Industry and Operation Environment
According to the Central Bank, The tremendous economic performance of the country has continued to form a basic element of the development of insurance in Bahrain (CBB, 2013). For instance, statistics pointed to the fact that in 2013, the Kingdom wrote 258.41 million insurance covers, which presented an 8% growth. There was also an increase in the contributions of Takaful, a principle of Islamic insurance, by about 7% and registered 57.22 million. In this case, the country had a total of 25 insurance firms registered locally on principles of both Takaful and conventional insurance (CBB, 2013). There were a further 11 companies, which were branches of international insurance companies that run their businesses in the Kingdom of Bahrain. In the same year, the value of the aggregate assets in both conventional and Takaful insurance increased by approximately 5% and brought a total of 1698.33 million.
A look at the structure of the insurance industry of Bahrain reveals that it is made up of two types of firms, the Takaful institutions and the conventional insurance companies (CBB, 2013). In this respect, data from the same year indicated that the nation had six incorporated Takaful insurance companies, which gave a gross contribution at a rate of 7% to the national insurance. The rest of the insurance industry of the Kingdom was made up of conventional insurance companies. The chart below is a representation of the structure of the insurance industry in Bahrain in 2013.
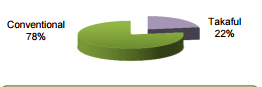
Zurich- Kingdom of Bahrain Company Outlook
Size of Assets, Equity, and Market Share
Zurich Insurance Company is one of the overseas companies that have a significant impact on the insurance industry of Bahrain. The business entity plays a leading role in the provision of multi-line insurance and engages in the provision of such services to both the locals and people abroad. Today, the corporation boasts of an employee base of about 55, 000 workers while offering a wide range of insurance contracts that range from general to life assurance and coupled with other types of services (ZIG, 2015). The company is not discriminative of the type of clients that it serves because it gives its services to all categories of customers such as individuals or companies both locally and abroad. To crown such a landmark, Zurich insurance company has operations in more than 170 nations across the globe.
In 2014, the company realized 27% of its profits from farmers, 22% from global life, and 50% from general insurance. By the end of December of 2014, the business had a total of $ 4.6 billion as its operating profit. The quoted figure was a slight decline after 2013, though a much better performance than what the business realized in 2012 (ZIG, 2015). At the same period, the company owned about 34.7$ billion in shareholders’ equity, which was the largest in the three consecutive years comparatively. The comparison of such data is as shown in the two charts that follow.
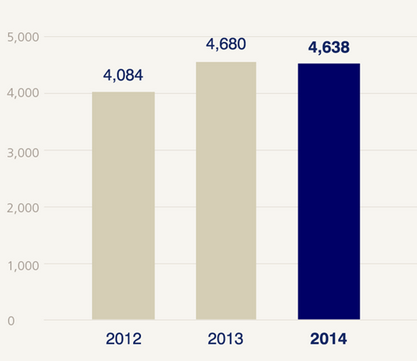
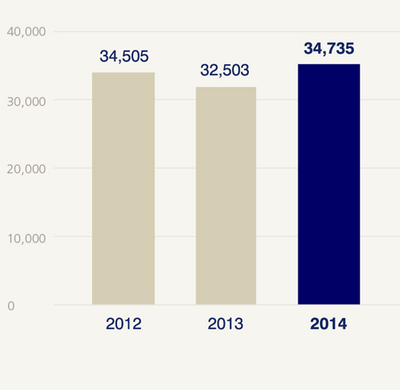
Organizational Structure of the Company
Zurich Insurance Ltd is a firm that has an efficient cooperation structure between its management board and other departments of the business. The institution has a board of directors comprising of eleven members with a director as the leader (ZIG, 2015). The eleven members are charged with the responsibility of establishing committees that deal with specific areas within the business, as well as the delegation of duty to other members of the business committee. The second category in order of rank is that consisting of the executive committee with the CEO as the leader (ZIG, 2015). This group of leaders plays the role of the strategic planner in a variety of issues that affect the business from all three perspectives; financial, human relations and corporate responsibility. It means, therefore, that the company’s executive group determines the various business strategies that they institute from their perspective of leadership. Next, there are departmental managers that have the responsibility of engineering the performance of the company at the departmental level. As observed, the company has a top-to-bottom style of management which places the chief executives in prime positions of strategic planning and ensuring that the plans materialize at departmental levels.
