Introduction
Background
Achieving success in the global community may not be as easy as doing the same in the local market. Cases, where highly successful firms struggle to achieve growth in foreign countries, have been becoming increasingly common. Li and Liu (2018) explain that differences in the socioeconomic and political environment are some of the reasons for such failures.
When they go global, these companies often plan to use the same strategy that enabled them to achieve success in the local market. However, it becomes apparent that cultural differences in the two countries make it impossible to replicate operational strategies. Walmart’s struggle in China is a perfect case of why highly successful firms may fail to achieve success in a foreign market.
Walmart was founded in 1950 and since then the company has achieved massive growth in North America. The company has dominated the American retail market and since 2014, it has been ranked as the largest company in the world in terms of revenue generation (Hatami, Firoozi, and Puhakka, 2018). The management was able to understand buyer behaviour in the United States and has been keen on meeting the expectations of its customers in the best way possible.
Its expansion to Canada and some European markets was also relatively successful. The ambitious management unit felt that it was time to explore the Chinese market because of the large population (Cao, Zhang, and Ma, 2019). This market was becoming increasingly attractive not only because of the large population but also the rapid economic growth. It was viewed as the next frontier in the company’s effort to dominate the global retail market.
Challenges started emerging in the Chinese market in the early years of operation. The management realized that it did not fully understand the Chinese market. In its first years of operation, the management noted that strategies that were effective in North America and parts of Europe could not deliver the same outcome in China. The problem was not unique to Walmart. Similar multinational retail stores from Europe were also suffering in this market (Lasserre, 2017).
In fact, Tesco was forced out of China because of numerous challenges that made it impossible to sustain its operations. The management of Walmart realized that the best way of addressing the problem was to operate as a joint venture instead of the traditional approach that it had been using in other markets.
It started operating as Walmart Supercenters, Neighbourhood Market, and Sam’s Club. The decision to work alongside local firms was meant to help the company to manage cultural integration challenges. Working alongside these local companies would help it understand the expectations of the local market. However, it is important to note that this was not a perfect strategy that addressed all the problems that this company was facing. Currently, Walmart is still operational in the Chinese market, but it is facing numerous problems. This study seeks to investigate challenges that Walmart faces in terms of its performance in the Chinese market.
Research Question
The study seeks to provide ways in which Walmart can overcome problems that it is facing in the Chinese market to ensure that it achieves sustainable growth. AsXie and Cooke (2018) note, one can only solve a problem if one understands the source. They also need to know who should be involved and how various steps should be taken to address the issues at hand. The following are the main questions that guided the process of collecting data for the study:
- What are the challenges that Walmart is facing in its operations in the Chinese market?
- What are the primary causes of the challenges that this company is facing in this market?
- How has the management tried to solve these challenges to enhance its success in China?
- How should the company address these challenges in ways that are more effective than what it is currently doing?
Definitions of Terms
It was necessary to define some of the specific terms used in this study to explain challenges that the company has encountered and strategies that have been used to address them. The following are some of the terms and phrases commonly used throughout this project:
- Culture shock – the disorientation that one experiences when suddenly subjected to a way of life that they consider strange;
- Cultural integration – different cultures getting amalgamated to form a new cultural practice;
- Joint ventures – a business strategy where two companies agree to work as a unit in the market but in a way that allows them to retain their identity;
- Bureaucracy – overly concerned with procedures in a way that negatively affects efficiency;
- Host country nationals (HCN) – employees who are nationals of the foreign country where a firm operates;
- Parent country nationals (PCN) – employees who are nationals of the country where the foreign company has its headquarters;
- Third-country nationals (TCN) – employees who are neither nationals of the host country nor the parent country of the company.
Literature Review
When a company decides to explore a foreign market, it is likely to face new challenges that probably did not exist in the home market. Challenges can be brought about by various factors, some of which may be beyond the control of the company. Culture shock is one of the encounters that the business will experience.
The business environment in the United States as defined by the country’s culture is significantly different from that in China. An American firm that comes to operate in China is likely to be affected by these differences. Chang and Hu (2020) explain that it may take a while to achieve cultural integration, which is critical in facilitating effective growth in the market.
When conducting this literature review, it was essential to critically analyze different forces that affect the ability of the targeted company to achieve success. Walmart is one of the most successful companies not only in the United States but also in other markets in North America and Europe (Wang and Coe, 2018). The management has been keen on analyzing a market before making an entry.
As such, due diligence was made before it was finally decided that it would be necessary to operate in China. The company had a carefully crafted plan on how it would operate in the country. It was obvious to the management that strategies that were used in the home market could not be replicated in the Chinese market to achieve the same outcome. It was obvious that a different strategy had to be employed. However, the company still faced stagnation despite these measures that were meant to bring about success.
The challenges that Walmart faces in the market cannot be attributed to a single problem. cultural differences that exist between the two countries is not the only problem that has created an environment that is relatively hostile for this firm compared to that in the home country. It is essential to conduct a comprehensive analysis to understand these forces and how they are related to the normal operations of the firm. Conducting a three-level analysis was considered essential at this stage.
The analysis focused on understanding the macro-environment at the national level, the industry forces that have affected the normal operations of Walmart, and organizational issues that help to explain the strengths and weaknesses of the company in the foreign market. Using various tools to analyze the macro-market forces, industry forces and the organizational environment was essential.
Macro-Market Analysis National Level
China remains one of the most attractive markets for many American companies. Liu et al. (2019) note that the decision that Apple Inc. made to transfer its production to China was motivated by many factors, top of which included the population, increasing purchasing power of people, technological improvements, and changing government policies that made it easier for foreign firms to explore this market. As such, it was not surprising that Walmart made the decision to expand its operations to China. It was keen on tapping into the potential that the country has. In this analysis, it was essential to use the PESTEL model to assess the external market forces in this foreign country.
Political Environment
The political environment in China is significantly different from that in the United States where Walmart has registered impressive success over the past several decades. China is currently one of the few communist states in the world (Alita, Dries, and Oosterveer, 2020). The government has a strong influence that it can use to influence the business environment.
Although there has been an effort to ensure that people can select those who govern them, the system is so rigid that it is almost impossible for them to make such decisions. It means that once someone ascends to a position of power in this country, they have immense power that cannot be easily challenged by the subordinates. Chinese are used to this political system as it is seen as being less disruptive for economic growth when compared with democratic systems where people regularly engage in emotive and highly divisive politics every four or five years.
The political environment in China has proven to be challenging for Walmart as it seeks to achieve growth in this market. When the company started its operations in the home market, it enjoyed operating in an environment where the political class is always keen on meddling with the business community. However, that is not the case in China. The powerful rulers in this foreign market can determine the destiny of a company (Zhao et al., 2018).
