Introduction
It is important to note that global societal problems can come in a wide range of shapes and forms, among which is unemployment, accompanied by the lack of economic opportunities. Having the majority of the population employed is critical for the economic and social stability of a nation. In addition, ensuring that there are economic opportunities and ladders between different social strata enables greater growth in prosperity. Therefore, having high rates of unemployment and lacking proper economic opportunities is a major problem. The reasons include increased inequality, rising social instability, facilitating crime, leading to economic stagnation, and weakening a nation in general. Unemployment and lack of economic opportunities are critical societal problems that must be addressed together as they create greater socioeconomic inequality, destabilize nations, increase crime rates, and have long-lasting effects on mental health and overall well-being. Employment and economic opportunities must go hand in hand, as employment alone is not sufficient for fair economic distribution. Hidden unemployment, inflation, and reduced circulation of capital in the economy are the three main reasons why employment and economic opportunities must be facilitated together. Thus, any employment-promoting policy or initiative must consider both employment and economic opportunities to have the desired effect.
Problem
One should be aware that the economy is all about the distribution of resources, and employment is a key piece of it. It provides each individual and family unit with the ability to acquire essential and vital resources in exchange for labor or entrepreneurship. If the majority of the population is employed, it means that people are generally fed, has a roof over their heads, has access to key services, and are able to climb the economic ladder. However, in order for the latter elements to be true, employment must be accompanied by economic opportunities because employment alone is not the guarantor of fair economic distribution. For example, a nation can have 1% unemployment, but 99% of all jobs pay below the living wage. The modern economy of the United States is a clear example of low unemployment without economic opportunities, which renders the former rather useless on its own (Kaufman et al., 2020). Therefore, both employment and economic opportunities must go together in order to have the desired effect. Having one without the other or none of them is a serious societal problem because it creates a greater level of socioeconomic inequality, destabilizes the nation, and increases the rate of crimes. Massive unemployment “has particularly detrimental effects on the subjective perception of social integration, life satisfaction, the access to economic resources and mental health” (Pohlan, 2019, p. 273). In addition, it reduces one’s ability to fulfill his or her psychosocial needs, and all of these effects are long-lasting.
Thus, why is it important to address unemployment and lack of economic opportunity together rather than focusing on one or the other? It is evident employment needs to be tied to economic opportunities because otherwise, any employment-promoting policy or initiative will fail. The key term here is ‘hidden unemployment,’ which refers to individuals who are excluded from unemployment statistics (Mehra, 2018). For example, research on U.S. wage-to-inflation growth shows “a strong negative relationship between wage growth and unemployment during periods of expansion when inflation is above its long-run trend” (Donayre & Panovska, 2018, p. 273). Therefore, the first reason why employment needs and is dependent on economic opportunities is that employment with one will lead to jobs that do not pay sufficiently. From the perspective of the labor market, the pool of jobs can be flooded with low-paying ones or part-time jobs, which are not able to sustain a worker or the household.
The second reason why employment and economic opportunities must go hand to hand can be shown from the perspective of inflation. With an increased supply of money and depreciation of the currency, the prices for essential goods and services increase incrementally and annually. The wages need to match the inflation rate in order for workers to retain their purchasing power. However, evidence shows that it was not the case for a long time, which is why the current debate around minimum wage increase is not only critical but might not restore purchasing power even if implemented (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). For example, the increases in the federal minimum wage were lagging behind the overall rate of inflation, which is why the working class is still losing its purchasing power (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). This is a prime demonstration of the lack of economic opportunities.
The third reason why employment and economic opportunities must be facilitated together is that it impacts the entire economy, which means it is detrimental from the perspective of the upper class as well as the lower class. Having a population without any ability to save or spend, which indicates a shrinking middle class, leads to reduced circulation of capital in the economy. The research found that it is based on the fact “a reduction in the availability of credit forces employers to cut investment and hiring because of the shortage of funds or higher financing costs” (Monacelli et al., 2023, p. 596). In other words, people earn less and spend or save less, which means banks have fewer deposits to leverage issuing credit to businesses. As a result, these employers cannot use credit to grow due to its expensiveness, which is why they stop hiring the workers leading to unemployment. It is a self-perpetuating cycle, which needs a solution addressing not only unemployment itself but economic opportunities as well.
