Sterile products for patient care are dependent on the effectiveness of sterilization and the unit design. Central processing aims to process medical and surgical equipment in an organized manner. They are also designed to safeguard patients from infection while reducing hazards to employees and keeping the value of the objects being recycled. Sterile processing facilities differ in size and complexity from huge, very sophisticated production settings that reprocess dozens of instrument combinations and devices to small, specialized facilities that reprocess a restricted quantity and variety of instruments (Swanson 245). In certain instances, sterile processing may occur wholly from where the equipment is used; alternatively, tiny remote clean production plants may be integrated within or next to a surgical suite’s semi-restricted zone. Irrespective of the location or kind of reprocessing treatments performed in these areas, the fundamental operational principles and workflow remains the same.
If someone is contemplating the construction of their ideal kitchen, design is sure to play a significant influence. Perhaps this means positioning the dishwasher adjacent to the sink for faster loading and placing the pull-out trash in an area preparing food or installing practical drawers to store goods that might otherwise accumulate on the counter. The argument is that design is critical. It is crucial that the Sterile Processing Department (SPD), where surgical instruments are processed and reprocessed every day, adhere to company standards set by organizations. These organizations include the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), the National Association of periOperative Nursing (APON), and the American Society for Quality (ASQ) (Neue). One needs an SPD department, whether you’re treating patients at an academic medical center or an outpatient surgery center. The placement of an SPD department is crucial in building a workflow that enables an SPD department to turn over, handle, and supply instruments efficiently.
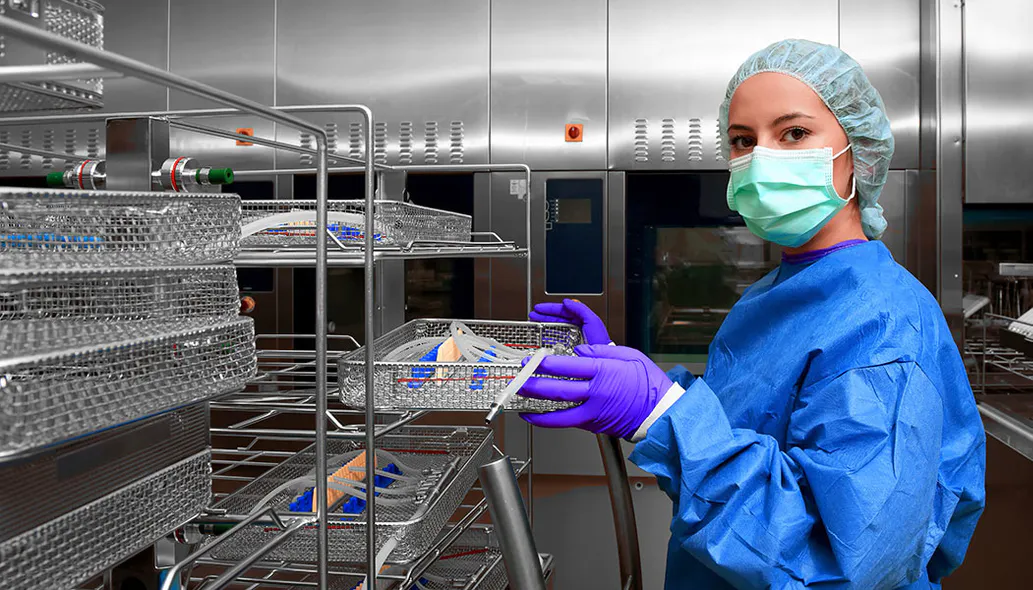

Before designing an SPD environment, it is a good idea to familiarize yourself with industry standards issued by associations like AAMI and AORN. They may assist with anything from the room’s layout to the amount of light and water required in the space. An SPD should have a distinct separation of dirty, clean, and sterilized tools with physical barriers, irrespective of the magnitude of your SPD (See fig. 1). Having a process that is as predictable as feasible might be beneficial.
The design of a sterile processing space is built on a dirty-to-clean workflow. Moving things from a contaminated to a decontaminated condition necessitates a one-way traffic arrangement for instruments and equipment. While the objects go through the process, this one-way movement is critical to preventing cross-contamination. To facilitate workflow, air circulation systems are intended to limit pollutants. In dirty work areas, it is done by providing negative airflow compared to clean spaces while also protecting clean work areas by providing positive airflow. There are several processes involved in cleaning specialized devices, making these operations very error-prone even if they seem straightforward on the surface. Complete separation from dirty and clean sections, proper ventilation, and the space, counters, sinks, or other equipment required to support the optimal workflow are all critical in a sterile processing room. As a result of the FGI Health Guidelines Revision Committee’s (HGRC) goal to “support supportive places for patients and employees wherever services are provided” (Damien, 229). Reprocessing practices are critical to preventing health give a damn infection, and thus patient safety is supported by the revised requirements.