There are several departments within the corporate institution, which the company recognizes as group management. From this perspective, there are three management groups within the company, namely, group risk management, group compliance, and group audit (ZIG, 2015). In the first place, Zurich Insurance Ltd grants the group administrators roles in regulating processes as well as the provision of technical issues in their relationship with insurance. The risk management group is charged with the execution of a framework that assesses the approach that Zurich Insurance Company should take regarding risk management. The leadership of this group depends on the creativity of the Chief Risk Officer who reports directly to the CEO (ZIG, 2015). Group compliance is a section of the managerial layout of the company that deals with the provision of insurance to management. The principal personnel for this group is the group compliance officer who reports to the chief audit officer. The group audit has the responsibility of auditing risk management and the process of governance (ZIG, 2015). The head of this group has established links with the board chairman. Therefore, the above analysis depicts Zurich Insurance Company as a tightly knitted organization in which the members have close communication with one another.
Range Of Services and Policies Provided
Zurich Insurance Ltd is among the most well-known insurance companies in the world because it provides an extremely wide range of services for its customers to choose from. The company provides insurance covers to individual customers in such areas as recoveries from natural disasters, for example. Other services provided to individual clients include home insurance, life insurance, critical illness, general liability, investments, and savings, planning for pensions, and retirement among others. Zurich Insurance Ltd also engages in the provision of insurance covers for SMEs (ZIG, 2015). It does so through property insurance, casualty insurance, worker man’s compensation skills, car insurance policies, corporate life and pensions among others. Another category of services concerns the big multinational corporations. In the first place, Zurich Insurance Ltd provides captive services for all parties interested in such a policy (ZIG, 2015). In addition, the organization also provides casualty services to parties interested in protecting themselves against the uncertainties of industrial operation. The company also helps its clients to make plans, administer the same projects, as well as manage corporate benefits through the provision of corporate life and pension schemes. Another service entails specialized underwriting as well as management of risks and its support for construction projects. Zurich Insurance Ltd also undertakes to ensure engineering risks in the field of energy production and supply. There are varying types of marine policies that the company provides for both domestic and international cargo transits. There is a couple of other insurance services that the company provides to parties in this category (ZIG, 2015). The company also offers brokers for hire at both local and international scenes. Such a service makes a company boast of provision diversified range of products.
Utilized Marketing Channels
The firm utilizes several channels in the marketing of its products, which are common in other insurance companies. One of such channels is the website. The site forms one of the best methods of selling a full range of coverages. The firm also utilizes the web through the use of social media advertising (ZIG, 2015). For this case, there is a realization that it runs a theme that seeks to establish proper and healthy relationships between itself and the market. In this respect, the firm runs a campaign called HumanConnections, which involves an interactive interface between the company and its customers on LinkedIn (ZIG, 2015). Through the use of such a channel, the company has an opportunity of strengthening its brand and capture a wider market base, which is essential for its productivity. The professionals that interact with customers from the company’s LinkedIn page have the effect of raising its popularity among the people and is a unique method of fitting in the target market. Apart from the website and social media, the company also utilizes other conventional means of product promotion such as print media in articles, newspapers, magazines, and periodicals. There is also a considerable level of utilization of visual media such as television, which gives the company a competitive edge against other institutions in the industry.
