkpoints make it frustrating for tourists to travel (Henzell 2012). If all of the checkpoints are saved, the number of tourists may decrease. At the same time, checkpoints are necessary for the proper protection of the country’s borders. This situation creates a kind of paradox within the United Arab Emirates’ border control system. This case may serve as a vivid example of the possible controversy of the system of border protection in the country. Also, it demonstrates that challenges may occur even in the smallest regions.
Madha is a special case within the UAE as this provides a unique situation wherein the region is blessed with both oil-resources and fertile land, a combination rarely found in the region. Therefore, this area becomes a hot spot for both the business elites of the world as well as the tourists because of its natural beauty. The land is wealthy in terms of its resources and natural endowments. Consequently, it has been an area of a dispute over the ages. The UAE had contested for this peninsula until the 1980s but left all its claims thereafter. Therefore, this region must be considered as a special case of border security, which presently is under Omani control.
The Role of Yemeni Conflict in Border Control
Current instability and military conflict in Yemen prove the necessity to improve border control in the United Arab Emirates. This can be explained by the risk of spillover war because Yemen is a neighboring country. In this way, improving border control in the UAE might prevent illegal immigration of spies and terrorists whose goal is to potentially escalate conflict within the country. In 2015, the country sent troops to Yemen along with Saudi Arabia to control the Zaidi Shiite Houthi rebels (Katzman 2015). According to intelligence reports, the Houthi rebels are supported by Iran in their effort to increase regional imbalance (Katzman 2015).
It is estimated that regional instability cannot be eliminated quickly. Consequently, there is a need to protect the borders and the state. Started in 2015, the situation in Yemen was about fighting for governmental power in the country. Four major forces are involved: the separatists, activists devoted to the government, forces of the former president, and ISIS people (Katzman 2015). Though the conflict is far from the UAE, the country supports the Gulf States in resolving the conflict (Katzman 2015). It has particular concerns because of the possible aggravation of the situation. The situation in Yemen is important for the United Arab Emirates because the neighboring country, Saudi Arabia, is involved in the conflict. In the case of intensification, the United Arab Emirates may be under the threat.
Development of Border
The United Arab Emirates spares no means to improve homeland security. The United Arab Emirates plans to double the expenses on border control (“UAE Sets $10 Billion for Homeland Security” 2014). Consequently, the state is going to contribute 10$ billion within the following decades for homeland security systems improvement (“UAE Sets $10 Billion for Homeland Security” 2014). The investments in the aviation infrastructure are more likely to reach almost 60$ million in one year (“UAE to invest $10 billion in 10 years for homeland security” 2014).
The United Arab Emirates plans to launch a system that employs eye scans, fingerprinting, and facial recognition. The need for change is largely predetermined by the foreseen increase of travelers (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). Sheikh Ahmed, Dubai civil aviation president, discussed the importance of borders at the Future of Borders conference in March 2015. He said, “Borders are strategic partners for airports. They should prepare themselves for a more important and challenging role in the future” (“Sheikh Ahmed raises the Importance of borders debate” 2015). Sheikh Ahmed introduced information about the state’s intention to constantly develop border control systems. E-technology, do-it-yourself methods, and smart gates are examples of recent innovations.
The increasing attention to the development of borders is predetermined by the government’s aim to prevent the entry of extremist groups in the country (Katzman 2015). Also, the United Arab Emirates becomes a popular destination for tourists (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). The government should make sure that the country is safe for the further development of this business sector.
The most recent innovation to the border control systems was introduced in October 2015. A new microscope can scan any documents, ID cards, and event tickets. The creator of this machine is a Sergeant Amer Al Jaberi of the Interior Ministry’s General Directorate of Residency and Foreigners Affairs. The quality of this microscope in twenty times betters than that is of other devices (see Appendix B for more details). Also, a low-cost, eco-friendly invention enhances security at airports significantly (WAM 2015). Thus, Lt. General Sheikh Saif bin Zayed Al Nahyan actively supports the innovation (WAM 2015). The support is predetermined by the need to improve border control due to potential threats constantly.
It should be added, that such a counterfeit passport detector belongs to advance technologies (WAM 2015). This factor proves the United Arab Emirates’ intention to make the country safe and protected. Also, the creator of the detection, Sergeant Amer Al Jaberi, is young, and this fact shows the youth’s devotion to the improvement of the country’s future. The efficiency of Al Jaberi’s device has been already proved. In October 2015, the border control service of Sharjah managed to detain individuals who had fake one hundred billion dollars (“Ministry sergeant invents ‘green’ passport scanner” 2015).