When the leadership of the country liberalized the economy to allow foreign companies to operate locally, measures were put in place to protect local firms at the expense of foreign companies. Leaders who are expected to review these policies to address challenges that foreign firms face in the country have failed to do so deliberately. It means that Walmart is operating at the mercy of the local leaders in China. As such a large and highly successful American company, it is obvious that Chinese leaders would be keen to curtail its growth in the country to ensure that it does not pose any significant threat to local retail outlets. In such an environment, the management of Walmart cannot make major expansion decisions or embrace radical marketing strategies without consulting those who are in power.
Economic Environment
The economic environment is one of the most important factors in the external environment that defines the success of a firm. As Michelson et al. (2018) explain, the size of the economy of a country and the purchasing power of individual citizens are some of the factors that companies consider when going global. China is currently the second-largest economy in the world after the United States (Wang and Elfstrom, 2017).
For decades, the country has been experiencing massive economic growth because of policies that were created by Chairman Mao and his predecessors (Si, Scott, and Mccordic, 2016). The leadership of the country has embraced radical policies meant to strengthen its economy and currently, it is the world’s largest export ahead of the United States. Recent studies have also shown that the country has over 400 million people classified as middle-class households. It means that its middle class is larger than the entire population of the United States. Any retail market in the world, Walmart included, would want to tap into the potential of this market.
Despite the growing economy and a high number of people falling into the middle class, studies have shown that the majority of Chinese still lead an impoverished lifestyle. The standards used to classify people into the middle class in China are also different from those used in the United States (Wang and Elfstrom, 2017). It means that although there is a general impression that many Chinese are financially stable and can indulge in shopping regularly, realities on the ground are different. Unlike in the United States where many people feel that they can easily spend their earnings and make more because of vast opportunities, many Chinese are concerned about their future.
They fear losing their jobs and the consequences of being jobless. As such, they prefer to save their earnings instead of engaging in unnecessary expenses (Cooke et al., 2019). For a retail outlet, impulse buying is one of the primary reasons why items are always displayed attractively to appeal to customers. However, such practices are not common in China. Here, most people are specific with what they want to buy and are often less influenced by visuals as it is the case in the United States. The company has been spending a significant amount of resources to improve its stores, but this is proving to be less capable of influencing customers. Although the economy of the country is developed and the size of the middle class is growing, that has failed to translate into market growth for this company.
Social Environment
The impact of the socio-cultural environment cannot be ignored when discussing how external environmental forces affect the normal operations of a firm. The culture of a people defines their buying behaviour. Sheldon and Sanders (2016) explain that the Chinese have significantly different buying behaviour from that of Americans. One of Hofstede’s cultural dimensions is individualism versus collectivism when defining the behavioural patterns of a society. Individualism is weaker in China than it is in the West.
According to Chiang, Lemański, and Birtch(2017), the Chinese value collectivism because of cultural practices. As such, many people often consult their family members before they can purchase an item. Such a culture means that a firm has to take a unique marketing approach to achieve success. In the West, many companies often classify their customers based on their age among other factors. In China, such a strategy may not have the desired outcome. An effective marketing strategy must target all members of society because they are likely to be consulted before one buys an item.
Hofstede’s model also identifies power distance as a major factor that defines the cultural practices and beliefs of a society. China has a significantly different belief about power distance from that of Americans. In China, people are expected to respect the authority and not to question those who are superior to them (Gallagher, 2017).
It was not easy for Walmart to adapt to such a culture because it is used to operating in a market where people feel comfortable questioning those in power and criticizing them for mistakes that they make. Uncertainty avoidance is also higher in China than it is in most Western countries. This cultural practice means that most Chinese would prefer saving than impulse buying as a way of protecting their future. The financially empowered market in China is therefore not as attractive to retailers as Walmart had expected.
Gender roles and positions in the society in China are some of the issues that companies operating in this country cannot ignore. For a long time, Walmart has been operating in a market where women and men are believed to have an equal capacity to achieve success. Rarely will women be denied a promotion at work primarily because of their gender. In China, the corporate world is dominated by men (Bruno, 2018). Although the practice is changing, for a long time Chinese believed that women had to rely on men to provide for all their needs.
Large corporations are still reluctant to promote women to the highest offices because of the fear that they may not be taken seriously when expected to negotiate on behalf of the company. It is also important to note that in the country, restraint is a virtue that many people embrace. Enjoying life and having fun is seen as a sign of showing off in this society, which is an undesirable virtue. Society expects people to act modestly at all times. Such behaviour directly influences the purchasing pattern that people embrace. Walmart had to understand how it stocks its stores and promotes products in a way that is in line with these societal expectations.
Technological Forces
Technology is another major force in the external environment that defines the success of a company, especially in a foreign market. China is one of the countries that have witnessed a massive growth of technology in different fields. Kubler (2017) explains that one of the fields where technology currently plays a crucial role in a firm’s operation is in marketing. Traditional platforms of promoting products in the market are becoming less effective in China.
Television and radio commercials are still used by many companies, but they no longer have the massive influence that they did several decades ago. Social media is redefining marketing in this country. Most adult Chinese are using smartphones and regularly use various social media platforms. They find it easy to get news and share information through these platforms. Marketing companies are shifting their focus from mass media to social media because of its immense potential.
The mode of payment in China has also changed significantly over the years. In major urban centres, the use of cash is becoming less common. People are shifting to the use of cards and various mobile-based forms of payment (Phillips and Rozworski, 2019). Retailers have to adjust their operations and ensure that they are capable of receiving payments in these non-cash forms. Online sales are also growing rapidly in China because of changes in socio-cultural practices.
Traditionally, women in China were not expected to work (Walker, 2019). As such, they had adequate time to visit brick-and-mortar stores for their groceries. However, the trend is changing as most families have both men and women as breadwinners. Time to visit supermarkets is limited because of the desire to achieve career growth. It means that many people find it easier to visit online stores to make most of their purchases.
The massive growth of technology in the country also presents new challenges that directly affect the normal operations of Walmart. Hacking is emerging as a major challenge in this country. Cybercriminals have developed sophisticated ways of gaining unauthorized access to databases of companies for various reasons.
As the world shifts from analogue to digital operations, many companies have developed databases where they store critical data (Powell, 2019). Criminals often target these databases to steal crucial information that may benefit a firm’s rival in the market. Others hack into such databases to collect information on behalf of the government. Being an American company, Walmart is prone to such government-sponsored attacks in China. Some of these cybercriminals target the financials of these organizations. They focus on stealing from them or their customers. Walmart has to develop unique ways of protecting itself and its customers from these criminals.