The Financial Highlights of the Company
According to data available at the Market Watch (2015), the company has a total of $197.48 billion in investment in the value of assets. The principal source of revenue for the company is the premiums earned from the underwriting processes that it engages in doing and they amounted to $ 44. 23 billion. The primary investment assets ($178.23) that the business owns are categorized as income on securities investment, which accounts for $1520.66 billion while bonds account for $ 152.66 billion. The company also has a redeemable preferred stock of $7.95 million. There is also total equity investment that amounts to $16 billion, real asset investments of 8.7 billion. The company’s syllabus reflects that it has 18.54 billion in mortgage and other Loans. Unspecified investments of the insurance group amounted to 1.53 billion (Market Watch, 2015). At the same time, the firm has the category of assets called premium asset receivables that amounted to 10.2 billion. The distribution of this type of asset was in the categories that follow; net property, unconsolidated assets, variable and separate assets, deferred charges, other tangible assets, and intangible assets. The values of the assets mentioned following as 1.26, 69.56, 170.95, 133.56, 19.42, 8.61, and 7.81 respectively. The business also holds its assets in the form of cash for which it had 7.55 billion and brought the value of total assets to $387.8 at the end of the 2013-2014 trading period (Market Watch, 2015). The two major expenses that the company incurs are the categories of capital expenditure, one for fixed assets, and the other for other assets. In this case, the cash flow data of the company indicated that the business had $1.27 billion in fixed assets and no expenditure on other assets. Lastly, the company had a gross loss reserve of $ 43.44 billion and an adjusted loss reserve of $ 31.64 billion (Market Watch, 2015).
Calculations and Interpretations Of
The Loss Ratio= (Incurred Losses + Loss Adjustment Expenses)/Premiums Earned
= (43.44+31.46)/44.23
=1.69
Therefore, the ratio indicates that the company is in a stable financial position because it collects more revenues than what it pays in claims. Such a ratio could provide an insight into the methods of financial management as well as the levels of investment required.
Expense Ratio=Underwriting Expense/Premiums Written
=9/44.23
=0.20
Therefore, the ratio indicates that the company gains about five times on underwriting the insurance policies than it spends on the same.
The Combined Ratio=Loss Ratio +Expense Ratio
=1.69+0.20
=1.89 (189%)
The ratio obtained means that the company makes profits out of its daily operations.
Investment Ratio=Net Investment Income/Premiums Earned
15.23/44.23
=0.34 (34%)
The ratio means that every single unit of investment by the company yields a 34% return. Therefore, the company enjoys a return of 34% on its invested capital.
The overall operating ratio= Operating Expenses / Net Sales
=9/66.7
=0.13 (13%)
The ratio implies that the company spends 13% of its cost to sell 100 units of its products and services. The ratio provides a useful element in the determination of the profitability of its daily operations. The firm therefore remains with 87% of its costs to carter for other non-operating costs.
A Five Year Comparison of the Ratios
Insurance Policies
Life Insurance Policy
This type of policy is the one extended by an insurance company to their client as a cover for their lives. There are two types of such policies, life assurance, and time insurance. The first type of life insurance is one that entails the cover of the lives of the insured for the entire lifetime. The contract becomes binding as soon as the insured agrees to the terms and conditions of the insurer and starts to pay premiums (Gulati, 2007). The requirements of the agreement specify that the compensation claims only be made in the event of the death of the insured. Therefore, it means that the insured usually targets the financial stability of their dependents and not themselves. However, the contract holds only on account that the insured pays premiums throughout their lives and stops only at death. The other type of life insurance entails a different approach because the insured pays premiums for some specified period, and compensation happens at the expiry of the period in the insurance contract. If the time occurs before the insured dies, then they benefit from the scheme, but if they die before the maturity of the contract, compensation benefits the dependents. Life insurance has a considerably high rate of deductibles, which means that the premiums paid by the insured are comparatively low over the period for which the contract holds.
Underwriting Process
The process of underwriting life insurance policies entails an extensive study of the public record of the insured to ascertain their life. The underwriters also consider the blood analysis of their clients as a way of determining their state of health (Gulati, 2007). Other premedical tests will provide essential information concerning the health status of the customers. If the insured has a bad record such as histories of crime, poor health, and other aspects, or if they are aged, the insured will have to pay more premiums.