Summary of the Chapter
Historical perspective and the current development of the United Arab Emirates are two primary reasons that define the need for advanced border control. Thus, Iran’s claims about three islands prove the abruptness of its activities. Nowadays, the increasing influx of travelers and the growing economy predetermine the necessity to improve border control systems as well. The international collaboration makes the United Arab Emirates an exemplary country in terms of nuclear activities and fighting terrorism. The government recognizes the necessity to enhance the efficiency of border control measures. The recent innovations include smart gates and new microscopes for the detection of fake passport holders.
Challenges in Border Security
Cyberspace
Cyberspace gives immense opportunities for development (Neaimi, Ranginya, and Lutaaya 2015). These opportunities attract the attention of different hackers or organized groups at the same time. Cyberspace of the United Arab Emirates has become a target for numerous cyber-attacks due to economic growth. Cyber-attacks can affect the state on the national level (“Cyber Terrorism: The Arab World’s Invisible Threat” 2012). Passwords manipulation, corrupted programs, malware, fishing belong to the active practices of cyber-attacks (Neaimi, Ranginya and Lutaaya 2015). In 2012, the government of the United Arab Emirates improved cyberspace criminal laws.
Besides, two new laws were introduced: “Law No. 3 of 2012 on Establishing the National Electronic Security Authority (E-Security Authority Law)” and “Law No. 5 of 2012 Concerning Combating Information Technology Crimes (Cyber Crimes Law)” (Beretta and Berached 2013). The recent investigation has demonstrated that the United Arab Emirates is the second country with the most numerous cyber-attacks in the Middle East (Katzman 2015). In 2016, the United Arab Emirates has started to collaborate with the UK to improve cybersecurity on the national level (Malek, “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure” 2014). The United Kingdom is known to have advanced cybersecurity systems. The United Arab Emirates is ready to cooperate with the UK and find some new ways to reduce cyber-attacks to the minimum.
An example of cyber terrorism can be malware known as Gauss. It is a virus designed to track banking data on the level of nations (Katzman 2015). It is not dangerous to the average user but can do a lot of harm to the country’s systems. The virus attacked nuclear information of Iran and was found in other countries including the United Arab Emirates (“Cyber Terrorism: The Arab World’s Invisible Threat” 2012). It is an example of the real danger that modern countries face. The significance of cybersecurity should not be neglected as far as it is crucial for homeland security (Neaimi, Ranginya and Lutaaya 2015).
Terrorism
Terrorism is another threat to the border security of the United Arab Emirates. The situation between Middle East countries is tense. That is why the United Arab Emirates faces the problem of possible terrorist attacks. The country is actively engaged in the process of eliminating any terrorism activity not only within the country but also within the other Arab states in the region. For instance, the United Arab Emirates provided financial assistance for moderate Islamic forces fighting in Syria. The United Arab Emirates spares no means for the prevention of the activity of extremist Islamic groups (Katzman 2015). Also, Katzman writes, “The UAE and Saudi Arabia also have worked to undermine other Muslim Brotherhood-related organizations in the region, including Hamas” (Katzman 2015, 13).
This information justifies the government’s investing in the improvement of border control and homeland security. One may conclude that terrorism comprises a continuous and developing threat to the country, and it is necessary to be ready to react to it. Described cases are examples of the successful confrontation with terrorism. However, the numerous and large investments of the country directed towards protection and identification devices demonstrate that the threat of terrorism cannot be eliminated easily. The United Arab Emirates realizes that terrorist groups use advanced technology too, and it makes the process of fighting terrorism long-lasting and constant.
Drug Trafficking
The smuggling of illegal substances is the other threat to border security. Trafficking of drugs and people undermines the idea of the rule of law in the country. UN names the UAE in the list that shows countries prone to illegal drug trafficking (“War on drugs: UAE raises the stakes for traffickers and dealers” 2014). The inner integrity is essential for border security as well. If there is the rule of law in all aspects, the country will be protected adequately. The United Arab Emirates utilizes strict measures such as death sentence for drug trafficking. For instance, in 2012, the Abu Dhabi Criminal Court conducted a trial on three Asian men who tried to smuggle more than fifty kilograms of hashish to Saudi Arabia. The accused were sentenced to death (“3 sentenced to death for drug trafficking” 2012).