Ecological Forces
Ecological forces have become powerful drivers in the economic development of a country. Scientists and environmentalists have proven that human activities are directly responsible for global warming and climate change. The need to protect the environment has forced many governments to redefine laws that guide the operations of different companies. China is currently the world’s leading emitter of greenhouse gases. It is also responsible for the massive generation of pollutants such as plastics (Schulte and Lee, 2019).
For a long time, the government has been ignoring this environmental issue in favour of rapid economic growth. However, the consequences of massive environmental pollution are becoming more evident and the government can no longer ignore these effects. The city of Shanghai has been so much affected by air pollution that sometimes the elderly and the young are advised to stay indoors at specific hours of the day to protect themselves from these pollutants.
Policy-makers in the country are developing tougher measures to protect the environment. Currently, the government is discouraging the use of plastic bags in the retail sector. Supermarkets are expected to make available reusable and environmentally friendly bags instead of plastic materials. Walmart has to find ways of adjusting to these new regulations when wrapping its products for customers. Another major regulation that is emerging in this country is the need to embrace electric cars.
McAnally (2017) explains that China currently is the largest market in the world for electric cars. This new trend may have major operational implications for Walmart and other retailers in the market. Recharging these electric cars has been identified as a major impediment to their use because of the time it takes. The company will need an alternative strategy of delivering its products at the right time despite these changes. It will also have to ensure that its operations do not pose any major threat to the environment. Sometimes these strategies may mean spending more on technological approaches to managing waste.
Legal Environment
The last element in this model, which is just as important as the other elements discussed above, is the legal environment. A company cannot operate successfully in a market that is not clearly defined by law. Ward (2019) explains that the legal environment is meant to protect a firm from unscrupulous customers, overzealous government officers, unethical suppliers, unfairly aggressive competitors, criminals, and any other party that may want to take advantage of the company.
At the same time, these laws protect the same stakeholders from being exploited by the company. China has strict laws and regulations that define the operations of companies in the market. Goldberg (2018) notes that despite major changes that have been made to open up the market for foreign investors, companies still have to go through lengthy processes to register their businesses. Walmart was able to overcome these bottlenecks to register its company in the country.
Walmart has to ensure that its marketing strategies do not exploit customers in this country. It must deliver what it promises to its clients. One of the challenges in the legal environment that the company has had to address was the inability of the government to protect intellectual rights. The country has weak laws when it comes to protecting copyrights, as Panibratov (2017) observes. It poses a major challenge to a firm keen on developing a unique design that needs some form of protection.
Cyber-attacks are common in the country but it is clear that the government is using double standards when implementing laws meant to discourage the practice. Cybercriminals working on behalf of the government enjoy some form of protection. However, when actions are viewed as being against the interest of the state, consequences can be dire.
Industry Analysis
When the macro-environmental forces in the market have been discussed, it is important to look at industry-specific forces. As Gopinath (2018) observes, industry analysis primarily focuses on factors that only affect a specific company. The retail industry in China has gone through major changes over the years. Technology, government policies, changing tastes and preferences, and many other evolutions in the socio-economic and political arena in the country are primarily responsible for these changes (Frynas and Mellahi, 2015).
One can use various models to analyze industry-specific forces within a given country. The researcher will use Porter’s five forces model to critically evaluate the forces that Walmart encounters in its operation in the Chinese retail industry. Figure 1 below shows the five forces that directly define a firm’s strategy in the market and its ability to achieve sustainable growth.
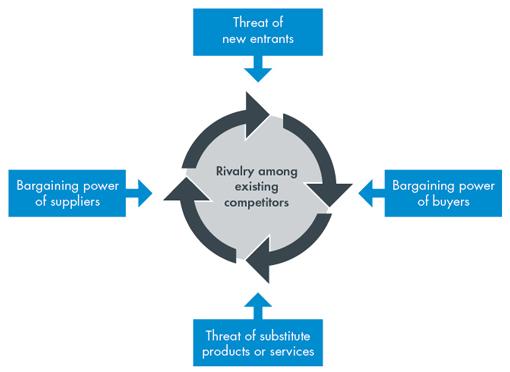
Market Rivalry
Market rivalry is one of the most important factors that a firm has to consider when defining its strategies in the market. In an industry where the level of rivalry is high, a company has to develop a unique strategy of attracting and retaining customers. The rivalry is heightened where many companies offer similar or closely related products to the same customers. The retail industry in China is highly competitive. Walmart is not the only multinational retail outlet that is operating in the country. Tesco had been operating in this country for years before it finally decided to exit and seek other opportunities in Europe and other parts of the world with favourable conditions.
The country is home to many other major international retailers keen on overcoming numerous challenges in this market. Besides these international brands, there are numerous other local retailers in the country. They operate both in the brick-and-mortar system and on the online platform. Alibaba.com is currently the largest online retailer in the country. Other small-scale retailers targeting specific markets or regions within the country also make significant contributions to the growth of this industry.
The stiff market rivalry in the Chinese retail sector is a major challenge to the growth of Walmart in this country. In China, there is a common practice where the Chinese prefer buying local brands. Even in the retail sector, these customers feel comfortable walking into a retail store that they consider Chinese. They feel that such stores will offer products that uniquely meet their needs (Franco-García, Carpio, and Bressers, 2019). Walmart realized this problem and made the decision of forming a joint venture with some local brands.
The decision was made, not because the company lacked the capacity to achieve success as a single business entity but because of the need to get the local identity. As Marr (2019) observes, the problem with joint ventures is that a firm is denied the capacity to make specific decisions independently as the partner will have to be consulted. Such consultations always take precious time, making it difficult to make quick decisions on how to take advantage of market opportunities. It also makes it necessary for the company to share profits earned from its operations.
The Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants is another major concern that cannot be ignored in this market as Walmart seeks to overcome numerous challenges in China to achieve sustainability. Kennedy (2017) explains that in a market where trade restrictions have been eliminated, companies often face a constant threat of a foreign firm making an entry into the local market.
In China, most of the trade restrictions that existed some decades ago have been eliminated. In fact, the government has created an environment that encourages foreign investors to come to the country. It may be challenging for a company to follow all the laws and regulations that the Chinese government has put in place to guide the business environment, but for a firm that is committed to achieving success, it may not be a major problem to start operations in China (Fransoo, Blanco and Mejía-Argueta, 2017). The threat of new entrants may also come from new local companies.
