Introduction
Since time immemorial the world has witnessed wars between different groups, states, countries, and allies. Initially, the motive behind wars was survival. Ancient people fought in order to usurp land for cultivation. Gradually, as the world population grew, the motives behind wars became multifarious.
Different groups and countries started fighting with each other in order to gain control of areas where there were natural resources such as gold. Another reason for war was to gain access to routes generally used for movement of commodities from the starting place to the consumption areas. It is understood that after a war, one group prospered at the cost of another. Religion also has been an instigating factor for many wars. However, in all the wars, the motive was to gain advantage of some sort.
During the past years, when countries came together as allies, there have been instances when allies of a particular group had to go to war just because they wanted to safeguard themselves from the disadvantages of not participating in the war. In this paper, we shall discuss the reasons that led to World War 1. “World War 1 began in eastern Europe. The war started when Serbia, Austria-Hungary, Russia, and Germany decided that war or the risk of war was an acceptable policy option.”
Causes of World War 1
General Causes
Alliances
1879 onwards, the world witnessed formation of alliances between nations having similar interests. Following are some of the major alliances that took place:
- The Dual Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance in 1879 in order to defend against Russia.
- Austro-Serbian Alliance: Austria-Hungary and Serbia entered into an alliance in 1881 in order to prevent Russia from asserting power in Serbia.
- The Triple Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance with Italy in 1882 so that the latter could not favor Russia’s moves.
- Franco-Russian Alliance: Russia and France entered into an alliance in 1894 in order to protect their countries from the Dual Alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary.
- Entente Cordiale: France and Britain entered into a formal agreement in 1904 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Anglo-Russian Entente: Britain and Russia entered into a formal agreement in 1907 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Triple Entente: Russia, France and Britain entered into an alliance to counteract Germany’s growing threats. Later, in 1914 and under the same alliance, all the three countries concurred that they will not sign any peace treaty without mutual consent.
All these alliances (from 1879 to 1914) forced some countries to go to war just because they were in some alliance.
Imperialism
Imperialism is a term used for instances where any country usurps any other country’s land and asserts its supremacy and power. Due to the incessant progress of industrialization, countries felt the need of venturing into fresh marketplaces.
By the year 1900, Britain had extended its empire in five continents and France controlled major parts of Africa. The increase of both these countries’ power did not go well with Germany; Germany had only small areas under its rule. Following is a map that depicts the colonies of these three major European players in 1914.
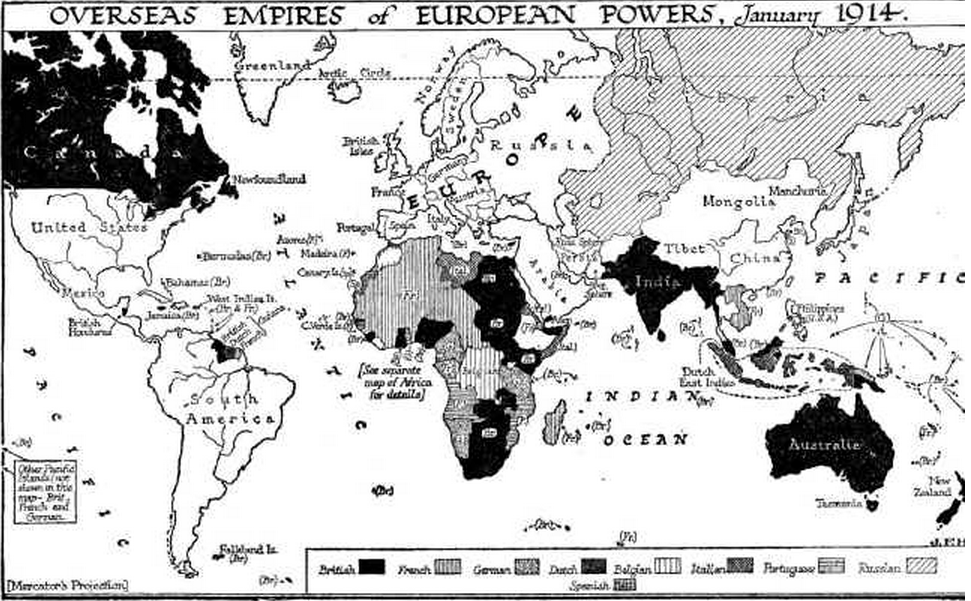
Source: Web.
William Anthony Hay claims that according to McMeekin, a tutor of international relations, “The war’s real catalyst lay in Russia’s ambition to supplant the waning Ottoman Empire in the Near East and to control the Turkish straits – the Bosphorus and Dardanelles – linking the Black Sea and the Mediterranean.”
But Richard Evans contradicts this opinion by stating that “In the end it was the Austro-Hungarian invasion of Serbia that set off the process that ended in the outbreak of World War 1, not Russian ambitions in the Straits. But if we think logically, no country will enter into a war without personal interests.
Alliances were also made to serve individual interests. So it is wrong to say that Russia did not have any interest or ambitions in the Straits. Russia was an industrialized nation and needed to sell its products to people in other nations. For this purpose, it needed a safe passage and new markets.
Militarism
When any country gives preference to its army, it is said to be following militarism. The growing alliances among various nations prompted nations to empower their army with more arms and ammunitions. France and Germany doubled the strengths of their respective armies.