Solution
The proposed solutions for the issue of unemployment and lack of economic opportunities can be approached from two different perspectives. Firstly, from the perspective of the working class and populations with low socioeconomic status, the issue lies in the lack of well-paying jobs. The minimum wage increase is among the most evident solutions. A study found that “minimum wage increases appear to reduce the suicide rate among those with a high school education or less, and may reduce disparities between socioeconomic groups” (Kaufman et al., 2020, p. 219). Statistically, the effect of minimum wage is the greatest when there is an already high level of unemployment, but the United States currently has a low rate of unemployment of 3.6% (Kaufman et al., 2020). In other words, its desired effect might not be as impactful as one might expect to justify the loss of small businesses that cannot afford to pay minimum wage jobs and people who would lose their low-paying jobs. Therefore, from the perspective the businesses, the minimum wage increase will force them to cut back on the number of workers or go out of business altogether (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). In other words, there are many drawbacks that would affect both unemployment and economic opportunities.
The second proposed solution is to improve the collective bargaining of the workers through unionization and debt bargaining channel. From the perspective of the employees, the key problem lies in the fact that they can be easily exploited for labor without fair compensation. An individual has to negotiate his or her worth as a worker with an organized structure in the form of a business or corporation, which tips the scales in the employer’s favor. Thus, unions bring the balancing counterweight by ensuring that an organized entity is negotiating with another organized entity. However, employers can be heavily hit by such developments, which is why providing them with a debt bargaining channel is critical. It is stated that “borrowing affects employment through a ‘debt bargaining channel’: higher debt improves the bargaining position of employers with workers and increases the incentive to hire” (Monacelli et al., 2023, p. 596). In other words, employers need to be provided with cheap access to capital for their hiring activities, which incentivizes them to grow and invest in the workforce in the long term (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). Unionization and debt bargaining channel can essentially decrease the rate of unemployment by creating more jobs with decent pay and improve economic opportunities by making sure that all jobs pay higher due to collective bargaining.
Evaluation of Evidence
The evidence utilized in the given section is valid and reliable with minimal potential bias. Kaufman et al.’s (2020) study have high validity as it used a large, nationally representative dataset of all US states over a period of 25 years (1990-2015). The statistical data suggests that “the effect of a US$1 increase in the minimum wage ranged from a 3.4% decrease (95% CI 0.4 to 6.4) to a 5.9% decrease (95% CI 1.4 to 10.2)” (Kaufman et al., 2020, p. 219). The study is highly reliable as it used a large sample size and followed a rigorous methodology in data collection and analysis. The authors controlled for multiple confounding factors, which is why there are no potential biases in the study.
Donayre & Panovska (2018) discuss the relationship between wage growth and unemployment in the United States during the 2013-2015 period. The study is valid because in order to study the relationship between wage growth and unemployment, the authors employ a nonlinear empirical model based on a threshold vector autoregression (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). They reliably find that the WPC changes according to the dynamics of both unemployment and inflation repeatedly. Specifically, it changes as the unemployment rate transitions above or below the two estimated thresholds, defined as 5.03% and 7.77% (Donayre & Panovska, 2018). There are no biases, and the authors present a balanced and objective overview of the theoretical and empirical foundations of a nonlinear model used to study the relationship between wage growth and unemployment in the U.S.
In terms of validity, Monacelli et al.’s (2023) article present a theoretical model that captures the relationship between financial market conditions and employment decisions. They find that the debt bargaining channel contributes to 26% of the observed US unemployment fluctuations (Monacelli et al., 2023). The authors use Bayesian methods to structurally estimate the parameters of the model, making it valid. In terms of reliability, the article is well-researched and presents a robust theoretical framework and empirical analysis. There are no evident or clear biases in their methods or assumptions.
For strengths, all three studies use a rigorous methodology in data collection and analysis. Kaufman et al. (2020) and Donayre & Panovska (2018) use large and representative datasets, which increase the generalizability of their findings. Monacelli et al. (2023) present a theoretical model that captures a different mechanism through which financial market conditions affect employment decisions, which adds to the existing literature. For limitations, Kaufman et al. (2020) only used two measures of minimum wage, which may not fully capture the complex effects of minimum wage policies on suicide rates. Donayre & Panovska (2018) only focuses on the 2013-2015 period and may not be generalizable to other time periods. Monacelli et al. (2023) present a simplified model and do not consider certain relevant features that could affect the studied issue.