The online market platform has eliminated the numerous challenges that small-scale retailers face, especially on the high cost of rent for the store. These firms no longer have to incur such costs. Gooderham, Grøgaard, and Foss (2019) explain that most small-scale retailers do not have physical retail outlets or stores. Instead, they have created a business model where they receive an order from a customer, receive payment, pick an item from the supplier and then deliver it to the customer. The only cost that they have to incur is on delivering the products. Others even avoid this cost by connecting a client with the seller directly and getting their commission in the process.
The threat of new entry into the Chinese market is a major concern for the management of Walmart. Competition is always healthy as it enables a company to develop unique strategies for meeting customers’ needs. However, when it becomes so stiff that companies consider price wars and such other undesirable practices, it becomes dangerous. Walmart is going through this challenge, especially because of the rate at which new online retail stores are emerging in the country (Griffith et al., 2018). These new entrants have developed ways of maintaining a low cost of operations. As such, they can afford to charge low profits without significantly affecting their profit margins.
Walmart cannot afford to sustain such competition because it operates some of the largest retail outlets in the country. It is costly to maintain the operations of these stores and these costs have to be transferred to customers. These are some of the challenges that Target could not withstand as it made the decision to exit this country. Walmart will need to find a way of overcoming the threat that these new entrants pose in this market.
The Threat of Substitute Products
The threat of substitute products is a major concern that may affect the ability of a firm to achieve success in a foreign market. In the retail industry, the threat of substitute products should be looked at from a unique angle because these companies often sell products made by other firms. The threat may come in the form of another company using a unique strategy that others do not to achieve success.
Online retailing has emerged as a major threat to the operations of firms using the traditional brick-and-mortar strategy of selling their products. However, that is not a major concern to Walmart because it has also created online platforms through which it can reach out to customers. A new trend of personal selling is gaining popularity in China that may be considered a threat of substitute products to traditional supermarkets in the country.
Some small-scale firms are now reaching out to specific customers to sell their products at the convenience of client’s offices or homes. They have created close personal relationships with these customers to the extent that when they want to buy something, they only need to call the seller and the product will be delivered in a short while (Lenssen and Smith, 2019). The strategy is gaining popularity among a section of society because of the speed with which the product is delivered.
The seller understands the specific tastes of each of the handful of customers, so it is unlikely that they will deliver the wrong product. There is also a strong bond and trust that is easily created between the seller and individual buyer. The large-scale nature of operations of Walmart makes it difficult to use this strategy to reach out to its customers.
The company can succeed in creating a lasting relationship with a client, but responding to their needs with an efficiency that matches that of personal sellers may be challenging. It may cost the company so much that its profitability in the country may not make any economic sense. The problem with these alternative service providers is that most of them are individuals who are only keen on making a living. They are not facing profitability pressure and some of them do not even have to pay taxes or meet numerous other costs that large retailers such as Walmart cannot afford to ignore. It means that they enjoy a playing ground that is highly unfavourable to their rivals.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers influences the ability of a firm to achieve growth in the market. Wang et al. (2020) explain that the power of the suppliers is often defined by the size, number, and uniqueness of products that they sell. Suppliers that dominate their industries tend to have larger bargaining power than those that are smaller. They are capable of dictating trends in the industry. Similarly, suppliers selling unique products that are not easily available tend to have the capacity to dictate the terms of sale f their products.
In terms of numbers, in a market where many suppliers are selling the same products, their power is often low. They understand that a retailer can choose from a wide variety of suppliers with good terms and conditions favourable to them (retailer).
In China, most of the suppliers that Walmart often deals with have low to medium power. Many other suppliers exist selling the same products manufactured locally. As such, they do not have any unique selling point that can enable them to dictate terms of sale. This condition is advantageous to the retailer because terms of sale are always favourable to it. Most of the products that it stocks are relatively cheap, making it possible for the company to lower its prices without compromising on the profits. It is important to note that some suppliers may have bargaining power. These few suppliers provide unique products that the retailer cannot easily accessible in the market.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The last element in Porter’s five forces model and which is just as important as those discussed above is the bargaining power of buyers. In a market where buyers have access to products they need from numerous sellers, they tend to be powerful. The fact that they have a wide variety to choose from means that they can demand low prices. The quality and quantity of products that they purchase must be favourable to them. On the other hand, when customers have to buy a given product from one or just a handful of retailers, they may lack the power of negotiation. They lack alternatives from which to choose and as such, they have to buy from the available retailer.
In China, the bargaining power of customers is significantly high. Besides Walmart, numerous other retailers exist across the country. They sell similar products to the same customers. One of the few ways that a firm can gain a competitive edge over its rivals is to lower the price.
Sheldon and Sanders (2016) explain that in China, customers are always willing to shop around as they try to get the best price for their products. As such, many companies would try to set favourable prices. The only problem with this strategy is that it may result in price wars. Walmart cannot afford price wars in this foreign country because it has to meet all the costs of its operations. These are some of the challenges that this company has to overcome as it seeks to achieve growth in the Chinese market.
Organizational Level Analysis
The third level of analysis focuses on the internal capabilities of a firm. According to Mayrhofer, Gooderham, and Brewster (2019), external forces in the market may be favourable to a firm’s growth, but its internal forces define its success. The ability of a company to master and manipulate external market forces depends on the leadership strategies and the capabilities of its employees. A firm may face numerous challenges but with an efficient workforce and committed managers, it is still able to achieve sustainable growth.
Walmart has achieved massive success in the United States and European markets because of its strategies. Currently, it is the largest company in the world in terms of sales value. However, the same excellent performance has not been replicated in the Chinese market. It is necessary to analyze the internal environmental factors and capabilities of this company using the VRIO model shown in Figure 2 below in the context of the Chinese market.