Workman Compensation Policy
According to Gulati (2007), this type of policy is one that an employer undertakes to cover their workers against injuries sustained while they are at their places of work. The contract becomes practical once the insured agrees to the terms of their insurer and starts paying premiums and will terminate when the insured stops paying premiums or when they violate any provisions of the contract. This type of policy has a considerably low rate of deductibles, which means that the insured persons have to pay higher rates of premiums throughout the period for which the policy holds.
Underwriting Process
The process of underwriting involves statistical analyses of the number of workers that the insured has insured. As such, there is a conclusion that an employer who wishes to protect many workers will have to pay more premiums than the one who only insures a few of them. The premium deductibles for this contract happen for the entire agreed period of the contract, which continues all the time until the occurrence of the insured risks. The policy demands that people who insure their workers who work in dangerous places should pay more than those who work in relatively safer places (Gulati, 2007).
Automobile Insurance
A cover of this type protects the insured from the damages caused to their car in the event of an accident. This type of protection cover ensures that the insured regains their financial status usually in the value of the car. Automobile insurance contacts are among those that have the highest rates of deductibles, which implies that the insured persons have to pay a considerably low rate of premiums for the period for which their contracts are valid.
Underwriting process
The process of underwriting considers mainly the value of the car and its maintenance levels (Gulati, 2007) Low-costing vehicle owners pay lower premiums than those who drive expensive cars. People who pay poorly-maintained vehicles also require paying more than their counterparts who drive better-maintained cars.
Contract Conditions
The first principle is that of insurable interest. This principle entails the fact that the claimer must have an economic interest in the assets that they want to acquire an insurance cover for and will endure monetary losses on the incidence of the insured event. This factor encompasses one of the most vital necessities of any insurance agreement. Hence, an individual can enter an insurance contract of those belongings where he stands to gain benefit if such property gets involved in any damage. There is also the principle of Utmost Good Faith. In comparison to other contracts, good faith is a vital characteristic of an insurance company (Gulati, 2007). In case an insurance contract is acquired through fraud or misrepresentation, it is termed to be invalid.
There is also the need for material facts disclosure. In the process of an insurance contract, the proposer must reveal to the insurer all the objective facts concerning the anticipated insurance. This task of revealing the objective facts not only applies to the object that the insured owns but also extends to objects that they are believed to know. Therefore, where life insurance involves is the subject, the proposer must reveal their accurate age and details of any existing diseases. Similarly, where there is the insurance of a building against damages resulting from fire, the proposer must unveil the details of stored products if any and the risk nature. There is also the principle of indemnity (Gulati, 2007). This rule states that the insurance contract ought to be always a contract of indemnity only and not anything more.
The principle of contribution is a consequence of the principle of indemnity. It applies to all contracts of indemnity in instances whereby the insured has acquired more than one insurance policy on a similar subject matter. In case one insurer clears full recompense then that insurer can allege proportionate claim from other insurers (Gulati, 2007). The nature of the contract is an elemental principle of an insurance agreement that covers approximately all insurable risks. This policy dictates that an insurance agreement comes into continuation when one party makes a bid or tenders for a contract, and the other party accepts the proposal. Besides, the deal ought to be straightforward and be a compelling contract and the individual entering into an agreement must enter with their free consent.
The Process of Claiming Compensation
As much as the insurance policies have their differences, the procedure of seeking compensation has some similarities. First, the insured should report the claims to the insured in the soonest time possible, usually before one week. The insured will then investigate the claims to ensure that the events that led to the loss incurred have a relationship to the insured risks (Gulati, 2007). In this case, they may either have caused the damage directly or were proximate causes of the insured risks. The investigation will also determine that the cause of the loss was not catastrophic and determine the levels of compensation required later on. If the company proves that the events that resulted in the loss had financial interests insured in the contract, they will compensate.
References
Gulati, N. C. (2007). Principles of insurance management: A special focus on developments in Indian insurance sector – pre and post liberalization. New Delhi: Excel Books.
Market Watch. (2015). Annual Financials for Zurich Insurance Group AG ADS. Web.
The Central Bank of Bahrain (CBB). Insurance Market Review 2013. Web.
Zurich Insurance Group (ZIG). (2015). About us Zurich Insurance Group. Web.