Those three criminals were caught on the borders of the United Arab Emirates. Abu Dhabi Criminal Court demonstrated that the severest measures should be applied to those who do not follow the rules. The case is one more example of the fact that threats never disappear, and the country should always be prepared for more serious violations. Legal regulations of the smuggling of illegal substances are directly connected to the social and religious background of the United Arab Emirates. This fact demonstrates that the country’s protection of border control is a means of protecting the purity of cultural values as well. The country has taken adequate steps to counter illicit drug trafficking in the UAE (“War on drugs: UAE raises the stakes for traffickers and dealers” 2014).
Illegal Weapon and Equipment Smuggling
Illegal weapons and equipment may be used for the manufacturing of different types of weaponry for wars. The United Arab Emirates has to control this aspect too, especially concerning Iraq that is the primary threat to border security. The United Arab Emirates has faced the problem of illegal trafficking for many times. For instance, in 2009, “authorities captured a cargo shipment illegally carrying North Korean weapons, which included nuclear missile-related materials and were headed to Iran” (Issa 2011). The same article describes the seizure of sixteen thousand pistols that were heading to Yemen. Smuggling of illegal weapons of this kind can unsettle the situation in the area (Issa 2011). In the article provided, both instances of smuggling to provide information about weapons that are to be used in large-scale military conflicts. This information also proves the topicality of the current research and the need to improve border control. The United Arab Emirates has to eliminate such practices to prove its intention to promote peace in the Middle East.
Summary of the Chapter
The government of the United Arab Emirates has to improve its system of law and security measures constantly. Although various modifications and advancements have been made, examples demonstrate that violations of border control law are still relevant. Thus, cyberspace of the countries is always under the threat of such malware as Gauss. News reports of terrorism show the presence of fanatics who want to unsettle the stability. Drug trafficking is an illegal activity that should be eliminated. Smuggling of weapons comprises the concern for the country as far as it can be used for the aggravation of the situation in the whole Gulf region. All these examples are challenges to border control and they prove the fact that the malefactors employ technologies that are more advanced in their activity too. Thereafter, the country has to address every challenge with maximum efficiency.
Research Findings
Results of Qualitative method
Numerous researchers have tried to investigate the homeland security and border control in the United Arab Emirates. Some of them state that the political stability of the United Arab Emirates is impressive if taking into consideration continuous conflicts in the Middle East region. Thus, Anne Aartun points out that the government of the United Arab Emirates, to maintain its political stability, used the oil-based economy and political behavior as a rentier state (Aartun 2002).
Despite this fact, some other sources emphasize the potential threat of instability in the region. Thus, the World Economic Forum mentions that the rapid economic development of the United Arab Emirates may be undermined by the geopolitical instability in the area (World Economic Forum 2007). Yet, there is a lack of research concerning the investigation of residents’ awareness of the border control measures and homeland security issues. The aim of the research below was to investigate knowledge of border control and homeland security issues of citizens of the United Arab Emirates. This information interests us for several reasons:
Recent news demonstrates that the government of the country finances the border control actively. It is worth to know whether people are aware of these intentions.
It is useful to know whether the residents of such an economically developed country comprehend the importance of border control for the overall prosperity.
Results of Data Collection
A questionnaire of ten questions was prepared for the research. The questionnaire was sent to fifty individuals for them to choose the most appropriate answer. Thus, all respondents were instructed to write down one of the following answers under each question: Agree, Strong Agree, Disagree, and Strong Disagree. One can find the full version of the questionnaire in Appendix C.
Thus, the current research was based on indirect interviews with fifty respondents. Respondents were chosen randomly. Before sending the questionnaire, everyone was asked about the willingness to answer several questions about border control and homeland security. Also, every potential respondent was notified that the questionnaire would be anonymous. After receiving the agreement, questionnaires were sent to respondents. The latter was given one week to answer the questions and send the file back.
The Results of Data Analysis
An inductive approach is used for the evaluation of results as far as conclusions should be based on data. One can find answers of five respondents in Appendix C. These five answers are provided as an example of what has been done. Answers of all fifty respondents may be summarized in the following table:
One week after sending the questionnaire, respondents’ answers were gathered and evaluated. All respondents were given the same questions about border control and homeland security in the United Arab Emirates. To make the process of questioning comfortable and not time-consuming, the questions were designed in such a way that they can be answered by choosing one of the suggested variants (Agree, Strong Agree, Disagree, and Strong Disagree).
It should be added, that all respondents provided answers to questions quickly and without delays. Together with the filled questionnaire, some respondents left remarks concerning the type of research. Some of them were glad to participate while others shared their opinion that they could not express what they wanted with the help of the suggested answers. Such information provides the opportunity for further improvements in the following types of research. Also, the accuracy of information depends on the respondents’ willingness to share their points of view.