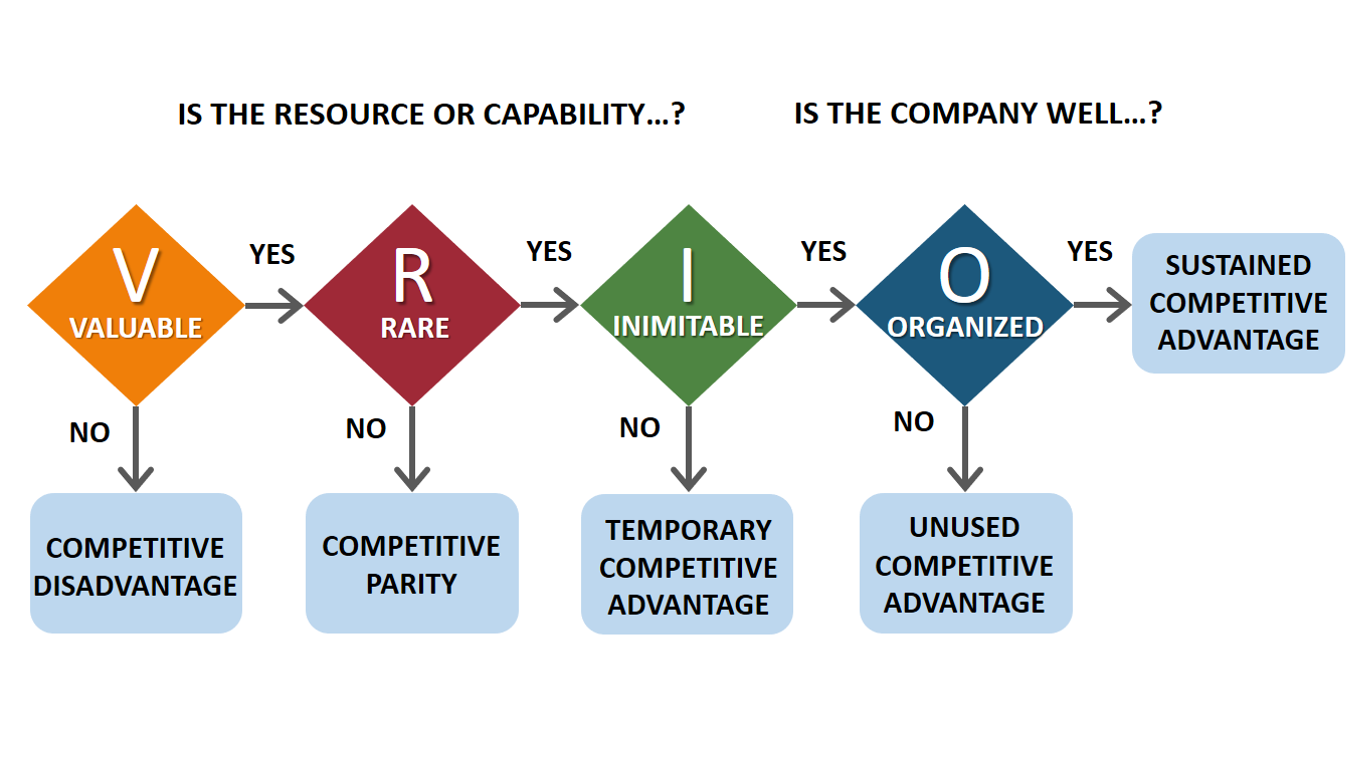
When using this model, one of the first factors that one has to consider is whether resources that a company offers to its clients are valuable. Walmart offers a wide range of products, from groceries to electronics and almost every household product. These products are highly valuable to customers. The electronics that the company sells to its customers are essential for entertainment and communication.
The value of these products means that in case the company fails to buy them from Walmart, they have to find alternative sellers for them to lead a normal life. This factor is important in enhancing the competitiveness of Walmart. Mockaitis, Zander, and Cieri (2018) argue that when assessing the ability of a firm to achieve sustained competitive advantage, one has to start by assessing how valuable its products are to customers. It helps to understand how often they will be needed in the market. It is a step towards achieving competitiveness in this foreign market.
The second factor is to establish the rarity of the resources that a company offers in the market. Boon et al. (2018) note that when the resource or capability of the firm is rare, then it will be moving closer to achieving sustained competitive advantage. In China, Walmart offers a wide range of products to its customers, which are readily available at other stores. In this context, one can easily consider the resource as not being rare, which means that the company will achieve competitive parity. However, the capability of this company is unique. Tesco has been one of the main competitors of Walmart in the international market.
In Europe, these two companies dominate the brick-and-mortar retail industry. However, Tesco could not match Walmart in terms of its resilience to overcome challenges in China. Tesco exited this market in 2020 by selling all its subsidiaries. It is important to note that Tesco’s case of leaving the Chinese market because of numerous challenges is not unique.
Best Buy is another major American retailer that also considered exploring the Chinese market. Back at home in the United States, Best Buy has been registering impressive success, just as Walmart. However, it could not sustain its Chinese operations. It exited the Chinese market in 2018 when its operations became unsustainable. Lotte Mart of South Korea was once a successful retailer in China. However, it only managed to operate in this market for 14 years.
It finally closed its operations in 2018 because of these challenges (Hewett et al., 2018). Carrefour also tried to tap into the immense opportunities in the Chinese market. It opened several stores in different parts of the country. However, it also learned the bitter lesson that successful strategies in the home market cannot be replicated in China. It gradually reduced its number of retail outlets until 2019 when it finally exited the market. Walmart has been operating in China since 1996. It means that it has been able to withstand these challenges for the last 24 years, a capability that is rare when compared with its rivals.
This model of analyzing a firm also requires one to look at the immutability of a firm’s resources or capabilities. Walmart, just like any other retailer in the market, offers products manufactured by other companies. As such, it is easy for rivals to imitate these products. However, the capability of this firm is unique, which explains why it has remained operational in a market where its rivals have suspended their operations. The management of this company has developed unique ways of analyzing market trends and forces, then developing an effective response mechanism. When it finds it favourable in parts of China, Walmart operates under its flagship of Sam’s Club.
Under this flagship, the company can offer its customers a wide variety of products using its traditional model of operation that has proven successful for decades. Sam’s Club is common in cosmopolitan areas where it is likely to have foreigners, especially from North America and Europe. At such outlets, these customers are guaranteed to be served in a standard approach that they are used to in the home market. In remote locations across the country, the company uses joint ventures. By partnering with local firms, the company can understand the needs of locals and provide them with a wide range of products in a format that they prefer. The company often allows these partners to define organizational culture because they have a better understanding of the locals’ needs.
The last factor in this model is to determine if the company is organized enough to tap into opportunities that the market offers. According to Chen, Su, and Zeng (2016), a firm needs to have a clearly defined management structure that is suitable for a given market. Its human resource should be properly coordinated and equipped to ensure that they can deliver desired results in the market.
Walmart has one of the most well-organized human resource management systems in China. The company emphasizes the need to conduct regular empowerment of its human resource through training. Tasks are assigned based on employees’ core competence and experience. The strategy is meant to eliminate most of the mistakes that often occur when tasks are assigned to an individual who lacks the capacity to accomplish them.
A clear system of communication has also been created to ensure that information can flow easily from the top management unit to junior employees and back. Despite its western culture, the company has been keen on understanding and embracing Chinese culture to ensure that its operations are not negatively affected in this country. Using this model, one can therefore conclude that Walmart has achieved a sustained competitive advantage in the Chinese market.
It is interesting to note that this model demonstrates that Walmart has sustained competitive advantage but it is still struggling in the Chinese market. Rowley et al. (2017) explain that it is possible for a firm to have sustained competitive advantage but still find it difficult to achieve success in a given market. It is important to note that this model focuses on a firm’s internal environment. It analyses its core competencies to help understand how well it can achieve growth.
