Introduction
Extensive techniques of molecular spectroscopy allow for combined analyses of the physical and chemical properties of substances. Among a large number of techniques, special attention should be paid to those that qualitatively describe the phenomena of luminescence. In general, luminescence is understood as the glow of substances not accompanied by heat production but initiated by the absorption of photons.
The nature of such luminescence can be due to various intramolecular mechanisms, one of which is the transition of an excited molecule from the lowest singlet vibrational level to the ground state. Broadly speaking, any multiplets transitions can be safely called fluorescence, whether in the singlet or triplet state. Consequently, the intensity of fluorescence emitted by matter is described by Equation 1. Considering the width b, the molar absorptivity ε, and the incident radiation power P0 as constant quantities, it is appropriate to light equation 1 to equation 2.

Then it becomes evident that there is a linear dependence with the coefficient K between the concentration of the substance and the intensity of the emission registered by the spectrofluorometer. This statement was used for this laboratory work, in which the concentration of quinine in a sample of tonic water was quantified by measuring the fluorescent emission intensity of the substance. Moreover, the study’s additional objective was to try to establish the effect of heavy atoms on fluorescence is commonly understood as the glow of substances not accompanied by heat production but initiated by absorption of photons.
Experimental
Reagents
- Sulfuric acid, H2SO4, high purity
- Potassium bromide, KBr, high purity
- Potassium iodide, KI, high purity
- Quinine, C20H24N2O2, high purity
Solutions
- sulfuric acid, 0.050 M. 3.0 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid was quantitatively transferred into a flask and diluted with 500 mL of distilled water. After vigorous stirring, the solution was transferred into a 1 L flask and diluted with distilled water to the mark.
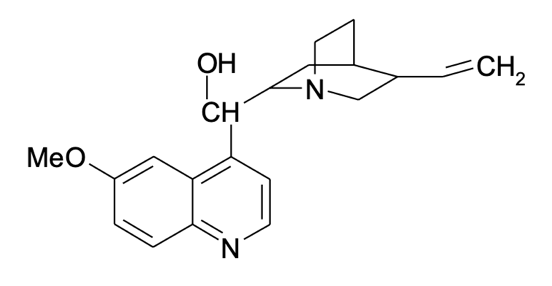
- stock quinine,
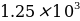 μg/mL. 0.3125 g of quinine were dissolved in 100 mL of 0.050 M sulfuric acid solution. After vigorous stirring, an additional amount of sulfuric acid was added until the mark was reached in 250 mL.
μg/mL. 0.3125 g of quinine were dissolved in 100 mL of 0.050 M sulfuric acid solution. After vigorous stirring, an additional amount of sulfuric acid was added until the mark was reached in 250 mL. - working standard quinine,
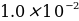 μg/mL. 2 mL of stock quinine were quantitatively transferred to a 250 mL flask and brought to the mark with a 0.050 M sulfuric acid solution.
μg/mL. 2 mL of stock quinine were quantitatively transferred to a 250 mL flask and brought to the mark with a 0.050 M sulfuric acid solution. - potassium bromide,
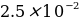 M. 0.2980 g of potassium bromide was placed in a 100 mL flask and diluted with distilled water to the mark.
M. 0.2980 g of potassium bromide was placed in a 100 mL flask and diluted with distilled water to the mark. - potassium iodide,
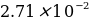 M. 0.4500 g of potassium iodide was placed in a 100 mL flask and diluted with distilled water to the mark.
M. 0.4500 g of potassium iodide was placed in a 100 mL flask and diluted with distilled water to the mark.
Instrumentation
- Cary Eclipse FL1005M010.
Procedure
This laboratory work was performed as described in the Instrumental Methods of Analysis Chem 447 Winter 2020 manual experiment titled Determination of Quinine in Tonic Water with Fluorescence Spectroscopy, and the External Heavy Atom Effect on Fluorescence written by Judith Bazzi. A series of five mixtures with different working solution concentrations was created by adding 0.050 M sulfuric acid to a given amount of the active substance.
Additionally, fivefold series for potassium bromide (0.025 M) and potassium iodide (0.0271 M) were prepared by mixing aliquots of different volumes of salt with 10 mL of working solution of quinine and the required amount of 0.050 M sulfuric acid. A sample of tonic water containing an unknown concentration of quinine was dissolved with 0.050 M sulfuric acid to the 100 mL mark: this procedure was performed three times to achieve more reliable results. The prepared solutions were examined qualitatively using a spectrofluorometer to create a calibration curve and subsequently establish quinine concentration.