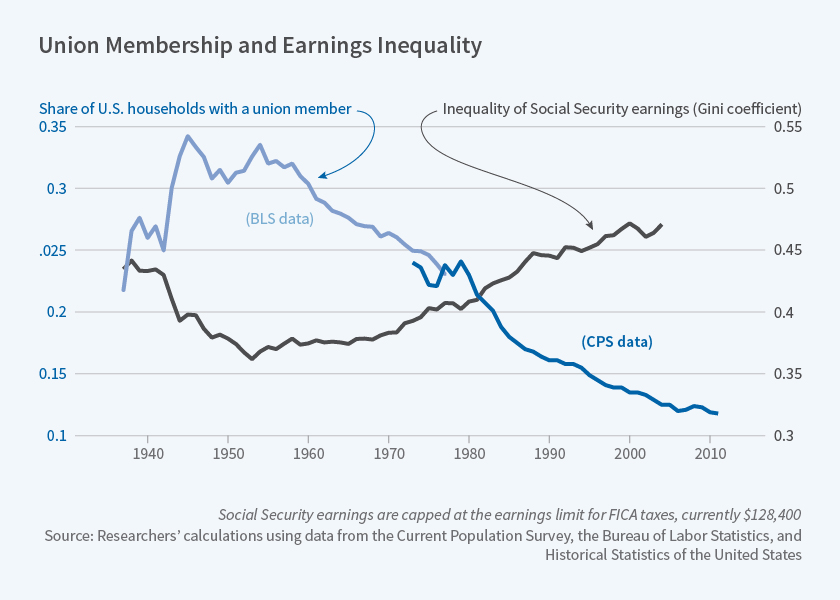
In the case of future research areas, Kaufman et al. (2020) could consider examining the potential heterogeneity in the effects of minimum wage policies across different population subgroups. Donayre & Panovska (2018) could extend their study to other time periods or countries to test the generalizability of their findings. Monacelli et al. (2023) could consider including additional modeling features to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between financial market conditions and employment decisions. Figure 1 below showcases the visual demonstration of the interpretation of the statistical information obtained from the studies.
Ethical Outcomes of Solution
One positive ethical outcome of the proposed solution is the improvement of workers’ rights and the reduction of exploitation in the labor market. By empowering workers through unionization and collective bargaining, they will have a stronger voice in negotiating for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. This could lead to greater job satisfaction, a better quality of life, and improved social welfare. The ethical issue related to this outcome is that employers may view this as a threat to their profits and may resist unionization efforts or even retaliate against workers who organize.
A possible negative ethical outcome is increased debt and financial risk for employers. The debt bargaining channel may incentivize employers to take on more debt to expand their businesses and hire more workers, but this could also lead to greater financial instability if they are unable to repay their debts. Another ethical issue related to this outcome is that the focus on providing cheap access to capital for employers may prioritize the needs of businesses over the needs of workers, potentially leading to exploitation or unequal bargaining power.
Conclusion
In conclusion, unemployment and lack of economic opportunities are critical societal problems that require a holistic approach to address. Employment and economic opportunities must go hand in hand to ensure fair economic distribution and stability. The proposed solutions for the issue of unemployment and lack of economic opportunities, such as minimum wage increase and unionization with debt bargaining channels, can have both positive and negative ethical outcomes. These outcomes must be carefully considered to ensure that workers’ rights are protected while also fostering a sustainable business environment. It is crucial to address these issues in a way that benefits all members of society rather than prioritizing the needs of one group over another. By doing so, people can create a more just and equitable society for all.
References
Donayre, L., & Panovska, I. (2018). U.S. wage growth and nonlinearities: The roles of inflation and unemployment. Economic Modelling, 68, 273-292. Web.
Kaufman, J. A., Salas-Hernandez, L. K., Komro, K. A., & Livingston, M. D. (2020). Effects of increased minimum wages by unemployment rate on suicide in the USA. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 74(3), 219-224. Web.
Maas, S. (2018). New evidence that unions raise wages for less-skilled workers. NBER. Web.
Mehra, G. (2018). Unemployment: Stumbling block to economic growth. International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Literature, 6(1), 71-78. Web.
Monacelli, T., Quadrini, V., & Trigari, A. (2023). Financial markets and unemployment. Journal of Financial Economics, 147(3), 596-626. Web.
Pohlan, L. (2019). Unemployment and social exclusion. Organization, 164, 273-299. Web.