A highly efficient firm such as Walmart will still be affected by numerous external forces discussed above. The investigation reveals that challenges that Walmart faces in China have little to do with its core competencies. Instead, it has everything to do with external forces such as cultural integration and a legal environment that is not effective in protecting copyrights. These unique traits of the company have enabled it to maintain its operations in China despite the numerous challenges that it faces. At a time when its major rivals are exiting the Chinese market, the company is still focused on finding ways of enhancing its success in the country.
The Case Analysis
Walmart remains one of the most successful retail outlets in the world. Its decision to enter the Chinese market was motivated by its success in other markets in Europe and part of North and South America. The United States remains the company’s single most important market. However, its performance in the international markets, especially in Mexico and the United Kingdom has been impressive. The management of this company was convinced that it could achieve similar success in the Chinese market.
Walmart’s entry into the Chinese Market
Walmart made an entry into the Chinese market in 1996 when it opened its first Sam’s Club and a supercenter in Shenzhen. The city was rapidly expanding and the company realized that there was an attractive opportunity it could tap into if it used effective strategies. In its initial years of operation, the company was affected by culture shock as it realized that there were significant differences in the socio-economic and political environment of China and the United States. The company proceeded to expand its locations across the country as a way of entrenching its position as a major player in the country’s retail market. Its stores were mainly located in major cities such as Beijing and Shanghai among others.
The company employed its pricing strategy as a means of achieving success in this market, especially through its Sam’s Club outlets. Schawbel (2018) explains that the pricing strategy had been successful in the United States and other international markets. The company wanted to use the same approach to dominate the market. This strategy was particularly important in China because, at that time, the vast majority of people were low-income earners. It meant that most buyers would shop around for the cheapest products they could find.
Sam’s Club was particularly successful because of its focus on pricing. Its supercenters were meant to create a unique shopping experience for customers. These discounted shopping centers were meant to ensure that customers could purchase all their groceries under one roof without the need to visit other outlets. These centers were successful in the United States and Mexico. The rapidly growing population in China convinced the management that it would be profitable if it embraced the same business model.
The management of Walmart sacrificed profits for expansion in China. The goal of the company was to ensure that it dominated the Chinese retail sector. In this strategy, the firm was to make its brand indispensable to its customers, especially in major urban centers. After creating a pool of loyal customers, it would then find unique ways of improving its profit margin. As such, it initiated an ambitious expansion strategy that went beyond the major cities in the country. The company was keen on hiring host country nationals both in the top management positions and junior officers (Phillips and Rozworski, 2019). It made sure that parent country nationals were also part of the management to ensure that the company’s traditional culture is retained in this new market.
Placing the locals at the management level helped in ensuring that policies that were developed remained sensitive to the local culture. It meant that the company could not develop practices that went against the beliefs of the locals. The strategy also made sure that the image of the firm reflected the expectations of those in leadership and the general population. It demonstrated the commitment of the firm to employ locals not only at the junior levels of management but also in top managerial positions. Currently, Xiaojing Christina Zhu is the president and chief executive officer of the company, a position she assumed this year. The step was meant to demonstrate that this company also trusts in the leadership of women.
Status of the Company and Sustaining Operations in China
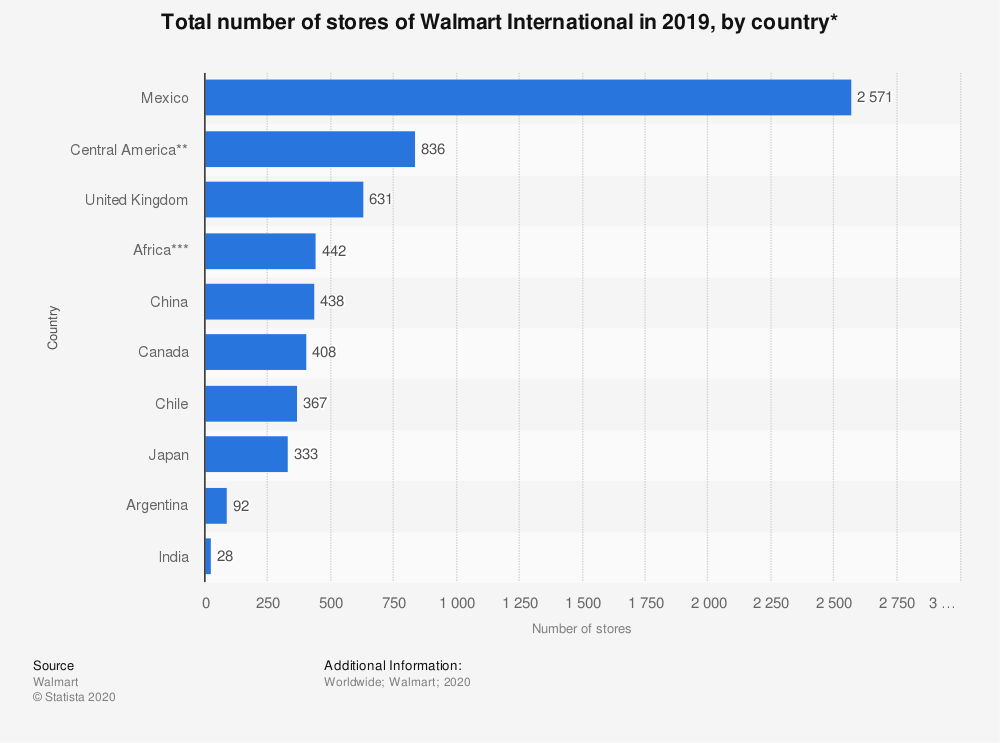
It is important to look at the status of the company in China to determine how it has been sustaining its operations in the country. According to a recent study by Wang et al. (2020), China is currently one of the major international markets for Walmart, as shown in figure 3 below. The comparative study demonstrated that Mexico, Central America, the United Kingdom, and Africa are the only markets that are more attractive to Walmart than China. The company has more stores in China than it does in Canada, Japan, and India. Although it may be true that the company still considers China one of its most attractive markets, the statistics clearly show that this firm is facing some major challenges in China.
Walmart made its entry into Mexico in 1991 through Sam’s Club. Five years later in 1996, it entered the Chinese market. The population of China is more than 10 times that of Mexico. However, the number of stores in Mexico is almost 6 times that in China. Comparatively, the statistics show that by far Mexico is a more attractive market for Walmart than China. The comparative study also shows that Africa is becoming a more attractive market than China. The retailer opened its first outlet in 2011, 15 years after making its entry into the Chinese market. Currently, it has 442 outlets in the region, more than the 438 in China.