Instruments and gadgets that may be reused must be disinfected or sterilized before being reprocessed as high-level disinfected or sterilized. The Spaulding categorization method classifies items as semicritical or critical based on whether or not they require high-level disinfection or sterilization. A “sterile” product has been sterilized to remove all microbiological life (Ninomura). Sterilized things are only regarded as sterile when all defined conditions for confirmation of the sterilization procedure have been satisfied. Sanitary items are handled and kept in a way that does not undermine their sterility. The “event-related sterility maintenance” criterion determines whether the sterility of stored sterile items has been maintained.
Cleaning removes bioburden (live germs left on a device’s surface after usage). Residual bioburden can spread germs or infections to the next patient who uses the device. Unclean instruments cannot be sterilized or efficiently high-level disinfected; hence the efficiency of any sterilization or elevated disinfection method depends on consistent protocols for removing or considerably lowering bioburden before processing. After cleaning, disinfecting instruments (William), cleaning via chemical (disinfectant) or thermal (washer-decontaminator) implies disinfecting devices to make them safe for employees to touch while processing continues. Inspected and packed for sterilization after decontamination, high-level disinfected items are reprocessed without filling and must be dried before storing (see fig.2).
To comprehend the changes in sterile processing facility requirements in the 2018 FGI Guidelines (Stanton), it is necessary first to understand the history of sterile processing in the surgical suite. In 2010 and previous editions, the Guidelines mandated one “sub sterile” chamber with a sink and a thermal sterilizer in between each two operating rooms. Unwrapped tools were exposed to a reduced sterilization cycle so that they may be reused right away according to a technique known as flash sterilization. The instruments were brought into the operation room wet in an open pan after being hand-washed and flash-sterilized. One or two unique instruments or an instrument that was accidentally infected during a process were the targets of this activity. Overuse of sterilization as a convenience or an alternative to acquiring different instrument sets emerged when sterilization procedures evolved. There were also severe worries about the growing size and complexity of flash sterilized instrument sets, and the capacity to maintain the sterility of instruments carried wet in an open pan.
Traditional flash sterilization was eventually deemed unacceptable due to these concerns. With a strategy that combines social media, advertising, and traditional media outreach it is possible to make your website easier to find. The committee said that the phrase flash sterilization was obsolete and replaced with Immediate Use Steam Sterilization (IUSS). Substerile rooms were no longer necessary in the 2010 FGI Guidelines, but the design criteria were preserved for use when a project’s functional program required them. Unwrapped products intended for use in the surgery room were traditionally referred to be “flash sterilized” in medical jargon (Salabasheva). When using flash or emergent sterilization, a sterilization cycle would typically last between three and ten minutes with no or little dry time or cooling phase, making the sterilization cycle quicker than that required to produce wrap or terminally sterilized products.
Open baskets were used in steam sterilizer chambers for flash sterilization, which put the target object into the sterilizer while it was still wet. The sterilized items were exposed to the outside world when the room door was opened, and they may be contaminated by poor treatment. When the sterile object was being transported, the open basket didn’t shield it from ambient pollutants (Berg 229). In order to do this, it was common practice to place numerous steam sterilizers around the surgical suite, usually one between every two operating rooms, to keep the sterilizer as near as possible to the operating room.
As a way to address concerns about only one sterile processing center, the infection facilities on-site on the 2018 HGRC and other domain experts looked at this requirement again. They wanted to make sure that the design of sterile production plants encourages clinical staff to follow professional standards and guidelines for cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing surgical equipment (Paul,48). When it came to sterile processing facilities, they took the dirty-to-clean workflow into account. They found that two rooms were the minimal requirement: a decontamination chamber and a clean workroom. Specifically, according to the 2018 Guidelines, a two-room sterile processing center must comprise a chemical cleaning room and a spotless small office. These are kept separate by an interior wall with a door or roll window that can be closed and secured or a constructed laundry with a pass-through window or door.
There is wording in the 2018 Hospital and Clinic Guidelines outlining the minimal physical criteria for the disinfection room and the sterile workroom. As a result, a three-basin sink and counter, appropriate counter space are necessary for sophisticated equipment to be cleaned, rinsed, and sanitized safely and efficiently. Sterile storage must be provided, whether in the clean place of work or a dedicated storage area. At first, the notion of a single-room sanitary processing unit to service the surgery suite seemed to be the solution. However, time and experience have shown that this approach is not the optimum design for supporting sterile processing best practices, and it was modified as part of the 2018 Guidelines editing process.
Decontamination aims to prevent the preparation and packaging personnel from obtaining infections caused by bacteria on medical devices during the decontamination procedure. Inanimate objects exposed to potentially hazardous microorganisms can be made safe for continuing use by applying physical or chemical methods of decontamination. According to FGI, specific steps are to be followed during decontamination. Sterile Processing Department’s Decontamination Area should be used to transport used equipment and supplies to avoid contamination of staff or the hospital (Rose). Closed containers, totes, or plastic bags should transport supplies and equipment, and equipment should be protected from the elements. Workers in the decontamination area must wear protective clothing, including a scrub jumpsuit wrapped by a humidity barrier, shoe coverings, latex or plastic gloves, and a hair covering (see fig 4). The face mask is recommended while doing manual cleaning activities when splashing is possible.