Britain and Germany seemed to be in a competition of better sea control. In 1906, Britain launched the ‘Dreadnought’, considered to be a very efficient battleship. Following the footsteps, Germany also launched its own version of impressive battleships. The following illustration shows how Germany planned to attack France in case Russia attacked Germany; France and Russia were allies. So due to the alliance, Russia was bound to retaliate when one of its allies was attacked.
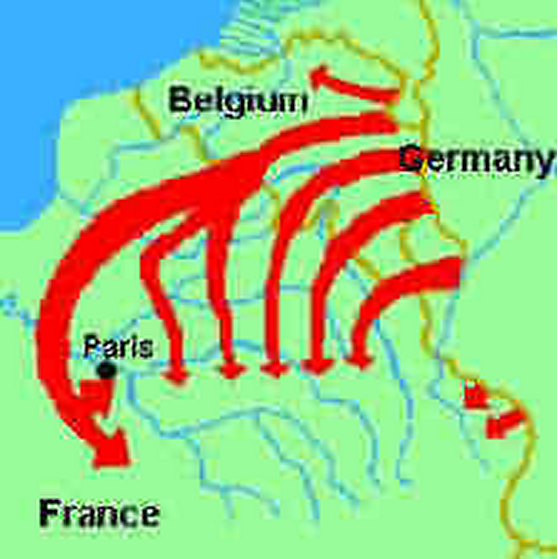
“A military revolution occurred in the seventeenth century. The most important of the many changes was a considerable growth in the size of the armies. Those large forces could no longer live off the land: steal supplies from the populace.”
Nationalism
We all have love for our respective countries. So did the people of that period. Austria-Hungary and Serbia had different radical groups trying to free their states from foreign involvement. Both Italy and Germany were divided. People of these countries wanted unification. “Along with the history of imperial machinations, however, World War 1 should be understood in the context of the popular imagination and the growth of nationalist sentiment in Europe.”
The Crisis
Moroccan Crisis
As part of an understanding, Britain gave control of Morocco to France in 1904. The Moroccan people wanted freedom. Germany, in order to take an advantage of the situation, proclaimed its support for the freedom of Morocco. A conference was held that allowed France to continue its control over Morocco and a war was averted. Again, in 1911, Germany started pronouncing its support for the Moroccan independence but again it was persuaded to compromise its stand on the issue.
Bosnian Crisis
Bosnia (a Turkish province) was taken over by Austria-Hungary in 1908. This action of Austria-Hungary did not go well with the Serbians. The Serbians thought Bosnia was under them. As such, a conflict aroused. Serbia proclaimed war over Austria-Hungary. Russia supported Serbia and Germany supported Austria-Hungary. A war was about to start but at the nick of the time Russia backed off and the war was averted.
But tensions were still mounting up between Serbia and Austria-Hungary. “It is true that during July the German decision makers sometimes expressed the hope that the conflict would be localized: in other words that Austria would be able to vanquish Serbia without Russian Intervention.” Dale Copeland argues that “Germany actively sought war in July 1914 and that German leaders by the end of July preferred world war to a negotiated peace, even to one that gave Austria most of what it wanted.”
The Immediate Trigger
World War 1 started in the year 1914. The assassination of Austria’s Archduke, Franz Ferdinand, acted as a trigger to World War 1. Franz Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in 1914 by Gavrilo Princip, member of a Bosnian radical group. “The crumbling Austro-Hungarian Empire decided, after the assassination on 28 June, to take action against Serbia, which was suspected of being behind the murder.”
This was considered to be an immediate reason for the war but the real reasons seem to be more complex and are still topics of debate among various historians. According to William Anthony Hay, “Germany bears responsibility for the war, in this view, because its leaders deliberately turned a regional clash between Austria-Hungary and Serbia into an existential Struggle of rival alliances.”
Hay is right in his opinion because history reveals that there were other options with Germany that could have averted the war. But since Germany wanted to gain on its own interests, it forced other countries to plunge into a war that they did not intend. “The size and wealth of the conquered Eastern territories easily outweighed what would have been lost had the Germans withdrawn from Belgium and France. Had they done so, France might have made peace and the anti-German coalition collapsed.”
Conclusion
All these instances make us to believe that Germany was behind waging the World War 1. In its ambitions to usurp power, Germany was thought to have instigated the war. But it is to be understood that down the years, historians put an end to the controversy as to which country was responsible for the World War 1.
Historians from the two main countries (Germany and France) came to an understanding that none of their countries should be blamed for instigating World War 1. It was the policies of militarization of each of the participating countries that led to the war. But certain facts still point the finger towards Germany. After the war started, some confidential documents were discovered that suggested that the German government had vast plans of extending its territory due to the economic requirements.
Bibliography
Copeland, Dale. The Origins of Major War. New York: Cornell University Press, 2001.
Evans, Richard. “The Road to Slaughter.” New Republic. 2011. Web.
Fergusan, Niall. “Germany and the origins of the First World War: New Perspectives.” The Historical Journal 35, no. 3 (1992): 725-752.
Hamilton, Richard and Holger Herwig. The Origins of World War 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.
Hay, William. “Ambition in the East.” The Wall Street Journal. 2011. Web.
Merriman, John. “The Origins of World War 1.” Yale University. 2013. Web.
Sheffield, Gary. “The Origins of World War One.” BBC. 2011. Web.
Williamson, Samuel. “The Origins of World War 1.” Journal of Interdisciplinary History 18, no. 4 (1988): 795-818.