The scientific Method as it Applies in Economics
The scientific method in economics involves research. Research is vital as it enables economists to find values of various economic aspects. There are five distinct stages of scientific method in economics.
- One has to ask a question. There must be a question to think about a hypothesis.
- One has to perform background Research Hypothesis. This may be done in the lab or through natural knowledge, for instance social science knowledge in geography or history.
- One has to test the hypothesis. There are steps to be followed in doing this, as we shall later see.
- Analysis/Conclusion Report Results. After writing the hypothesis and researching on it, the appropriate conclusion is made.
Economic Assumptions made in scientific methods
All factors must remain constant (ceteris paribus)
Econometrics
Econometrics refers to the application of mathematics, statistics, and information technology in economic data. An example of a model in econometrics is
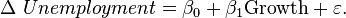
Such a model may be tested for statistical significance.
Econometrics may be applied in different areas. It may be applied in setting prices for goods and services, calculating minimum wages that should be paid to workers, calculating gross domestic product and the national income or inflation levels. However, to apply effectively, econometrics must be based on facts so that it may not mislead.
Classical Political Economy
This approach is the first modern thought in economics. In this approach, prices relate to the restoration of the conditions of commodities production. Classical economists believe that free markets regulate themselves with an invisible hand that drives them.
Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economics refers to approaches that focus on the specification of prices, income distributions, and output in markets by forces in supply and demand. Prices in this economy relate to the optimal allocation of a set of endowed prices among and between individual agents. The correct set of prices allows for the optimal allocation of commodities leading to maximum social welfare.
Assumptions
- Consumers make preferences between outcomes that have a direct link to values.
- The major objective of firms is profits maximization. Individuals aim at maximizing utility.
- Buyers act independently using the information that they have regarding the market.
System of Production equations
(A11P1+A21P2)(1+r)+L1w=Q1P1
(A12P1+A22P2)(1+r)+L2w=Q2P2
From the basic assumptions of neoclassical economics, many theories are evident, e.g. Maximization of profits. The theory of the firm helps us understand the consumption of goods, while the supply curve helps us understand the factors of production. Market supply and demand are also vital in economics. The interaction of demand and supply determines price and output in the market.
Hypothesis Testing in Economics
A hypothesis refers to a claim. There are two types of hypothesis:
- The Null Hypothesis
- The Alternative Hypothesis
A hypothesis such as K=1 is called the null hypothesis. It is mainly represented by H0.
The alternative hypothesis is denoted by the symbol H1. It can take three forms.
If H1: K1 > 1, this is a one-sided alternative hypothesis.
If H1: K1 < 1, this alternative hypothesis is also a one-sided.
H1: K1 greater or equal to one, this alternative hypothesis is two-sided.
Procedure for testing hypothesis in economics involves
Steps in the Test of Hypothesis
- State the hypothesis that needs testing.
- Select an appropriate statistical measure to rephrase the hypothesis, e. g. p.
- Choose whether the hypothesis should be one or two-sided.
- State the hypothesis with respect to the statistical measure initially selected.
- State the “confidence level” α of the test.
- Choose a sensible test statistic, considering the information present and the assumptions.
- Find the critical value of the test static.
- Make the decision as below:
- If the value is within the rejected area, reject the null hypothesis.
- If the value is not within the rejected area, qualify the null hypothesis.
- Draw a conclusion with respect to the original question.
Minimum Wages
A minimum wage is the lowest payment that employees are legally entitled to. It is the lowest possible wage rate at which employers can buy labor. There are different opinions concerning the effect of setting a standard minimum wage. Those that support it say that it helps to raise the living standards of people. They also add that it helps to eradicate poverty, increase workers’ morale, and improve efficiency at work.
Opponents state that a minimum wage rate would increase poverty and unemployment. They also say that it may damage business. Indicators that may be used to set a minimum wage rate include those that minimize loss of jobs and also maintain such conditions as labor supply and demand, labor costs, costs of operating business, standards of living, as well as the prevailing wage rate.
Increasing wage rates may lead to increased costs of doing business. It also threatens profitability. It may also lead to increased levels of unemployment since businesses may hire few people for a task of an extremely high magnitude because they shy away from paying a lot of money.
The issue of a minimum wage has been highly contentious in many states of the world. In the United States, workers must not be paid anything below the statutory requirement. The national government stipulates that no one should earn less than $ 7.25 an hour. Some states have set their minimum wages at a level higher than that of the national government. The fair Minimum wage act of 2007 was the reason for the increase of the minimum wage bill. A debate is ongoing as to whether to raise the minimum wage bill to $ 22.
Conclusion
Economics operates just like other scientific fields. They use models that apply specific principles and that make certain specific assumptions.
The application of hypotheses is rigorous in economics.
It is vital to test the hypotheses repeatedly for purposes of econometric standards. Repeat: If there is a conflict, then modify model assumptions and start from the beginning. If they match, this is okay. The remaining step is to check if the theorized and estimated effects are meaningful.