The process of sorting starts at the place of usage. Handling contaminated materials should be avoided unless the device’s operator is already wearing complete personal protective equipment, such as while doing care inside the operating room. Sorting should solely consist of eliminating throwaway sharps and disposing of other single-use goods in places where employees are not wearing any or minimum protective clothing. It is only essential to soak lumens, or different intricate patterns clogged with dirt or are incredibly bloody and cannot be washed or cleaned at the point of application (Rose). The detergent used should be compatible with the device’s components and appropriate for the soil it will be washing. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions. Many cleaning tools are available, but the most frequent include washer/decontaminator, ultrasonic, cart washers, and tunnel washers. All instruments should be inspected after cleaning before being packed for reuse or storage. The cleanliness of box locks, serrations, and crevices must be thoroughly examined.
After objects have been cleaned, dried, and examined, those that need sterilization should be wrapped or put in rigid containers and organized in instrument trays/baskets by the AAMI and other expert organizations’ criteria. These guidelines state that: Unless the equipment manufacturer or researchers offer detailed guidance or test data to the contrary, hinged equipment should be opened (Thomas). Items with detachable parts should be disassembled, and complex devices should be ready and sterilized by the device manufacturer’s instructions and test data. Devices with a concave outer surface should be placed to facilitate water drainage. Sterilization wraps and roll stock like paper-plastic mixtures of tubing enable the user to cut and close the ends to create a pouch. Self-sealing or high-temperature plastic or paper pouches are a few options for keeping surgical instruments sterile (woven and nonwoven) (Adrianzen). Healthcare establishments of all sizes may use various of these packing choices. An adequate barrier to microorganisms must be included in the packaging to ensure that the sterilization can reach the processed item and that the sterility is maintained even after sterilization. Staff should have access to and use written and visual protocols when performing packaging activities to prepare things to be packed.
Sterilization objects should be positioned such that the sterilizing agent is immediately exposed to all surfaces. Steam (or similar sterilant) must circulate freely around each item during loading (Waluk). The maximum dimensions, weight, and density for muslin fabric packets were 12 inches wide x 12 inches high x 20 inches long, 12 pounds per cubic foot, and 7.2 pounds for each cubic foot. When it comes to textiles and metal/plastic packaging, the manufacturer and sterilizer manufacturer should be contacted for advice on pack pretreatment and density criteria because of the wide range of options available.
According to research conducted by FGI, surgical trays covered in various materials retained their sterility for different amounts of time. A sterile pack’s storage period may be affected by its porosity and storage circumstances. Nine months after sterilization, heat-sealed, plastic peel-down pouches and packaged packets covered in 3-mil (3/1000 inch) plastic overwrap have been documented. After disinfection, the 3-mil plastic is utilized to increase the shelf life of seldom-used items (Paul). For at least 30 days, medical supplies wrapped in four layers of double-thick muslin or similar stay sanitary. If the disinfected package is damp, damaged, or punctured, it can not be used just after the expiry date has passed. It’s safe to assume that a heat-sealed impermeable plastic product is still free of contamination if the cover is still intact. Items wrapped in plastic do not need to be reprocessed if they are in good condition.
In conclusion, since steam sterilization days, the essential stages in reprocessing surgical tools have remained unchanged. However, since the complexity and number of surgical instruments needing reprocessing have grown dramatically, modifications in how these and other equipment are maintained in the surgery suite and beyond have become necessary. This shift in sterile processing center needs demonstrates that the approach is practical. These operational changes have influenced the development of design specifications for sanitary processing facilities, regardless of their location.
Works cited
Adrianzen, Diego. “Implementing Lean Process Improvement in the Sterile Processing Department at the Academic Medical Center.” Worcester Polytechnic Institute Digital WPI (2020).
Berg, Damien S. “When Technology Meets Standards… The Challenge of the Modern Sterile Processing Department.” Biomedical Instrumentation & Technology 42.3 (2021): 229.
Ninomura, Paul, Chris Rousseau, and Judene Bartley. “Updated guidelines for design and construction of hospital and health care facilities.” ASHRAE Journal 48.6 (2021): H33.
Nadeau Kara “Experience is power”; Salary Survey confirms education, certification key to SPD recognition and career success 2022, Web.
Rutala, William Anthony, and David Jay Weber. “Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities, 2019.” (2019). Web.
Swanson, Scott C. “Shifting the Sterile Processing Department Paradigm: A Mandate for Change.” AORN Journal, vol. 88, no. 2, 2020, pp. 241-247. Web.
Stanton Madeleine. “3-zone sterile processing” Harness the productivity and value in this modern workflow. 2019, Web.
Salabasheva, Maya, Travis English, and Erica Stewart. “Environmental parameters for decontamination rooms in sterile processing departments in our hospitals.” ASHRAE Transactions 123.1 (2020).
Seavey, Rose. ” Sterile & Materials Processing Department.”Basics on Processing & Sterilization 4.2 2018. Web.
Waluk, Thomas, et al. “Supply Chain Reduction for WellStar Kennestone Sterile Processing Department.” (2020). Web.