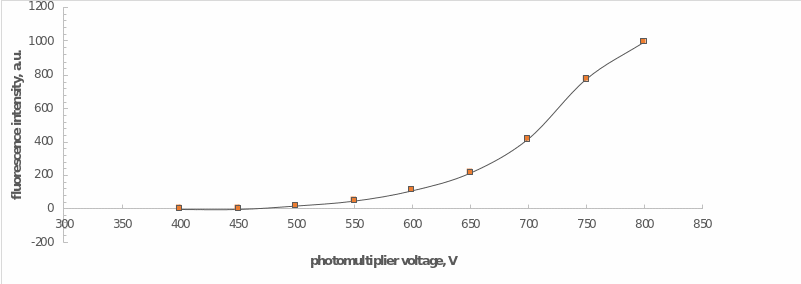
An additional procedure preceding the examinations was to determine the necessary and sufficient conditions for recording the fluorescence. For this purpose, a sample of the calibration solution was placed in the cell of the apparatus and measured at a photomultiplier tube voltage range of 400 V to 800 V in increments of 50 V. After selecting the actual empirical parameters, spectroscopic measurements were made for a series of previously prepared solutions.
Results and Discussion
For a series of calibration solutions, the intensity of fluorescence radiation was measured at different photomultiplier tube voltages. The graphical dependence of intensity on voltage is shown in Figure 2, from which it can be noted that the optimum value of PMT voltage was 700 V. The choice of this value was justified by the boundary condition, at which the graph shows a rapid increase after this value. To put it another way, a voltage of 700 V was the maximum sufficient to carry out further investigations.
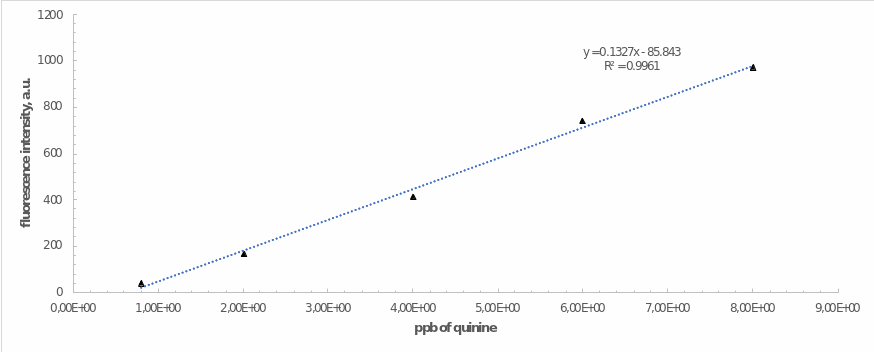
The optimal voltage was used to examine the dependence of the emission intensity on the amount (ppb) of quinine in the working standard solutions as shown in Table 1. The linear regression for working standard solutions is shown in Figure 3. This regression automatically projected for this relationship has high reliability, as evidenced by the square of the coefficient of determination. This was well supported by the data from equation 2.
Table 1. Concentration for Working Solutions of Quinine, Potassium Bromide, and Potassium Iodide and Measured Fluorescence Values.
A linear regression equation was used to determine the amount of quinine (ppm) in the two tonic water samples: calculations are presented in equations 3 and 4. The data given are significantly different from the FDA standard, as reflected in equation 5. More specifically, the Agency set the upper limit for quinine in tonic water at 83 ppm. In addition, the calculated values differ from typical values for tonic water, the quinine content of which varies from 50 to 60 ppm. Such a marked discrepancy between the results could indicate, for example, a highly diluted quinine tonic solution.

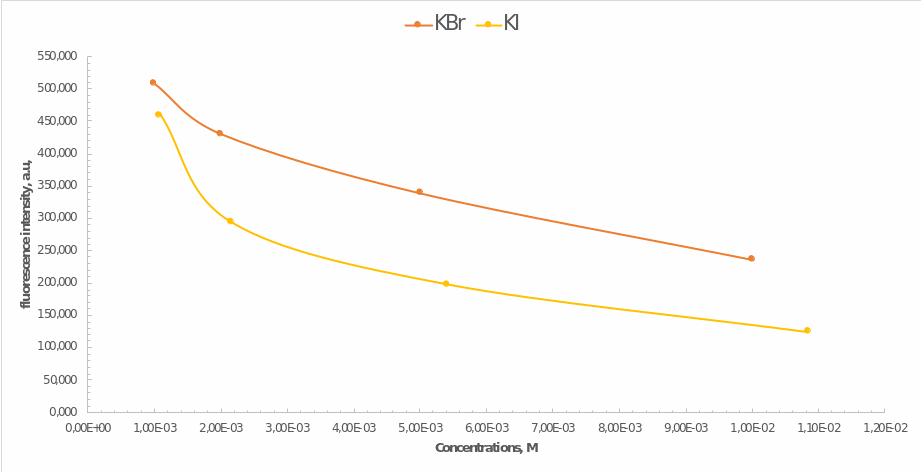
Finally, the last step of the work was to determine the effects of the presence of heavy atoms in the mixture on the fluorescence yield. Samples of potassium bromide and potassium iodide of equal concentrations were used for this purpose. Hence Figure 4 illustrates how the fluorescence intensity of quinine depended on these compounds’ concentration. Most noticeably, the less heavy potassium bromide had less effect on the decrease in intensity, which means that the presence of heavy atoms causes it. In addition, the higher was the concentration of the impurity compound, the lower was the final intensity of emission. These effects can be determined by the phenomenon of fluorescence quenching initiated by particle collisions or the formation of non-luminescent products.