The research was completed in seven months. The first month was planning and searching for information, statistic, and data. The next two month was for writing the proposals and working with my supervisors. After the approval of proposals, it takes three months to gather information, writing, and visiting several locations such as Madha and Emirates center for strategic studies and research. Also, there was a time I spend looking for meeting peoples to interview and have a clear idea about the system works in borders such as the IRIS System.
On the other hand, Two weeks were devoted to the development of questions and finding respondents. Also, two-week times were given for respondents to submit their answers. The evaluation and analysis of results lasted for the rest of the time.
The reason for the questionnaire was the fact that little attention is paid to the awareness of masses of border control and homeland security issues. On the one hand, there is no need to dwell on possible threats constantly to avoid panic or exaggerations. On the other side, it is useful to analyze the people’s awareness of the problem and study their attitude towards the government’s activities in this sector.
Analysis of Questionnaire
The general outcome of the survey demonstrates that respondents are aware of the most significant notions referring to border control and homeland security issues. It is necessary to evaluate every answer separately. Thus, the predominant part of respondents considers that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and illegal activity. Thus, they know the most important function of homeland security. Based on the results of the research, one can state that residents realize the significance of economic development and agree that there is a connection between the economy and homeland security. Most people believe that border control influences the life of the common people, though seven respondents express the opposite opinion. This statement is proved by answers deriving from the fifth question.
Thus, forty-five responders do not believe that border control influences only those who work there. All respondents unanimously agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country. The sixth question presents that there is a lack of knowledge about types of border control procedures because respondents are not sure whether fingerprinting is the most efficient way of checking. Despite the majority’s understanding of the primary function of border control, respondents do not support the government’s initiatives to finance border control intensely. Perhaps, this attitude is caused by the unawareness of reasons for such actions as it is proved in the next question. Twenty-eight respondents consider that there are other significant threats to homeland security. Finally, all interviewees agree that the current situations in Yemen and Syria serve as a sign for the government’s concern about homeland security.
Outcomes
The questioning aimed to evaluate the level of residents’ awareness about homeland security and border control in the United Arab Emirates. The research is motivated by the fact that there is a lack of investigations of people’s opinions about homeland security. Results have shown that most respondents realize the importance of homeland security. However, they are not sure about the reasons for the recent initiative to finance border control actively.
The results of the questionnaire have demonstrated that residents are aware of the most widespread challenges to border control. They realize that the government invests in border control to protect the country from terrorism, smuggling, and drug trafficking. Also, residents of the United Arab Emirates comprehend that the protection of border control is crucial for the further development and prosperity of the country and its citizens.
The research findings demonstrate that general awareness of the public is present in the UAE regarding the threats to the border and homeland security. This is important for policymakers, as public awareness of the issue will help garner support from the masses towards security measures undertaken by the government. Further, public opinion also allows the government to take strong measures to control the terrorist threats that the country faces and take a strong stand amidst regional unrest. As the citizens are aware of the regional volatility and political instability, they are more likely to have a strong opinion regarding the countries stand in the situation. This helps the government to gauge public opinion and take action accordingly.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Summary of Findings
The United Arab Emirates is a modern country with a developed infrastructure and economy. The instability of the region, as well as the country’s prosperity, predetermines the need to improve border control measures. The United Arab Emirates is an active participant in the international agreements concerning the regulation of nuclear activities in the countries. Even more, the state is a model of excellent collaboration. Besides, the government continues investing in new methods of border control such as smart gates.
The level of residents’ awareness in terms of homeland security and border control is rather good. Thus, they comprehend that there is a connection between border control and economic condition in the country. Also, all respondents agree that the existing disturbing situations in Yemen and Syria prove the geopolitical instability in the Middle East.
The United Arab Emirates realizes that the instability in the region cannot be eliminated in the soon future. The government should always finance and improve border control to prevent potential threats. The state is moving in the right direction and conducts everything required to provide travelers with a safe service and residents with protected lands. The United Arab Emirates’ initiative to establish a zone free of nuclear weapons demonstrates its intention to enhance the development of the whole region of the Middle East. Still, a peaceful environment in the area is not possible until numerous conflicts are solved.
Analysis
The analysis of the secondary research shows that the borders of the UAE are porous, which makes it susceptible to terrorist attacks, illegal trafficking of drugs, or trafficking. Regional unrest due to the building tension with Iran increases the propensity of a military attack on the country. Given this situation, the awareness of the people of the strategic security condition is necessary. The primary survey shows that people are aware of the security condition in the country and the factors that ail the country.
