Introduction
Electricity and magnetism have become indispensable for our life today. All the appliances we can imagine to live with work on the underlying principles of electromagnetism and therefore, it is important to understand electromagnetism. Why I am stressing electromagnetism and not magnetism is the fact that the two are inseparable.
There was a time when magnetism was discovered in some stone and was considered something altogether different from electricity. But this has changed long back due to the experimental observation by scientists like Faraday, Ampere. Maxwell etc. and today electricity and magnetism are seen as two sides of the same coin. In scientific terminology, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field and a changing magnetic field produces a changing electric field. In the backdrop of this brief introduction, this report attempts to explain important terminologies related to the magnetic field.
Important Terminologies
Magnetization
An atom consists of a nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons and with each electron, there is an associated magnetic moment. The electrons exist in pairs to cancel the magnetic moment of each other. However, some atoms have unpaired electrons and therefore, a net magnetic moment. If we take an object of finite size then the constituent atoms (which are very large in number) are oriented in a random direction and thus cancel the magnetic moment of each other. However, sometimes, these atoms somehow align to give a net magnetic moment. One can define a quantity known as magnetization vector (I) which is magnetic moment per unit volume. This is also termed as the intensity of magnetization or simply magnetization. This is expressed as:
I = M/V(Net Magnetic Moment)/Volume ………. (1)
For a bar magnet of pole strength m, length 2l and area of cross section A, the magnetic moment is M = 2ml and therefore, the intensity of magnetization is
I=M/V=2ml/A(2I)=m/A i.e. pole strength per unit area
Magnetic Intensity (H)
When a material is put in a magnetic field then it gets magnetized. The magnetic field inside the material is the sum of the applied magnetic field and the magnetic field due to magnetization.
Now one can define a new vector field such that H=B/μ0-I…………. (2)
Here, I is the intensity of magnetization, B is the resultant magnetic field and H is magnetizing field intensity or magnetic intensity. In vacuum I = 0 because no material is present and the
equation (2) reduces to H=B/μ0 …………. (3)
The magnetic intensity due to a magnet of pole strength m at a distance r from it is given by the following equation: H=m/4πr²………… (4)
Magnetic Susceptibility
For paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials, the intensity of magnetization (I) is directly proportional to the magnetic intensity (H) i.e. I=χH ………… (5)
This proportionality constant χ is known as the susceptibility of the material. This is a dimensionless constant as I and H have the same units. Its value is zero for vacuum, positive for paramagnetic materials, and negative for diamagnetic materials.
Permeability
Rearranging equation (2) gives, B=μ(H+I)=μ(H+χH)=μ(1+χ)H
i.e. B=μH ……………. (6)
m is called the permeability of the material and its value is 1 for vacuum.
Dia, Para and Ferromagnetic materials:
Diamagnetic materials repel the magnetic field because of their negative magnetization and paramagnetic materials weakly attract the magnetic field. However, there is a strong attraction of ferromagnetic materials towards the applied magnetic field because of a large number of magnetization moments available for alignment along the applied magnetic field.
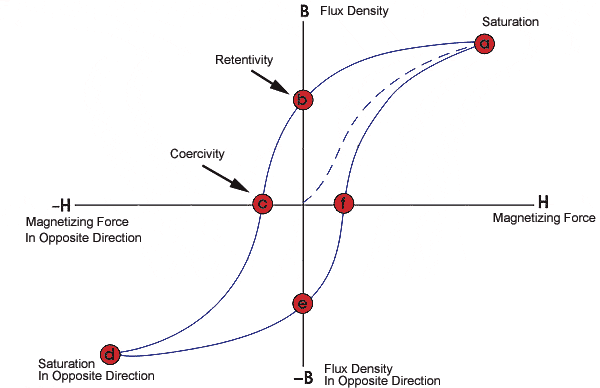
Hysteresis
If material is magnetized by applying an external magnetic field and the external magnetic field is then turned off then the material retains some amount of magnetism and to remove this one needs to apply a magnetic field in the reverse direction. This leads to the formation of a hysteresis loop. The size of this loop tells whether the material is soft magnetic material or hard magnetic material. A smaller hysteresis loop implies a soft magnetic material and vice versa. A typical hysteresis loop is presented below.
Summary
Important concepts related to magnetism have been briefly discussed in this report. These concepts provide a reasonably good understanding of magnetism. However, understanding of magnetism remains incomplete unless and until electromagnetism is also covered. Further reading on electromagnetism is envisaged to get a complete understanding of the subject.
References
Magnetization. Web.