Executive summary
Saudi Arabia has a rich collection of both natural and chronological attractions ranging from the mountain destinations of Taif and the magnificent display of prehistoric Nabatean tombs to the colorful coral reefs in the Red Sea. The larger percentage of tourists in this country has mainly been drawn from the conventional Muslim world out for pilgrimage. Currently, there is an upcoming trend laying a lot of importance on tourism in the country.
This led to the establishment of the Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities (SCTA) in 2000, whose purpose is to support tourism in the Kingdom. This forms the overall agent body that represent public bodies, which are concerned with the tourism industry. This report seeks to analyze the character and contribution of tourism in this country, with some mention of some of the most attractive sites in the kingdom.
Introduction
Tourism ranks as one of the major enterprises surrounding trade and governmental restructuring, which was taken up by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia following a designed and rigorous improvement plan. It was based on an economic redistribution program aimed at surmounting growth obstacles.
This was inclusive of the Saudi’s Cabinet decision No., (9) dated 17/04/2000, regarding making an allowance for tourism as an industrious sector. This initiative aimed at persuading Saudi tourists to spend their holiday within the kingdom alongside growing investment prospect. This also aimed at widening and improving state human resources.
As a result, tourism expansion is seen as a nationwide economic venture. In the light of improving Saudi tourism through management, advancement and back-up, it is expected that this will overcome expansion barrier as the sector is deemed as a crucial component of the economy. At the same time, these ventures must seem to comply with the principles and ideals of the Kingdom.
The objective is also directed at preserving and safeguarding antiquities, while catering for their contribution towards cultural and economic progress. These include museums and supporting archeological ventures. On the other hand, the private sector has taken a leading role by setting up tourist oriented trade amenities.
Saudi Arabia has a rich collection of both natural and chronological attractions ranging from the mountain destinations of Taif and the magnificent display of prehistoric Nabatean tombs to the colorful coral reefs in the Red Sea.
Whereas Saudi Arabia has a formidable presence on the tourism scene over the centuries with millions of visitors flocking to the Kingdom annually, the larger percentage of these visitors have been drawn from the conventional Muslim world out for pilgrimage. Currently, there is an upcoming trend laying a lot of importance on tourism in the country. This led to the establishment of the Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities (SCTA) in 2000, whose purpose is to support tourism in the Kingdom.
Saudi commission for tourism & archeological treasure
Supreme Commission of Tourism (SCT) was launched in 2000 as a corporate entity. Article 3 of SCT’s statute affirmed that, SCT’s functions and tasks are pegged around tourism in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia with an aim of extending, advancing and boosting the tourism industry while conquering growth hindrances with an understanding that tourism is central to the national economy.
The private sector has been integral in setting up tourism oriented trade facilities. Its board forms the overall agent body that represent public bodies, which are concerned with the tourism industry.
The group’s Secretary General is charged with the management of managerial affairs of the SCT through the Secretariat General Department. Afterwards, the Saudi Cabinet decreed on resolution No., (9), of 16th April, 2000, which legitimized the formation of the Supreme Commission of Tourism (SCT).
This validated tourism as a major economic division with an objective of encouraging Saudi tourists to spend holidays within the kingdoms’ vast destinations, thus growing investment prospects, developing the national human resource capacity and generating job openings for Saudi citizens.
Considering the paramount value for museums and archeological treasures, the Royal decree No. 2/a of 30/04/2003, stipulated that, in regards to Museums and Antiquities Agency, SCT was to be charged with the operations around the antiquities body alongside tourism division affairs.
The Cabinet’s declaration No. (78) Of 23/03/2008, which adopted the name ‘Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities (SCTA)’, argued that domestic tourism as a national concern needed public establishments to contribute towards its success and expansion based on its exclusive tourism prospects.
Major Tourism attraction sites in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia’s Global Tourism
The overall worth for International tourists calculated as the number of arrivals in Saudi Arabia was 10,850,000 in 2010. From the graph below, it is clear that, over the past 15 years, this pointer hit a high value of 14,757,000 in 2008 and a minimum value of 3,325,000 in 1995.
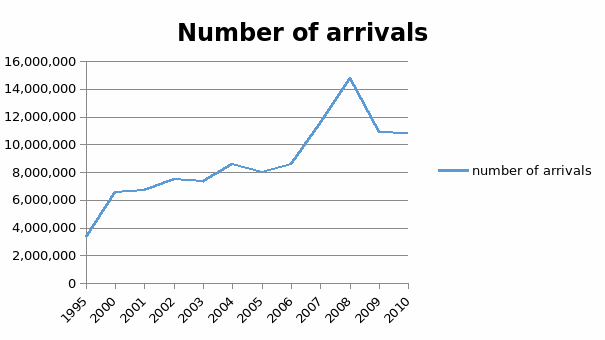
Origin: Global Tourism Organization; Annual Tourism Figures, Compendium of Tourism Data and Figures and Records.
Contribution of Transport & tourism in Saudi Arabia
Express Contribution
The express input from Tourism to the GDP reproduces the internal expenditure on Transport & Tourism (overall spending inside a particular country on Travel & Tourism by inhabitants and non natives for business and pleasure together with administration’s individual expenses). These may translate into expenses accrued by a government on Transport & Tourism services, which is directly associated with visitors.
These include factors like culture and recreation. The direct input from Transport & Tourism to GDP is estimated in relation to the output. This is consistent with National Accounting in tourist oriented sectors such as lodges, airlines, tour agents and leisure spots, which are directly in contact with tourists.
The direct input of Transport & Tourism to GDP is determined by total domestic expenditure, after netting out the procurements made within the tourism departments This quantity is associated with the meaning of Tourism GDP, as defined in the 2008 Tourism Satellite Account: Optional Methodological Structure (TSA: RMF 2008).
Total contribution
The overall contribution of Transport & Tourism takes account of its wider influences, which include indirect and stimulated forces on the country’s economy. The indirect input consists of GDP and jobs sustained by Transport & Tourism venture expenses, which is a crucial aspect of existing and potential operations such as aircraft purchase and tourism infrastructural expenditure.
The government’s joint expenditure supports Transport & Tourism operations in various ways, especially based on its contribution to the community. These operations may include marketing and sponsorship, aviation, management, security, resort area back up and sanitation.
There are a number of purchased domestic goods and services that deal with tourists directly. They include: IT services by travel agents, catering services by airlines, cleaning fuel and hotels, and buying of food. The GDP and employments maintained by the expenditures of employees who are indirectly and directly employed by the travel and tourism industry, are engaged in an induced contribution. The statics shows high prospects for tourism industry in Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia economic contribution in tourism: Real 2011
Sources: world travel & tourism council
Conclusion
The potential outlook of the Saudi Kingdom, in relation to the tourism industry is pegged on several themes, including the country being viewed as the land of Islam. The Kingdom aims at seeking out liberal and notable tourism growth, with common, cultural, environmental and financial benefits within its Islamic principles and customary hospitality.
To accomplish this dream, SCTA lays emphasis on several tasks, most importantly including realization of sustainable and fair tourism progress, accomplishing economic multiplicity and social enhancement, and generating job openings and protecting the environment.
The potential for growth of this industry is very evident, especially from the statics and other critical information that shows the Kingdom’s concerted efforts in promoting the industry, besides being naturally endowed with amazing tourists attraction sites.