Future Research & further investigations
Homeland security and border control issues should be further investigated and compared to the primary data. First is that the level of border control and homeland security will be improving. Because of particular changes, residents’ opinions concerning border control issues can be altered. This change can be measured with the help of further investigations. Also, other pieces of research will be appropriate for the comparison of the citizens’ attitudes towards governmental activities and finding the level of satisfaction. It can be useful to evaluate the country’s approach to homeland security and border control and define the theoretical background for it. The constant development of both security measures and threats makes this topic relevant. Future research may investigate the influence of security advances on the prevention of threats and overcoming challenges.
Lessons Learned
The United Arab Emirates is a young country that has demonstrated impressive economic growth and overall development (World Economic Forum). The United Arab Emirates is rich in oil. This resource is central to the country, and it has brought it prosperity as well. The United Arab Emirates has been developing as a rentier country. Two oil booms in the 1970s and 2000s resulted in the United Arab Emirates becoming one of the most successful countries in the world (MERI 2015).
The United Arab Emirates may be classified as a rentier state because natural resource comprises the largest part of its revenues (Aartun 2002). However, the country develops the private and public sectors as well. This statement can be proved by the flexible system of taxation and the fact that seventy percent of Emirate is engaged in non-oil sectors (Aartun 2002). As a well-developed country, the United Arab Emirates should protect borders and face numerous challenges. Apart from this, the location of the country is one more challenge.
The United Arab Emirates is located in the Middle East – region that is characterized by constant instability. There is a threat of possible aggravation of the situation. Other threats to homeland security include cyber-attacks, terrorism, drug trafficking, and weapon smuggling. The country realizes the significance to eliminate these perils. The government spares no means to improve border control (“UAE to invest $10 billion in 10 years for homeland security” 2014). The United Arab Emirates implements various ways of identity verification — an important procedure that allows identifying intruders. Iris recognition is considered to be one of the most recent innovations that make it possible to check the individual with maximum efficiency and accuracy (Al-Raisi and Al-Khouri 2008).
The country does not underestimate the role of robotic devices for the monitoring of the activities at the borders. In 2014, remote flying drones were used for the control of Abu Dhabi’s port (The National 2014). The use of the recently invented machine that identifies fake documents is another proof of the United Arab Emirates’ intention to have superior border control and homeland security (WAM 2015). We have learned that the country has significant reasons to improve border control such as the increasing development and the constant changes in the Middle East region. Also, it was found that the United Arab Emirates employs advanced and new methods to protect the country.
Conclusions and Proposals
The central objective of the research paper was to investigate the current issues related to the border security of the United Arab Emirates and speculate on ways to improve the system. The need for further improvements is motivated by the instability in the Gulf region and potential risks caused by Iraq’s nuclear program and the rise of ISIS in the region, not to mention the fact that the latter’s power is constantly growing. Also, the UAE is a country comprised of a non-homogeneous population, and most of the immigrants come from politically unstable regions, which means that the risk of spillover antisocial behaviors and chaos is high. Also, like other countries located in the Gulf region, the economy of the UAE is dependent on oil. This means that any issues over oil trade or oil prices might lead to potential conflict. Keeping in mind the country’s recent economic growth and financial stability, as well as some geographically posed vulnerabilities of the border security system, the challenge is significant and should be addressed.
That is why it is critical to propose ways to make the system more effective. For instance, it is imperative to allocate resources to strengthen the system of physical security at the border, especially in locations that are easier to reach, such as deserts, mountains, and coastline. More than that, it is critical to enhance regional cooperation to oppose the rise of ISIS and to recognize the long-term risks of its activities. Finally, it is paramount to make the border operational and cope with the nominal functioning connected to the shared historical past, as well as the cultural and regional background of the Gulf region citizens. From this perspective, realizing that all foreigners should undergo the same examination regardless of the country of origin and the location of checkpoints would benefit the whole system.
Recommendations
According to the findings of this research, the primary risks and threats derive from political unrest in the Gulf region, turning the existing borders into vulnerable and volatile areas. That is why the central recommendation is to pay specific attention to illegal immigration, cyber-attacks, smuggling, and rising militarization in the region. In this way, further implementation of the newest technologies such as iris recognition and technologically advanced traffic checks is advisable.
References
Books
Brouwer, Riemer. “Industrial Cybersecurity Governance.” Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference. Abu Dhabi, UAE: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2015.
Gavrilis, George. “The dynamics of interstate boundaries.” Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008.
Guéraiche, William. “The UAE and Iran: The Different Layers of a Complex Security Issue.” In Iran in the World, by Shahram Akbarzadeh and Dara Conduit, 77-92. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2016.