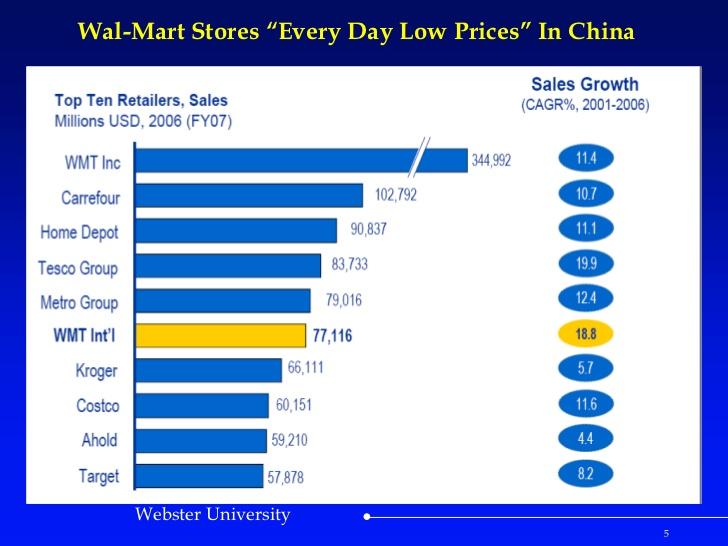
Walmart has been forced to operate under different models in China as a way of overcoming specific challenges and meeting different objectives. Under the model Walmart Inc, sales of the company ranked highest among various other retailers in China in 2006 (Powell, 2019). It had a better score than its main multinational competitors such as Carrefour, Tesco Group, Home Depot, Target, Costco, and Kroger.
It is important to note that some of these rivals such as Carrefour, Home Depot, and Tesco Group have since exited the Chinese market because their operations were no longer sustainable. In that period, Walmart Int’l section sixth in the same market. However, statistics in figure 4 below show that this segment registered a better score in terms of sales growth for the period from 2001 to 2006. Its sales growth within that period was 18.8%, which was the second-highest among the top retailers that were under review. Walmart Inc had a sales growth of 11.4% within the same period.
The company has been keen on ensuring that its operations are sustainable despite the many challenges which have forced some of its major rivals out of the country. One of the traditional strategies that have enabled this company to be successful for decades both in Europe and North America is setting favorable prices on its products. Most companies avoid this strategy and marketing experts often advise against it because it is not sustainable in the long term, especially if the company is relatively small in size.
However, this firm has been using it for a long period and it knows how to use the strategy in a way that does not threaten its sustainability in the market. Goldberg (2018) explains that it is possible this strategy is one of the main reasons why Walmart has remained operational in a market where most of its rivals from Europe and North America have failed.
Challenges that Walmart Faces in its Operations in China
Analysis of this company shows that it is facing numerous challenges in the Chinese market that continue to threaten its sustainability. One of the main challenges evident from this analysis is culture shock. In Europe and Central American markets, the company was able to achieve cultural integration with ease. However, the same has not been witnessed in China.
Walker (2019) blames it on cultural rigidity where people are unwilling to embrace new practices despite being exposed to the international community. The company has been forced to retain just a handful of parent country nationals in China. Most of its employees, from the top executives to junior workers are host country nationals. They have a better understanding of the local culture and practices that people find acceptable in the country. The biggest problem with having most of the employees being host country nationals is that the company loses its original organizational culture.
Some of the executives who are currently responsible for policy formulation and implementation at these branches are locals who have never worked outside of China. When policies come from the head office in the United States to be implemented locally, most of these employees do not understand what is expected of them (Griffith, et al., 2018). As such, it is common to find them making mistakes that would have otherwise been avoided if the implementation was headed by someone who understands the traditions of Walmart.
Cyber attacks are becoming common in this country, which is a worrying trend given the fact that the data management system at the company has gone digital. Some of the hacks are sanctioned by the Chinese government and the information may be used in a way that disadvantages the company. Relaxed law that is meant to protect copyrights and other intellectual properties is another major cause of concern for the firm. The company is not assured of protection from the government if it develops new ideas.
Competition is a challenge that this company has learned to manage in this market over the years. However, creating an uneven playing ground where local firms are favored at the expense of foreign multinationals may pose a new threat. The emerging trend of personal selling is also another major concern that should be addressed to ensure that the sustainability of this company is not threatened. These small firms do not have to incur warehousing costs. Some of them are not even registered, which means that they do not pay tax. They can afford to sell their products at low prices. They can create and maintain a close and personal relationship with their competitors in the market. This new frontier of competition in the market is posing a new challenge for major retailers, especially when the number of these small entities continues to increase.
Recommendations
Walmart is currently the largest company in the world in terms of revenues generated from its sales. It has been successful in the United States, Europe, and parts of North and Central American markets. The decision to explore the Chinese market was seen as a good move that would help it tap into opportunities that the country presented. Its rapidly growing population and rapidly growing economy made it an obvious choice for Walmart and many other multinational retailers.
For close to 20 years, the company has managed to remain operational in a market where many major rivals such as Tesco, Home Depot, and Carrefour have exited. It has demonstrated its capacity to overcome major challenges in the country. However, it is obvious that the company is struggling to achieve sustainable growth despite its unique potential. In fact, China is no longer the most attractive market outside the United States despite its potential. Based on the investigation conducted, the researcher believes that these challenges can be addressed through various strategies:
- The management of Walmart should consider rebranding in China as a way of overcoming the problem of preferences for local brands. For a long time, there has been a policy of buying local build the local economy among Chinese. They feel that when they buy from international brands, they are not patriotic enough (Schawbel, 2018). At a time when China and the United States have strained relations, the tension may have an impact on buyer decisions. As a known American firm, some Chinese may deliberately avoid buying its products as a way of demonstrating their support for their country. The rebranding will give the company a local image that many will find more acceptable.
- Walmart should consider having a considerable number of parent country nationals at important decision-making positions in all the regional head offices in the country. Having Chinese at the top management level and other positions that are more conspicuous is essential to create the image that the company is local (Goldberg, 2018). However, the few parent country nationals will help these local managers in implementing policies from the head office. They will also ensure that the interests of the company are not compromised by the locals.
- Cultural integration has remained a major challenge that many foreign companies have had to address in this country. The management of Walmart should stop spending more resources and time on this issue. Studies have shown that it may not be easy to change the cultural practices of Chinese within their country (Powell, 2019). As such, the focus should be to learn this culture and find ways of operating in it. The strategy of employing locals to senior managerial positions is one of the best ways of embracing the local culture. Parent country nationals who have to work in this country will need to embrace the local culture.
