Executive Summary
The aim of this paper is to investigate the acceleration of a ball that is moving down an inclined plane. It is known that a body moving a long inclined plane, experiences acceleration due to the force of gravity, which is further affected by the mass of the body and the angle of inclination of the plane.
Discussion
In all three setups (15°,30°, and 45°) the common trend is that the time interval that the ball takes to move between two points reduces as we progress to the last finishing point of 120 cm. This decrement in time interval indicates that there is an increase in velocity as we move towards the last finishing point of 120cm. We can therefore say that the ball accelerates with time since progressive distances of 30cm are covered within a short period and higher speeds.
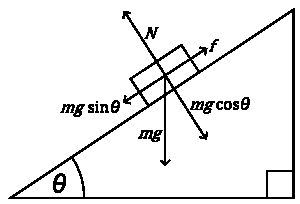
It should also be noted that an increase in the angle of inclination of the ramp increases the speed of the ball and subsequently the acceleration. For instance, using results from tables 3.1, 3.2, and 3.3 above, the acceleration calculated at the 30cm finishing point is 223.9541cm/sec2 for a15° incline, 382.6531cm/sec2 for 30° incline, and 702.3933cm/sec245° Incline. This is explained by the fact that any increase in the angle θ tends to increase the force mgsin θ. If this force is increased and the mass of the ball is kept constant, then using Newton’s second law of motion (Force = Mass Acceleration), there will be an increase in acceleration (see figure 1 below).
Solutions
Velocity is the rate at which a body is displaced in respect to time (see equation 1). By displacement, we mean motion in a specified direction. This is different from speed, which is defined as the rate of movement of a body in respect to time. Whereas the direction of motion is necessary for the determination of velocity, evaluation of speed does not incorporate the direction of motion.
Velocity = Displacement/time
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity or speed with time. To calculate acceleration, we need to determine the change in speed or velocity then divide by the time duration that the change has occurred. Whereas acceleration is concerned with the change of velocity or speed with time, velocity is concerned with the change in displacement with time. The SI unit of measurement for acceleration and velocity are m/s² (meters per second squared) and m/s (meters per second), respectively. Equation 2 and 3 illustrates the difference between acceleration and velocity.
Velocity = Displacement/time
Acceleration = Velocity/Time or Speed/Time
Some of the conditions that will change the acceleration of the rolling objects include:
- Mass of the object; – the gravitational force is defined as F = ma
- The angle of inclination of the ramp
The difference between the falling rate of the feather and the rock on the moon and on the earth comes about because of force of gravity. The moon exerts zero gravitational force on objects while the earth exerts a gravitational force on all objects, defined as follows.
F = Ma, where F = gravitational force, M = mass of body, and a = acceleration
It is this gravitational force that generates the difference witnessed in the falling of the rock and the feather on the moon and on the earth.
Friction will definitely affect the speed at which a ball rolls down the inclined plane. Friction is a force that resists motion. This force acts in the opposite direction to a moving body and it is governed by the surfaces of the bodies in contact, the normal force incident on the bodies. Air pressure does not affect the motion of the body on an incline plane.