Krane, Jim. Dubai: The Story of the World’s Fastest City. London: Atlantic Books, 2009.
Linden, Edward. Focus on Terrorism. New York: Nova Publishers, 2007.
Mallakh, Ragaei. The Economic Development of the United Arab Emirates. London: Routledge, 2014.
Maoz, Zeev. “Regional Security in the Middle East: Past, Present, and Future Challenges.” In Regional Security in the Middle East: Past, Present, and Future, by Zeev Maoz, 1-46. London: Psychology Press, 1997.
Mohammed, Barakat,” Arabs border problem and its psychological causes and adverse effect”. Publish 2005.
Morton, Michael Quentin. Buraimi: The Struggle for Power, Influence and Oil in Arabia. New York: I.B.Tauris, 2013.
Sadik, Giray. Global Politics of Resources and Rentierism, Edited by John Ishiyama and Marijke Breuning. Thousand Oaks: SAGE, 2010.
Stiftung, Bertelsmann. United Arab Emirates Country Report. Gutersloh: Bertelsmann Stiftung, 2014.
Thomas, Gavin. The Rough Guide to Dubai.London: Penguin, 2013. United Arab Emirates: MERI Report. London: Routledge, 2015.
Journal Articles
Neaimi, Abdulla, Tago Ranginya, and Philip Lutaaya. “A Framework for Effectiveness of Cyber-Security Defenses, a Case of the United Arab Emirates.” International Journal of Cyber-Security and Digital Forensics 4, no. 1 (2015): 290-301.
Salim, Al-Rawashdeh Mohammad. “Gulf Cooperation Council States (GCC), Military power, between temporary alliances and Permanent joint Mechanisms.” International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention 4, no.8 (2015): 71-88.
Shayah, M. Hazem. “Economic Diversification by Boosting Non-Oil Exports (Case of UAE).” Journal of Economics, Business, and Management 3, no. 7 (2015): 735-738.
Thomas, David. “A General Inductive Approach for Analyzing Qualitative Evaluation Data.” America Journal of Evaluation 27, no. 2 (2006):237-246.
Web Sources
Abdulkhaleq Abdullah. “Why the UAE is fighting in Yemen?” Web.
Al Altar, Ahmed. “Border insecurity is a shared threat as it affects all the region.” Web.
Al Khan, Mohammed. “UAE and Oman look to ease border woe for tourists.” Web.
Algethami, Sarah. “Map variables values for portrait image UAE to spend more than $300 billion on infrastructure development by 2030.” Web.
Al Khoori, Ayesha. “Terrorists Planned to Bomb Mall.” Web.
Al Nahyan, Moza T., et al. “Transportation infrastructure development in the UAE: Stakeholder perspectives on management practice.” Construction Innovation 12, no. 4 (2012): 492 – 514. Web.
Al Nahyan, sheikh shamma. “Political & Social Security in the Arabian Gulf Region and United Arab Emirates after the Second Gulf War. sfpa.sk. Web.
Arabian Aerospace,“ Sheikh Ahmed Raises the Importance of Borders Debate.” Web.
Augustine, Babu Das. UAE economy headed for soft landing amid low oil prices. Web.
Baik, D. A. (2013). uae-uncovers-muslim-brotherhood-cell-arrests-its-members. Web.
Bellavita, Christopher. “Waiting for Homeland Security Theory.” Homeland Security Affairs. Web.
Chronicle fanack “Economy.” Web.
Committee for Goods & Materials Subject to Import & Export Control. “Executive Office.” Web.
Cordesman, Anthony H. “America, Saudi Arabia, and the Strategic Importance of Yemen.” Web.
Country studies, “Foreign Relations.” Web.
CPC,“United Arab Emirates: Forty Years of Progress.” Web.
D’Mello, Sandhya, ‘Diversity vital for UAE’s growth: Shaikh Mohammed’. 2015, Web.
Deulgaonkar, Parag. “6 mega infrastructure projects worth Dh202bn underway in UAE.” Web.
Dp world,“ Our History.” Web.
Dr. Karasik , Theodore “GCC robust plans for border control” Web.
Dubai customs, “Dubai Customs Calls for Strengthening Cooperation on Export Control.” Web.
Dunne, Aaron. “Strategic Trade Controls in the United Arab Emirates.” Web.
Ecfr,“Key fronts.” Web.
Emirates, 24/7 news “UAE Invests Device to Catch Fake Passport Holders of Any Country.” Web.
Fahy, Michael. “IMF urges prudence on Dubai’s implementation of major infrastructure projects.” The Nation. Web.