- The top management unit of Walmart China should consider maintaining a close relationship with the political leadership of the country. Studies have shown that these politicians have a major influence on the success of both local and foreign companies operating in the country (Walker, 2019). Maintaining such close relationships requires delicate balancing to avoid getting involved in the country’s politics. It should never be seen that the company is supporting a section of the political class.
Reference List
Alita, L., Dries, L. and Oosterveer, P. (2020) ‘Chemical vegetable safety in China: supermarketisation and its limits’, British Food Journal, 4(1), 1-14.
Boon, C. et al. (2018) ‘Integrating strategic human capital and strategic human resource management’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(1), 34-67.
Bruno, G. C. (2018) Blessings from Beijing: inside China’s soft-power war on Tibet. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Cao, Y., Zhang, J. and Ma, X. (2019) ‘Optimal financing and production decisions for a supply chain with buyer-backed purchase order financing contract’, IEEE Explore, 7(1), pp. 119384-119392.
Chang,Y. and Hu, J. (2020) ‘Analysis on the mode of multinational retail enterprises entering Chinese market’, Modern Economy,11(1), 1-11.
Chen, L., Su, Z. and Zeng, X. (2016) ‘Path dependence and the evolution of HRM in China’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 27(18), pp. 2034-2057.
Chiang, F., Lemański, M. and Birtch, T. (2017) ‘The transfer and diffusion of HRM practices within MNCs: lessons learned and future research directions’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(1), pp. 234-258.
Cooke, F. et al. (2019) ‘Human resource management and industrial relations in multinational corporations in and from China: challenges and new insights’, Human Resource Management, 58(5), pp. 455-471.
Franco-García, L., Carpio, J. and Bressers, H. (eds.) (2019) Towards zero waste: circular economy boost, waste to resources. Cham: Springer.
Fransoo, C., Blanco, E. and Mejía-Argueta, C. (2017) Reaching 50 million nanostores: retail distribution in emerging megacities. Lavergne, TN: CreateSpace Independent Publisher Platform.
Frynas, J. G. and Mellahi, K. (2015) Global strategic management. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Gallaghe, M. (2017) Authoritarian legality in china: law, workers and the state. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Goldberg, R. A. (2018) Food citizenship: food system advocates in an era of distrust. New York, NY: Oxford University Press
Gooderham, N., Grøgaard, B. and Foss, K. (2019) Global strategy and management: theory and practice. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gopinath, C. (2018) Globalization: a multidimensional system. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Griffith, S. et al. (eds.) (2018) Research handbook on representative shareholder litigation. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Hatami, A., Firoozi, N. and Puhakka, V. (2018) ‘In search of Bauman’s moral impulse in shadow factories of China,’ International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 12(30), pp. 334-343.
Hewett, R. et al. (2018) ‘Attribution theories in human resource management research: a review and research agenda’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(1), pp. 87-126.
Kennedy, M. R. (2017) Shape-holders: business success in the age of activism. New York, NY: Columbia University Press.
Kubler, C. (2017) Basic Mandarin Chinese: speaking & listening. Tokyo: Tuttle Publishing.
Lenssen, G. and Smith, C. (eds.) (2019) Managing sustainable business: an executive education case and textbook. Dordrecht: Springer.
Lasserre, P. (2017) Global strategic management. London: Palgrave.
Li, C. and Liu, M (2018) ‘Overcoming collective action problems facing Chinese workers: lessons from four protests against Walmart’, ILR Review, 71(5), pp. 1078-1105.
Liu, X. et al. (2019) ‘The colour of faults depends on the lens: MNCs’ legitimacy repair in response to framing by local governments in China’, Management and Organization Review, 15(2), pp. 429-458.
Marr, B. (2019) Artificial intelligence in practice: how 50 successful companies used artificial intelligence to solve problems. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Mayrhofer, W., Gooderham, P. and Brewster, C. (2019) ‘Context and HRM: theory, evidence and proposals’, International Studies of Management & Organization, 49(4), pp. 355-371.
Mcennally, G. (2017) China: behind the mask. London: Austin Macauley Publishers.
Michelson, H. et al. (2018) ‘Connecting supermarkets and farms: the role of intermediaries in Walmart China’s fresh produce supply chains’, Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems, 33(1), pp. 47-59.
Mockaitis, A., Zander L. and Cieri, H. (2018) ‘The benefits of global teams for international organizations: HR implications’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(14), 2137-2158.
Panibratov, A. (2017) International strategy of emerging market firms: absorbing global knowledge and building competitive advantage. London: Routledge.
Phillips, L. and Rozworski, M. (2019) The people’s republic of Walmart: how the world’s biggest corporations are laying the foundation for socialism. London: Verso.
Powell, E. (2019) Big trouble in little China. London: Boom Studios.
Rowley, C. et al. (2017) ‘Distinctiveness of human resource management in the Asia Pacific region: typologies and levels’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 28(10), pp. 1393-1408.
Schawbel, D. (2018). Back to human: how great leaders create connection in the age of isolation. London: Piatkus.
Schulte, P. and Lee, D. (2019) AI & quantum computing for finance & insurance: fortunes and challenges for China and America. Hackensack, NJ: World Scientific Publishing.
Sheldon, P. and Sanders, K. (2016) ‘Contextualizing HRM in China: differences within the country’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 27(18), pp. 2017-2033.
Si, Z., Scott, S. and Mccordic, C. (2016) ‘Supermarkets, wet markets and food patronage in Nanjing, China’, Waterloo, 43(1), pp. 1-11.
Walker, B. (2019) Powerful different equal: overcoming the misconceptions and differences between China and the US. London: LID Publishing Limited.
Wang, K. and Elfstrom, M. (2017) ‘Worker unrest and institutional change: perceptions of local trade union leaders in China’, China Information, 31(1), pp. 84-106.
Wang, Y. and Coe, N. (2018) ‘Power dynamics, supply network restructuring and modernised retailing in china: a comparison of two food staples’, Ageing and the Economy, 109(3), pp. 386-401.
Wang, Y. et al. (2020) ‘Employee perceptions of HR practices: a critical review and future directions’, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 31(1), pp. 128-173.
Ward, J. (2019) China’s vision of victory. Fayetteville, NC: Atlas Publishing and Media Company.
Xie, Y. and Cooke, F. (2018) ‘Quality and cost? The evolution of Walmart’s business strategy and human resource policies and practices in China and their impact (1996–2017)’, Human Resource Management, 58(5), pp. 521-541.
Zhao, L. et al. (2018), ‘Market Incentive, government regulation and the behavior of pesticide application of vegetable farmers in China’, Food Control, 85(1), pp. 308-317.