Summary
In this work, a spectrographic study of the concentration of quinine in tonic water samples was carried out using fluorescence. In particular, the concentration of an organic molecule emitting upon excitation was determined using the calibration method, and it was confirmed that the relationship between the substance concentration and the fluorescence intensity was close to linear. The determined amounts of quinine in the two tonic water samples were 1.47 ppm for 5 mL and 4.18 ppm for 10 mL or 2.825 ppm on average with %RSD = 67.9%.
This value shows an insufficient level of confidence in the data. Such errors could have been caused by an outdated tonic water preparation, measurement errors, or inherently low quinine content in commercially available samples. In addition, it has been shown that the calculated amounts of quinine in tonic water differ greatly from the normal values and the maximum threshold set by the FDA. Furthermore, it was shown empirically that the presence of heavy atoms in the mixture initiates quenching of the fluorescence, resulting in a consistent decrease in emission intensity.
Reference
- Izawa, K.; Amino, Y.; Kohmura, M.; Ueda, Y.; Kuroda, M. 4.16 Human Environment Interactions — Taste. Comp. Nat. Prod. 2010, II, 631-671.
- Zieschang, F.; Grant, K. Quantify Quinine in Beverages Using the Agilent Cary Eclipse Spectrofluorometer and a Fiber Optic Dip Probe. Web.
Appendix 1. Answers to Questions
In the introduction, it was stated that quinine may be excited with two bands centered at 250 nm and 350 nm. Regardless of which band is used to excite quinine, the λ of maximum emission is at 450 nm. What is the reason for this phenomenon?
In fact, quinine has several peaks responsible for different transitions. At 250 nm, the singlet S0→S2 transition occurs at 350 nm S0→S1; however, the maximum peak is observed only at 450 nm, where the S1→S0 level transition occurs. The reason for this effect lies in the simultaneous phenomena of fluorescence and internal transformations initiated by photon absorption. Fluorescence leads to excitation of the molecule, while the substantial overlap of excited states, on the contrary, leads to energy dissipation. As a result, the maximum peak is noticeable at the longest incident wavelength.
Why is fluorescence more sensitive than absorbance spectrophotometric methods? Are there any disadvantages to the fluorescence technique?
The intensity of fluorescence flux is usually measured directly, whereas other spectrophotometric processes’ absorbance is evaluated through the difference between the reference best and the observed one. Despite its obvious advantage, however, fluorescence has a critical disadvantage: not all molecules are able to fluoresce. In addition, this method is susceptible to interference and also has a relatively short analysis time.
Compare and contrast fluorescence and chemiluminescence with respect to instrumentation requirements and design.
Both luminescence methods use the effects of a molecule’s radiation upon excitation, but the design and principle of the equipment used are different. In particular, fluorometers require an external EMR source, whereas a chemical reaction initiates chemiluminescence. In addition, a chemiluminescence spectrometer does not require a set wavelength setting, and since this type, unlike fluorescence, is not multi-wavelength selective, an output wavelength recorder is not required.
What is the difference between excitation and emission spectra? Be sure to point out what is held constant and what is plotted for each?
An excitation spectrum occurs when electromagnetic radiation passes through an absorbing medium that absorbs a certain wavelength’s radiation. Graphically it is a continuous spectrum with dark lines. In other words, it is a picture of light rays after passing through a given substance. On the other hand, emission spectra (constant wavelength) arise when electrons, atoms, particles, or fragments of molecules being excited, go from a higher energy state to a lower energy state. Graphically, this looks like a series of well-separated frequencies, which spectrometers record as bands: the arrangement of these bands indicates a particular element in the gas and is called the atomic spectrum.
Why does fluorescence not take place from the highest vibrational level of the excited state?
Since fluorescence is a slow process, it is a highly undesirable way for a particle to dissipate excess energy, especially in energy states above the first level. Moreover, assuming that higher states initiate fluorescence, it should be noted that energy will be dissipated by vibrational relaxation and internal conversion.
What is the difference between internal and external heavy atom effect?
The external heavy atom effect appears in the case of heavy atoms (halogens) in the medium, which leads to the formation of a system of charge-transfer complexes and, consequently, to quenching of fluorescence. In the case of the internal effect, the heavy atom is chemically incorporated into the molecule under study and covalently bound to it.
Would the fluorescence measurements be affected if the source of quinine used to prepare the solutions were quinine hydrobromide?
Definitely yes, because the structure of quinine hydrobromide contains a bromine atom, which is a heavy particle. Thus, if this compound were used as the quinine source, it would be reasonable to expect lower intensity values.