Federal Competitiveness and Data Authority. Web.
Fitzgerald, Denis. UN report: UAE, Saudi using Eritrean land, sea, airspace, and possibly Eritrean troops in Yemen battle. Web.
Flietz, Fred. As Predicted, the Iran Deal has begun to wreck Global Nuclear Non-Proliferation Efforts. Web.
Foley, Sean. “The UAE: political issues and security dilemmas.” Middle East 3, no. 1 (1999): 25-45. Web.
Forbes. “United Arab Emirates.” Forbes Best Countries for Business. Web.
Grey, Matthew. “A theory of “Late Rentierism” in the Arab States of the Gulf.” Web.
Global security “Gulf Cooperation Council.” Web.
Global security “History”. Web.
Global security “UAE Security Wall / Security Fence.” Web.
Gulf News A. Al Madam-Hatta diversion: Expats not allowed on Oman E44. Web.
Gulf News B “New deal signed on worker health issues.” Web.
Gulf News C “UAE aims to be first country globally in quality of infrastructure for ports, roads, Minister of Infrastructure Development says.” Web.
Gulf news D,” UAE focuses on free market principles”, Web.
Gulf News E “UAE Sets $10 Billion for Homeland Security.” Web.
Henzell, John.” Madha village’s pledge of allegiance changed the map forever.” Web.
Hugo, Proença,” Iris Recognition” University of Beira Interior, Web.
Inbari, Pinhas, “ISIS: Iran’s Instrument for Regional Hegemony”, Web.
Indonesia border” current border security issue” Web.
Investopedia,” Free Market Definition” Web.
Issa, Wafa. “16 000 Pistols Bound for Yemen Seized in Dubai.” Web.
Jared Newman. “Gauss Malware: What You Need to Know.” Web.
Joby , Beretta, and Simar Berached. “UAE Issues New Cyber Crime Law and Establishes a National E-security Authority.” Web.
John Daugman,” Iris recognition border-crossing system in the UAE”. Web.
Katzman, Kenneth. “The United Arab Emirates (UAE): Issues for U.S. Policy.” Web.
KCS Briefing Paper, “Cyber Terrorism: The Arab’s World Invisible Threat.” Web.
Khaleej times,“3 Sentenced to Death for Drug Trafficking.” Web.
Khaleej Times, “Ministry sergeant invents ‘green’ passport scanner.” Web.
Kumar, Himendra” UAE sings border security deal with Abu Dhabi firm” Web.
Lee, Justin. UAE airports implementing Morpho’s iris at a distance technology. Web.
Malek, Caline A. “Abu Dhabi conference to address regional security threats.” The National. Web.
Malek, Caline B. “New Biometrics System to Speed up Travel through UAE.” Web.
Malek, Caline C. “Praise for UAE Stand on Non-Proliferation.” Web.
Malek, Caline D. “UAE cooperates with UK to increase its cyber security.” Web.
Malek, Caline E “UAE Reaffirms its Commitment to Fighting Terrorism.” Web.
Malek, Caline F “UAE needs better protection of critical infrastructure.” Web.
Manafth, General Authority of Ports Borders and Free Zone Security. Web.
Mark Fitzpatrick, “Export Control and Combating Terror Financing.” Web.
Mick O’Reilly, ”Truck line at UAE-Saudi border stretches to 22km Tuesday afternoon”. Web.
Middle East Research Institute,” United Arab Emirates MERI Report”, 1985, Web.
National Security Summit. National Progress Report: United Arab Emirates. Web.
World nuclear Association “Nuclear Power in the United Arab Emirates”. Web.
OSAC, “United Arab Emirates 2015 Crime and Safety Report: Abu Dhabi.” Web.
Oxford Economics. “Economic Benefits from Air and Transport in the UAE.” Web.
Samoglou, Emmanuel. “UAE researcher calls for more stringent cyber security.” Web.
The National A, “Eye in the Sky: Abu Dhabi’s Ports now protected by drones.” Web.
The National B “War on drugs: UAE raises the stakes for traffickers and dealers.” Web.
The national security advisory group,” Reducing Nuclear Threats and Preventing Nuclear Terrorism”. Web.
The Nuclear threat initiative “Overview.” Web.
Trading Economics, “United Arab Emirates GDP”. Web.
Saif, Ibrahim. “The Oil Boom in the GGC Countries, 2002-2008: Old Challenges, Changing Dynamics.” Web.
Shah, Omar, et al. “The Impact of the New UAE Competition Law on Business.” Web.
Six Senses Zighy Bay,“ UAE Visa & Border Pass Requirements.” Web.
Snoj, Jure. “UAE’s population — by nationality.” Bq-magazine.com. Web.
UAE embassy, ” Non-proliferation” published 2012, Web.
UAE Government,” Seven-emirates”, Web.
UAE Interact, “Infrastructure.” Web.
UAE Interact, “Ports.” Web.
UAE Interact. “Visas and Immigrations.” Web.
Ulrichsen, Kristian Coates. “Internal and External Security in the Arab Gulf States.” Middle East Policy Council vol. XVI, no. 2. Web.
UNODC, “Drug Trafficking.” Web.
UNODC, “International Convention for the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism (New York, 9 December 1999).” Web.
WAM emirates news, “Interior Minister Views New Advanced Counterfeit Passport Detector.” Web.
WAM “UAE President issues law on commodities subject to import and export control procedures.” Web.
WAM/SA,” UAE, Oman to sign on detailed border demarcation maps”, Web.
William M K. “Qualitative Approaches.” Web.
World Economic Forum. “The United Arab Emirates and the World: Scenarios to 2025.” Web.
World population review “United Arab Emirates Population 2015.” Web.
Zicchieri, Alessandro. “Is Rentier State Theory Sufficient to Explain the Politics of the UAE.” E-ir.info, Web.
Images
“GDP Distribution by Sector.” Economists Pick Research. Web.
“Population of UAE by nationality graphic depiction.” bq-magazine. Web.
“Saif bin Zayed reviews passport and document scanner.” Emirates 24/7. Web.
“Smart Gates.” Arabian Aerospace. Web.
“State Borders UAE.” Chronickle.fanack.com. Web.
“Strait of Hormuz.” Worldatlas.com. Web.
“TOP 5 Nationalities Living in UAE.” BQ Magazine. Web.
“UAE Airports Map.” Web.
“UAE Jewel of the World.” Web.
“UAE Map.” Web.
“UAE Map with Roads.” Web.
“UAE 7 Emirates.” Web.
Other Sources
Aartun, Anne. “The Political Economy of the United Arab Emirates.” Thesis for Cand. Polit. Degree in Political Science, University of Oslo, 2002.
Al Kaabi, Yousef, and Al Kaabi, Khaled. “The Iranian Century: The Tension Between Iran and the Gulf State.” Thesis for Master of Science Degree in Defense Analysis, Naval Postgraduate School, 2011.
Definition Web Source
Border Control Law & Legal Definition,” USLegal, Web.
Drug Trafficking,” UNODC, Web.
Smuggling Law & Legal Definition,” USLegal, Web.
Terrorism,” Oxford Dictionaries, Web.
Appendix A
Population of the United Arab Emirates by nationality
Appendix B

Appendix C
Questionnaire
Under each of the questions, write your variant. The possible answers are:
Agree Strong agree Disagree Strong disagree
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity?
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security?
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people?
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control?
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country?
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures?
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively?
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat?
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security?
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security?
Respondent 1
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity? – Agree
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security? – Strong agree
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people? – Disagree
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control? – Agree
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country? – Agree
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures? – Strong agree
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively? – Disagree
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat? – Strong agree
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security? – Agree
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security? – Strong agree
Respondent 2
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity? – Agree
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security? – Agree
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people? – Agree
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country? – Agree
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures? – Strong disagree
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively? – Disagree
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat? – Agree
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security? – Disagree
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security? – Strong agree
Respondent 3
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security? – Agree
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people? – Agree
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country? – Agree
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures? – Disagree
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively? – Agree
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat? – Agree
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security? – Disagree
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security? – Strong agree
Respondent 4
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security? – Strong agree
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people? – Agree
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country? – Agree
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures? – Agree
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively? – Disagree
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat? – Disagree
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security? – Disagree
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security? – Agree
Respondent 5
- Do you agree that homeland security is primarily about preventing terrorism and other illegal activity? – Agree
- Do you agree that the economic situation in the country is connected with potential threats to homeland security? – Agree
- Do you believe that homeland security influences the everyday lives of people? – Agree
- Do you think that homeland security influences only those people who work in border control? – Disagree
- Do you agree that the primary function of border control is to protect the country? – Agree
- Do you consider fingerprinting to be the most efficient method of border control procedures? – Disagree
- Do you support government’ initiatives to finance border control actively? – Agree
- Do you think that active financing of border control is caused by some external threat? – Disagree
- Do you agree that terrorism is the only threat to homeland security? – Strong agree
- Do you agree that current situations in Yemen and Syria influence governments’ concern about homeland security? – Agree